Unit 4 Genetics Vocabulary (OL)
1/39
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
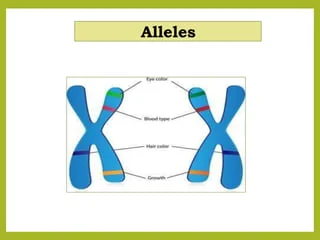
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene that can result in different traits.
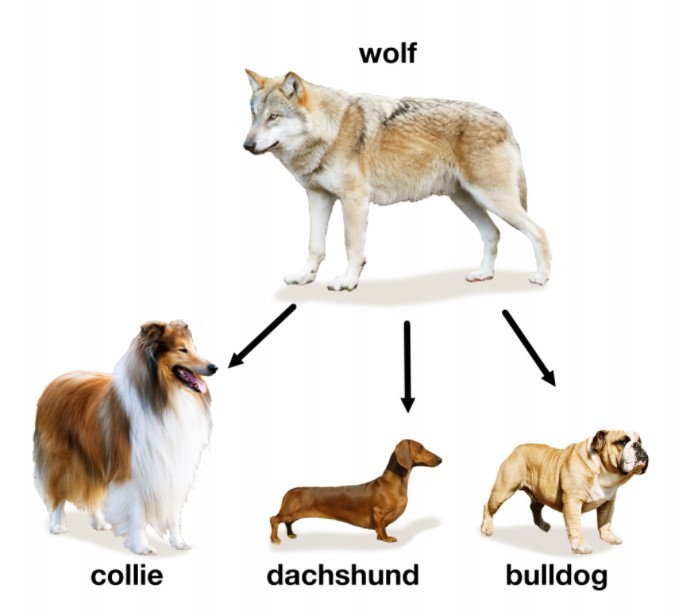
Artificial selection (selective breeding)
When humans choose which plants or animals to breed to get desired traits in their offspring.
Asexual reproduction
A type of reproduction that involves only one parent, and the offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
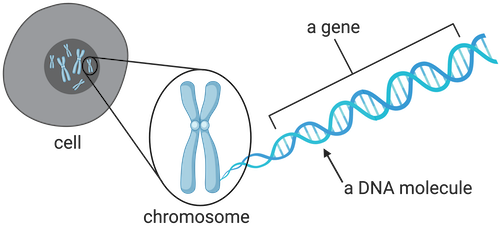
Chromosomes
