Connective Tissue Fibers
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Collagen fibers
Relatively thick, thread like, composed of collagen and occuring in long parallel bunders which withstand force when pulled along axis.
Elastic fibers
Thinner and form complex networks. Return to original length after stretching.
Reticular fibers
Highly branched and delicate supporting networks. Able to resist forces applied from many branches.
Areolar connective tissue
Located in papillary layer of dermis and epidermis and around organs
Functions are movement and stretching, support
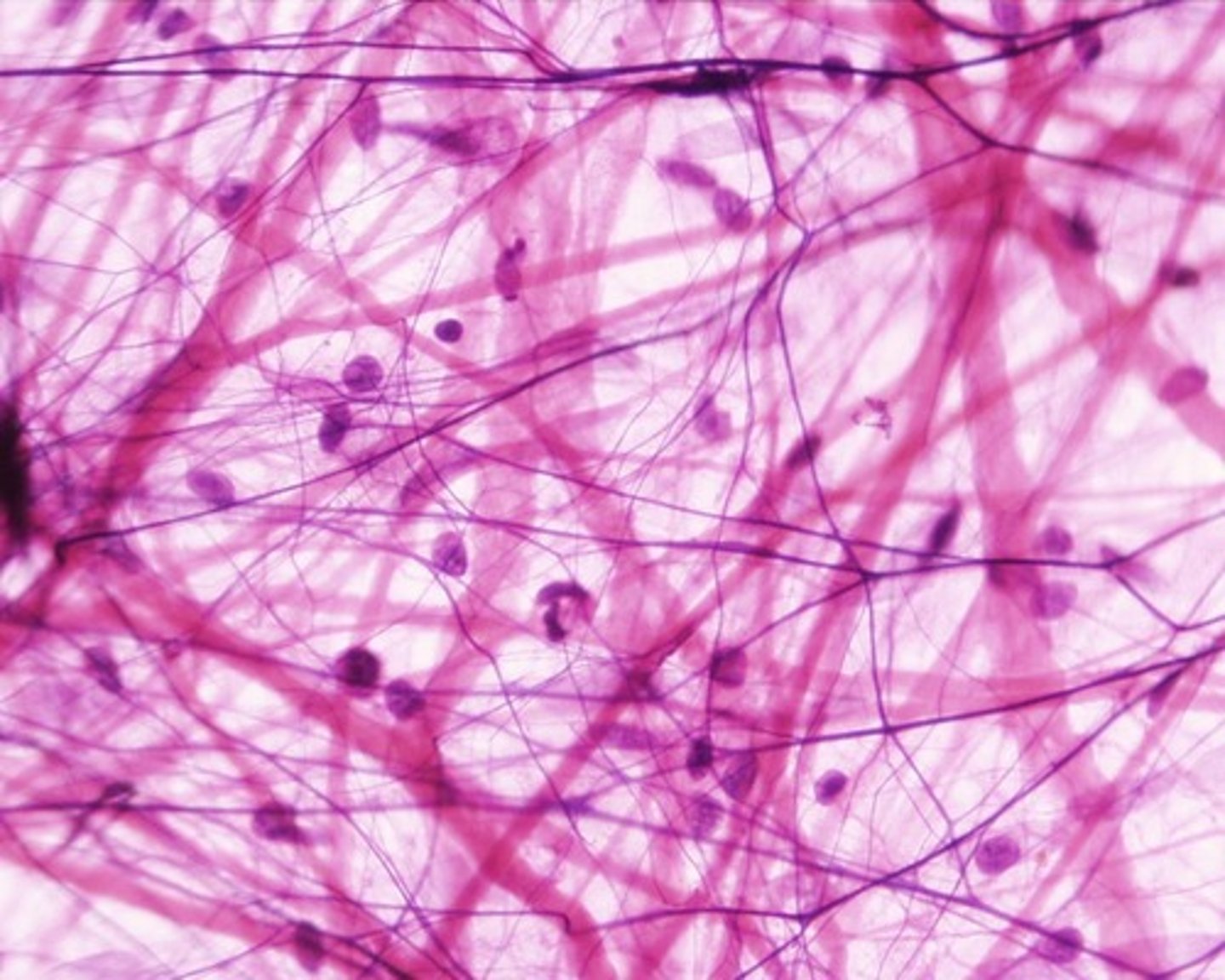
Reticular connective tissue
Located in bone marrow, spleen, and liver.
Function is removes worn out RBCs in spleen and support.
Hint: looks like chicken wire.
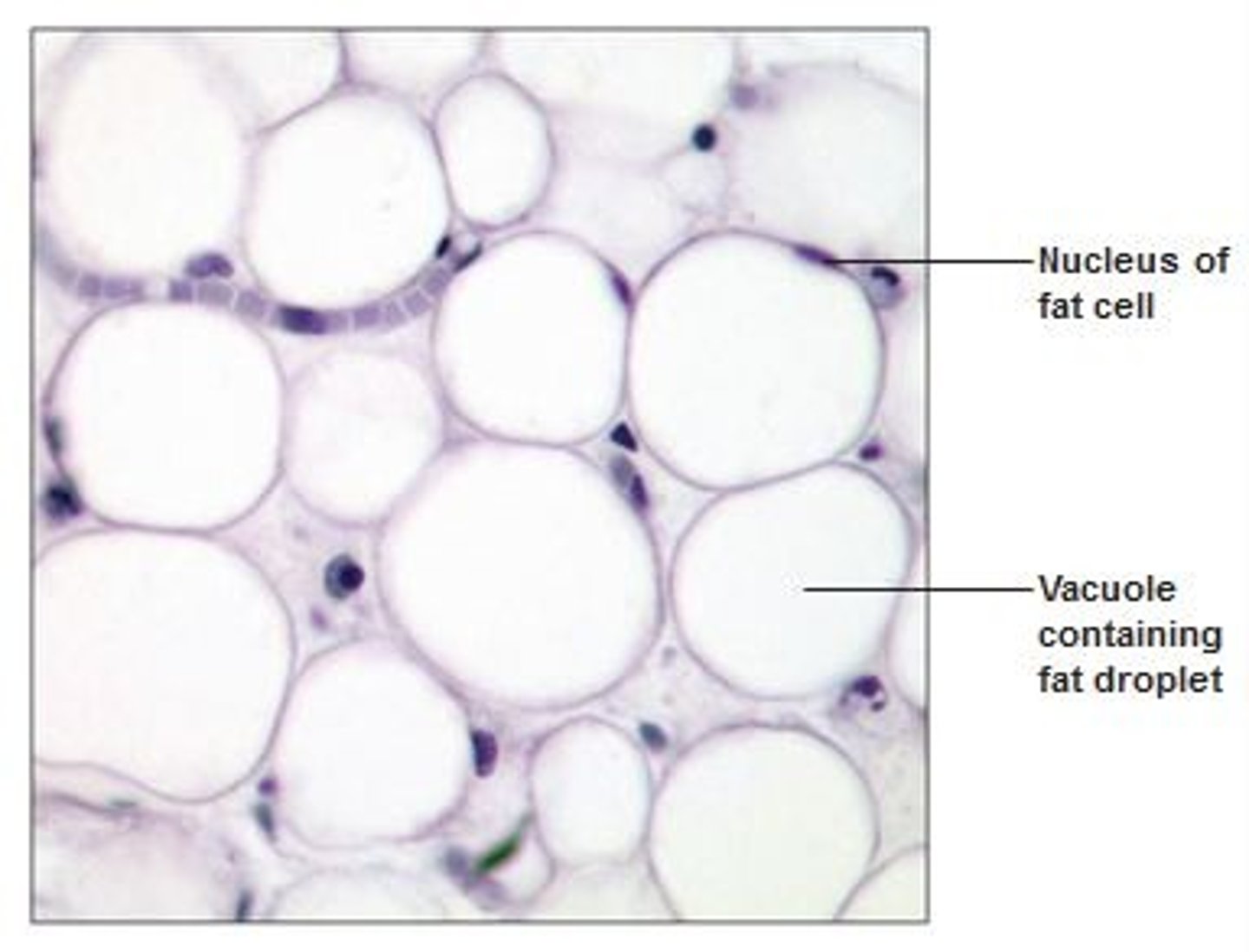
Adipose connective tissue
Has modified fibroblasts which store fat and thus become swollen, pushing nucleus to edge of cell.
Located: throughout body
Function: supports/protects organs, energy reserve, reduces heat loss through skin.
Dense regular connective tissue
Fibers are all parallel. Function is to pull force in one direction, strength.
Located: tendons, ligaments, covers skeletal muscle.
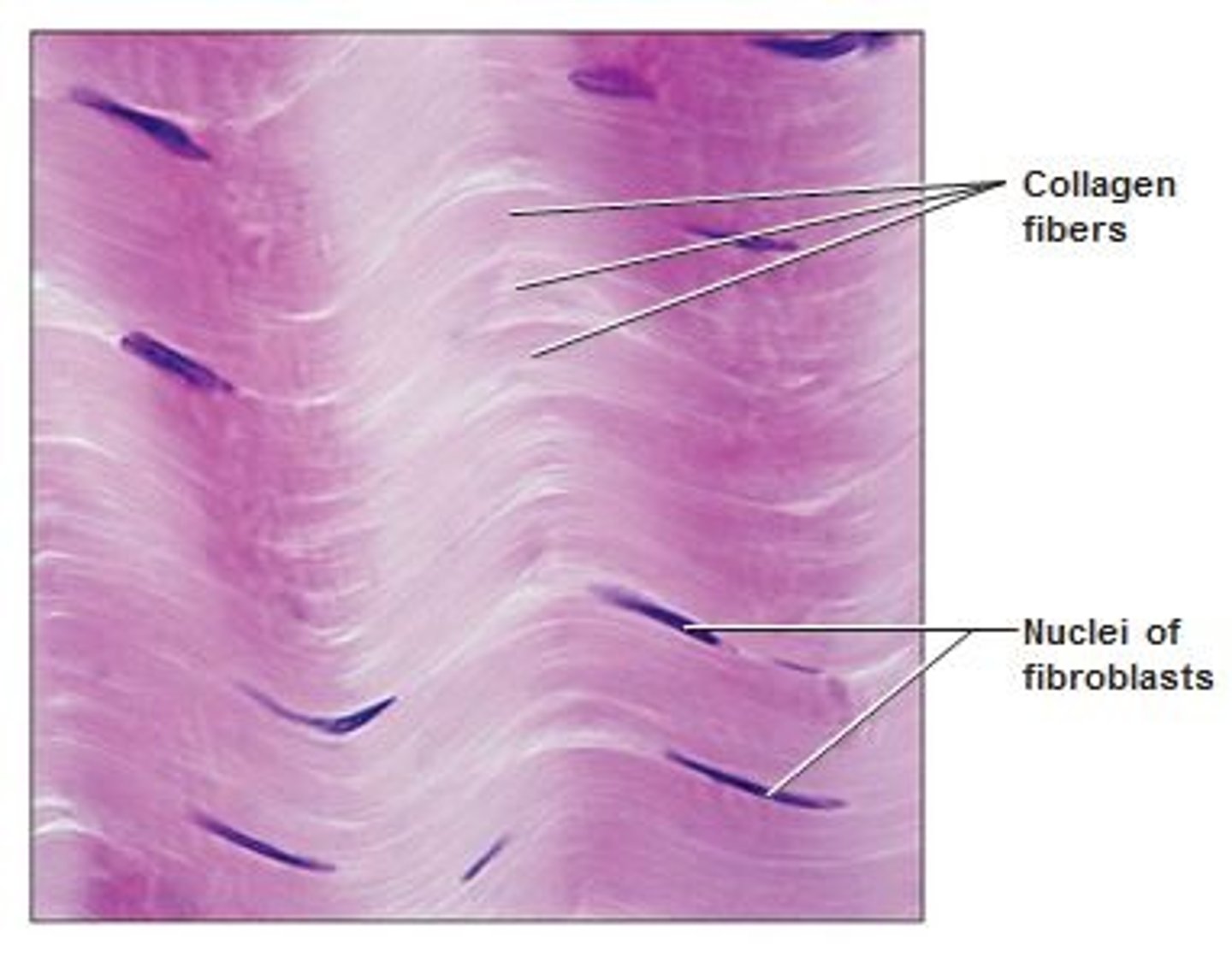
Dense irregular connective tissue
Located in nerve and muscle sheaths and perichondria of cartilage, organs/joints.
