Biology - Chapter 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Know the subatomic parts of the atom and their charges
proton positive, neutron nuetral, electron negative
Cover right. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in atom?
6 P, 6 E, 6 N. P = + sign, N = nothing, E = - (or just on outside)
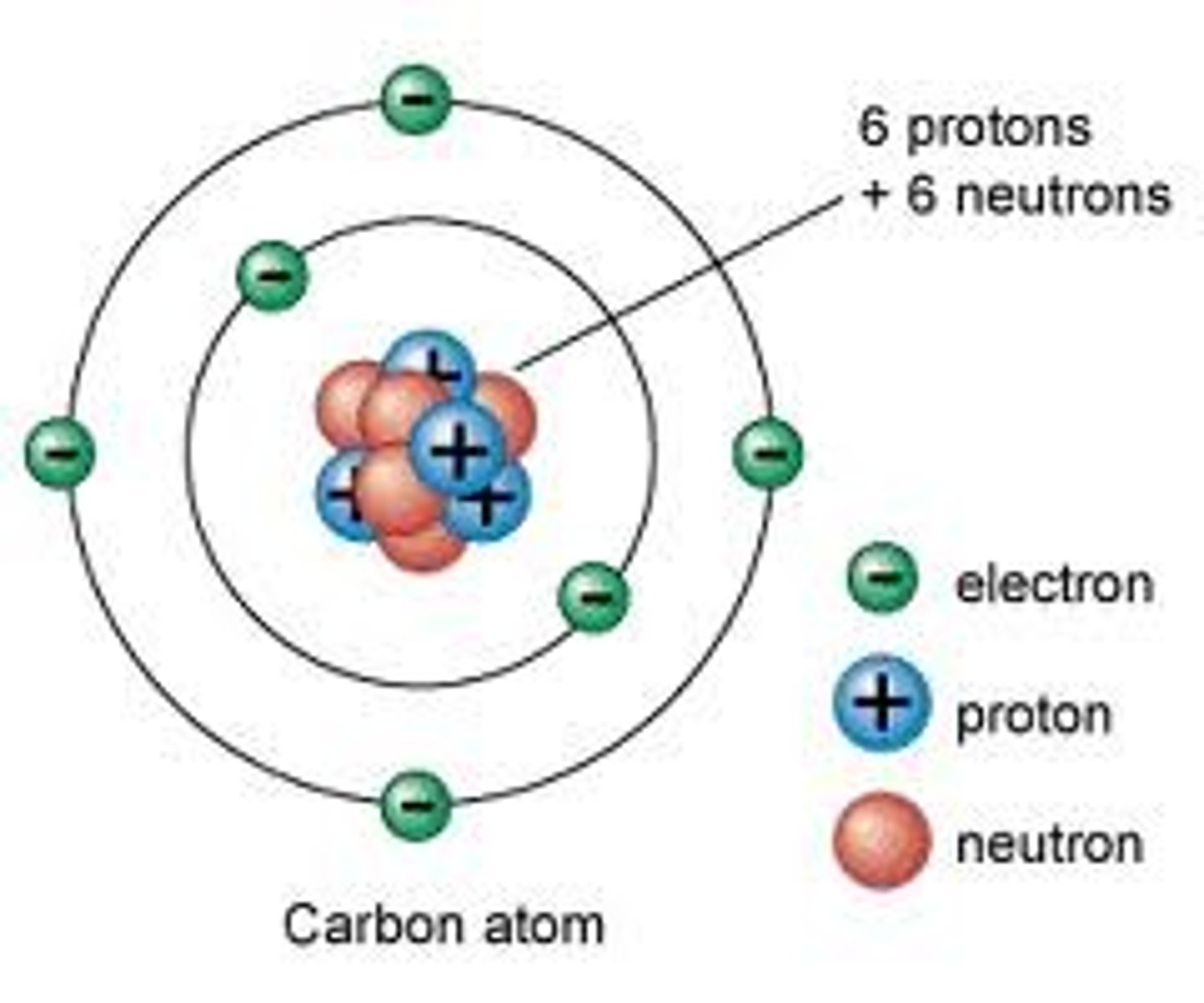
How do isotopes differ?
