4-Carbohydrates
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What function do carbs have?
-structural components in RNA and DNA
-immediate energy need
-energy for nervous system
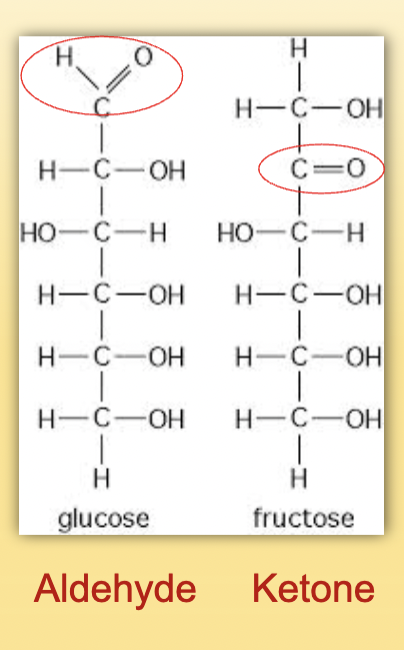
Aldehyde vs ketone
Aldehyde= carbonyl group at end
Ketine= carbonyl group within
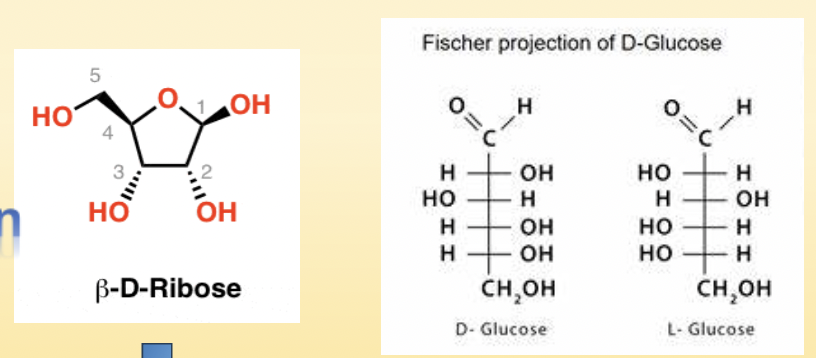
Fisher Projection
Drawn in this manner
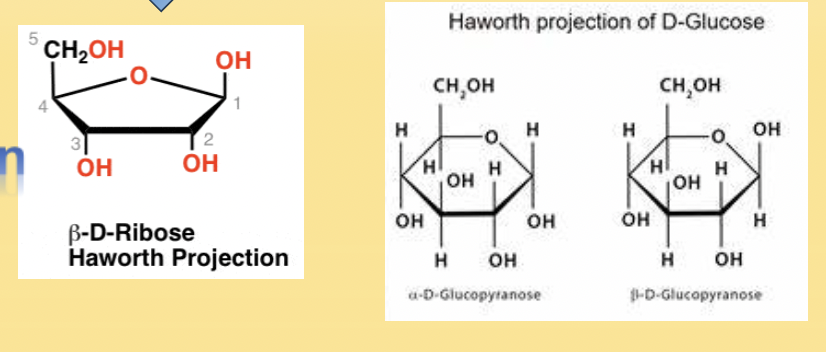
Haworth Projection
Drawn in this manner
Monosaccharides
simple sugar that has a single polyhydroxyl aldehyde or ketone
What makes monosaccharides different from other sugars?
They cannot be hydrolyzed further
List 3 monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
What are disaccharides?
2 monosaccharides bonded by an O-glycosidic bond
List 3 disaccharides
sucrose
lactose
maltose
What are polysaccharides?
-multiple monosaccharides linked
-serve as carbohydrate storage
What are polysaccharides referred to in regards to animals and pplants?
animals: glycogen
plants: starch
Glucose
-primary sugar in blood
-major energy source
-used to make ATP
Glycolysis
-breakdown of glucose to lactate or pyruvate
Gluconeogenesis
-new glucose from non-carbohydrate sources (protein or fat)
Glycogen
-main form of carb storage
-stored in liver or muscle
-readily converted to glucose with the help of hormone glucagon
Glycogenesis
Formation/synthesis of glycogen from glucose with the help of hormone insulin
Glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen to glucose
What enzymes break down disaccharides and polysaccharides
-amylase: polysaccharides
-maltase, sucrase, lactase: disaccharides
How many ATP will 1 glucose yield by the end of oxidative phosphorylation?