Function: Strength, tensile strength in all directions.
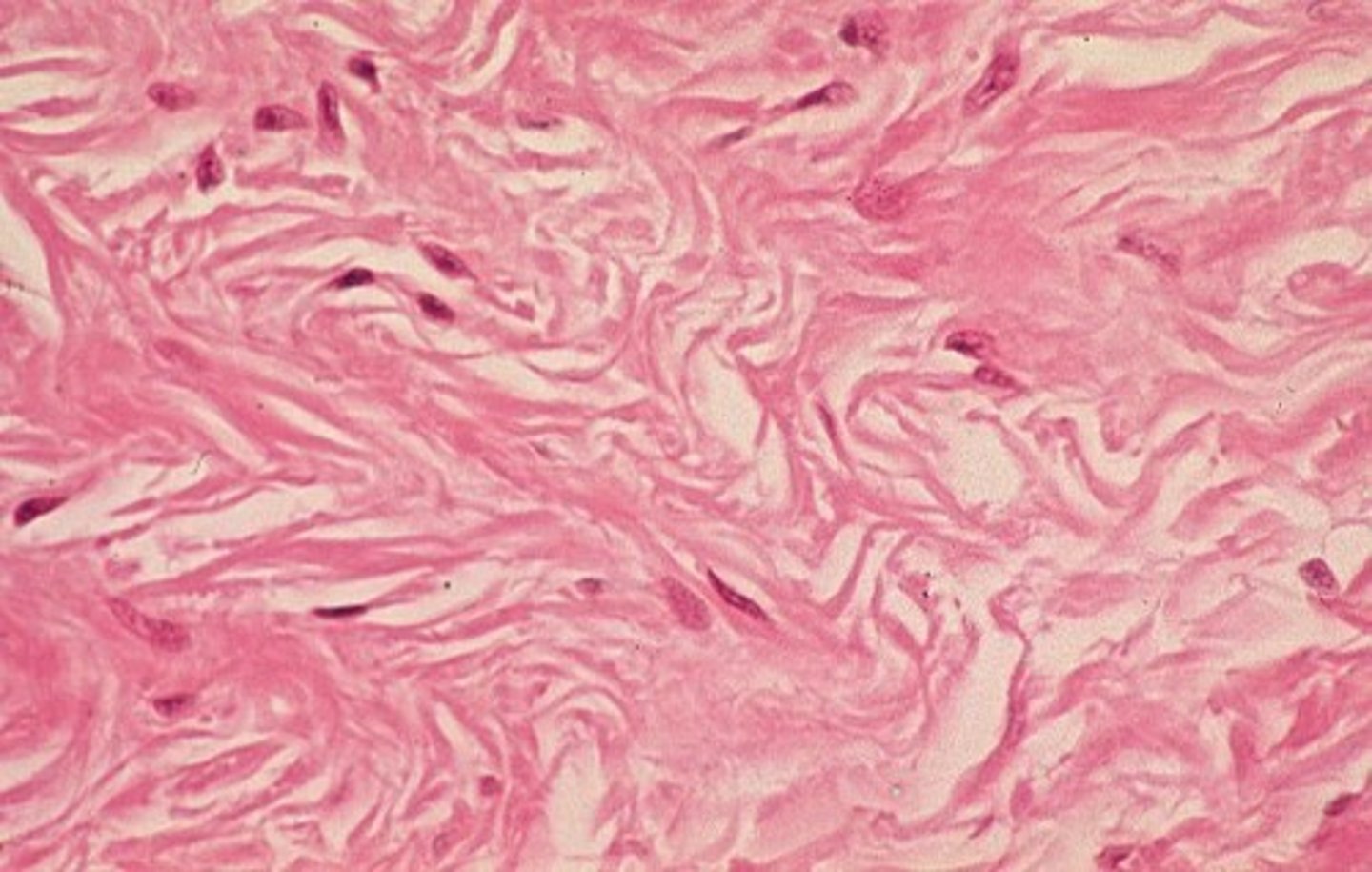
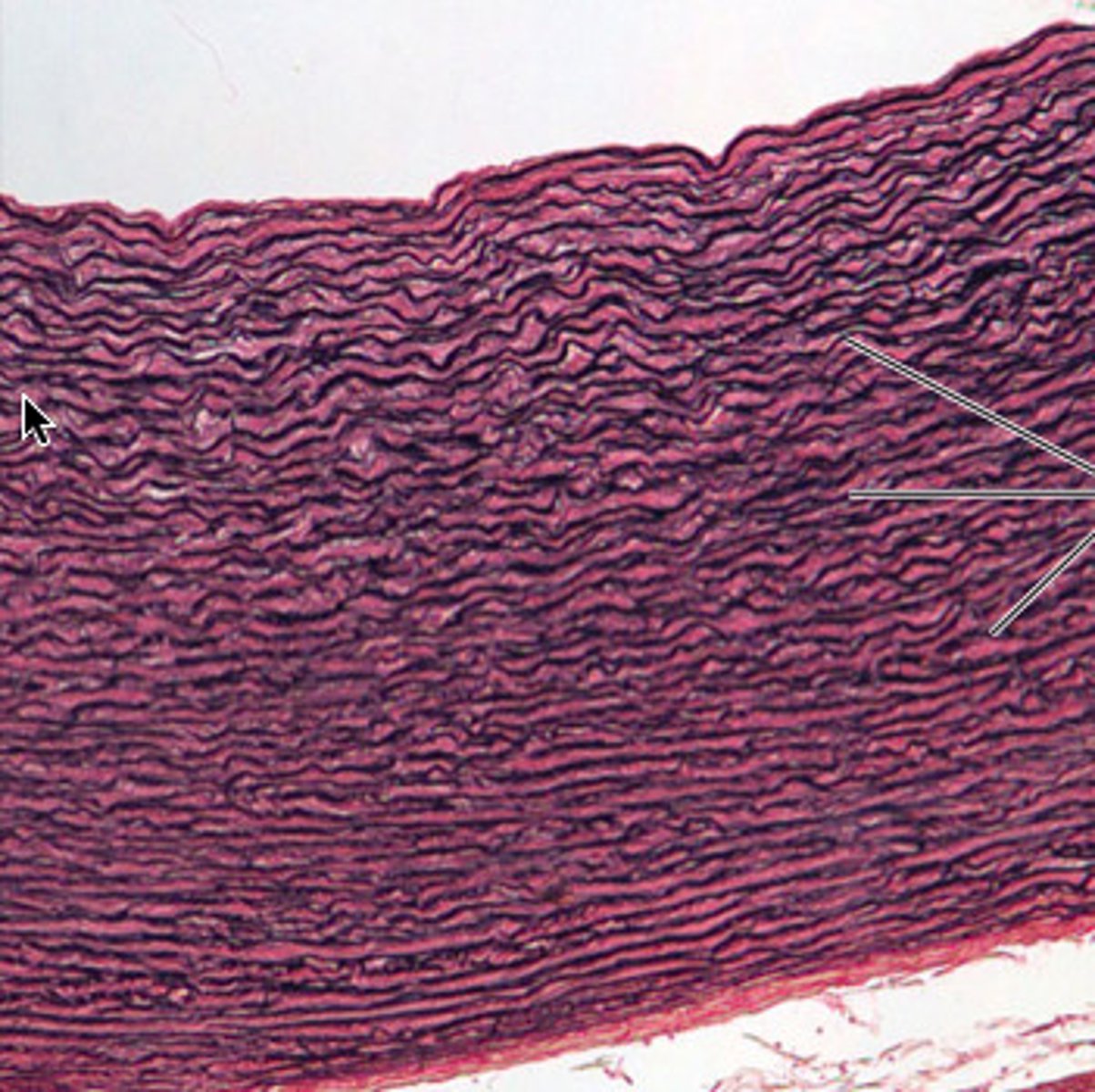
Elastic connective tissue
Located: Lung tissue, aorta, vocal cords, respiratory passages.
Function: Stretch, ability to go back to original shape.
Cartilage
A supporting connective tissue made up of chondrocytes(cartilage cells) surrounded by a semisolid gel like matrix. Avascular.
