Final Week for Physics 2
1/459
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all the slides info of flashcards and general information to study and review after reviewing other flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
460 Terms
TRUE OR FALSE?
To achieve thin slices, a shallow slice-select slope and broad transmit bandwidth is applied. To achieve thick slices a steep slice-select slope and narrow transmit bandwidth is applied.
False - To achieve thin slices a steep slice-select slope and narrow transmit bandwidth is applied. To achieve thick slices a shallow slice-select slope and broad transmit bandwidth is applied.
What is the formula for a conventional spin echo scan time?
TR x Phase Matrix x NEX (NSA)
TRUE OR FALSE?
The Y gradient selects sagittal slices while the Z gradient selects the axial slices.
FALSE
The X gradient selects sagittal slices while the Z gradient
selects the axial slices
Which gradient is turned on after the application of the excitation pulse?
Phase encoding gradient
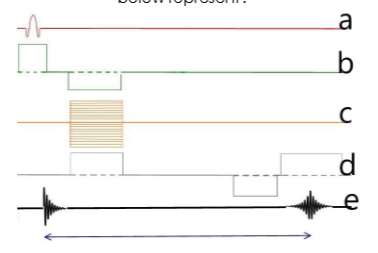
What type of sequence does the image below represent?
Gradient Echo (GRE)
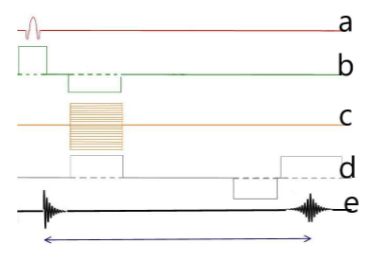
Which letter represents the phase gradient?
C
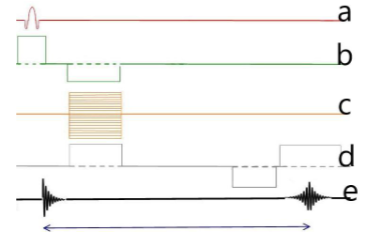
Which letter represents the slice select gradient?
B
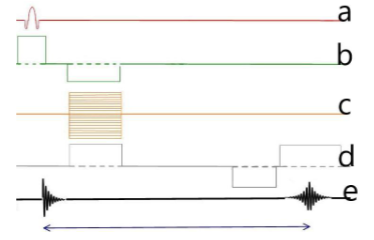
Which letter represents the frequency gradient?
D
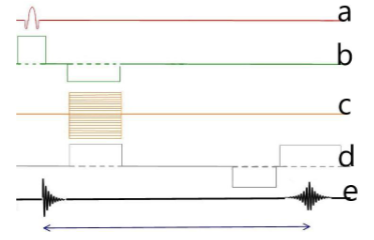
Which letter represents the RF pulses and how many are there?
A, 1
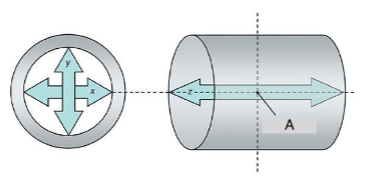
What does “A” represent?
Isocenter
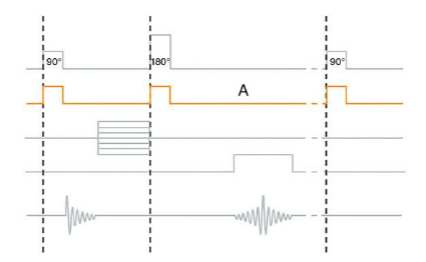
What is ”A”?
Slice Select Gradient
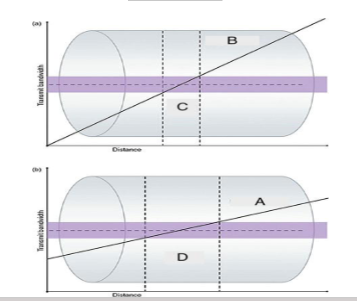
What is ”A”?
Shallow Gradient

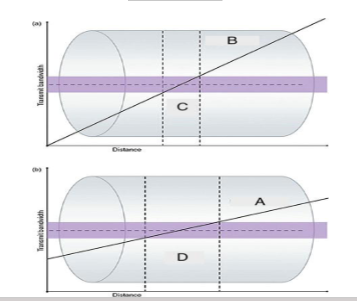
What is ”B”?
