Pathophys FINAL
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Blood tests
are used to determine hormone levels in the blood so as to detect certain endocrine conditions
Computed Tomography
is used to evaluate internal structures for evidence of tumors and other anatomical abnormalities in the endocrine system
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (M R I) or Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (N M R I)
is used to visualize internal soft tissue structures including glands.
Urinalysis
evaluates physical, chemical, and microscopic changes in the urine looking for hormonal metabolites.

Growth disorders
are a problem of G H secretion from the anterior pituitary


Acromegaly
Too much growth hormone from the pituitary

Diabetes insipidus
a problem of insufficient A D H (antidiuretic hormone)/AVP (arginine vasopressin) secretion from the posterior pituitary
Disorder that affects the posterior pituitary gland
The symptoms are excessive thirst and excessive urine production.
Goiters
Goiters can result from hyposecretion or hypersecretion of thyroid hormone
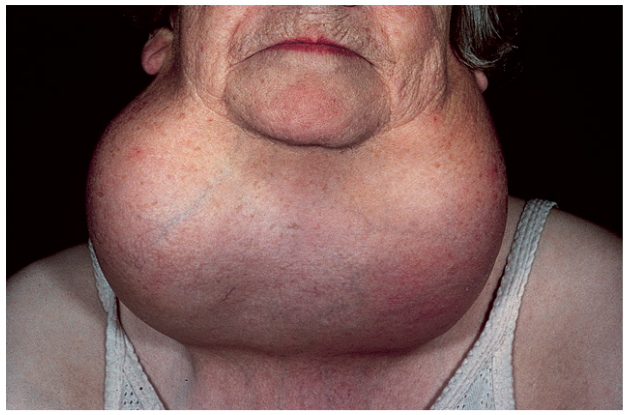
Endemic goiter
is the most common due to iodine deficiency
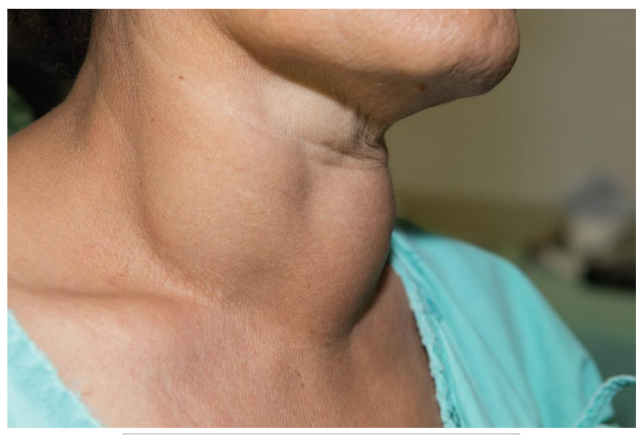
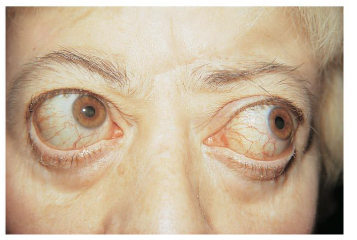
Graves Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder
It is characterized by hypersecretion of thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism)
Can cause what is called a Toxic Goiter
Is often associated with exophthalmos, also know as proptosis
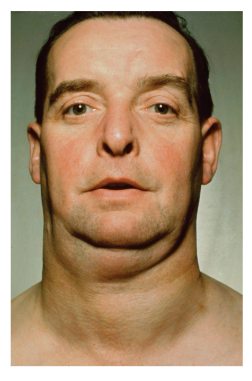
Hashimoto’s Disease
Hashimoto’s disease is an autoimmune disorder
It is characterized by hyposecretion of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism)
Myxedema
swelling of the skin caused by a buildup of mucin
can be caused by hypothyroidism
can lead to myxedema coma
Diabetes mellitus
Disorder affecting the pancreas
is a problem with insulin in blood glucose regulation. It has two forms: type 1 and type 2
Symptoms for both types are excessive thirst (polydipsia), excessive urine production (polyuria), and glucose in the urine (glucosuria)
If uncontrolled, both types may lead to life-threatening complications
Insulin
Stimulates cells to take in glucose to lower blood glucose levels; tells liver to store glucose as glycogen
Glucagon
Stimulates glycogen conversion to glucose and then its
secretion to raise blood glucose levels
Simple carbohydrates
increase insulin levels.

