ANSC 301 exam 3 review
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Will animals that are not fed well reproduce optimally or at all?
No they will not optimally reproduce, some animals require a stockpile in order to reproduce/ need a basic level of leptin which regulate sex hormones
What is required before an animal will become fertile? What predicts age at puberty?
An animal needs to meet certain levels f growth before it can become fertile (faster growth = faster purity) body weight and adipose amount can determines leptin quantity which determines puberty
What hormone signals energy status that allows reproductive cycles to start? What
hormones does it change in the brain? How does this control population size in wild
rodents?
Leptin, GnRH which releases FSH and LH
food supply limits reproductive rate thus population size
Why would there generally be a negative relationship between fertility and milk
production in dairy cows?
negative energy balance and weight loss in early lactation
Body fat loss decreases leptin signaling, leading to delayed estrous cycles and lower fertility
Increasing fatness before calving can worsen these effects by causing more body fat loss earlier in lactation
What maternal tissues contribute to the requirement for pregnancy?
Nutrients are required by uterus, placentaGes and fetus
What two factors are important to know to determine the impact of a pregnancy on the
mother/dam?
Gestational length and fetal % of dam BW
What period of gestation are nutrient requirements the highest? Why?
last trimester because most growth occurs here
Is under or over-feeding an issue in early pregnancy?
yes this results in (barker hypothesis) and thrifty phenotype
Why do we not want to over feed during late gestation?
Over-feeding during late gestation can cause complications for both mother and fetus.
If an animal is underfed during late gestation who gets higher priority for the nutrients- mom or fetus
Fetus
What is fetal programming and the “Barker Hypothesis”? What is the biological
explanation?
inadequate nutrition is a significant contributor to adult disease later in life. explained by epigenetics
What is unique about the kangaroo?
it has 2 teats which can produce different milk fat levels for different joeys
What is unique about the Northern Elephant Seal? How does their milk composition
differ from a cow?
Northern elephant seal does not eat during lactation. Their milk fat composition is significantly higher
To determine amount of a nutrient required for milk synthesis (say Ca) we need to know
milk yield and ?
Milk nutrient conc.
Does milk composition match growth rate and requirement of the offspring? What are
some examples?
—-
How do we classify sugars?
Mono-
Diacc-
Tris- (need microbes to break down)
Polysaccharides
What happens to glucose requirement during lactation? Where does the cow get this glucose?
Cows glucose requirement is much higher during lactation. gluconeogenesis
What is the link between milk protein and milk lactose? Do all animals have the same
amount of casein (the protein that makes cheese)?
Both lactose (sugar) and casein (protein) are standard components of all mammalian milks, but they are chemically, nutritionally, and physiologically different.
The amount and kind of casein varies significantly between cows, humans, goats, sheep, and other animals, affecting cheese-making properties and nutritional aspects
What happens to energy requirements during lactation? Where does the energy come from?
There is a dramatic increase in nutrient requirements. The energy comes from mobilization of endogenous reserves, especially fat
When we release fatty acids from adipose tissue how are they transported in blood?
Are they quickly or slowly used?
NEFA is transported into the blood via Lipolysis of adipose tissue triglyceride TG to Glycerol and NEFA
Transport of NEFA to other tissues
Fatty acid uptake an oxidation by these tissues
NEFA is rapidly used
Where and how do we complete oxidize fatty acids? What cells are not able to do this?
mitochondria oxidizes a long chain fatty acid by a 2 stage process called beta-oxidation
What are the key steps of beta-oxidation?
Fatty acids are transported into the mitochondria for oxidation
Fatty acid are activated to fatty acyl-CoA
The two carbon- Acetyl CoA is formed in each round of the cycle
When are we not able to completely oxidize acetyl-coA coming from beta-oxidation?
What do we do with the acetyl-CoA? What tissue does this occur in?
When the TCA cycle does not run due to low OAA the liver uses the Actyl-CoA to do ketone synthesis
When an animal has high ketones, what can we smell on their breath?
fruity smell
If the liver is taking up more fatty acids than it can export as vLDL, oxidize completely, or
make ketones our of, what does it do with them?
Stored them as triglycerides within the liver leading to hepatic lipidosis
What can ketones be used for by other tissues in the body?