36-38 ATP
Free fatty acids lead to _____CoA which eventually creates acetoacetate that is then broken down to ____and ____
acetyl CoA—> acetoacetate —→ acetone and β-Hydroxybutyrate
What is the normal range for glucose
65-99 mg/dL
What is created in the alpha cells of the pancreas?
glucagon
What is glucagon responsible for?
incr glucose conc by stimulating:
-glycogenolysis
-gluconeogenesis
-lipolysis
-ketogenesis
-protein catabolism
What is created in the beta cells of the pancreas
insulin
What is insulin responsible for?
decr plasma glucose by incr GLU T transporters to push glucose into cells
Insulin is the body’s only____agent
hypoglycemic
What does insulin do overall?
decr blood glucose
What are the main target organs of insulin?
adipose tissue, liver, skeletal muscle
Insulin promotes the conversion of___to glycogen or fat
glucose
Insulin inhibits ___production by the liver
glucose
Insulin stimulates ___synthesis and inhibits____
protein synthesis; protein breakdown
At the end of insulin synthesis, it’s cleaved into insulin and ____
C-peptide
Testing for____will tell us how much insulin is in the body
C-peptide
Insulin Release: In the first phase, rapid release of____insulin ends within___mins
stored; 10 mins
Insulin release: The second phase starts at the end of the first and lasts until___is restored which is around____mins of continued insulin synthesis
normoglycemia; 60-120mins
Draw the insulin phase for early and late type 2 DM
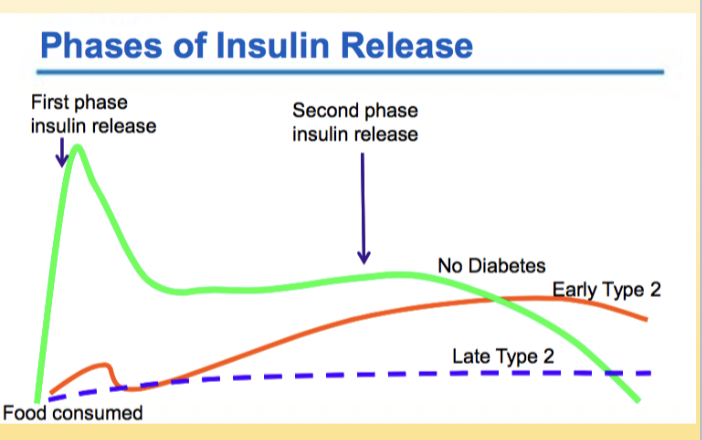
How would the chart look for Type 1 DM
Type 1 DM do not make insulin. The curve would be flat.
What hormone appears first to counteract insulin?
glucagon
epinephrine: counter regulator when glucagon is impaired
Which hormones appear second to counteract insulin?
cortisol: stimulates glycogenolysis
growth hormone
What is the glucose value for hypoglycemia?
<55 mg/dL
Hypoglycemia Adrenergic symptoms
-sweating
-heart palpitations
-hunger
-nervousness
-faintness
-weakness
Hypoglycemia neurological symptoms
-headache
-lack of coordination
-double vision
-slurred speech
-confusion
-numbness
-can lead to seizures or coma
What is the glucose fasting value for hyperglycemia?
>99mg/dL
What type of metabolic disorder is DM and what is underused?
-carbohydrate metabolism disorder
-glucose is underused
DM pts are at risk for ___ and ____.
retinopathy and neuropathy (from renal failure)
Gestational DM
carbohydrate intolerance during pregnancy
What is a pt with gestational DM at risk for?
DM
What symptoms are present in type 1 DM?
polyuria, polydipsia, rapid weight loss
What is type 1 diabetes caused by?
insulinopenia: due to loss of beta cells of the pancreas
2 most common autoantibodies in Type 1DM
Islet cell cytoplasmic antibodies (ICA)
Insulin autoantibodies (IAA)
What is the purpose of testing for autoantibodies in type 1 DM
to asses risk in relatives of pt
What 2 major defects happen in Type 2 DM?
insulin resistance
loss of β cell function
What are the 3 common complications of chronic DM?
Retinopathy
Diabetic Nephropathy
Neuropathy
hgb A1C: Where does the glucose molecule attach?
N-terminus valine of Hgb A
Is Hgb A1C reversible?
No
What does A1c represent glucose wise?
represents intrgrated glucose level over 8-12 weeks
What happens with pts who have hemoglobinopathies in regards to A1c?