Tiny structures found in the nucleus of cells that carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
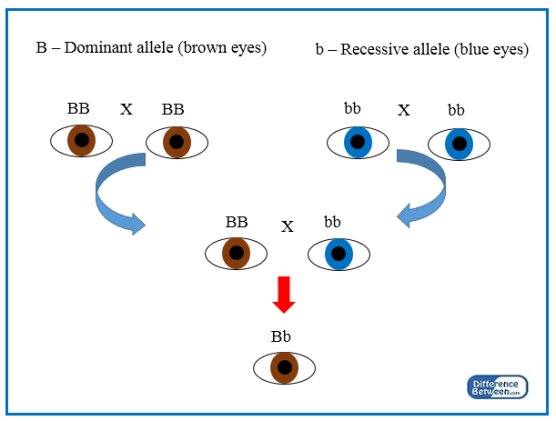
Dominant allele
An allele that is expressed or observed when present in either one or both copies in an individual's genotype.
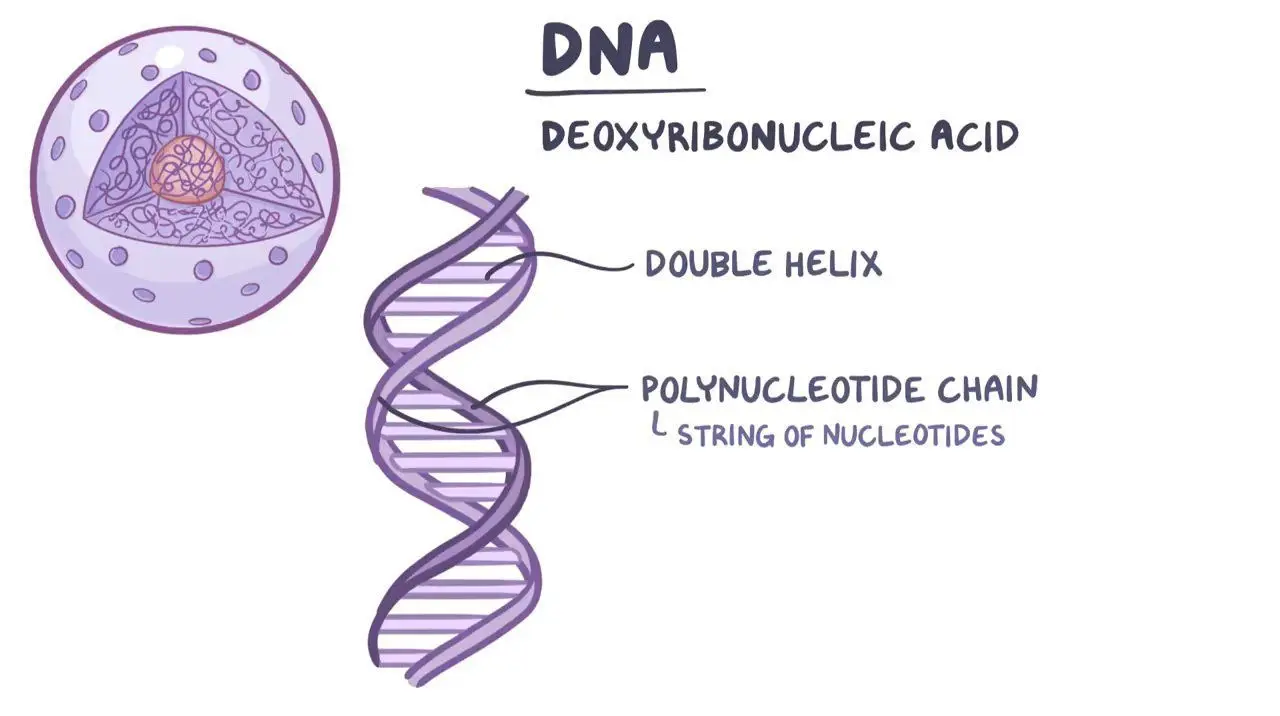
DNA
Molecule present in all living things; contains the genetic information that determines what traits an organism will have.
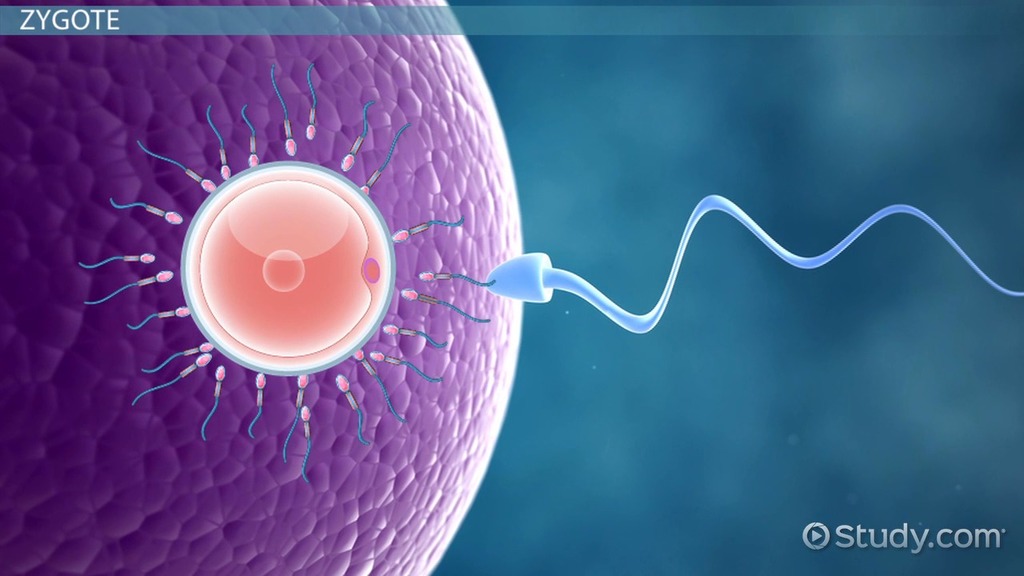
Fertilization
Fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
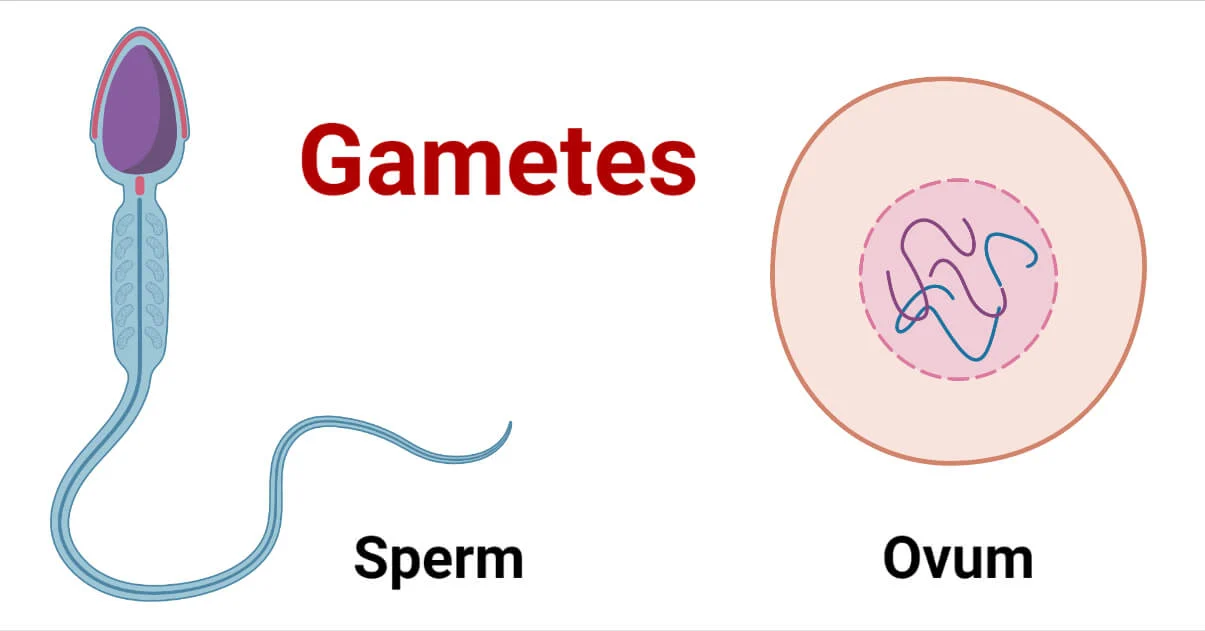
Gametes
Reproductive cells, such as sperm and eggs, that have half the usual number of chromosomes.
