Chapter 24 Schizophrenia
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Explain the term of psychosis
a state in which a person experiences hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized thoughts, speech, or behavior
is the key diagnostic factor in schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
Schizophrenia
Split minds,1st rank symptoms (psychosis), 2nd rank symptoms, Bizzare delusions
Chronic illness: detrtioates with time and then plateaus
Core symptoms: Positive & negative symptoms for significant portion of 1month period but with continuous signs of disturbance for ≥6months
Neurocognitive impairment
Disorganized thinking: confused speech and thinking
Disorganized behavior
Disruption of sense of self: self-disturbance
Schizoaffective disorder (SAD)
PSYCHOSIS + MOOD DISTURBANCE OCCUR AT SAME TIME
Periods of intense symptom exacerbation alternative with periods of adequate psychosocial functioning
Maked by psychosis and other times marked by Mood disturbance
Longterm SAD better outcome than schizophrenia but worse than mood disorder patients
Higher functioning than schizophrenics
Risk for suicide
Increase with use of:
ETOH
Cigarette smoking
Previous suicide attempts
Hospitalizations
Treatments:
Enhance social network & contact
Focused on helping patients protect selves against environmental stressors
Delusional disorder
1 or more delusion present for at least 1 month
Delusions are primary symptoms
Stable and well-systematized delusions that occur in the absence of other psychiatric disorders
Can be acute or chronic
Rarely receive help
Acting on delusion can violate laws or social norms
Behavior is remarkably normal except when patient focuses on delusions
Personality does not change but they get more involved with delusional concern
UNCOMMON
Examples of delusions
Being followed
Poisoned
Infected
Loved at distance
Deceived by spouse or lover
Schizophreniform
Similar to schizophrenia but duration is >6months
Symptoms present for ≥1 month to be classified
1/3 recover & 2/3 develop schizophrenia
Brief psychotic disorder
Episode lasts 1 month>x ≥1day
Sudden onset with ≥1 positive sign of schizophrenia
Emotional turmoil or overwhelming confusion and rapid, intense shifts of affect
Severe impairment
Supervision needed
Suicide risk in younger patients especially
Psychotic disorders attributable to a substance
Prominent hallucinations or delusions thata re direct physiologic effects of substance
During intoxication sympyoms continue as long as substance continues
Withdrawal symptoms last ≤4wks
Differential diagnosis recommended
Describe the clinical course of schizophrenia (prodromal, acute, stabilization, and recovery but include issues of relapse)
Prodromal.
Acute Illness period
Stabilization
Recovery.
Relapses
Prodromal
Early changes that are a precursor to the disorder
iiBegin in childhood
Finding at this stage treatment can begin earlier
50%+ report symptoms:
Tension
Nervousness
Lack of interest in eating
Difficulty concentrating
Disturbed sleep
Decreased enjoyment
Loss of interest in things
Feeling too excited
Hearing voices or seeing things
. Acute Illness period
Occur during adolescence and Young Adulthood
Subtle–Bizarre/disruptive behaviors¬¬
As symptoms worsen, they are unable to perform ADL
High risk of Suicide, may need hospitalization
Symptoms:
Staying up all night for several nights
Incoherent conversations
Aggressive acts against self or others
Treatment:
alleviate of symptoms through therapy with medications
Normalizing sleep
Reduce substance use
Stabilization
The focus after diagnosis
Less acute but present symptoms
Treatment is intense with medication regiments established
Substances are eliminated
Family needs to cope
Socialization with others increases so rehab begins
Recovery
Goal-live well, no cure
Relapses
Main reason is non adherence to meds
Define the positive symptoms of schizophrenia
a. Sensory Hallucinations & delusions (grandiose, nihilistic, persecutory, and somatic)
b. excessive or distorted thoughts and perceptions that occur within the individual but are not experienced by others.
c. reflect an excess or distortion of normal functions
Define the negative symptoms of schizophrenia
emotions and behaviors that should be present but are diminished in persons with schizophrenia.
Flat affect
Diminished emotional expression
Alogia
avolition (lack of interest or motivation in goal-directed behavior such as getting dressed, going to work or school) effects ADL
Ambivalence
Anhedonia
Define the neurocognitive symptoms of schizophrenia
May be independent of positive & negative symptoms
Short and Long-term memory
Long-term isn’t necessarily impacted
Vigilance or sustained attention
Verbal fluency or ability to generate new words
Executive functioning: Volition, planning, purposeful action, & self-monitoring
Cognitive dysfunction can exist evin if positive symptoms are in remission
Manifested in disorganized symptoms
Low intellectual functioning
Describe the disorganized thinking terms
Confused speech and thinking
DEF: findings that make it difficult for the person to understand and respond to the ordinary sights and sounds of daily living.