RBC lifespan may be shorter so will give inacacurate result
What is eAG and what does 1% change mean?
estimated average glucose= (28.7 xA1c)-46.7
For every 1% change in A1c there is 28mg/dL change in eAG
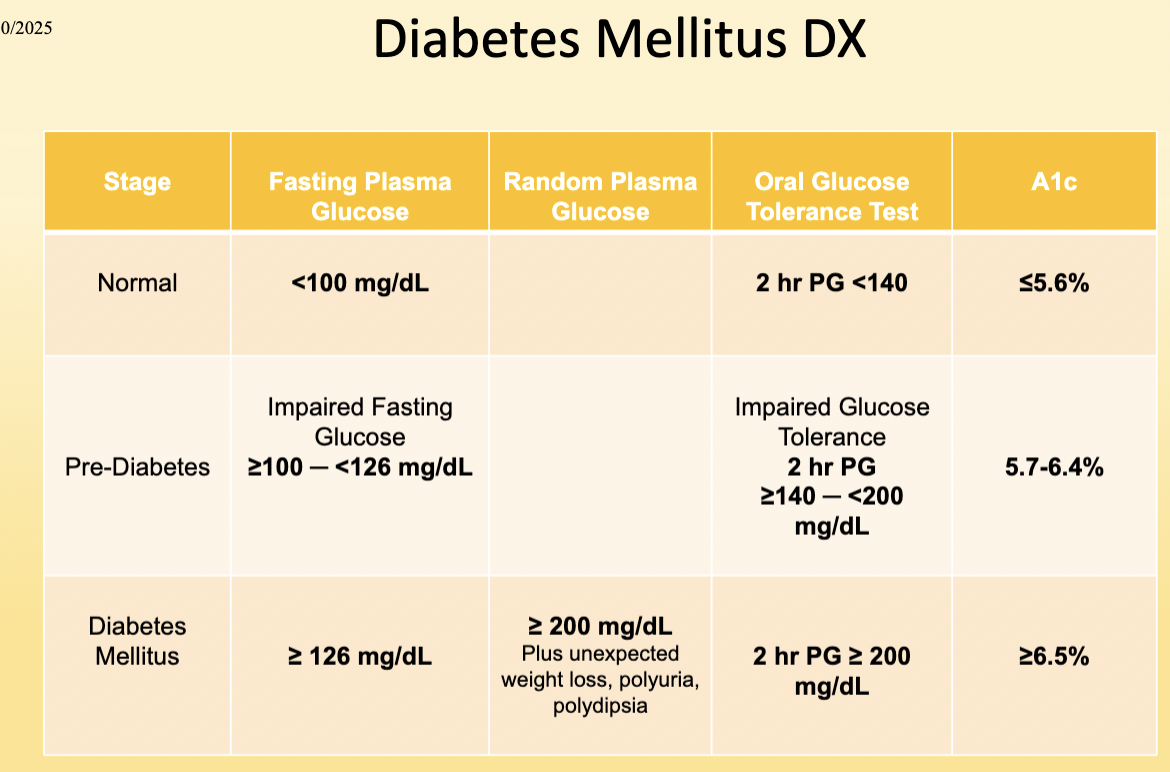
Fasting glucose abnormal is anything over ___
100mg/dL
Pre-diabetes is seen with values of :
100-126 mg/dL
DM is seen with values of:
≥ 126 mg/dL
A diet containing 1.75g carbs/kg of carbohydates for 3 days is needed for:
Glucose Tolerance Test
A low carb intake before a glucose tolerance tests can create:
a false diabetic curve
What are the requirements for a glucose tolerance test?
-in early morning
-do not eat evening meal the day before
-remain at rest during test
-refrain from smoking or eating
How many grams of glucose are give for OGTT?
-adults:100g
-children: 2g per kg of weight
When are blood specimens for OGTT taken?