Number of neutrons
Covalent vs. ionic bond
Atoms share electrons, atoms take/transfer electrons
properties of water
polarity, form hydrogen bonds, surface tension, high heat capacity
solute vs. solvent
being dissolved, doing the dissolving
pH scale
Scale that shows how much acid something has. 0-6 = acidic, 7 = neutral, 8-14 = basic. Lower the number the more acid
atoms that make up carbohydrates
CHO, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen. 1:2:1 ratio
atoms that make up lipids
CHO carbon, hydrogen, oxygen. More C and H, some O
atoms that make up protein
CHON carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen.
atoms what make up nucleic acid
CHONP carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
Monomer and polymer of carbohydrate
Monosaccaride(gluclose). starch, chitin, cellulose
Monomer and polymer of lipid
Glycerol and fatty acid. Lipid
Monomer and polymer of protein
amino acid. polypeptide
Monomer and polymer of nucleic acid
nucleotide. Nucleic Acid, DNA, RNA
Function of carbohydrate
Short and fast energy
Function of protein
cell transport, speed up chem reaction, support cells in body
Function of lipid
long term energy, structure for cell membrane
Function of nucleic acid
carries genetic info
What is occurring when a chemical reaction happens
Bonds break as reactants in the reaction and form new ones when creating products
Know which are the reactants and which are the products in a reaction
R = before. P = after
Know energy-releasing vs. energy-absorbing reactions
Exothermic. Endothermic
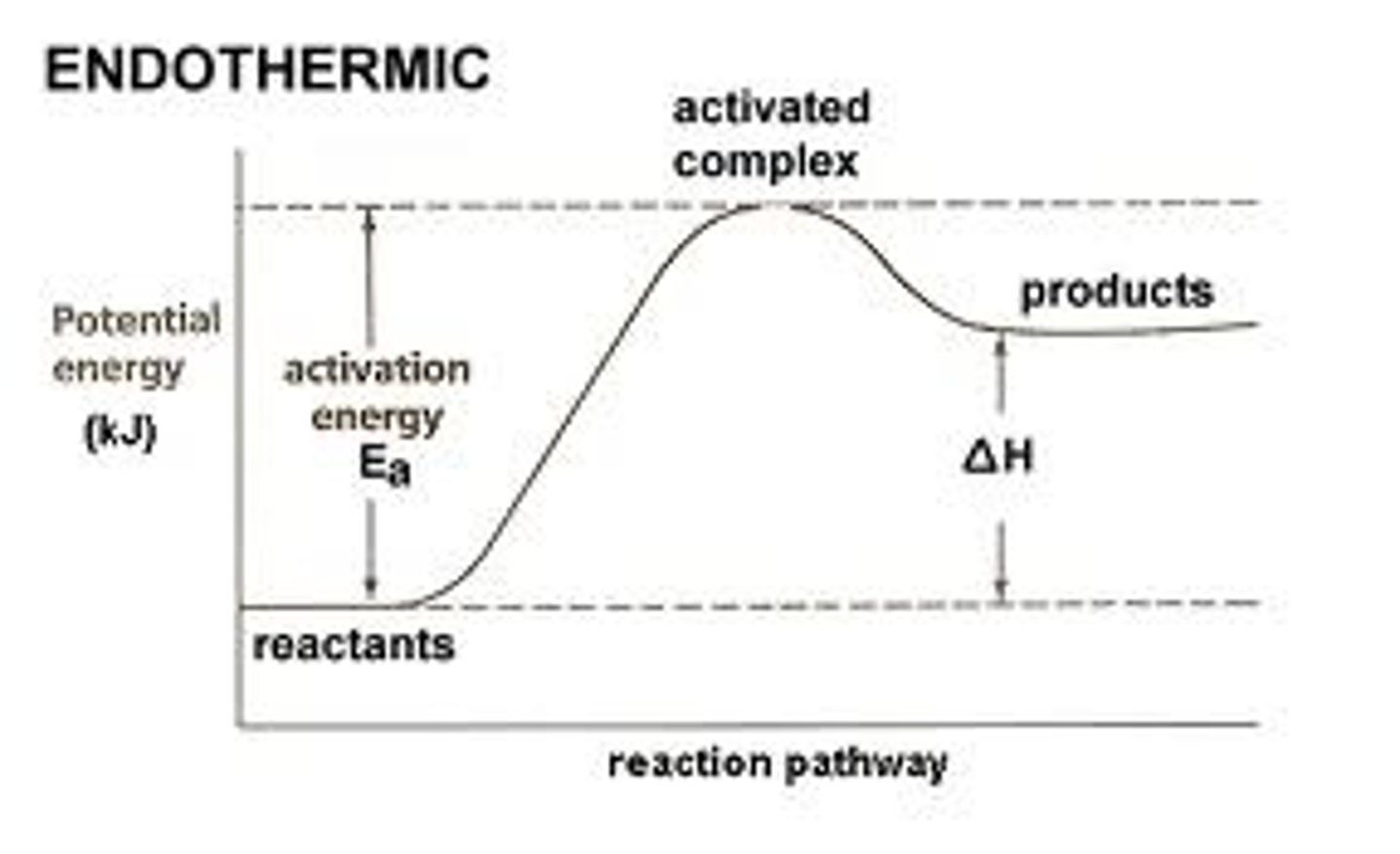
Cover top. Which reaction is this, endothermic or exothermic. Why?
