Subcortex & Limbic System (Ch. 5: Neuroanatomy)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
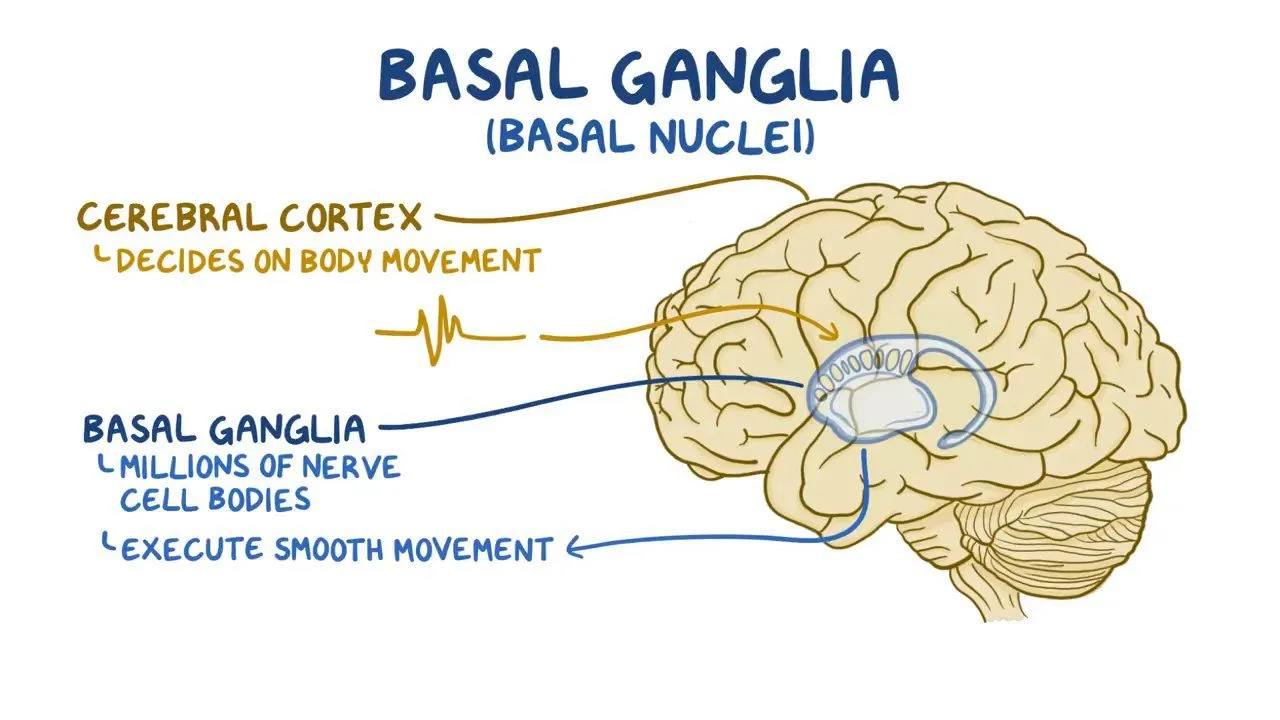
what is the basal ganglia?
a large network of embedded gray matter structures (a cluster of nuclei)
what are the functions of the basal ganglia? name some diseases of the basal ganglia
releasing desired movements and cognitive processes, inhibiting competing/undesired thoughts and movements. parkinson’s and tourette’s
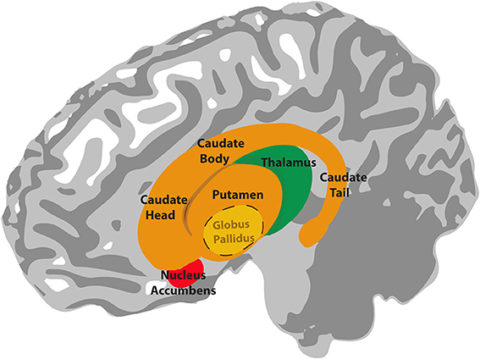
the basal ganglia consists of what 3 major structures?
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
what 2 other parts are included in the basal ganglia?
substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus
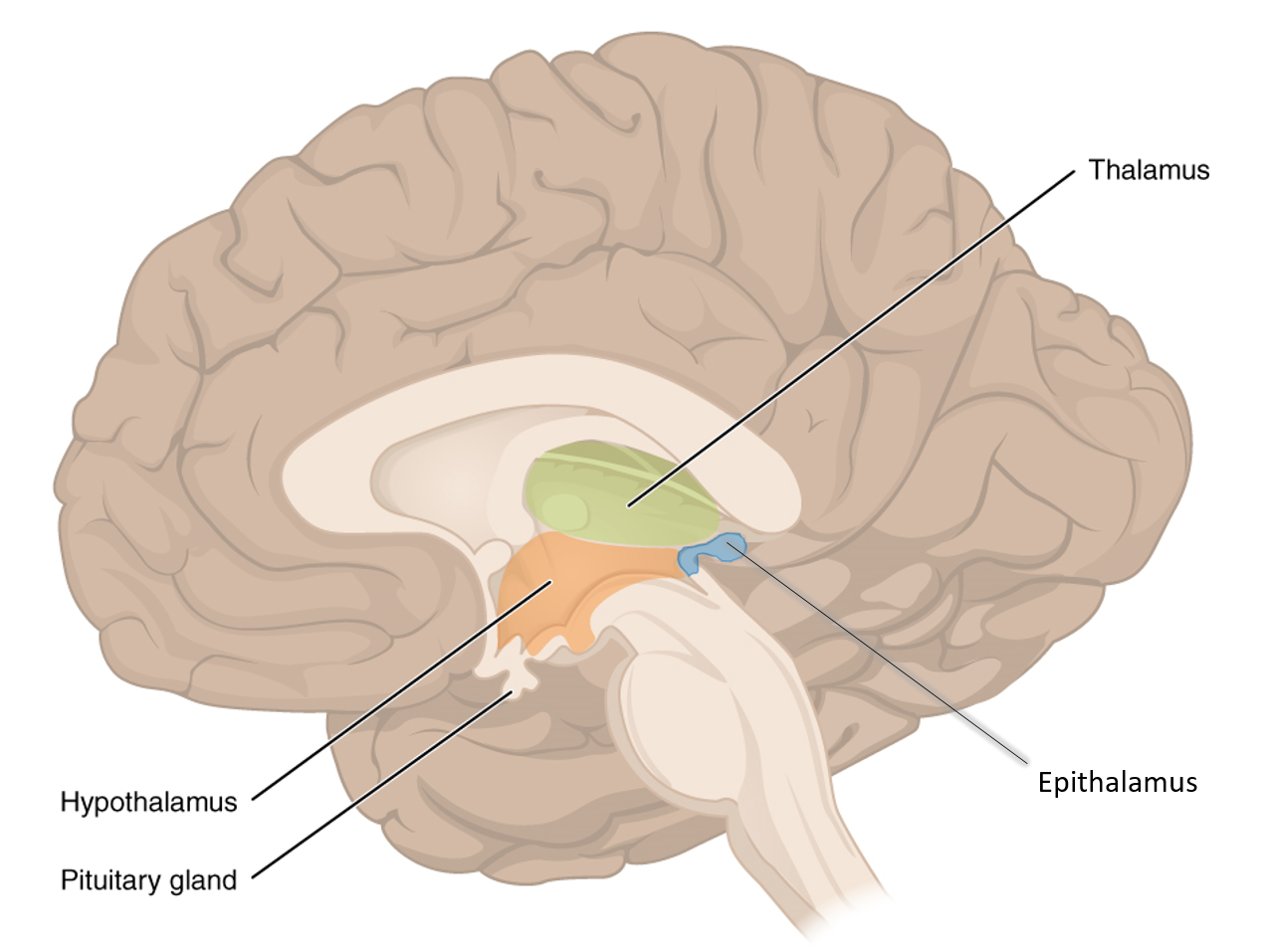
what 3 major structures make up the diencephalon?
thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus
what is the function of the thalamus? where is it located?
it’s a relay station for sensory and motor information. located in the center of the forebrain and posterior to the basal ganglia
what happens if the thalamus is damaged?
uncoordinated movement or processing
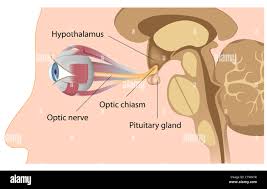
what is the hypothalamus?
a cone shaped structure beneath the thalamus that is bounded by the optic chiasm
what is the function of the hypothalamus?
nonconscious regulation of bodily homeostasis (temp, BP, heart rate), eating, drinking, and hormone secretion via the pituitary gland
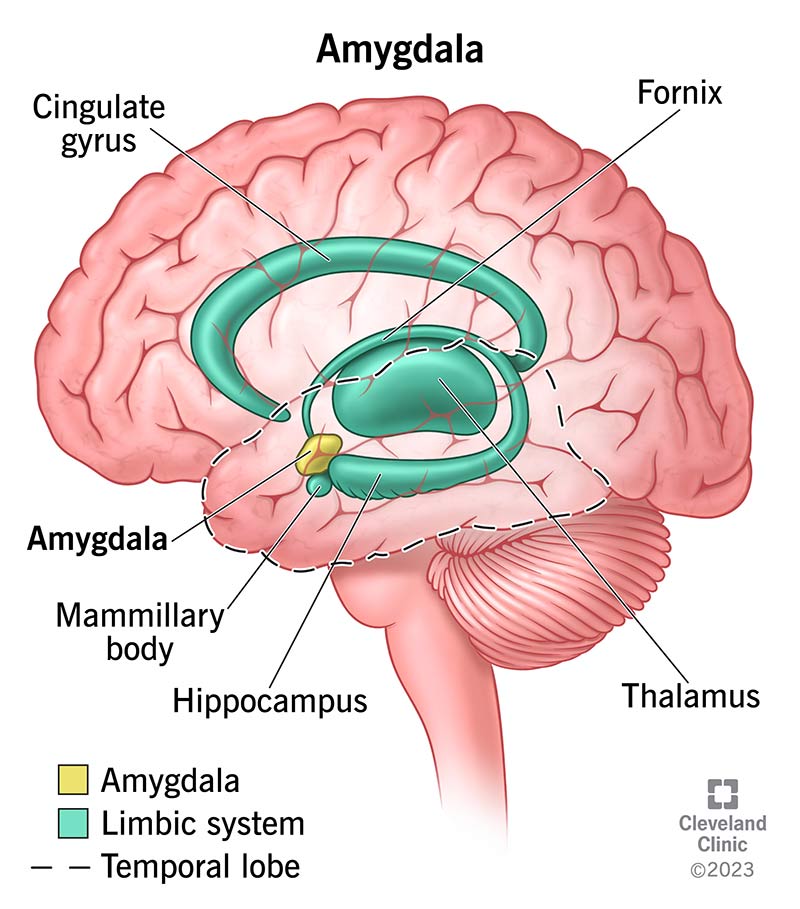
what are the primary structures of the limbic system that we will be covering? (3). what are the 2 major functions of the limbic system?
hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus. emotional regulation and memory formation

what is the function of the hippocampus?
critical for memory formation - dementia patients have a shrunken hippocampus. it is seahorse-shaped

what is the function of the amygdala? what is it shaped like?
emotional response, especially fear and anger. shaped like an almond