1, 2, and 3 hrs after glu-cola
If hypoglycemia is suspected blood specimens are taken at __ and __hrs
4 and 5 hrs
Chart of OGTT with various pts
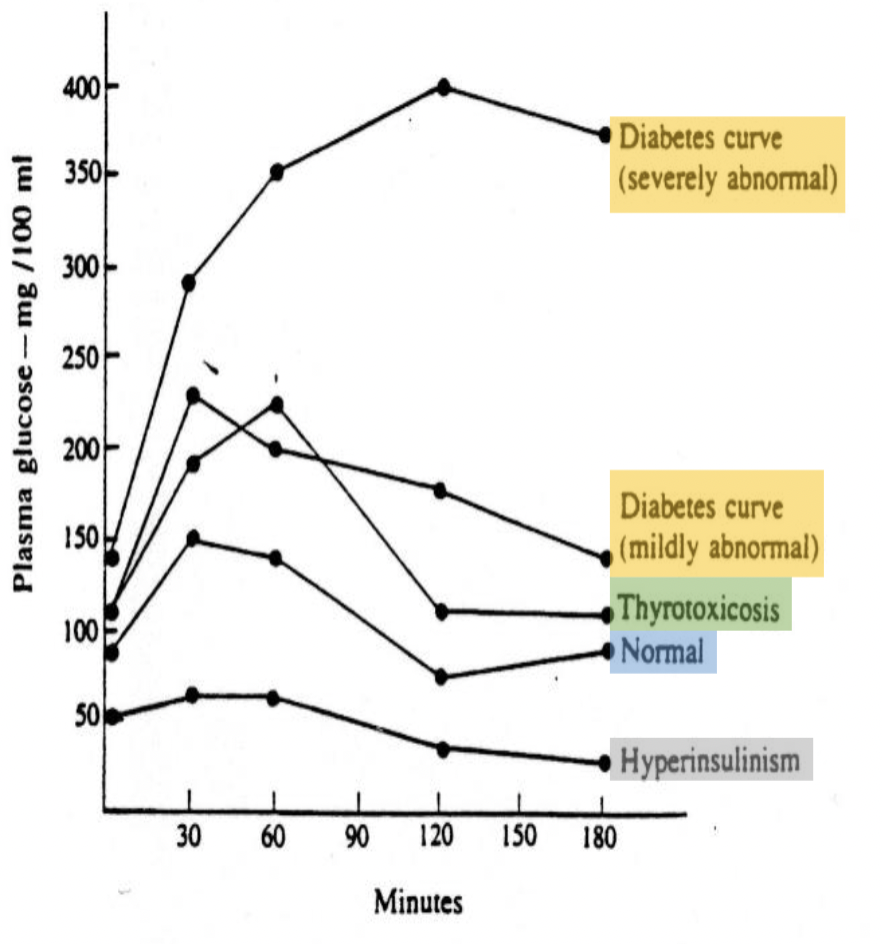
Know all the values for DM Dx
Screening for gestational DM
-no fasting; time doesn’t matter
-50g of glucose
-measure at 1 hr
-If glucose ≥ 140 mg/dL perform glucose tolerance test
Diagnosis for gestational DM
-fast for 8 hrs
-75g or 100g of glucose given
-at least 2 values must meet or exceed threshold
Fasting whole blood is ___% less than plasma glucose
10-15%
Fasting capillary blood glucose is___mg/dL higher than venous blood
2-5mg/dL
Analyze CSF___
immediately
CSF glucose is ~____% of blood glucose
~60%
24 hr urine needs to be preserved with 5mL of _____
glacial acetic acid
-refrigerate
_____reduces glucose ____% in _____hr
Glycolysis reduces glucose 5-7% in 1 hr
Can unspun samples be tested after an hour?
NO
What additive is a glycolytic inhibitors and extends stability to 3 days?
Sodium fluoride (gray)
What is the reference method for glucose enzymatic methods?
Glucose Hexokinase
Glucose Hexokinase method measures the___in absornbance at ___as NADPH is formed
incr in abs @340nm
Amount of____reduced is proportional to amount of glucose
NADPH
glucose oxidase and peroxidase is specific for:
β-D-glucose
What interference may the glucose oxidase and peroxidase encounter?
uric acid, ascorbic acid, bilirubin, hemoglobin, tetracycline, and glutathione cause falsely low values
What can cause a false (+) with glucose oxidase and peroxidase test?
bleach
Diabetes, with low levels of insulin, leads____ to causing an ↑
FFA
This in turns causes an accumulation of _____in the blood
Acetoacetate turns mostly into___ and a small portion goes into_____
Diabetes, with low levels of insulin, leads_lipolysis_to causing an ↑
FFA
This in turns causes an accumulation of _acetoacetate_in the blood
Acetoacetate turns mostly into_beta-hydroxybutyrate_ and a small portion goes into_acetone_
Where are ketones seen?
in impaired carbohydrate metabolism
What disease would we see ketones in?
DM, glycogen, storage diseases, alkalosis
Instead of B-hydroxybutyrate, what do small labs use for ketones?
-Acetest and Ketostix
-negative does not rule out diabetic ketoacidosis
Lactic acid is an ___in carb metabolism
intermediary
Lactic acid is an indicator of:
oxygen deprivation
Lactic acid in CSF should_____blood lactic acid conc
parallel
Lactic Acidosis Type A seen in:
-shock
-hypovolemia
-left ventricular failure
Lactic Acidosis Type B is seen:
-DM, neoplasia, liver disease
-Drugs/toxins
-inborn errors of metabolism
DM pts are at high risk for____damage
renal
Most common cause of renal failure in US
Diabetes
Microalbumin
detect low levels of albumin to identify early renal damage
How many rare inherited disorders of glycogen storage?
10
Each glycogen storage disorder is due to a deficiency of a ______
specific enzyme
Type 1 (von Gierkes), most common, with def/absence in____
glucose-6-phosphate