Energy goes up
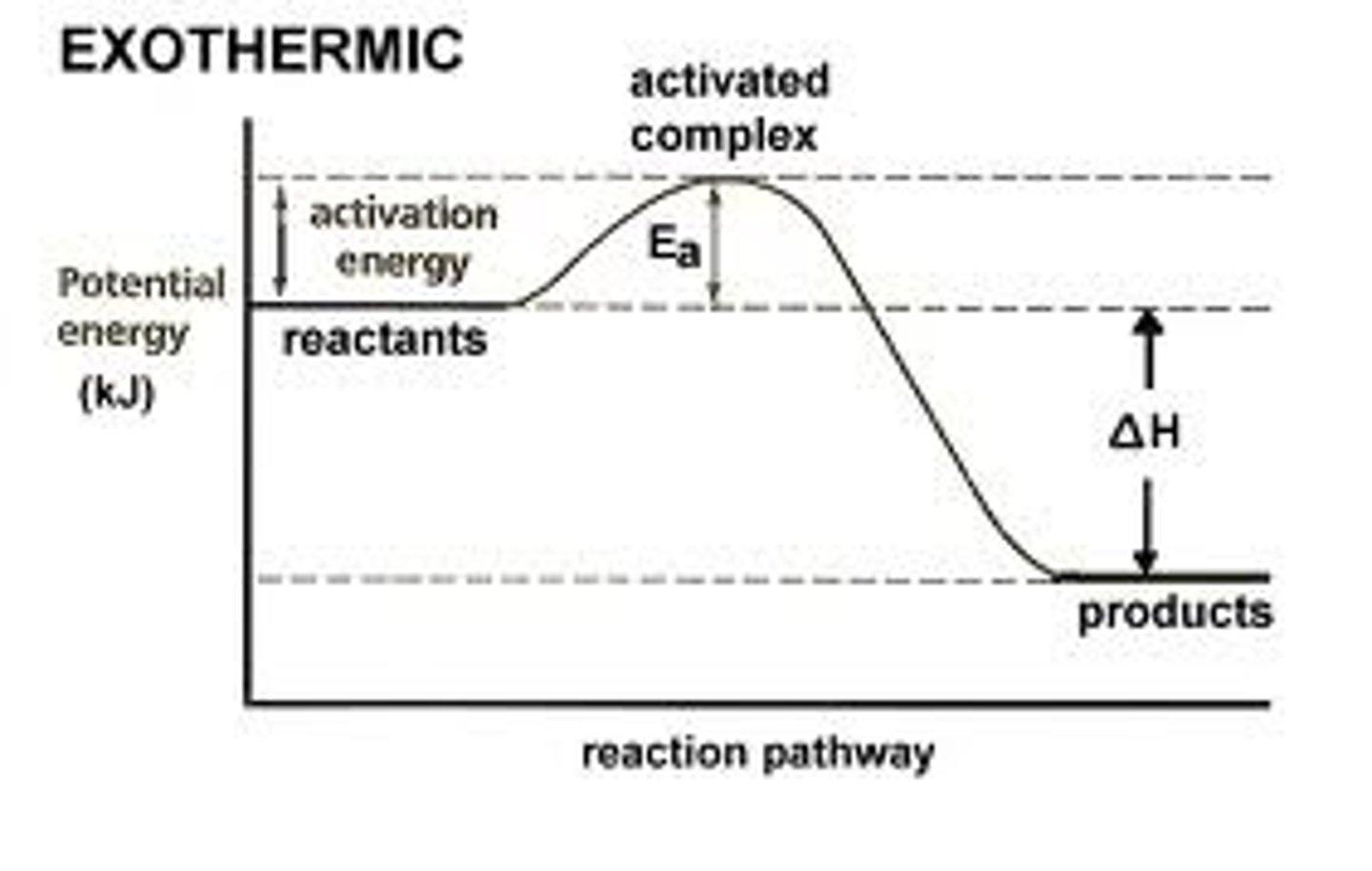
Cover top. Which reaction is this, endothermic or exothermic. Why?