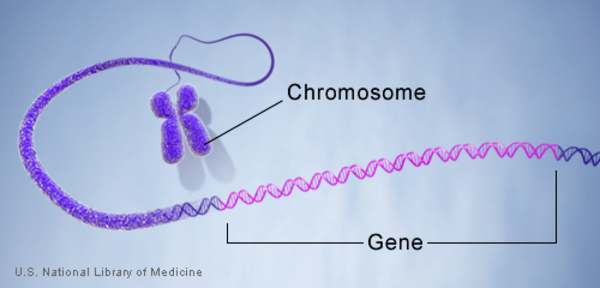
Gene
A small segment (piece) of DNA that gives instructions for a specific trait, like eye color or height.
Genetics
The study of how traits are passed down from parents to offspring (heredity).

Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism for a particular trait.
Heredity
The passing on of traits from parents to offspring through genetic information.

Heterozygous
Having two different alleles of a gene for a trait.

Homozygous
Having two of the same versions (alleles) of a gene for a trait.

Hybrid
An offspring that comes from parents with different traits.
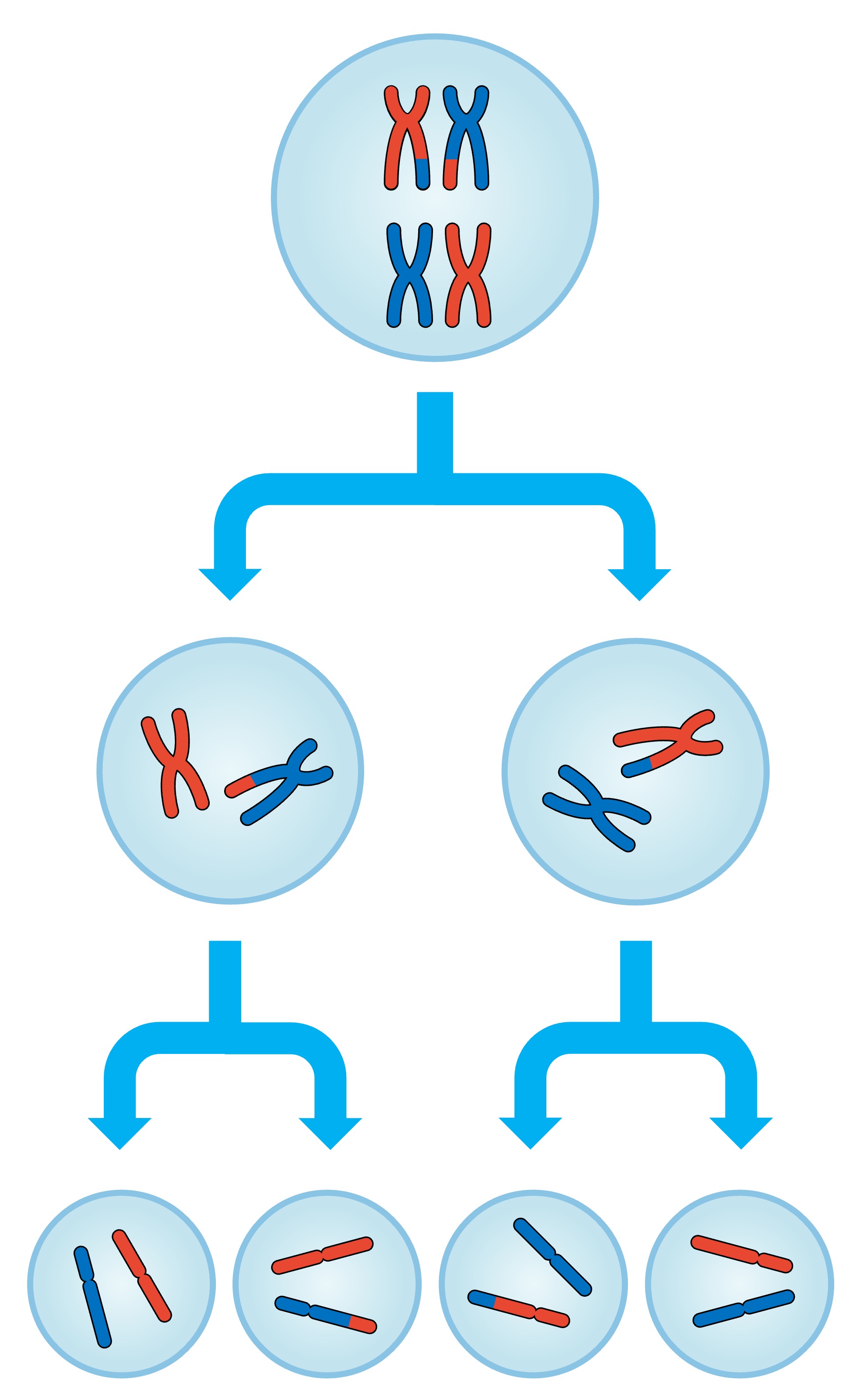
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with half the number of chromosomes.