The heart brain and muscle can use them to make acetyl CoA but too many can become a problem
Where can we look for ketones to determine if an animal is ketotic.
Blood then urine then milk
What are four things that can contribute to metabolic diseases?
Failure to adapt to new physiological state
Very low intake
Hormone deficiency/imbalance
Obesity
What is a primary metabolic disease? A secondary metabolic disease? Do we have to treat the secondary? What happens if we only treat the secondary?
Primary disease is something like diabetes
Secondary is symptoms directly related to dysfunction like ketosis which reduced intake due to milk fever
To treat the secondary we must address the primary
What causes lactation ketosis, pregnancy toxemia?
Cant eat enough to keep up to demand for lactation
Cant keep up with the demand for fetal growth in ewes carrying twins or triplets
What happens in Feline Hepatic Lipidosis? What increases the risk? What is the short
and long-term treatment?
NEFA is mobilized from adipose tissue and uptake excessively in liver limiting livers ability to export TAG or VLDL
Older obese cats are at risk
Short term is tube feeding
long term is weight loss
What is a common description of lipids
Lipids function in a cell as structure, signaling, and storage
Which lipids have the highest energy density? Which have very little nutritional value?
Triglycerides are most energy dense
Cholesterol / steroids provide very little nutritional value
Which lipid do we make to store energy?
Triglycerides
Which lipid do mostly find in forages? Are they as energy dense as triglycerides?
Glycolipids, and they are less energy dense than triglycerides (2 fatty acid chains rather than 3)
What do we use phospholipids for in cells? Are they as energy dense as triglycerides?
Typically used as a structural aspect in membranes
They are less energy dense than Triglycerides
What are some examples of steroid derived compounds?
Cholesterol, Vitamin D, Steroid hormones
How can fatty acids be different from each other? Are these important to their
metabolism?
Structure is very important to their metabolism
differences include # of carbons, # of double bonds, Location of bonds and cis vs trans bonds
Where do we find trans fatty acids? Are they all bad?
Trans fatty acids re commonly found in industrial processed oils and ruminant fat and are considered very bad if produced industrially
What is palmitic acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid? Are arachidonic
acid, EPA, and DHA omega-3 or omega-6 FA?
16:0
18:0
18:1 cis-9
18:2 n-6
What oil is high in palmitic acid? High in oleic acid? High in omega-6 FA? Highest in omega- 3 FA? What common oil is considered more “balanced” because of more omega 3 and less
omega-6?
Palm oil
olive oil
Corn and soybean oil
Flax oil
Canola oil
Forages and corn and soybean are generally high in omega-3 or omega-6? Tallow (and also lard) are higher or lower in saturated, mon-unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids
compared to normal plant oils?
Corn soybean omega 6
Forges omega 3
tallow saturated
Has genetic selection been successful in changing fatty acid profile of oilseeds?
Yes a good example is canola oil
What does saponification number, iodine number, and fatty acid profile tell of about an oil?
Saponification number- average chain length of FA
Iodine number- measure of unsaturated fat (double bonds)
Fatty acid profile- actual conc of fatty acid in the oil
What is produced after hydrolytic rancidity? What problems does it cause?
triglycerides are broken down into free fatty acids and may lead to odors
What is produced during oxidative rancidity? What problems does it cause?
free radicals are formed
free radicals can be potentially dangerous
How do we prevent oxidative rancidity?
Antioxidants like BTH
Where are VFA absorbed? Where are long-chain fatty acids absorbed?
short chain are absorbed in rumen, omasum and hindgut
long chain are absorbed in jejunum
How does lipase assist in triglyceride digestion?
lipase breaks down triglycerides into monoglycerides
What do bile salts do to assist in lipid digestion and absorption?
they emulsify fats into micelles
What molecules are absorbed from triglycerides?
free fatty acids
monoglycerides
Cows don’t have monoglycerides, how do they form micelles?
they use lysolecithin
What do we need to synthesize bile? What happens to bile salts? What do we do to bile
salts to decrease plasma cholesterol?
cholesterol
most bile salts are reabsorbed so we prevent the reuptake of them to reduce cholesterol
Fatty acids are packaged into ________ in the intestine? How do they enter the circulation?
chylomicrons they enter circulation through lymph vessels
What are some key components and aspects of a lipoprotein that allows it carry fatty acids in the blood?
phospholipids, apolipoproteins
VLDL come from _________ and carries __________ to the peripheral tissues.