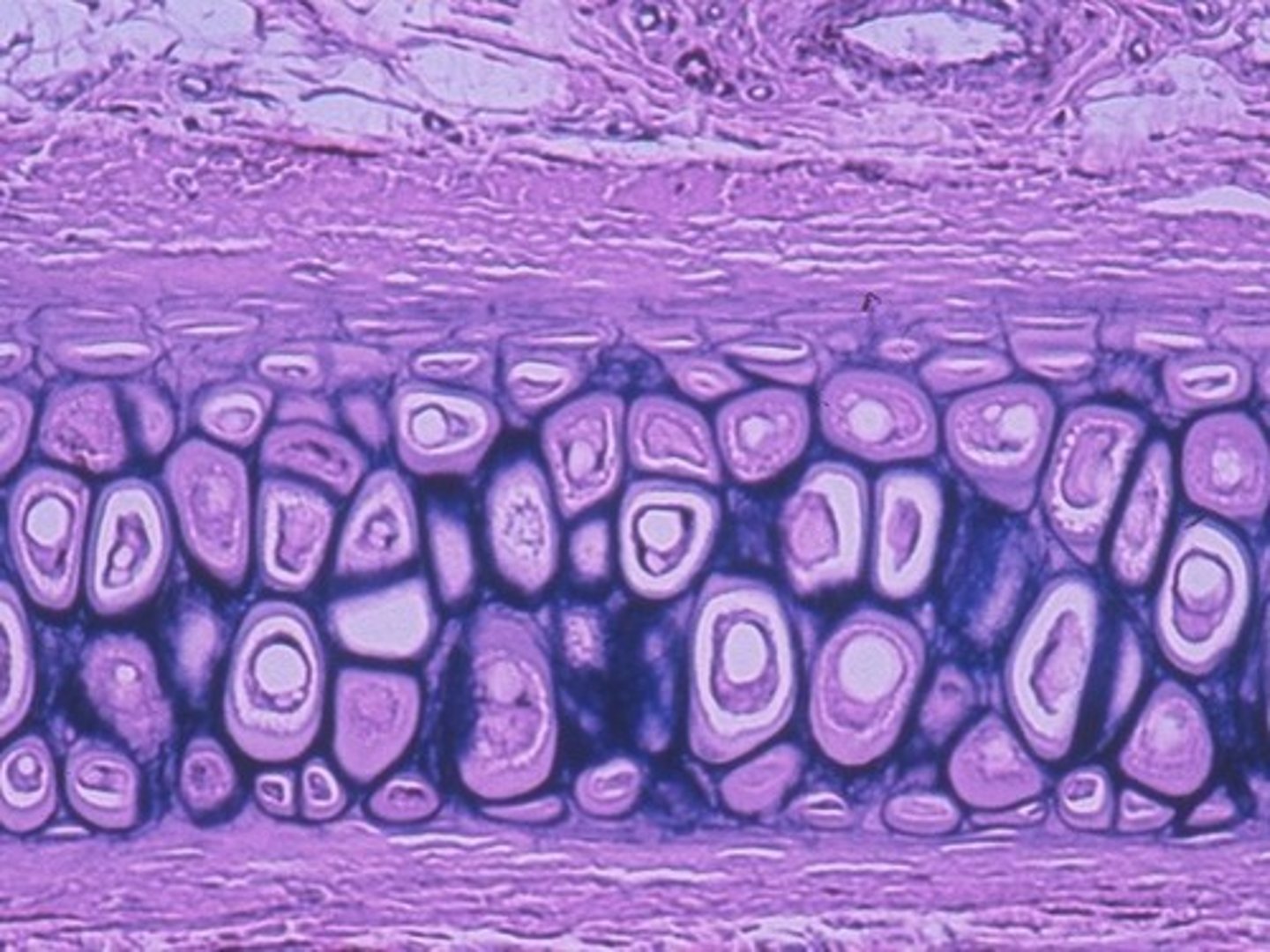
Lacunae
hole that holds chondrocytes.
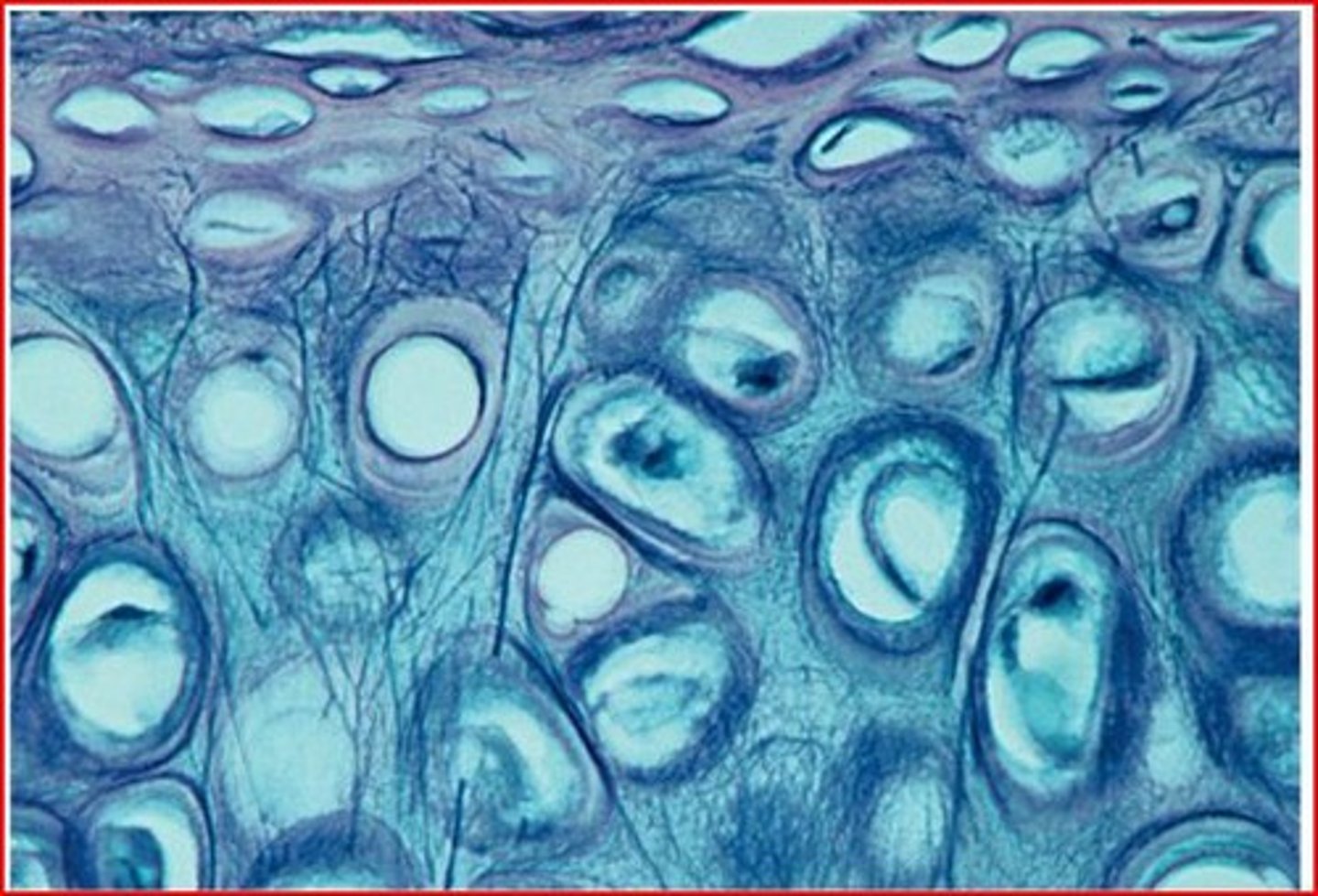
Hyaline cartilage
Matrix of closely packed collagen fibers. Found in costal cartilages of bronchi, ribs, tracheal rings. Function: support, flexibility.
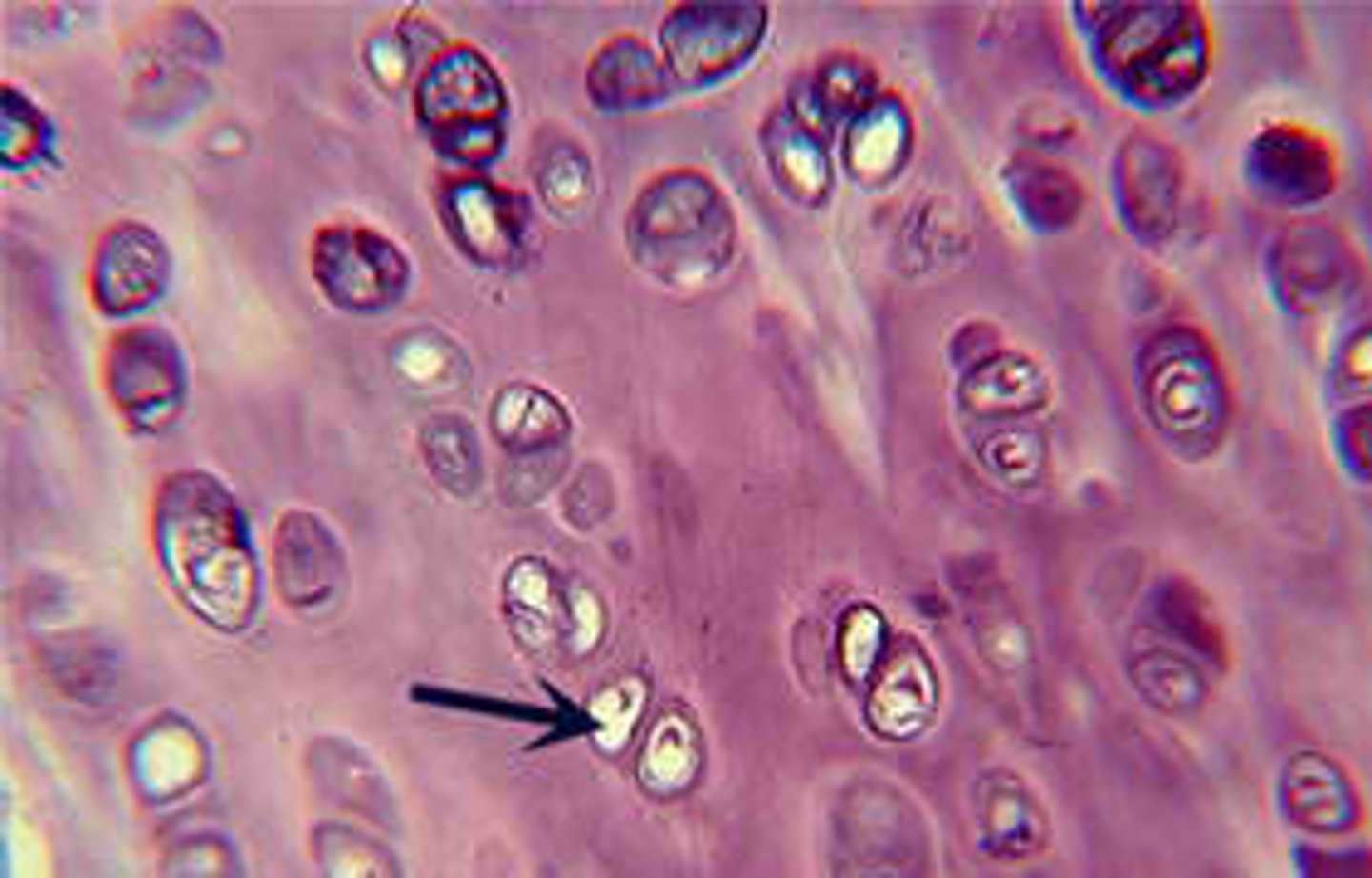
Fibrocartilage
Matrix is suppored by collagenous fibers which are densly packed and regularly arranged.
Located: menisci of knees, intervertabrel discs. Function: Prevent bone=bone contact, support.