Echolalia | Repetition of another person’s words or phrases, often in a parrot-like manner. |
Circumstantiality | Overly detailed speech that eventually reaches the point — the person includes unnecessary information but does return to the main idea. |
Loose association | Ideas shift from one topic to another with little or no logical connection. The conversation is hard to follow. |
Tangentiality | Person goes off-topic and never returns to the main point. The answer is only loosely related or unrelated to the question. |
Flight of ideas | Rapid, continuous speech with frequent topic changes based on loosely connected or play-on-word associations. |
Neologisms | Made-up words or expressions that have meaning only to the person using them. |
Paranoia | Irrational distrust or suspicion of others; belief that others are out to harm, deceive, or persecute. |
Referential thinking (Ideas of reference) | Belief that ordinary events or people have special personal meaning or messages for the individual (e.g., “The TV is talking to me”). |
Autistic thinking | Private, inward-focused thinking that is disconnected from reality or logic; preoccupation with one’s own inner world or fantasies. |
Concrete thinking | Literal interpretation of information; difficulty understanding abstract concepts, jokes, or metaphors. |
Verbigeration (sometimes called Vervigeration) | Senseless repetition of words, phrases, or sentences, often without meaning or connection to conversation. |
Metonymic speech | Use of words with related meaning instead of the exact term, often showing disorganized thought. |
Clang association | Speech based on sound or rhyme rather than meaning, e.g., “The train brain rain pain.” |
Stilted language | Overly formal, pompous, or artificial speech, often inappropriate to the situation. |
Pressured speech | Rapid, uninterruptible speech that feels driven or urgent; the person talks nonstop and can’t be interrupted. |
Describe the disorganized behavior terms
DEF: Disorganized behavior (which may manifest as very slow, rhythmic, or ritualistic movement), coupled with disorganized speech, makes it difficult for the person to partake in daily activities
Here are definitions for the terms you listed, primarily used in psychiatry and mental health contexts:
1. Agitation
A state of excessive psychomotor activity that is often associated with a feeling of inner tension.
Features: Restlessness, pacing, hand-wringing, inability to sit still, irritability.
Common in: Anxiety, mania, delirium, psychosis.
2. Catatonia
A neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by abnormal movements, behaviors, and postures.
Symptoms: Can include stupor, mutism, negativism, posturing, rigidity, and waxy flexibility.
Seen in: Schizophrenia, mood disorders, and some medical conditions.
3. Catatonic Excitement
A subtype of catatonia marked by extreme motor agitation and purposeless, excessive movement.
Behaviors: Running, shouting, impulsivity, aggression.
Danger: High risk of exhaustion, injury, or harm to others.
4. Echopraxia
The involuntary imitation of another person's movements or gestures.
Associated with: Schizophrenia (especially catatonic type), autism spectrum disorders, and other neurological conditions.
5. Regressed Behavior
A return to an earlier stage of development, typically in response to stress or psychological conflict.
Examples: Childlike behaviors such as thumb-sucking, bed-wetting, or temper tantrums in adults.
6. Hypervigilance
An enhanced state of sensory sensitivity and exaggerated intensity of behaviors aimed at detecting threats.
Signs: Being constantly on guard, easily startled, scanning the environment.
Common in: PTSD, anxiety disorders.
7. Waxy Flexibility
A symptom of catatonia where a person maintains a position in which their body is placed, even if it is unusual or uncomfortable.
Example: If you raise their arm, they keep it in that position like a wax figure.
Diagnostic Clue: Strong indicator of catatonia.
Let me know if you want clinical examples or differentiations between similar terms.
Explain the concerns of schizophrenia across the life-span: Children
Rare occurrence
Same symptoms as adults
More genes that can give them schizophrenia
iWorse diagnosis
VH
Less developed delusions
disorganized speech and behavior may be explained better by other disorders that are more common in childhood, those disorders should be considered before applying the diagnosis of schizophrenia to a child.