Steep Gradient
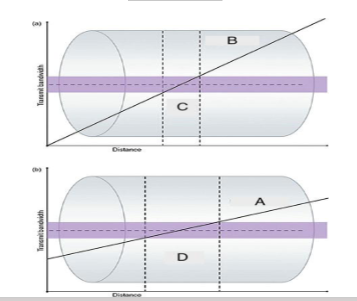
What is ”C”?
Thin Slice
What is ”D”?
Thick Slice

What is ”A”?
Rephasing
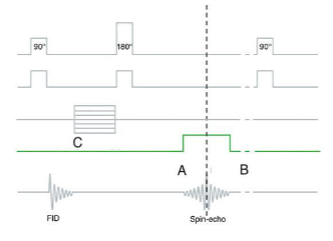
What is ”B”?
Dephasing

What is ”C”?
Frequency Encoding gradient
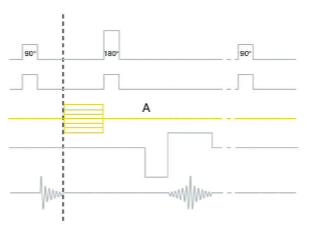
What is “A”?
Phase encoding gradient
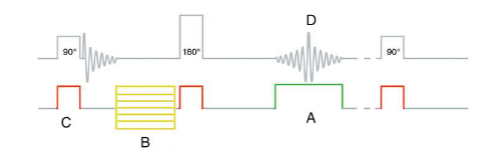
What is “A”?
Phase encoding gradient
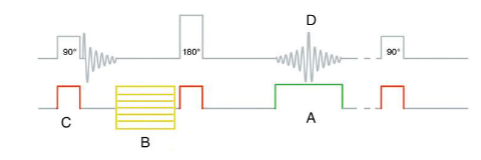
What is “A”?
Frequency Encoding
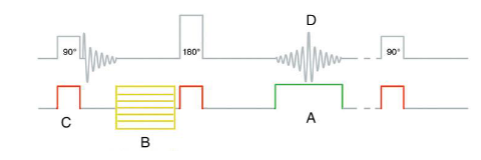
What is “B”?
Phase Encoding
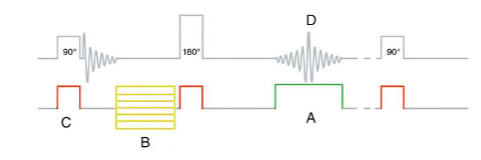
What is “C”?
Slice-select
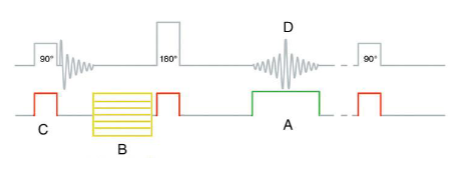
What is “D”?
Spin-Echo
What is “A”?
Steep Phase encoding gradient
What is “B”?
Shallow Phase encoding gradient
What are the three main functions of MRI gradients?
Slice selection, phase encoding, frequency encoding
Which gradient selects coronal slices?
Y‑gradient
Which gradient selects sagittal slices?
X‑gradient
Which gradient selects axial slices?
Z‑gradient
What determines the FOV in the long axis of an image?
Slope of the frequency‑encoding gradient
What determines the FOV in the short axis of the anatomy?
Phase encoding
What is sampling in MRI?
When the scanner reads and digitizes the signal
What is k‑space?
Storage of spatial frequency data before reconstruction
What information is stored in the central lines of k‑space?
Image contrast (high signal, low resolution)
What information is stored in the outer lines of k‑space?
High resolution (low signal amplitude)
What is the difference between 2D and 3D MRI sequences?
2D is acquired in slices; 3D is acquired in a volume/slab
When is the frequency‑encoding gradient turned on during a pulse sequence?
During rephasing/dephasing and at the echo peak
In a coronal brain scan, which gradient performs frequency encoding?
Z‑gradient
When is phase encoding performed in a sequence?
Prior to frequency encoding
What gradient is active during the production of the echo?
Frequency‑encoding gradient
What is another term for the readout gradient?
Measurement gradient
When does slice selection occur in a gradient‑echo sequence?
During the RF excitation pulse
What is the magnetic isocenter?
The center of the magnet in X, Y, and Z planes
What controls slice thickness?
Gradient slope (steepness) and transmit bandwidth
What happens when a steep frequency‑encoding gradient is applied?
A small FOV is acquired in the frequency direction
What determines gradient amplitude?
Amount of current passing through the gradient coil
What causes a large phase shift between two points along a gradient?
A steep phase‑encoding gradient
What determines how many times the phase‑encoding gradient is switched on?