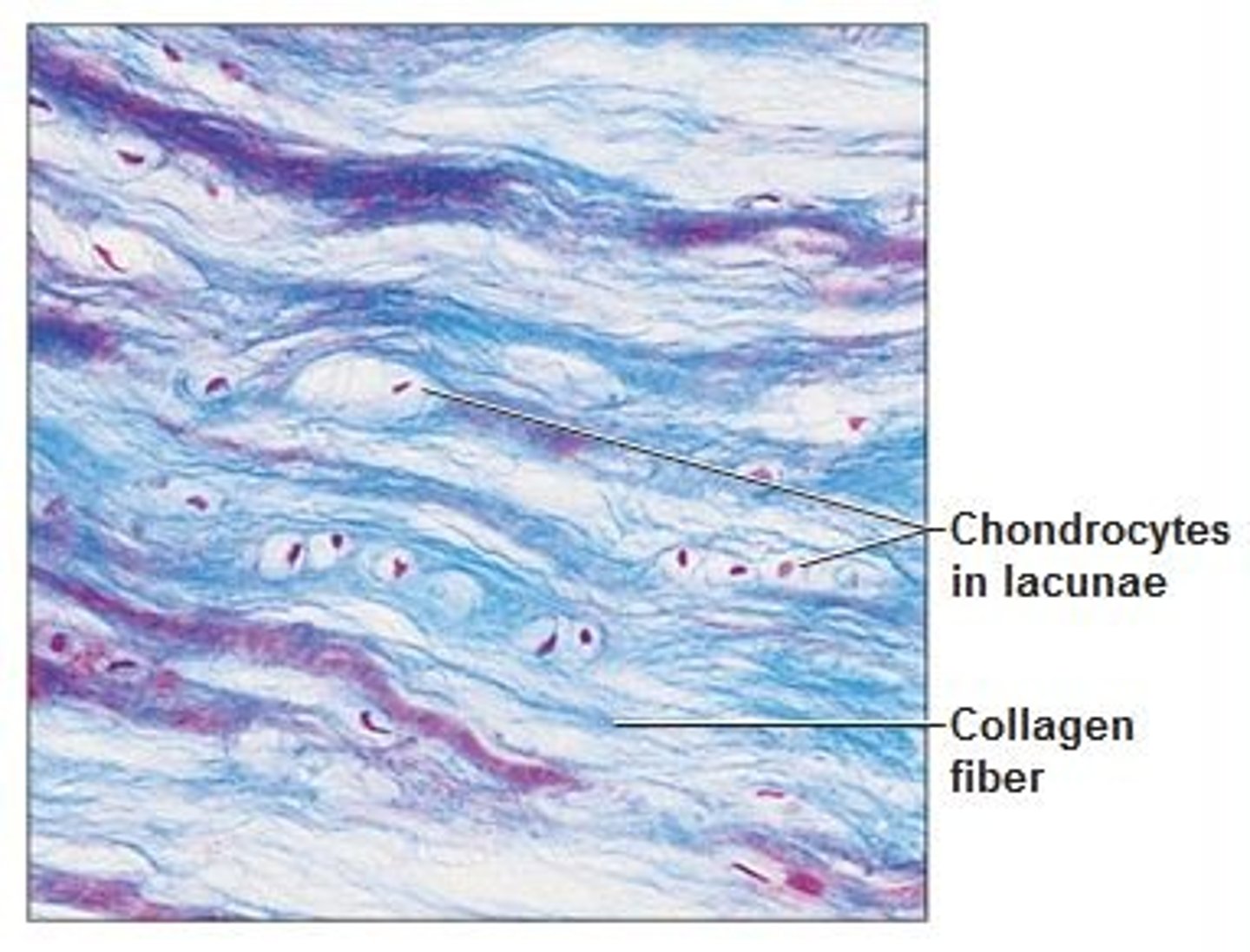
Elastic cartilage
Located: pinna of ear, auditory canal, tip of nose.
Function: Strength and elasticity. Matrix is supported by elastic fibers which make it resilient and flexible and are less densly packed and arranged irregularly.
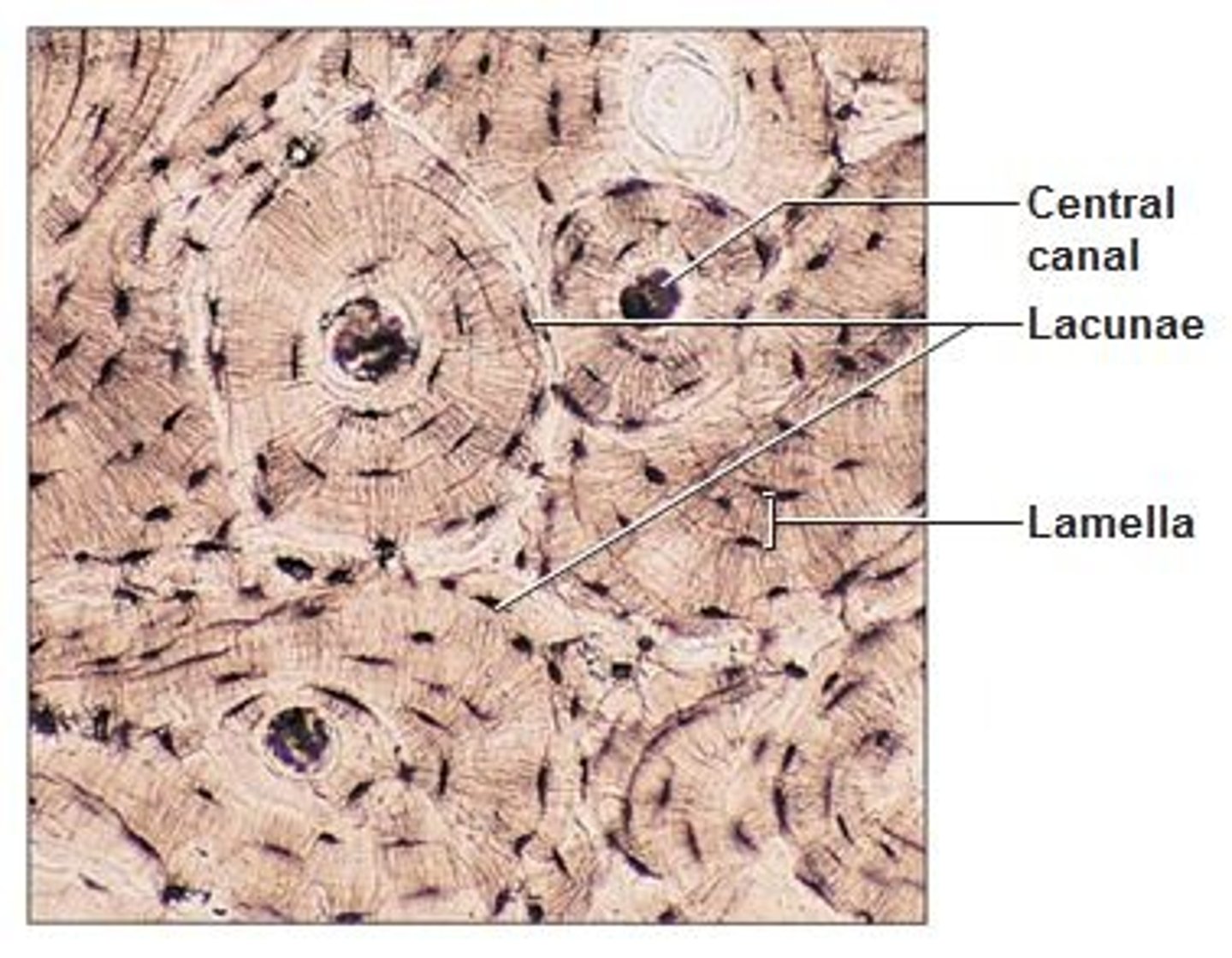
Bone
A supporting connective tissue, one third of its matrix is collagenous fibers.
blood
Fluid connective tissue.