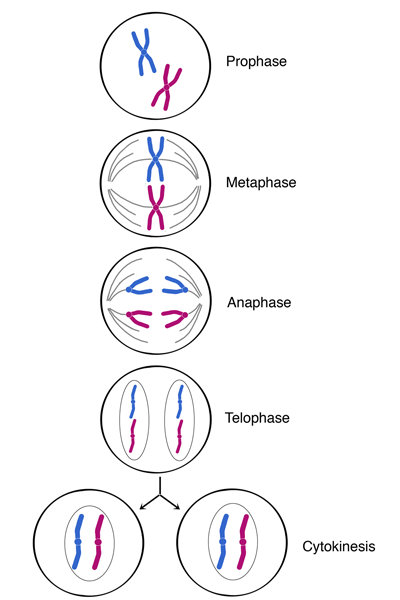
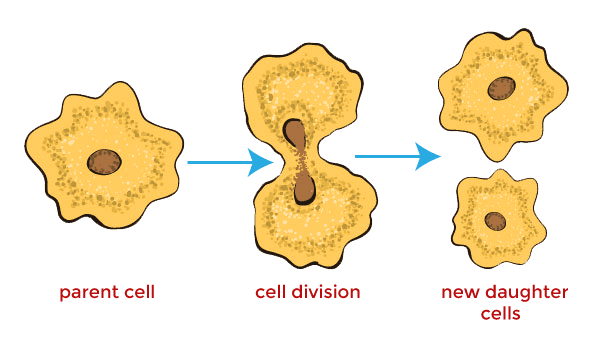
Mitosis
The process of cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells.
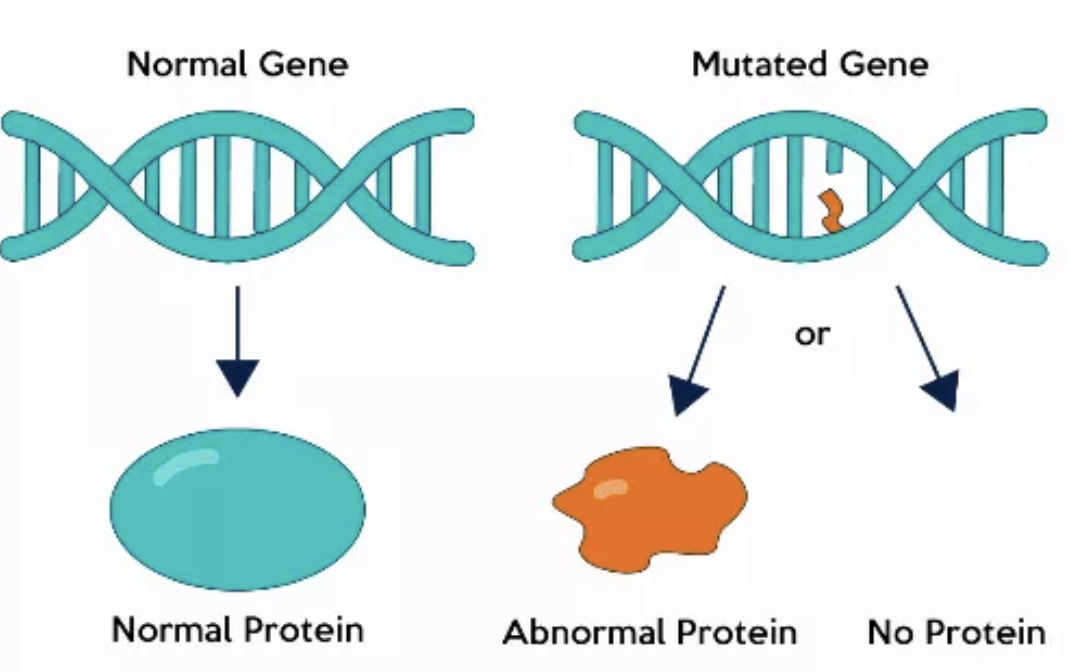
Mutation
A change in DNA that can create new traits.