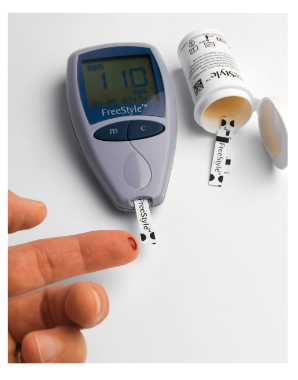
Glucometer
measures blood glucose
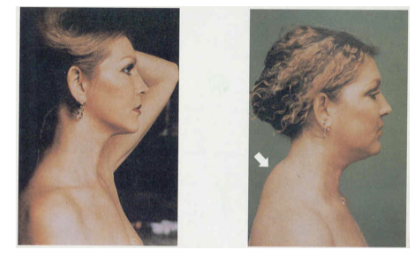
Cushing’s Syndrome
affecting the adreanal gland
is due to hypersecretion of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (A C T H) from the pituitary gland
This causes the adrenal gland to produce too much cortisol
buffalo hump
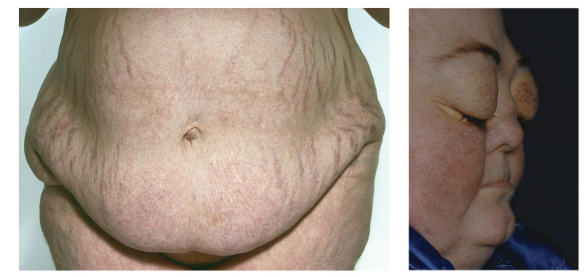
Addison’s disease
Degeneration of the adrenal cortex, which results in the inability to produce adequate amounts of glucocorticoid hormones, mineralocorticoid hormones, and androgens
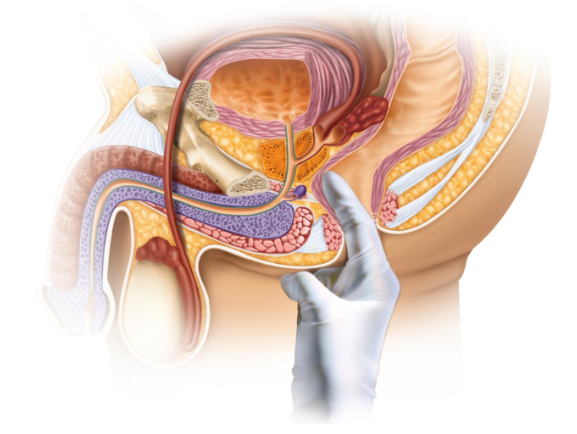
Digital rectal exam (DRE)
A procedure in which the doctor inserts fingers into the rectum
to detect any abnormalities, such as an enlarged prostate
Laboratory tests/ microscopic
examination of samples
Procedures that involve collecting urine or specimen samples
from the urinary tract to determine the presence of viruses or bacteria that may cause infection
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test
A test that measures the presence of prostate-specific antigens
in the blood. Increased levels may indicate prostate cancer
Transrectal ultrasound and biopsy of the prostate
A procedure in which ultrasound technology is used to assess
the prostate for evidence of cancer. If a mass is detected, a sample is collected & examined by a laboratory for the presence of cancerous cells.
Ultrasound
An imaging technique in which sound waves create visual images
of internal structures. In the male reproductive system, ultrasound may be used to determine the cause of a hydrocele, examine a
mass in the testis, and diagnose epididymitis & cryptorchidism.
Prostate cancer
Nine percent of men over the age of 50 will develop prostate cancer
Prostate cancer can be detected by a digital rectal exam and a blood test that measures prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is most common in males between the ages of 15 and 34.
Routine testicular self-exams are recommended for early detection
Hypospadias
is a congenital defect in which the urethra opens on the ventral side or base of the penis instead of on the tip of the glans
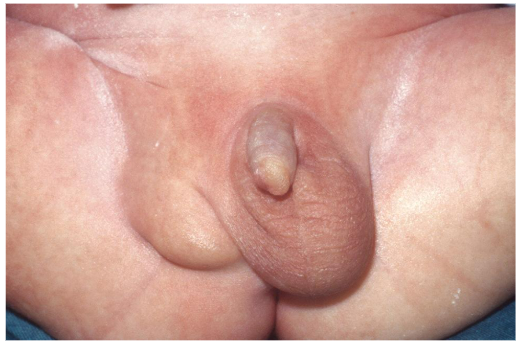
Hydrocele
is a condition in which fluid has accumulated and causes swelling in the scrotum.
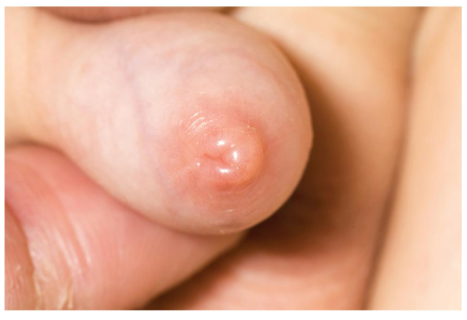
Epididymitis
is inflammation of the epididymis, usually caused by a bacterial infection
Phimosis
is a condition of the penis characterized by tight foreskin that cannot be pulled back over the glans penis
Sexually Transmitted Infections
Also known as sexually transmitted diseases (S TDs): infections that are passed through sexual contact
Most common are herpes, H I V, human papillomavirus (HP V), gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis
Gonorrhea
Caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Causes burning during urination and a discharge
Chlamydia
Bacterial, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis
Symptoms are burning during urination and discharge
Syphilis
Caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum
Sores on the genitals, anus, rectum, or mouth
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Untreated STIs can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Can cause damage to the reproductive tract, resulting in infertility, ectopic pregnancies, abscess formation, and chronic pain in the lower abdomen
Herpes
A viral infection that causes sores on the genitals, anus, or mouth
HIV
The virus that causes AIDS
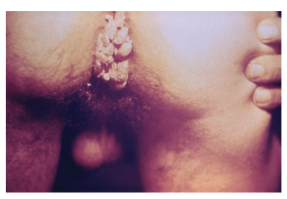
HPV
A viral infection resulting in the growth of warts on the genitals. The infection is caused by the human papillomavirus.