Lymph
Fluid connective tissue
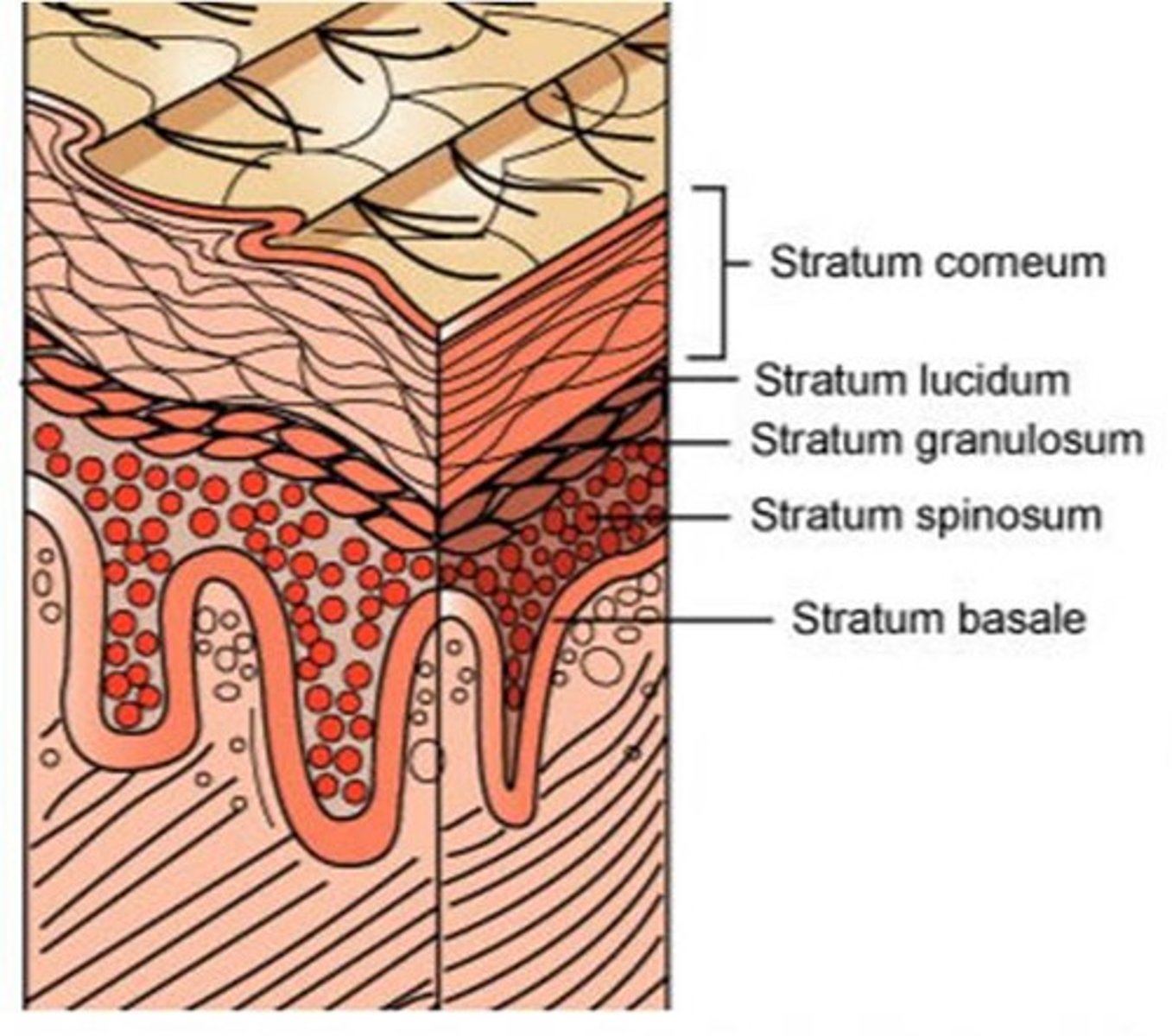
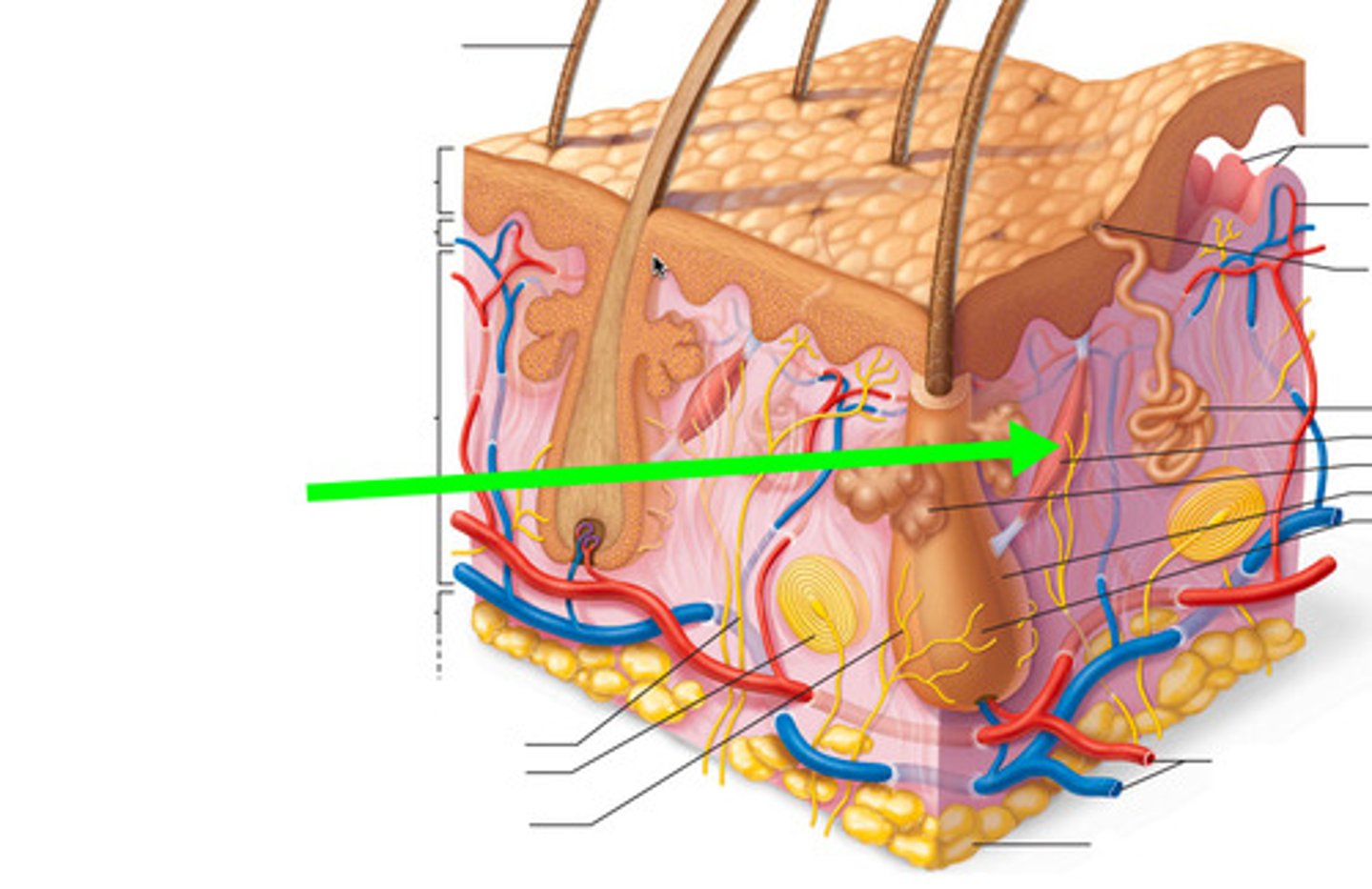
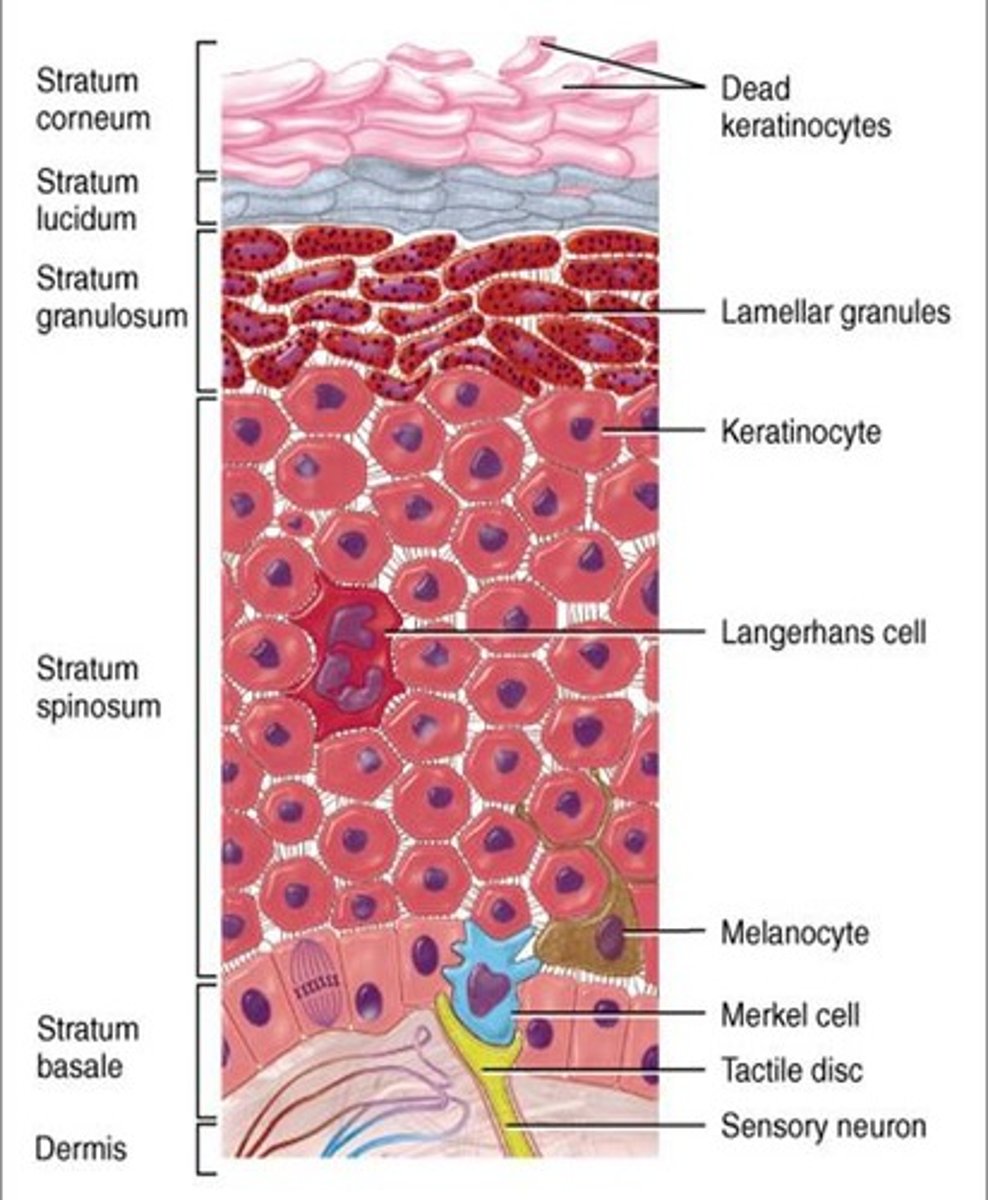
Epidermis layers
Stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum.
Dermis
Divided into papillary and reticular regions.
Papillary layer of dermis
Areolar connective tissue and makes up 1/5 of dermis.