The selected phase matrix in the scan protocol
What are the two main elements of MRI image data?
Pixel (2D) and voxel (3D)
What is spatial encoding?
Locating signal in 3D space within the imaging volume
What is the purpose of k‑space in MRI?
It is a storage device for spatial frequency data created from spatial encoding
What is the shape of k‑space?
Rectangular with two perpendicular axe
What does the horizontal axis of k‑space represent?
Frequency‑encoding axis
What does the vertical axis of k‑space represent?
Phase‑encoding axis
How is k‑space filled?
With data from echoes from a slice
What determines the total number of k‑space areas?
The total number of selected slices
How are k‑space lines numbered?
Lowest numbers near the center, highest numbers at the outer edges
What is the polarity of k‑space lines?
Upper portion positive, lower portion negative
What determines whether a k‑space line is positive or negative?
Polarity of the phase‑encoding gradient
What is the simplest method of filling k‑space?
Cartesian (linear, top‑to‑bottom)
What are other methods of filling k‑space?
Partial/fractional, partial echo, parallel imaging, single shot, spiral, propeller/radial, sequential, 3D
When are echoes digitized and placed into k‑space?
When the frequency‑encoding gradient is turned on
What determines the number of data points in each k‑space line?
The frequency matrix
What determines how and when k‑space is filled?
Each gradient (slice‑select, phase, frequency)
What determines the number of k‑space columns?
The phase matrix
What determines the number of k‑space rows?
The frequency matrix
What does each filled line of k‑space represent?
A single TR period
How is a waveform created for k‑space data?
By plotting the change of phase of magnetic moments over time or distance
What is the first step in preparing echo data for FFT reconstruction?
Simplifying the frequencies and amplitudes in the echo (frequency & amplitude modulation)
What is the second step in preparing echo data for FFT reconstruction?
Digitizing the echo through analog‑to‑digital conversion (ADC)
What is analog information in MRI?
A variable represented as a continuous waveform
What is digital information in MRI?
The same signal represented in binary numbers
Where does digitization of the analog MR signal occur?
In the receiver coil or scanner body
What determines the number of data points horizontally in each k‑space line?
The frequency matrix (horizontal/longitudinal)
What determines the number of data points vertically in each k‑space column?
The phase matrix
What does the frequency matrix represent in MRI?
The long axis of the anatomy
What does the phase matrix represent in MRI?
The short axis of the anatomy
What are the two main components of an MRI pulse sequence?
RF pulses and gradient
What does the Nyquist Theorem determine in MRI?
The optimal and minimal digital sampling frequency needed to acquire enough data points for an accurate image
How must the highest frequency be sampled according to Nyquist?
At least twice as often as the highest frequency present
What happens if a signal is sampled at less than once per cycle?
An incorrect frequency is produced, causing aliasing
What is the sampling window in MRI?
The time the system has to acquire data while the frequency‑encoding gradient is on
What is the digital sampling frequency?
How often the system samples frequencies per second during the sampling time
When Nyquist is obeyed, what has the same numerical value as the digital sampling frequency?
The receive bandwidth
What does the frequency matrix represent?
The number of data points collected during the sampling time
What determines how many data points can be collected during sampling?
Digital sampling frequency and sampling window
How does altering the receive bandwidth or frequency matrix affect TE?
It changes the sampling window, shifting the echo peak to the middle of the new window
What does the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) do?
Converts data from frequency/time domain to frequency/amplitude domain
After FFT, what determines the shade of gray assigned to each pixel?
The amplitude of frequencies coming from the spatial location within that pixel
What information does each data point in k‑space contain?
Phase and frequency information from the whole slice
What happens when the slope of the phase‑encoding gradient changes every TR?
It changes the phase shift across a certain distance in the patient
What does steep phase encoding produce compared to shallow encoding?
More phase shift
What creates a waveform across the entire slice in MRI?
The phase position of magnetic moments in voxels across the slice
What determines the spatial frequency of the waveform across the slice?
The amount of phase shift over distance
What is pseudo‑frequency in MRI?
A frequency indirectly derived from the pattern of phase change at a spatial location throughout the scan
Why does each pixel have its own pseudo‑frequency?
Because each pixel experiences a unique pattern of phase change
What does each data point in k‑space contain?
Information about the spatial encoding process for the entire slice
What does FFT do to k‑space data?
Unlocks each data point to calculate signal intensity for each pixel position
What type of data is stored in the central portion of k‑space?
High signal amplitude and low resolution