Energy goes down
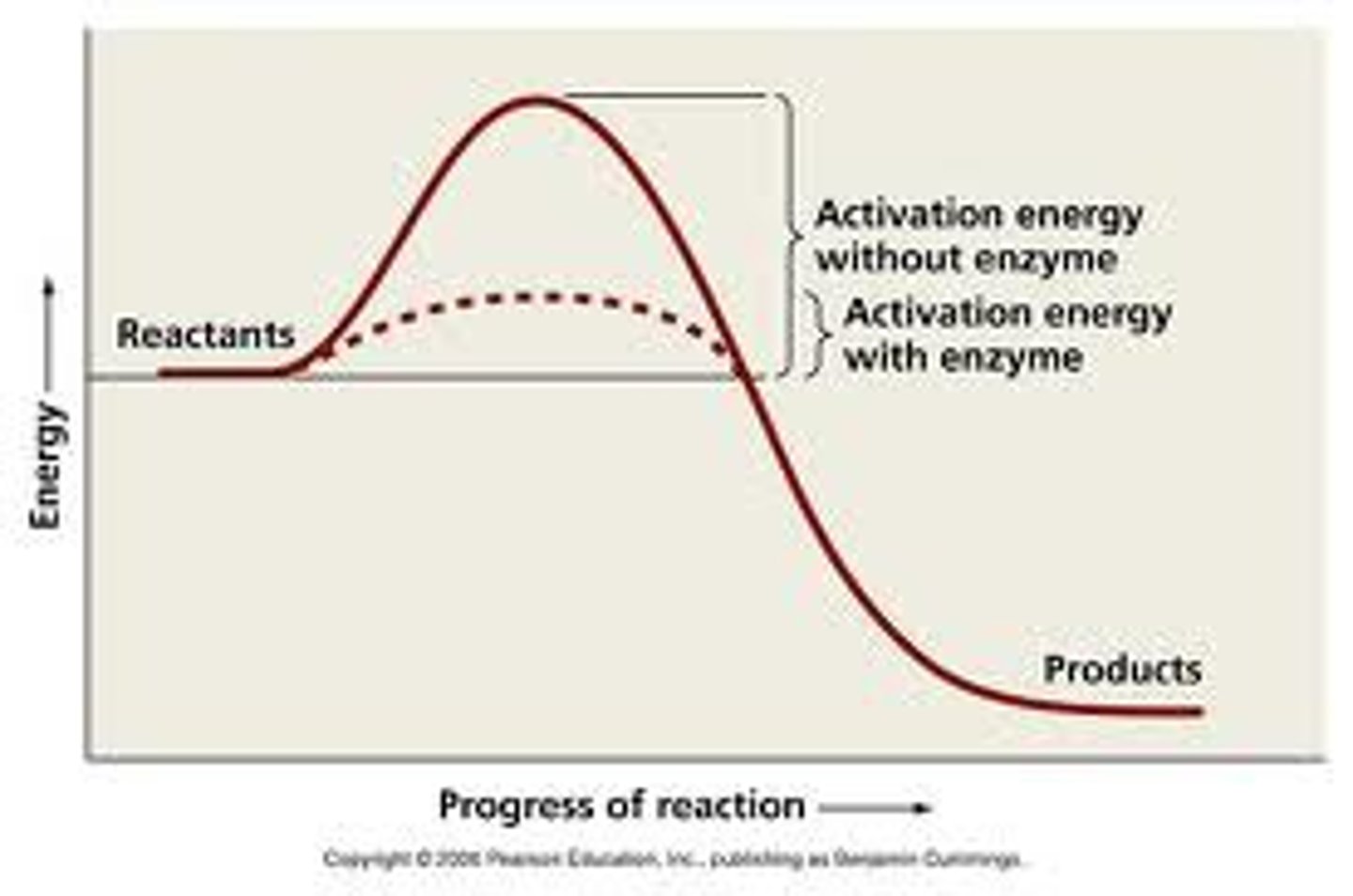
The jobs of enzymes in a chemical reaction
Cataylists that speed up chemical reactions making them possible
graph of energy, know to label
Optimum environments for enzymes and the affects if put in an environment if not optimum
The correct pH, temperature, and salinity for each enzyme. they break and cannot be used