Genital Warts
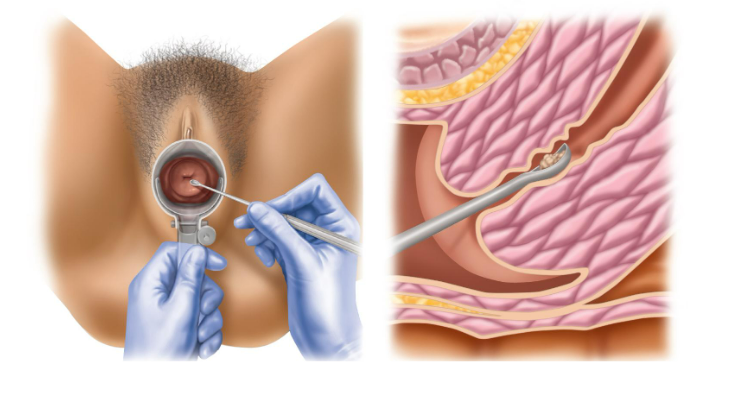
Pap smear
examines cells from the cervix
pregnancy test
detects human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG) hormone during pregnancy
ultrasound
is an imaging technique in which sound waves are used to visualize internal female reproductive structures
Ovarian Cancer
Cancer of the ovaries
Often lacks symptoms
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is often caused by human papillomavirus (H P V) infection
Usually detected with a Pap smear.
Treatment options include the removal of the uterus (Hysterectomy)
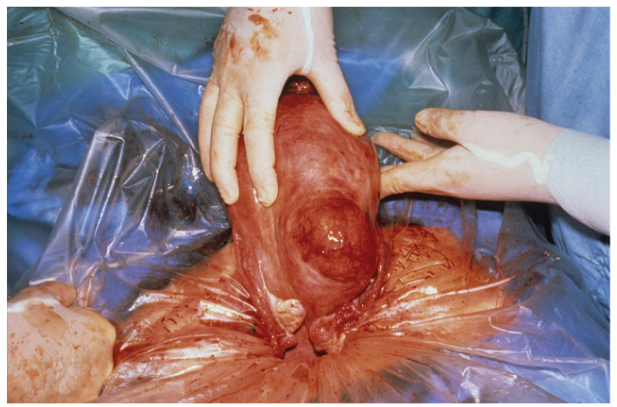
Fibroids
Noncancerous growths composed of muscular and fibrous tissue.
Found in the uterus, endometrium, or on the outside of the uterus.
Usually left alone if it is not causing problems
Usually removed if it is causing pain or bleeding; or if it grows too large; can cause infertility
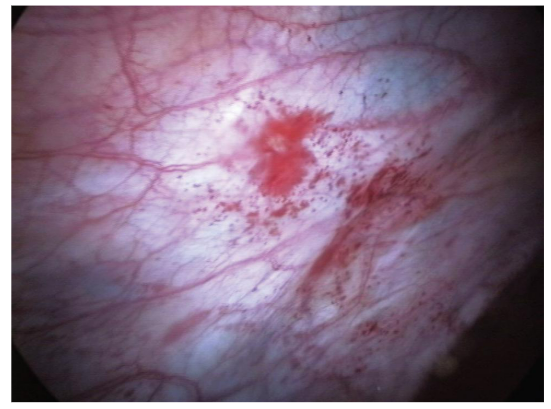
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is the growth of endometrium in places other than the uterus
The endometrium goes through the menstrual cycle no matter where it is located.
Endometriosis can lead to infertility and painful periods (dysmenorrhea).
Disorders of Pregnancy
Fifty percent of zygotes do not survive. Most are lost before they implant
Of the zygotes that do implant, 10 to 15% end in spontaneous abortion due to fetal abnormalities, improper implantation, premature detachment of the placenta, and other causes
Ectopic pregnancy
occurs if the fertilized egg implants anywhere other than in the uterus.
Preeclampsia
is pregnancy-induced hypertension accompanied by protein in the urine.
Placental abruption
placenta becomes prematurely detached from the uterine wall
Placenta previa
the placenta is positioned over the cervix, blocking the opening to the uterus.
Breast cancer
Abnormal growth of breast tissue, usually occurring in the lactiferous ducts and lobules of the breast
Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
The loss of a zygote before delivery, either before or after implantation. Reasons include fetal abnormalities, improper implantation, or placental abruption.