Signs can predict development of schizophrenia later in life
Delays in attainment and motor development
Problems in social adjustment
Poor Academic and cognitive performance
Explain the concerns of schizophrenia across the life-span: Elderly
People who have it since childhood may experience improvement l8r in life
Depends on effectiveness of earlier treatment, presence of support system, and interaction of environmental stressors and patient’s functional impairments
More likely than other older adults to develop cognitive impairment
High cost for care because many are no longer cared for in institutions and because community-based treatment has developed more slowly for this age group than for younger adults
Describe key epidemiology and risk factors with schizophrenia: Familial differences
1st degree biologic relatives have 10x greater risk for schizophrenia than general population
SAD increased for other relatives
Describe key epidemiology and risk factors with schizophrenia: Age of onset
Usually diagnosed in late adolescence and early adulthood
Men: 18-25
Women: 25-35
The earlier the diagnosis and the longer the psychosis remains untreated, the more severe the disorder becomes
Describe key epidemiology and risk factors with schizophrenia: Gender differences
Men diagnosed earlier with poorer prognosis than women
When women are diagnosed early, they are at higher risk for physical comorbidities than men
Describe key epidemiology and risk factors with schizophrenia: Ethnicity and culture
AA overdiagnosed
African American and Latinx individuals with bipolar disorder are more likely to have misdiagnoses of schizophrenia than are White individuals
Asian undiagnosed
a All cultures and countries, 0.48% world wide
Recognize the complexity of comorbidities with schizophrenia
Mortality: people die 20yrs earlier than gen pop
Natural
Cardiovascular
Cancer
COPD
DM
Influenza
Pneumonia
ii. Unnatural
Suicide
Substance abuse
ETOH abuse
Legal interventions
MORE susceptible to TB, Human immunodeficiency disease, Hep B & C, osteoporosis, poor dentition, impaired lung function, altered (reduced) pain sensitivity, sexual dysfunction, obsreric complications, cardiovascular problems, hyperpigmentation, obesity, DM, metabolic syndrome with hyperlipidemia, polydipsia, thryroids dysfunction, hyperprolactinemia
Describe key etiology aspects of schizophrenia
Biologic predisposition or vulnerability and environmental stressors
Diathesis-stress model
Environmental stressors
Pregnancy
Obstetric complications
Social adversity
Migration
Unemployment
Urban living
Childhood abuse
Social isolation/abscense of close friends
Biologic theories
Psychosocial theories
Explain the concern of suicide risk with patients with schizophrenia
Acts of aggression to staff or self during psychosis
displaying negative symptoms, side effects of antipsychotic medications, or actual depression and demoralization as a result of this illness.
Voices can tell them to harm self or others
Describe key areas of assessment (biological, psychological and social) and the unique challenges with each area (e.g. hallucinations vs. delusions)
Biological
Pyschological
Social
Hallucinations vs. Delusions
Explain the interventions to promote recovery and wellness with patients with schizophrenia
Consider medication side effects
Temperature regulation
monitor temp
observe reaction to temp
protect from weather
Fluid and electrolyte balance
observe for polydipsia