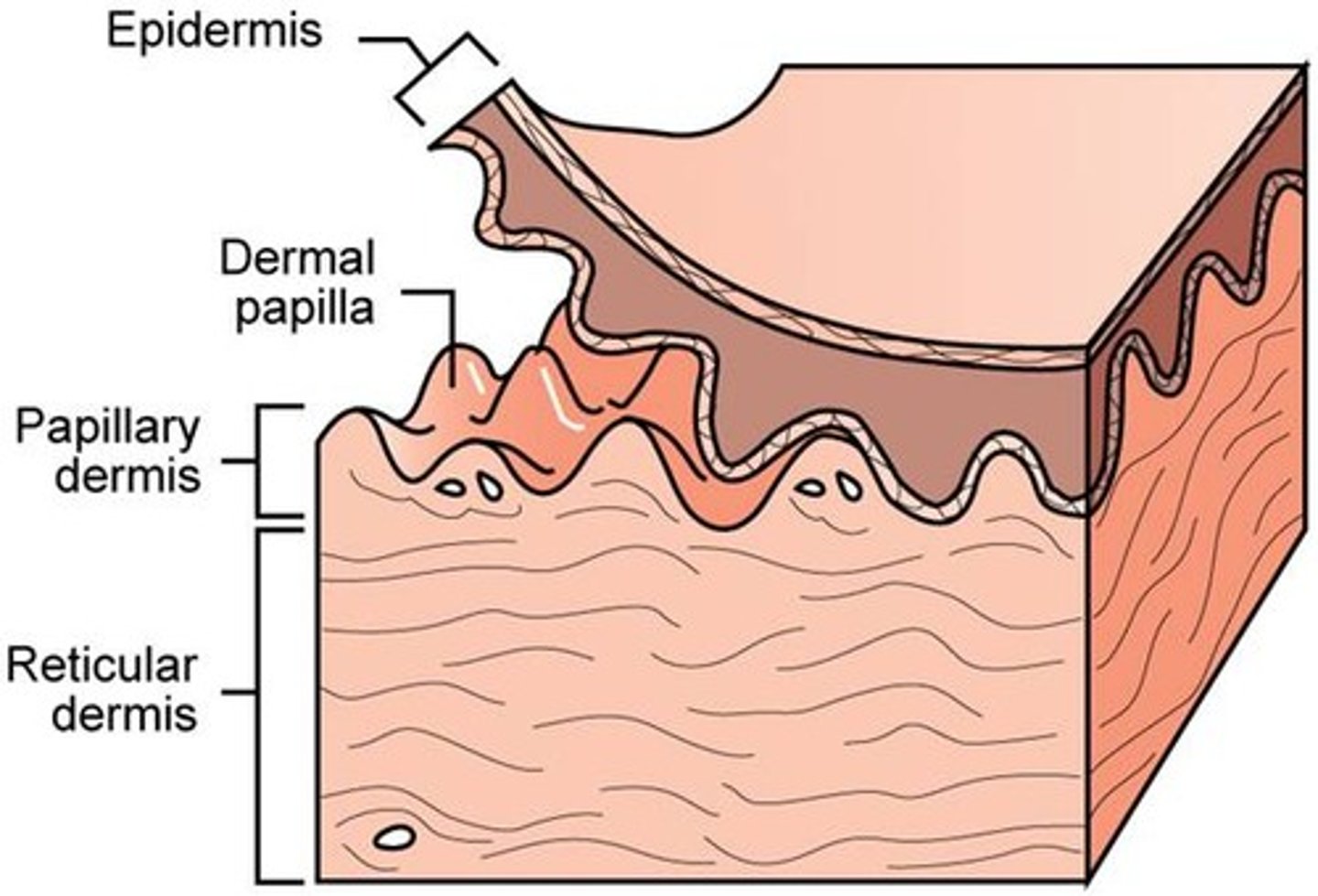
Reticular layer of dermis
Deep to papillary and is dense irregular tissue. 4/5 of dermis
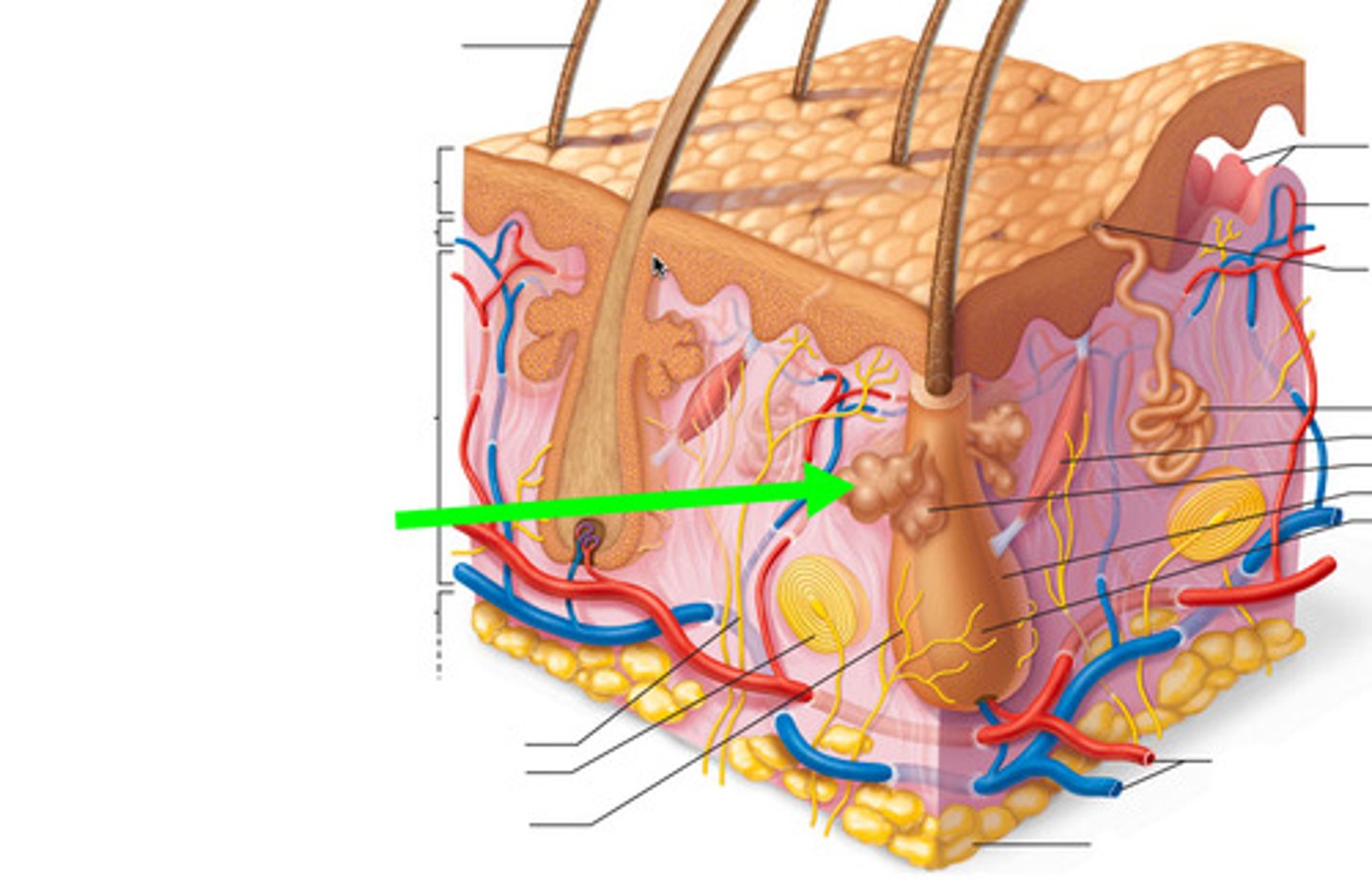
Sebaceous glands
Found around hair follicle, secrete sebum, oil.
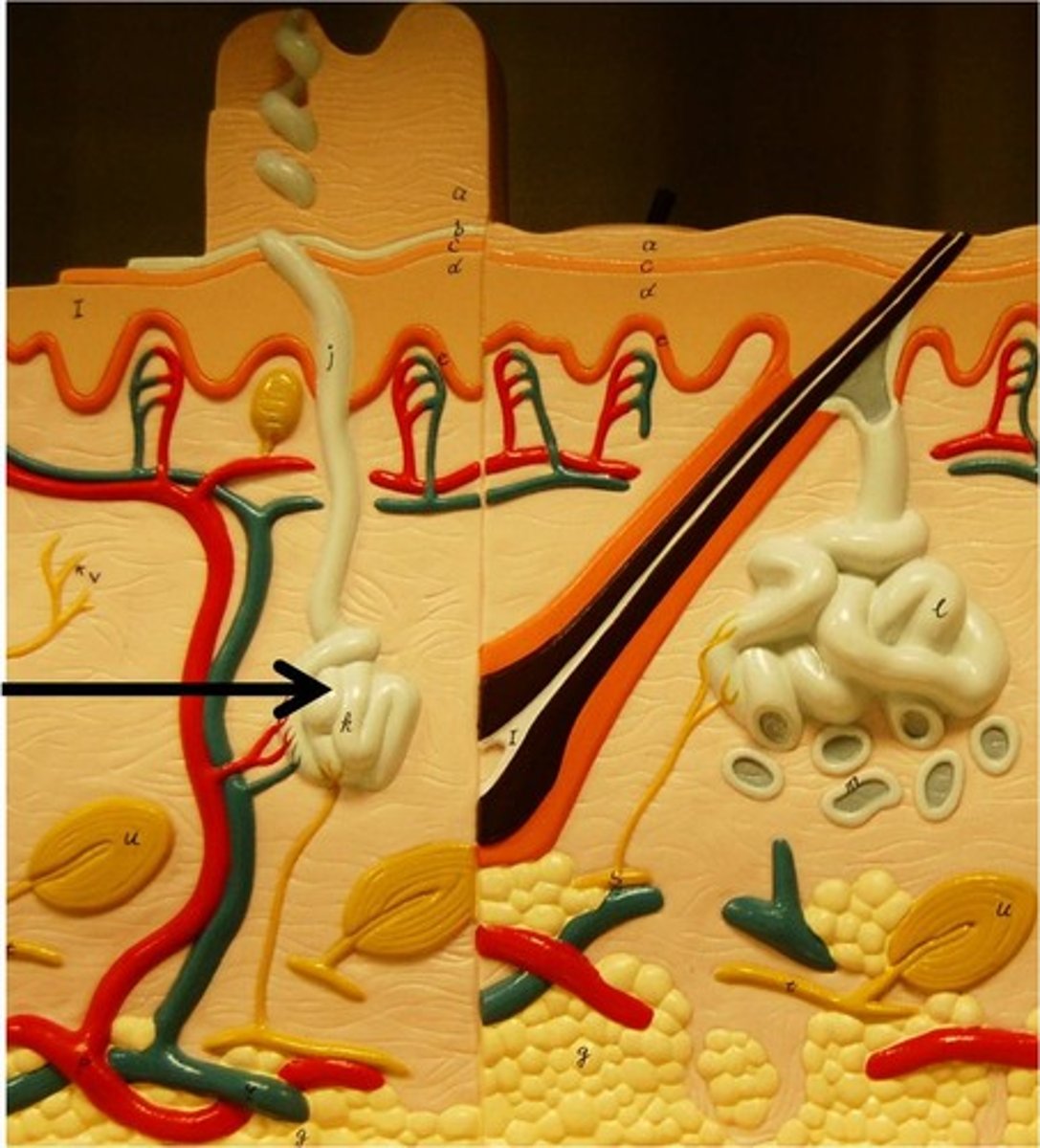
Sudoriferous apocrine glands
None in thick skin. Not present til puberty. Located in axilla, groin, nipples. Larger in size. FUnction is body odor, sweat
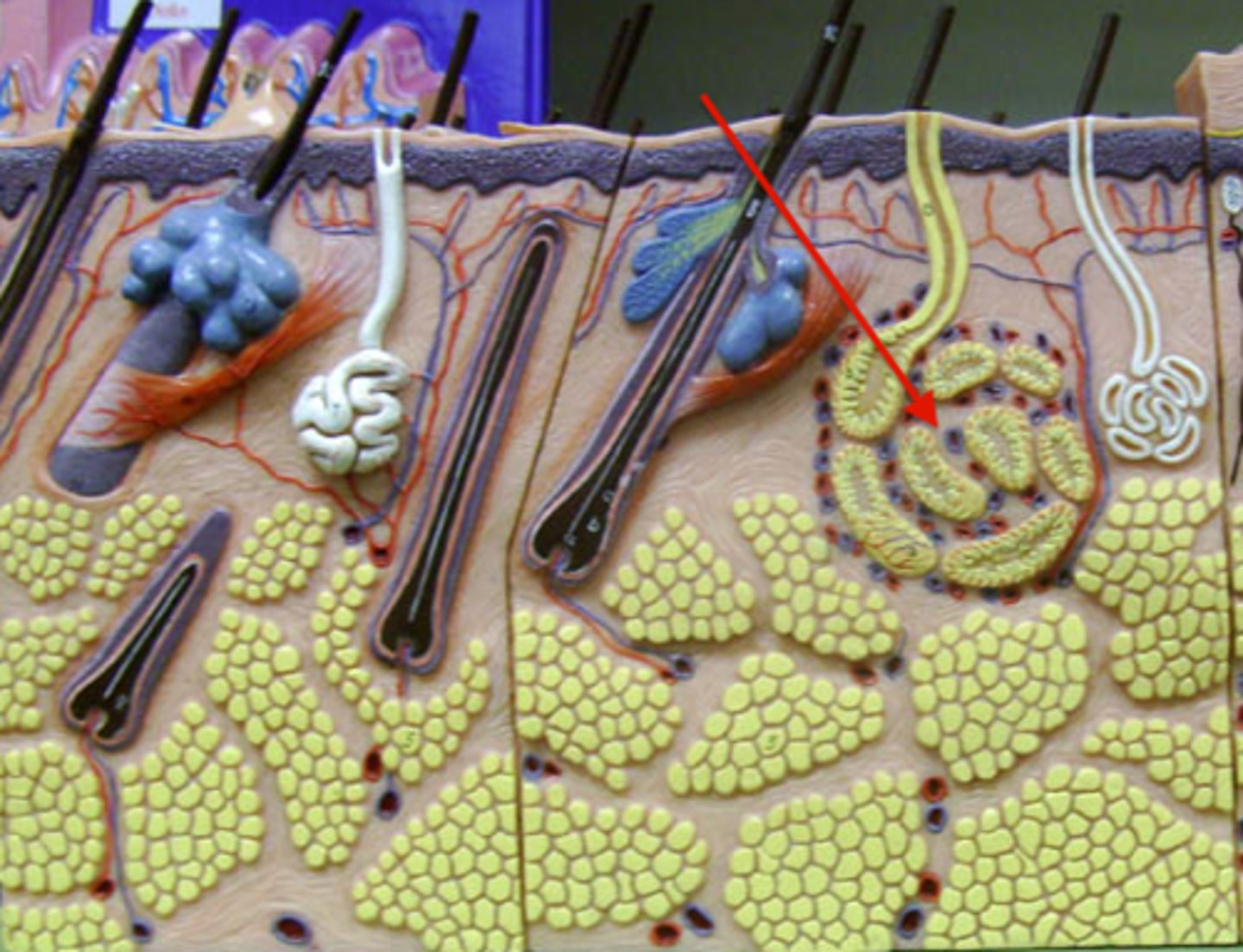
sudoriferous eccrine glands
MOst common, thermoregulation

Vellous hair
Peach fuzz
Terminal hair
Thick and coarse. Found on head, groin, axilla, eyebrows.