Phenotype
The physical characteristics of an organism.

Purebred
An organism that has two of the same alleles for a particular trait.
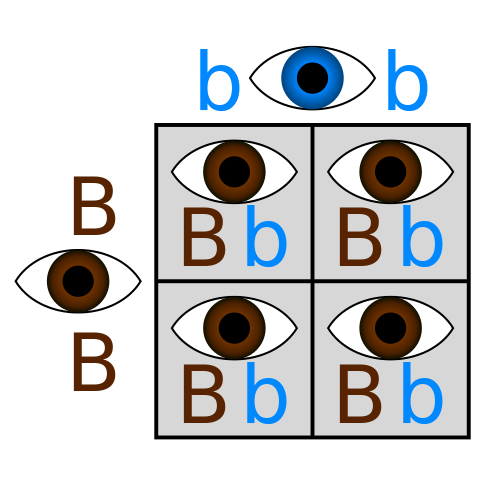
Punnett Square
A diagram that helps predict what traits offspring might have based on their parents' genes.
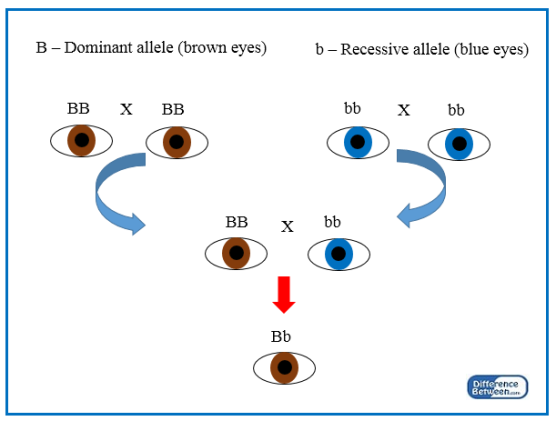
Recessive Allele
An allele that is expressed only when there are two copies of it.

Sexual reproduction
Type of reproduction that involves the fusion of gametes from two parents to produce offspring.
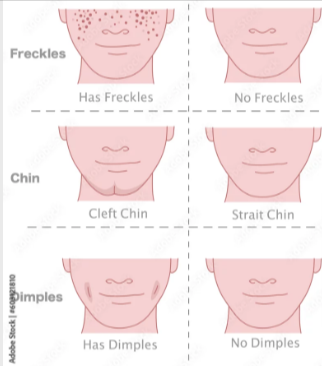
Trait
A specific characteristic or feature of an organism.
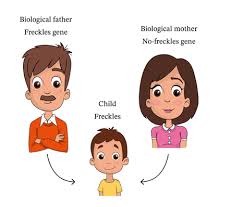
Inherited trait
A trait that is passed down from parents to offspring through genes.
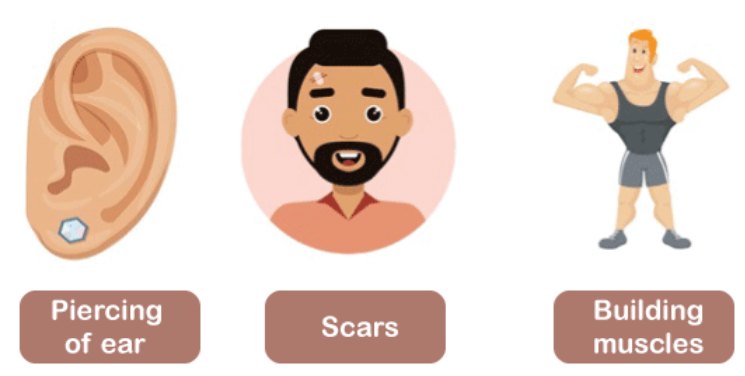
Acquired trait
A trait that an organism gets during its life, not from its genes.

Variation
Differences between individuals of the same type of organism.