Liver, triglycerides
HDL comes from _________ and carries _________ back to the liver.
Liver and Intestines, cholesterol
VLDL break down to ________. This is considered good or bad cholesterol?
LDL (bad)
Triglycerides in lipoproteins are broken down to what by what enzyme?
LPL (lipoprotein lipase)
How are triglycerides transported into an egg yolk? Is LPL involved?
VLDLy, LPL is sorta involved
What is the energy density of lipids compared to carbohydrates and proteins?
2.25
What are some uses of fatty acids in the body?
energy
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Essential fatty acids
Carrier of fat-soluble vitamins
What are the two “essential” fatty acids? What do we mean by a conditionally essential FA and which ones are they?
Linoleic (C18:2) and Linolenic (C18:3)
Arachidoic acid can be synthesized from C18:2
EPA and DHA can be synthesized from C18:3
What are made from the essential fatty acids?
Eicosanoids
What is a symptom of essential fatty acid deficiency? Is it commonly observed?
skin lesions, reproductive failure, edema, subcutaneous hemorrhage
Is synthesis of the “very long-chain” omega-3 fatty acids from C18:3 efficient? Do we find
EPA in plants?
No very inefficient not in plants
What do we make the eicosanoids from? What is the different between eicosanoids made from omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids? How does this explain omega-6 to omega-3 ratio?
They are made from Arachidonic acid or EPA
Omega 3 are more anti-inflammatory
Omega 6 are more pro-inflammatory
Which FA are essential to brain development? Reduce inflammation?
EPA (omega-3)
Are industrially produced trans fatty acids good or bad for humans? Ruminant trans FA?
Yes ruminant trans FA are considered good
How do absorbed fatty acids differ from the diet in the ruminant?
Fatty acids absorbed do not absorb directly
What happens to triglycerides in the rumen?
Fatty acids are hydrolyzed to release free fatty acids by bacteria in rumen
What happens to double bonds in fatty acids in the rumen?
Biohydrogenation convers cis to trans before removing the double bond
What happens when the microbial population changes and the “alternate” pathways of biohydrogenation is used? What is the mechanism (how does this occur)?
Microbial community changes alter which bacteria dominate biohydrogenation.
Different bacteria have different pathways, leading to “alternate” trans-10 intermediates instead of typical trans-11.
This shift occurs due to dietary/environmental pressures favoring bacteria with alternate enzymatic activity.
Mechanism is driven by changes in enzymatic isomerization and hydrogenation steps encoded by microbial populations.
What three things do we use glucose for when we synthesize fatty acids from scratch?
Glucose carbon→ fatty acid carbon
(de novo fatty acid synthesis)
Glucose metabolism → reducing equivalents for de novo fatty acid synthesis
Glucose→ glycerol 3-P for fatty acid esterification→ triglyceride
What does insulin do to lipogenesis?
it increases it
During de novo fatty acid synthesis we make fatty acids up to __ carbons long. What can
then happen to these fatty acids?
16 After synthesis, these 16-carbon fatty acids can undergo several modifications:
They may be elongated to longer chains (more than 16 carbons) by elongase enzymes, often in the endoplasmic reticulum.
They can be desaturated by desaturase enzymes to introduce double bonds, creating unsaturated fatty acids.
These modified fatty acids can then be incorporated into complex lipids such as triglycerides, phospholipids, or cholesterol esters for storage or membrane synthesis.
They also serve as precursors for bioactive lipid molecules and signaling compounds.
Can we synthesize omega-3 fatty acids?
No
What is the carbon source for fatty acids in ruminants? Non-ruminants?
Ruminant- acetate and ketones
Nonruminant- glucose
Both ruminants and non-ruminants get around half of their NADPH from? What is the implication for glucose requirement for the cow?
Pentose Phosphate Cycle
In cows, the glucose requirement is high because glucose supplies substrates for NADPH generation needed for biosynthesis.