Intermediate hair
Finer than terminal. Located on limbs.
Arrector pili muscle.
Smooth muscle on hair follicle. Function to create goosebumps and push sebum up through hair follicle.
Merkel cells
Fine touch and only found in the stratum basale of epidermis.
Meissner's corpuscles
Light touch receptors in dermis
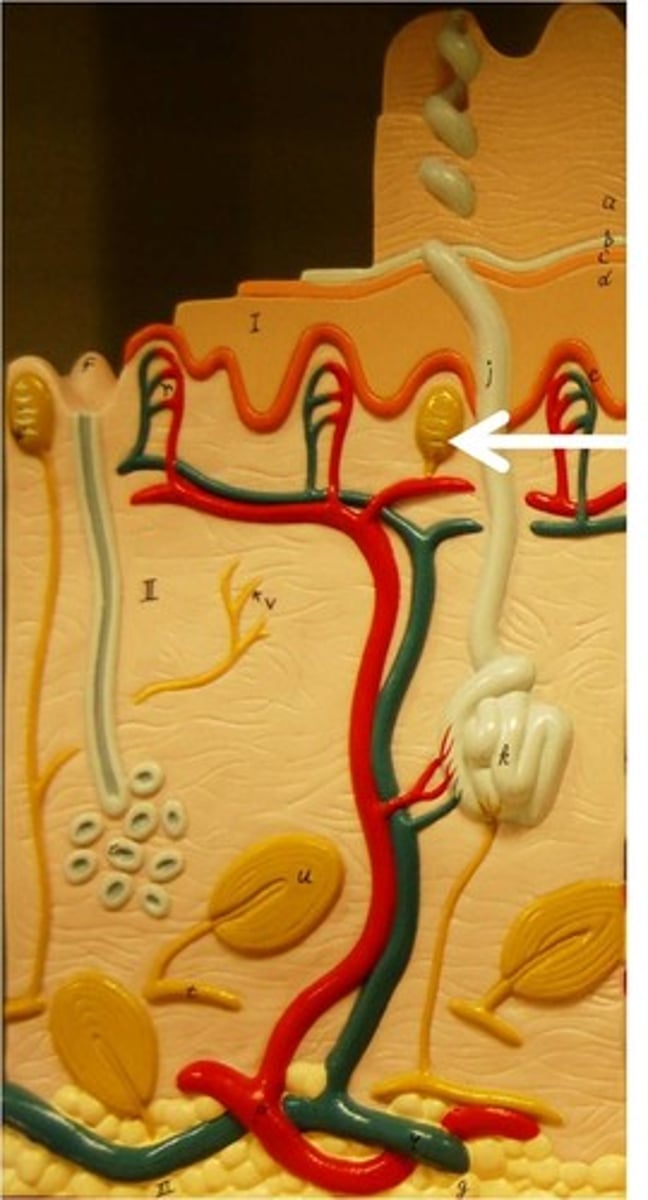
Ruffini corpuscle
Touch receptors in dermis for stretch and torsion.
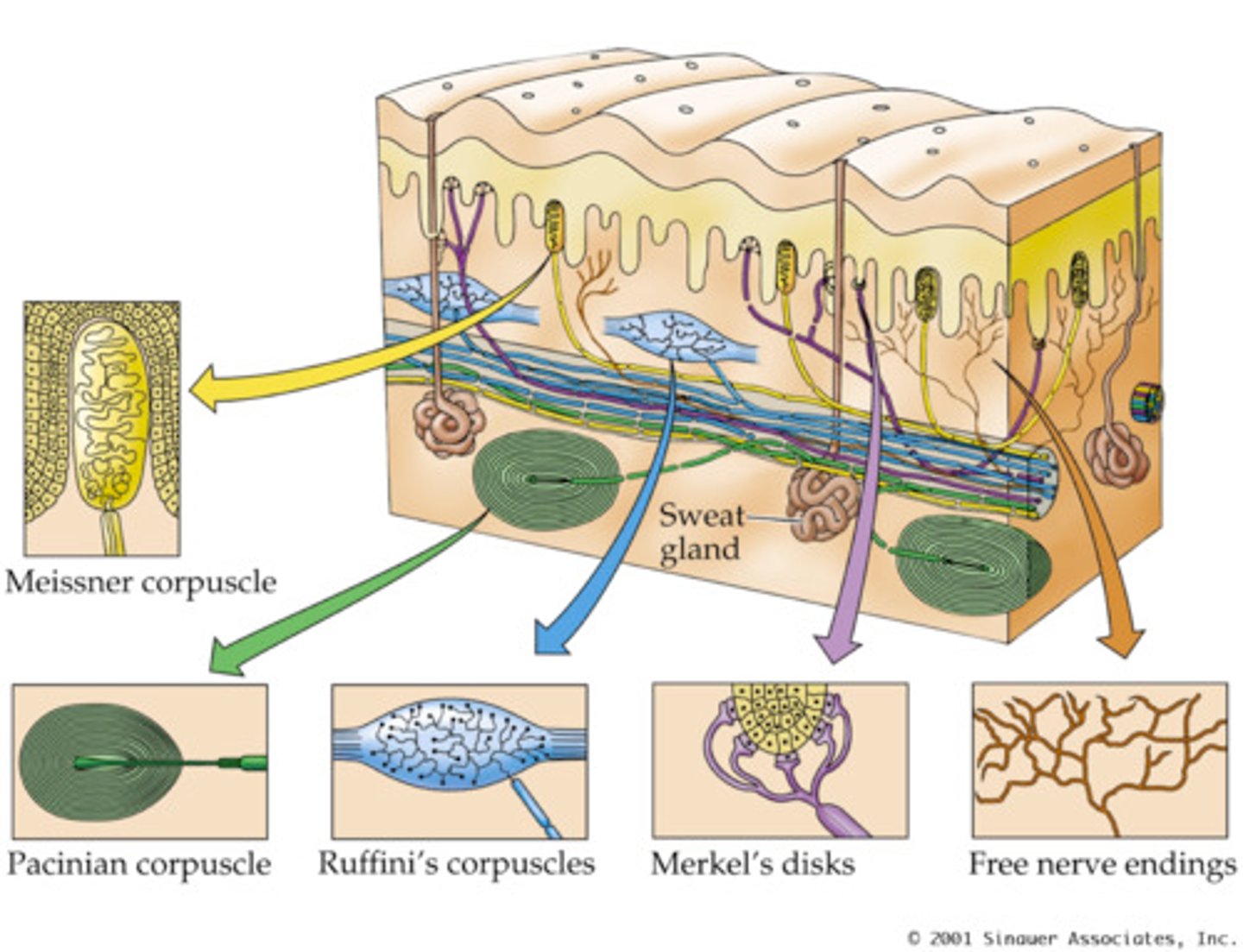
Pacinian corpuscle
Deep pressure/vibration receptors found deepest in dermis. Think Pac Man

Burn
Tissue damage from heat, chemicals, radiation, electricity. Protein in skin cells denature and no longer can function to prevent infection, regulate temperature, and hydration.