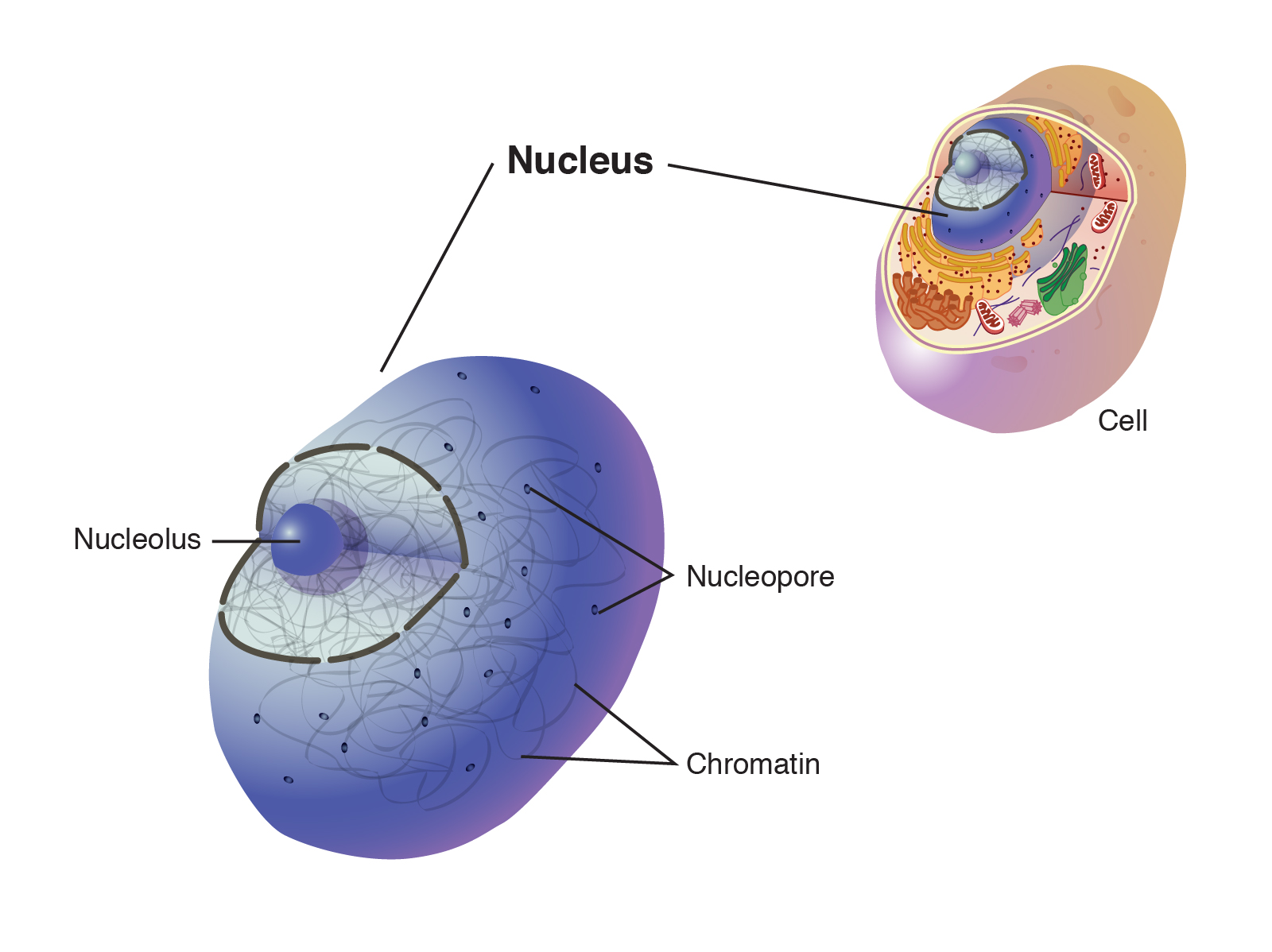
Nucleus
An organelle that contains the cell’s DNA.
Offspring
New individuals that are produced as a result of reproduction.
Probability
The chance or likelihood that a certain event will occur.

Clone/Cloning
The process of creating an identical copy of an organism or gene.
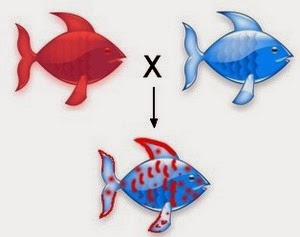
Codominance
When both alleles of a gene are fully expressed in the phenotype of an individual.
Genome
All of the genetic material (DNA) in an organism.

Karyotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell, arranged by size and shape.