monitor urine specific gravity
Help with ADL, hygiene, exercise, and nutrition
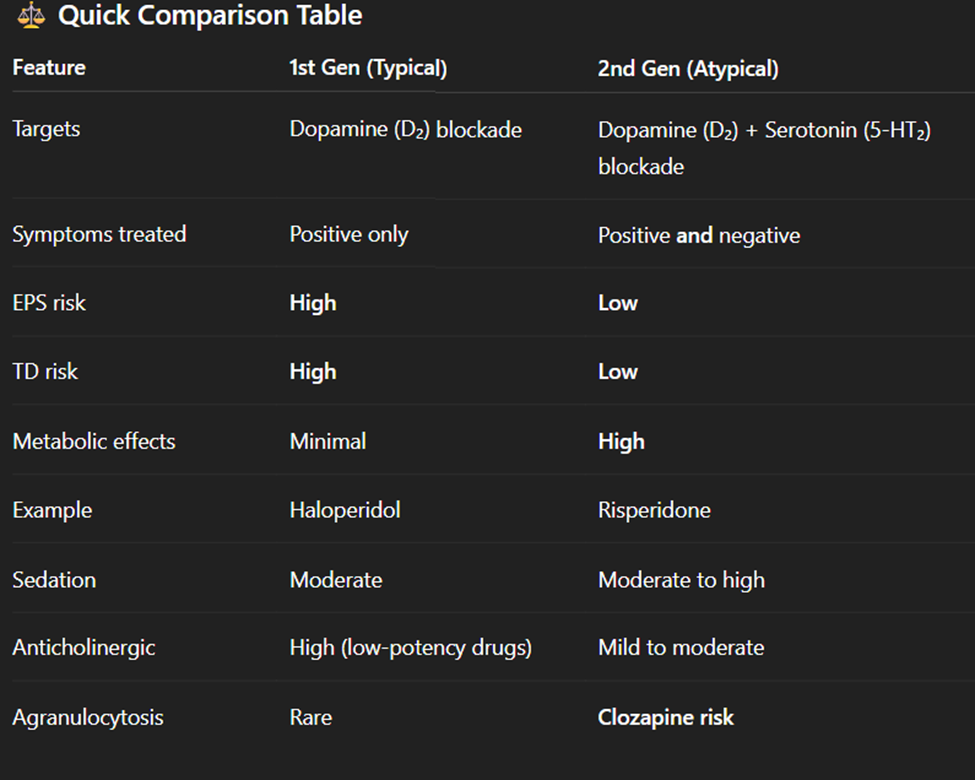
Describe the two categories of antipsychotics and how they are different
1st generation Typical antipsychotics
Haldol
Thorazine
Block D2 receptors
For positve signs of schizophrenia
Side effects:
EPS
TD
NMS
sedation and weight gain
orthostatic hypotension
2nd generation Atypical antipsychotics
Abilify
Clozaril
Risperdal
Blocks D2 and serotonin
Positive and negative signs
Side effects:
Metabolic syndrome
Sedation
orthostatic hypotension
(clozapine)
Agranulosis
New Onset DM
weight gain
Risperidal
Hyperlactecemia
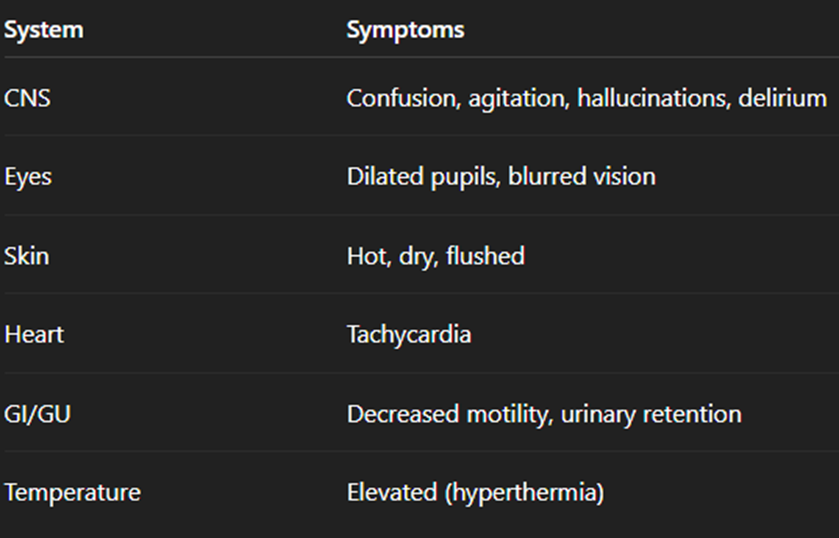
Explain the concerns and treatments of cholinergic rebound and anticholinergic crisis
Cholinergic rebound
Patient stops taking abruptly anticholinergic
SYMPTOMS:
Vomiting
Excessive sweating
Altered dreams
Nightmares
Anticholinergic crisis
AKA anticholinergic delirium
Life threatening emergency caused by OD of or sensitivity to drugs with anticholinergic properties
Atropinr, scopolamine, belladonna alkoids
Symptoms:

Describe the nurses role in psychosocial interventions (therapeutic interactions, enhancing cognitive functioning, and behavioral interventions)
a. Therapeutic interactions
b. Enhancing cognitive functioning
c. Behavioral interactions
Describe areas of psychoeducation to encourage recovery (teaching strategies, teaching about symptoms, stress, wellness, social skills and family education)
Teaching strategies
cogntive deficits
learn best in errorless environment, directly give correct information
ask encouraging questions
minimal distractions
Unambiguous directions
Teaching about symptoms
teach hallucinations and delusions are part of disorder and meds make it easier
learn self regulation, symptom monitoring
Stress
establish regular counseling sessions
positive coping
Wellness
bot just physical health
(1) cognitive training and remediation that focus on cognitive impairments and social functioning (Miley et al., 2020) and could incorporate new methodologies that use virtual reality (Souto et al., 2020);
(2) support that provides information about the illness, addresses emotional needs, acknowledges the challenges of the illness, encourages the person, and provides guidance (Beentjes et al., 2020);
(3) goal setting with the individual that uses methodologies like the “Choose-Get-Keep” model that supports client goals over the imposition of provider goals
Social skills
behaviors for social interactions
Family education
family support
disease course
support systems
life manegment skills
Describe the Continuum of Care priorities
Discharge planning encourages follow-up care in the communit
Primary recovery strategy for patients becoming lost after discharge
Emergency care
in hospital
trained crisis team
medication side effect
water intoxicatio
Inpatient-Focused care
brief stabalization
Community Care
Public support
Virtual Mental Health care
rural ares
mobile or telephone
CBT
Describe the adverse effects of antipsychotics and nursing interventions
a. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
b. Agranulocytosis
c. Extrapyramidal
d. Orthostatic hypotension
e. Hyperprolactinemia
f. Sedation
g. Weight gain
h. New-onset DM
i. Cardiac arrythmias
j. DRESS
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Definition:
A rare, life-threatening reaction to antipsychotic medications caused by severe dopamine blockade in the brain.