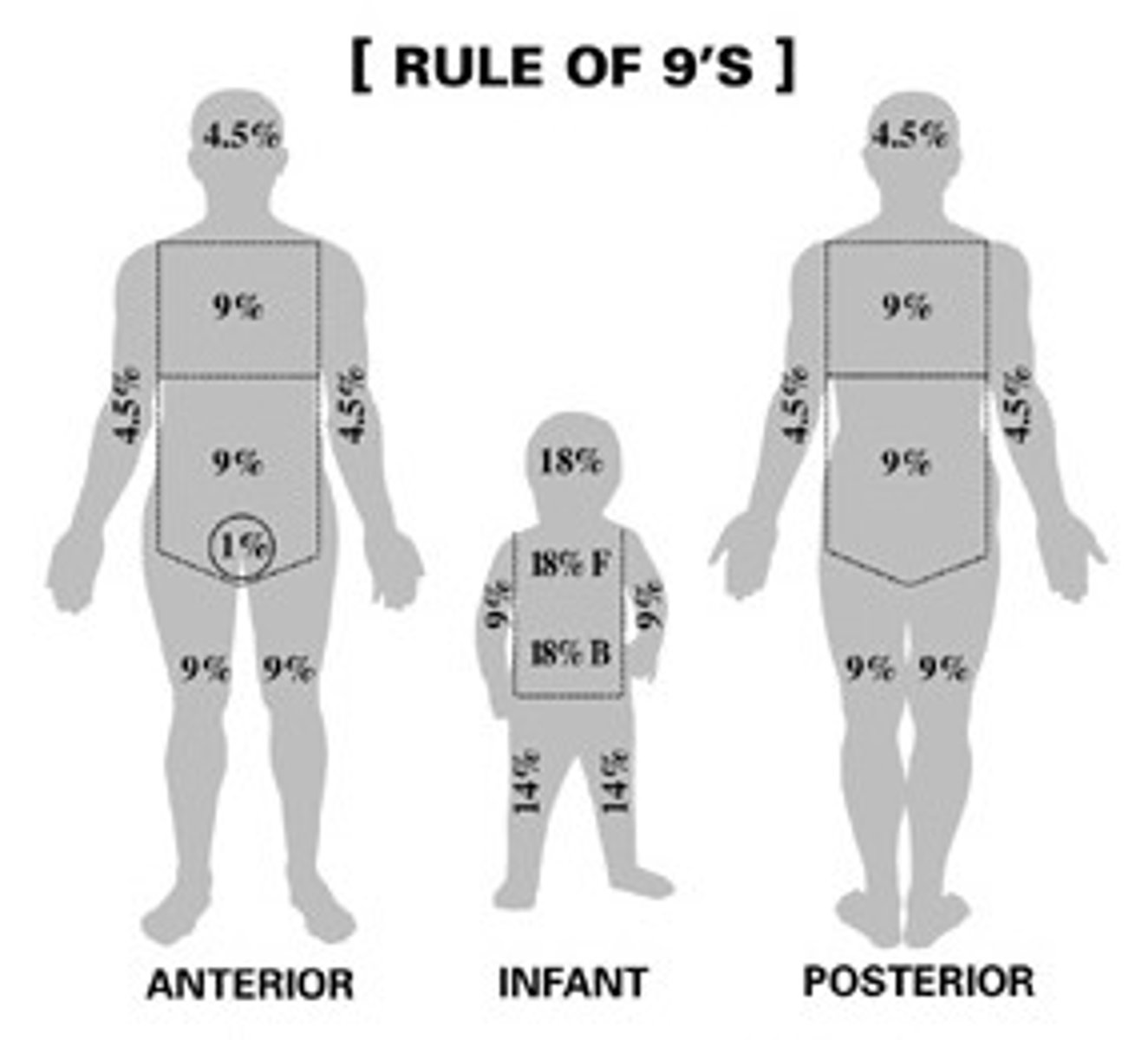
Rule of 9
TO assess burns by percentages in ER. 9% for Head/neck, 36% for trunk, 36% for lower limbs 18% for upper lims, and 1% for perineum.
1st Degree burn
Sunburn. Epidermis is damaged and is characterized by mild pain, redness but have normal skin fucntion.
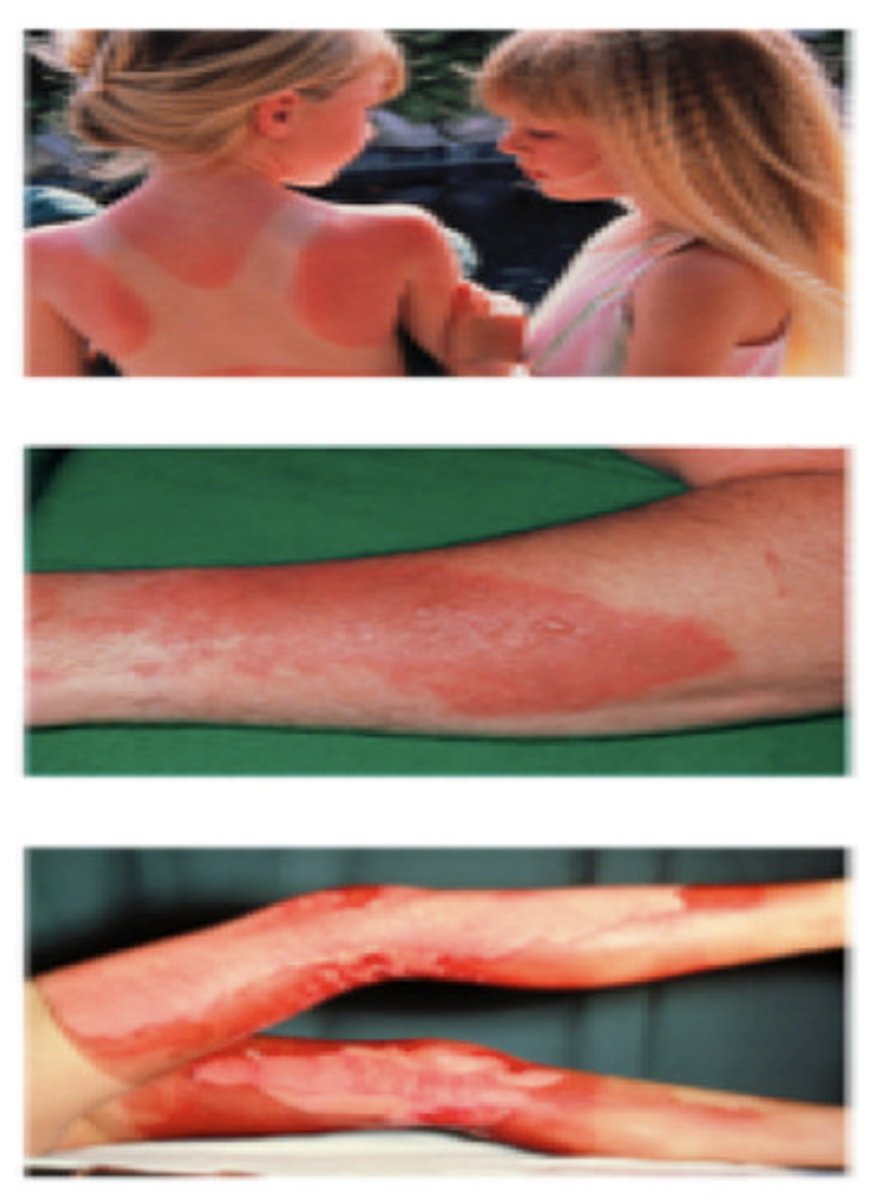
2nd Degree burn
Epidermis and partial dermis damage. Lose skin function, but sweat and hair not damaged. Characterized by pain, edema, and takes 3-4 weeks to heal.
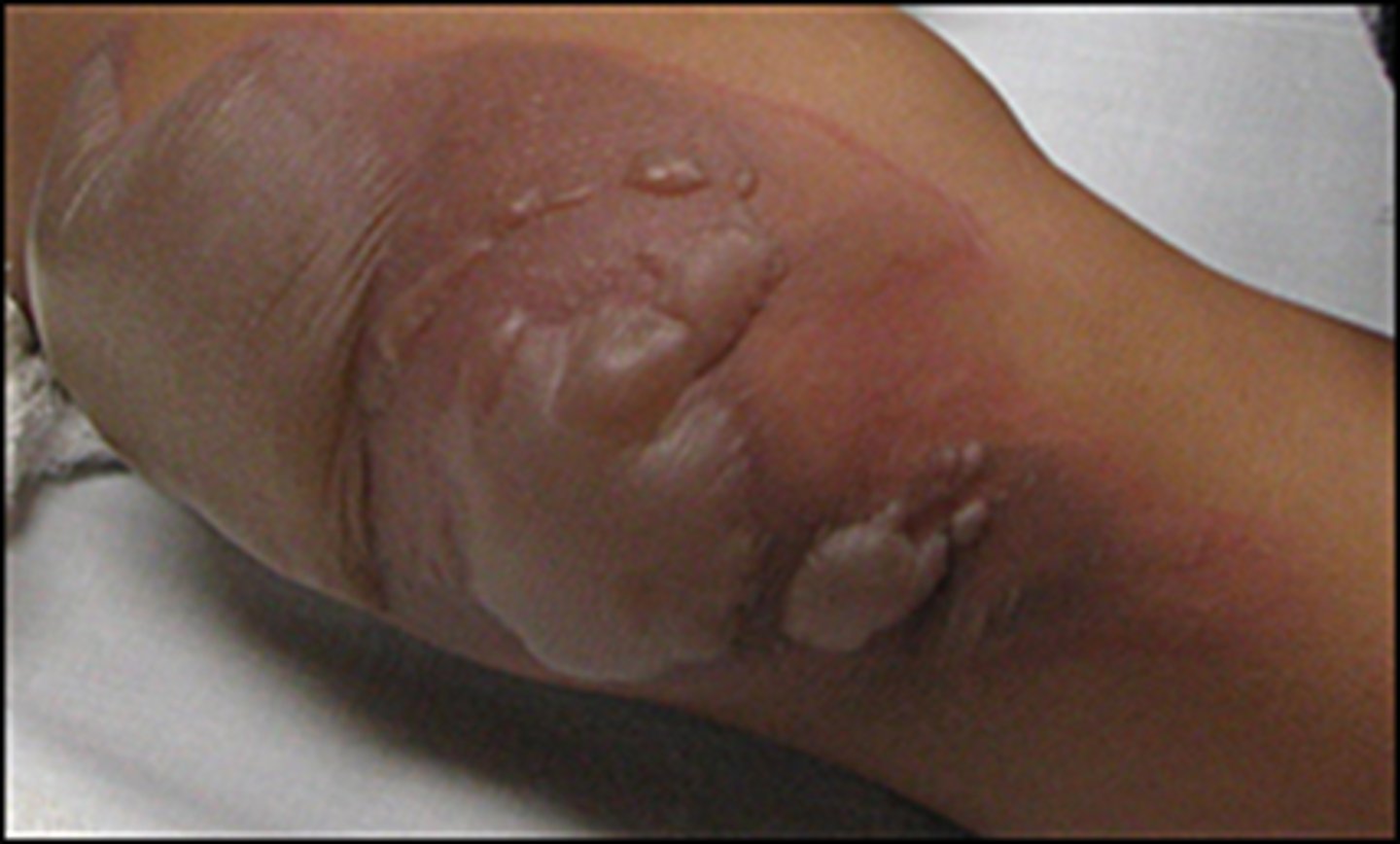
3rd degree burn
Damages epidermis, dermis and other structures. Total skin function loss. Characterized by numbness, edema. Systemic effects include infections, dehydration, decreased urine production, reduced circulation of blood, and decreased immune response. Skin graft necesary.