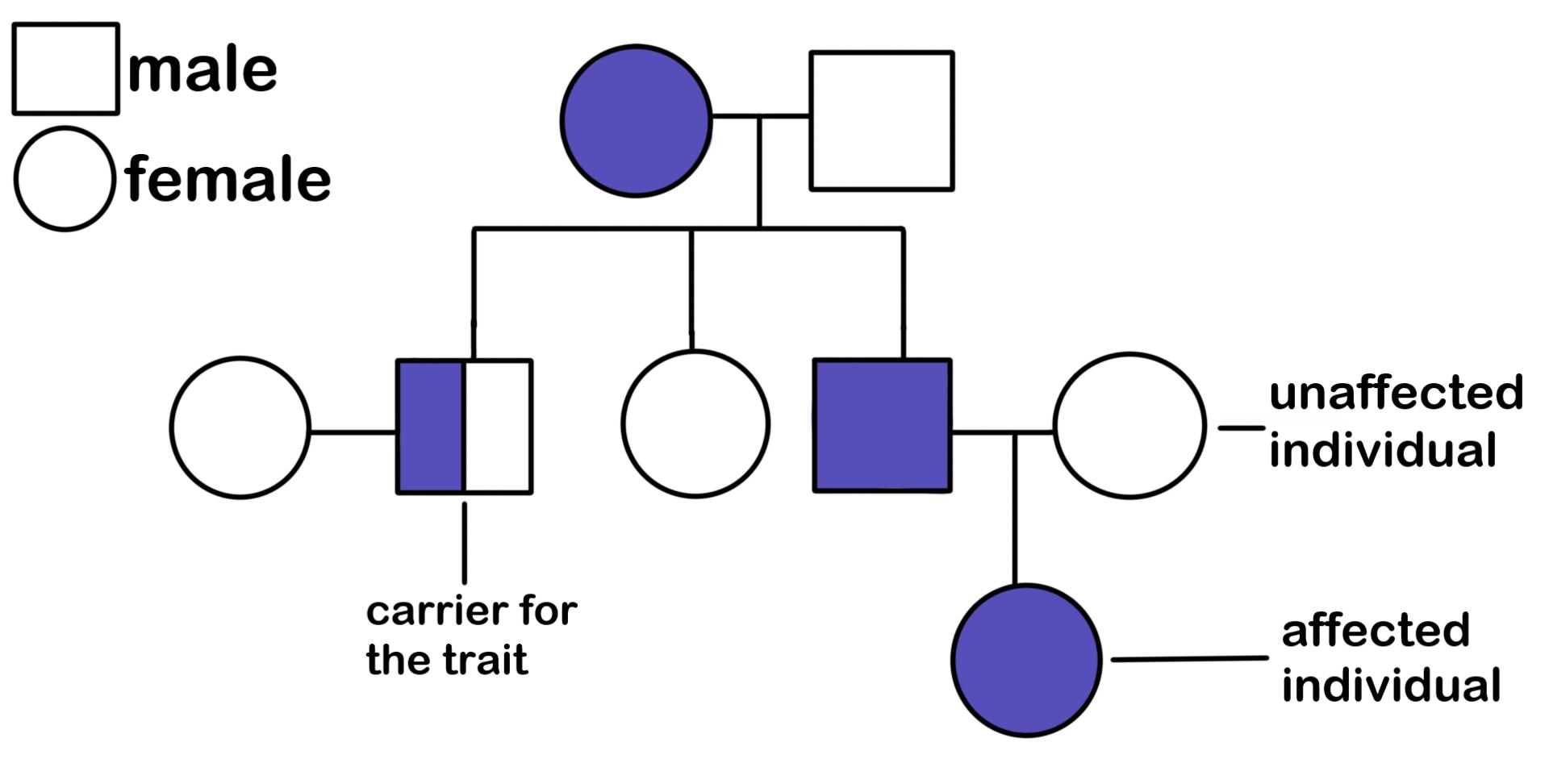
Pedigree
A family tree that shows how genetic traits are passed down through generations.
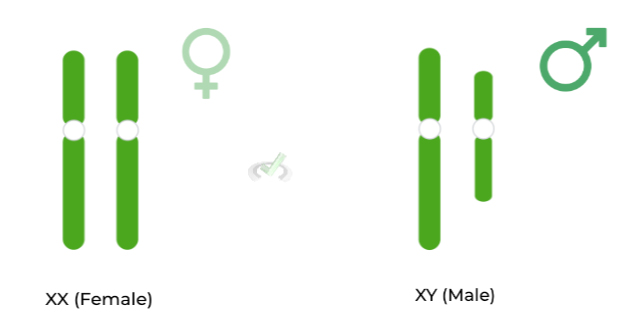
Sex-linked
Traits or genes that are connected to the sex chromosomes.
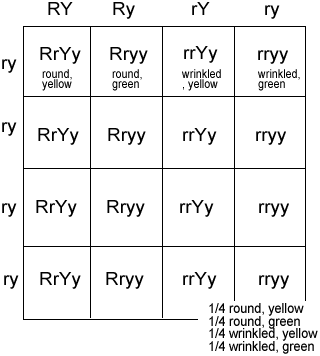
Dihybrid
A cross involving two different traits.