Ruminants get the rest of the NADPH from? Normal non-ruminants get them from?
isocitrate and malate pathway
When non-ruminants bring NADPH out of the mitochondria they also bring out ___ that is used in fatty acid synthesis?
citrate
Are horses and other non-ruminant herbivores (for example the horse) are more like ruminants or traditional ruminants
What is the glucose source for ruminant and non ruminant
Non-ruminant- Glucose, MTC+PP
Ruminant- Acetate, PP+ IC
After a high fat meal we would expect what to be high in the plasma?
chylomicrons
Would lipid synthesis be high or low after a high carbohydrate meal?
high
What form of lipids are high in blood during fasting?
Chylomicrons
What are some advantages of storing lipids as fat?
high energy value 2.25
not associated with water
Efficient synthesis
If a cow made fat from acetate while she was not lactating, stored the fat, and then
mobilized that fat for use during lactation would the energy loss be high or low?
Low
What is a key tissue that helps keep young animals warm? How is the mitochondria and
the electron transport chain involved? Is this mechanism present in adults?
Brown adipose tissue
Uncoupling protein 1 allows H to flow back into the matrix without making ATP and heat instead
Where will a newborn animal get its blood glucose?
Lactose
Is protein deposition high or low in a young animal? How does milk support this?
very high milk protein is rich in EAA( high biological value)
What does a normal growth curve look like? What does the curve look like for bone,
muscle and fat?
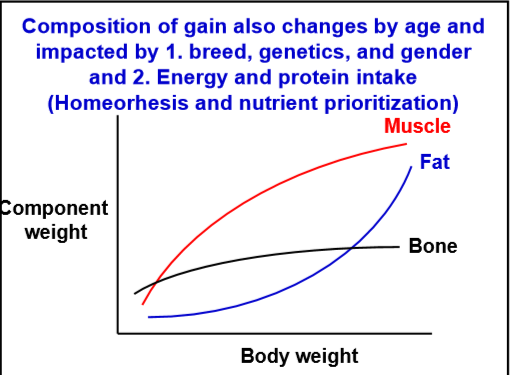
What do proteins contain that make them unique? What is true protein vs non-protein
N?
Nitrogen
True protein has amino acids and chains of AA
Non protein is ammonia or urea
Does the concentration of proteins change much over development?
no they are rather consistent
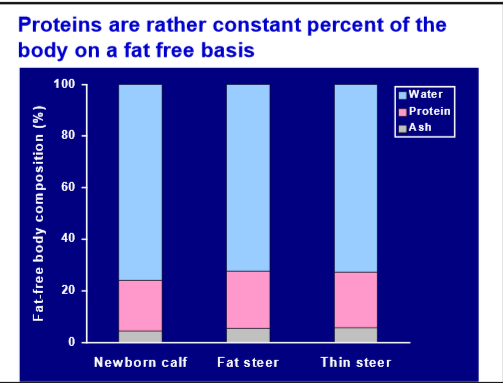
What is the largest protein depot in the body?
Body fluids 37%
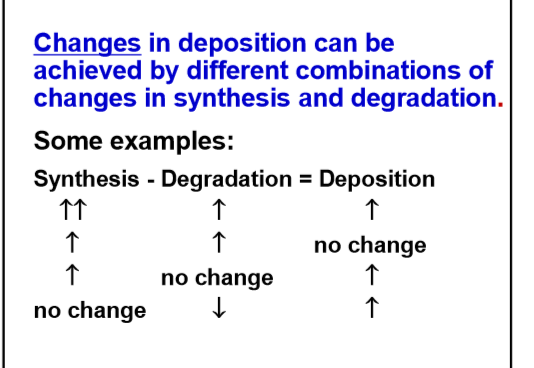
What does protein turn-over mean? Why is body protein turn-over? Do all proteins
have the same turn-over? What happens to AA during protein turnover?
Proteins need continuous replacement
Turn over rates vary with biological role
Turned over AA are recycles up to 75-80%
How do we make proteins?
Expression of mRNA for the protein and then synthesis of the protein on a ribosome
What tissue has the highest rate of protein synthesis, gut or muscle?
gut
How would you increase protein deposition even if protein degradation was increased?
increase synthesis
What optical form of amino acids are found in normal feeds?
L and D isomers (L is natural)