Key signs/symptoms:
High fever (hyperthermia)
Severe muscle rigidity (“lead pipe” stiffness)
Altered mental status
Autonomic instability (↑ HR, BP fluctuations)
Elevated creatine kinase (CK)
Nursing note:
Medical emergency — stop the antipsychotic immediately, provide cooling, IV fluids, and administer dantrolene or bromocriptine as prescribed
Agranulocytosis
Definition:
A dangerous drop in white blood cell count (neutrophils), leading to a high risk of infection.
Common cause:
Seen with Clozapine (Clozaril) use.
Symptoms:
Fever, sore throat, malaise
Signs of infection
Nursing note:
Monitor WBC and ANC regularly; hold the drug and notify the provider if infection signs appear.
Extrapyramidal
Definition:
Movement disorders caused by dopamine blockade from 1st-generation antipsychotics.
Types:
Acute dystonia: muscle spasms, stiff neck, oculogyric crisis
Akathisia: restlessness, can’t sit still
Parkinsonism: tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia
Tardive dyskinesia: repetitive mouth, tongue, facial movements (long-term)
Nursing note:
Treat with anticholinergics (e.g., benztropine or diphenhydramine).
Orthostatic hypotension
Definition:
A sudden drop in blood pressure when standing up from sitting or lying down.
Symptoms:
Dizziness
Lightheadedness
Fainting
Nursing note:
Encourage patient to rise slowly; monitor BP lying, sitting, standing
Hyperprolactinemia
Definition:
An increase in prolactin hormone levels due to dopamine inhibition by antipsychotics.
Symptoms:
Women: galactorrhea (milk secretion), amenorrhea
Men: gynecomastia, sexual dysfunction
Nursing note:
Common with Risperidone; may require dose adjustment or switching meds.
Sedation
Definition:
A calming or drowsy effect caused by CNS depression from many antipsychotics.
Nursing note:
Give medication at bedtime, avoid driving or operating heavy machinery until effects are known.
Weight gain
Definition:
An increase in body weight due to changes in metabolism and appetite regulation.
Common with:
2nd-generation antipsychotics, especially Clozapine and Olanzapine.
Nursing note:
Monitor weight and BMI; encourage healthy diet and exercise.
New-Onset DM
Definition:
Development of high blood glucose due to insulin resistance from atypical antipsychotics.
Common with:
Olanzapine and Clozapine.
Nursing note:
Monitor blood glucose, A1C, and teach patient about diet and symptoms of hyperglycemia (thirst, urination, fatigue).
Cardiac arrythmias
Definition:
Abnormal heart rhythms that may result from QT interval prolongation caused by some antipsychotics.
Common offenders:
Ziprasidone (Geodon), Haloperidol (especially IV).
Nursing note:
Monitor ECG, avoid combining with other QT-prolonging drugs.
DRESS
(Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms)
Definition:
A rare but serious hypersensitivity reaction to certain medications involving the skin and internal organs.
Symptoms:
Rash
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes
Eosinophilia (↑ eosinophils)
Liver, kidney, or heart inflammation
Nursing note:
Stop the medication immediately; treat supportively; can be fatal if not recognized early.