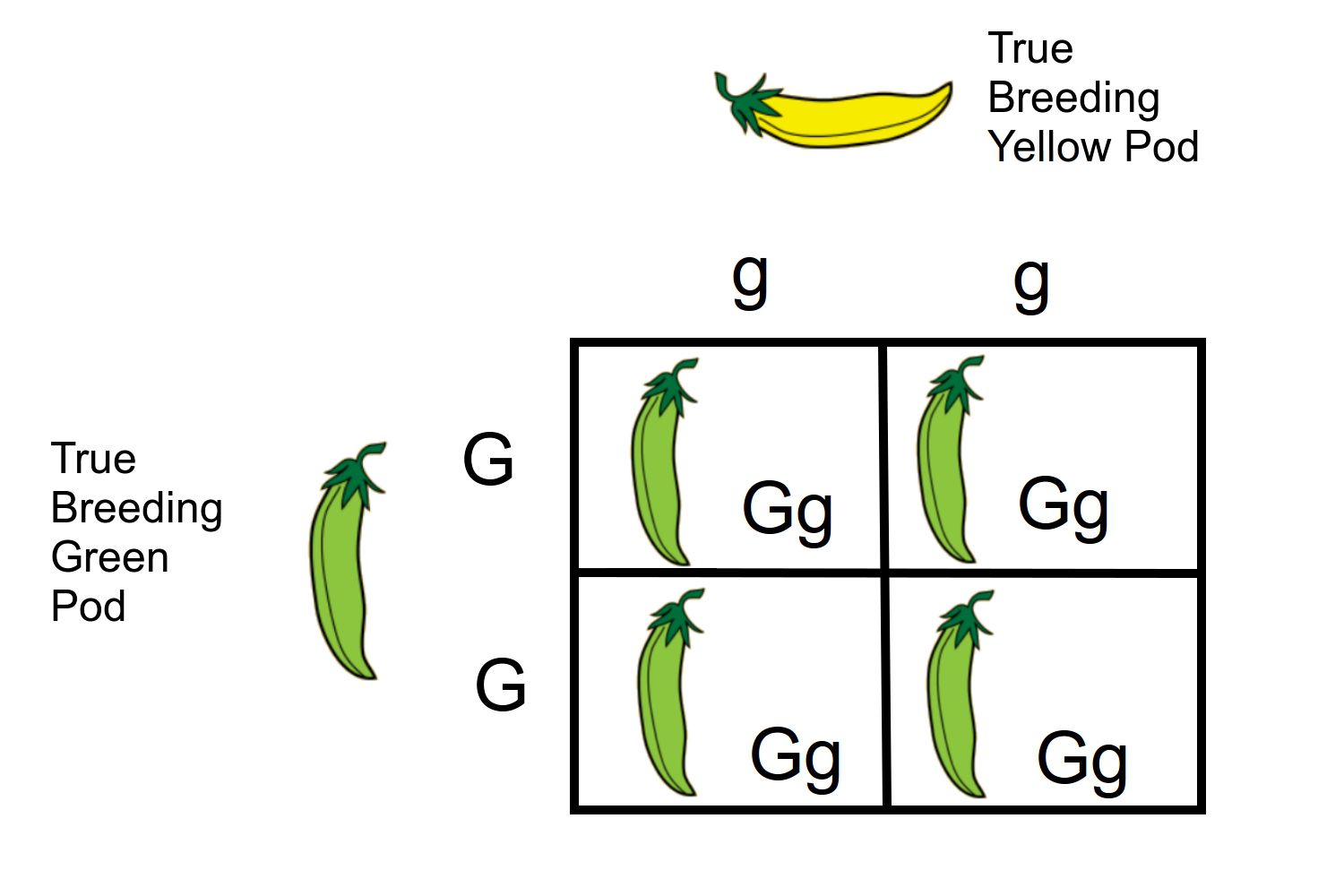
Monohybrid
A cross involving a single trait.

Gene therapy
A medical treatment that tries to fix or replace faulty genes to treat or prevent genetic disorders.
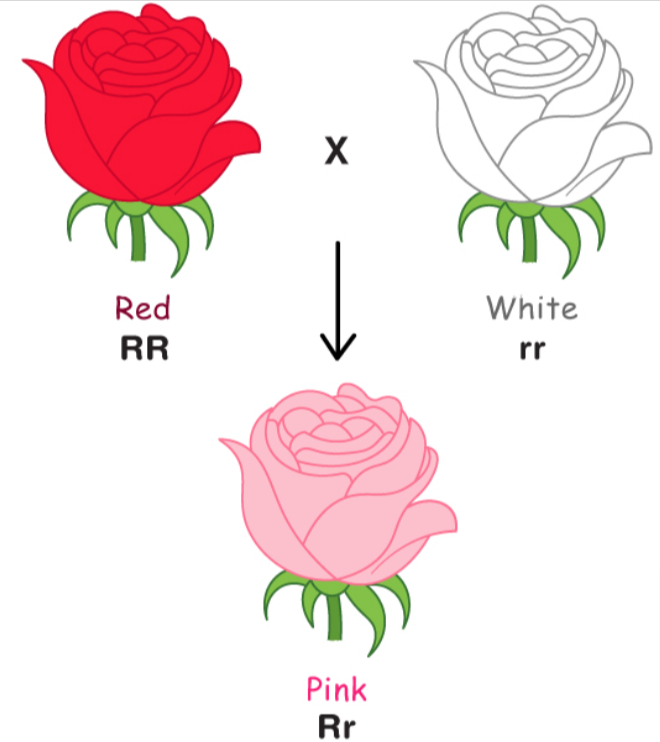
Incomplete dominance
When neither version of a gene is completely dominant, resulting in a blend of the two traits.