Neurological Aspects of Communication and Cognition Unit 1
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Caudel
toward the tail
Superior
Towards the head end of the body
Inferior
Towards the feet end of the body
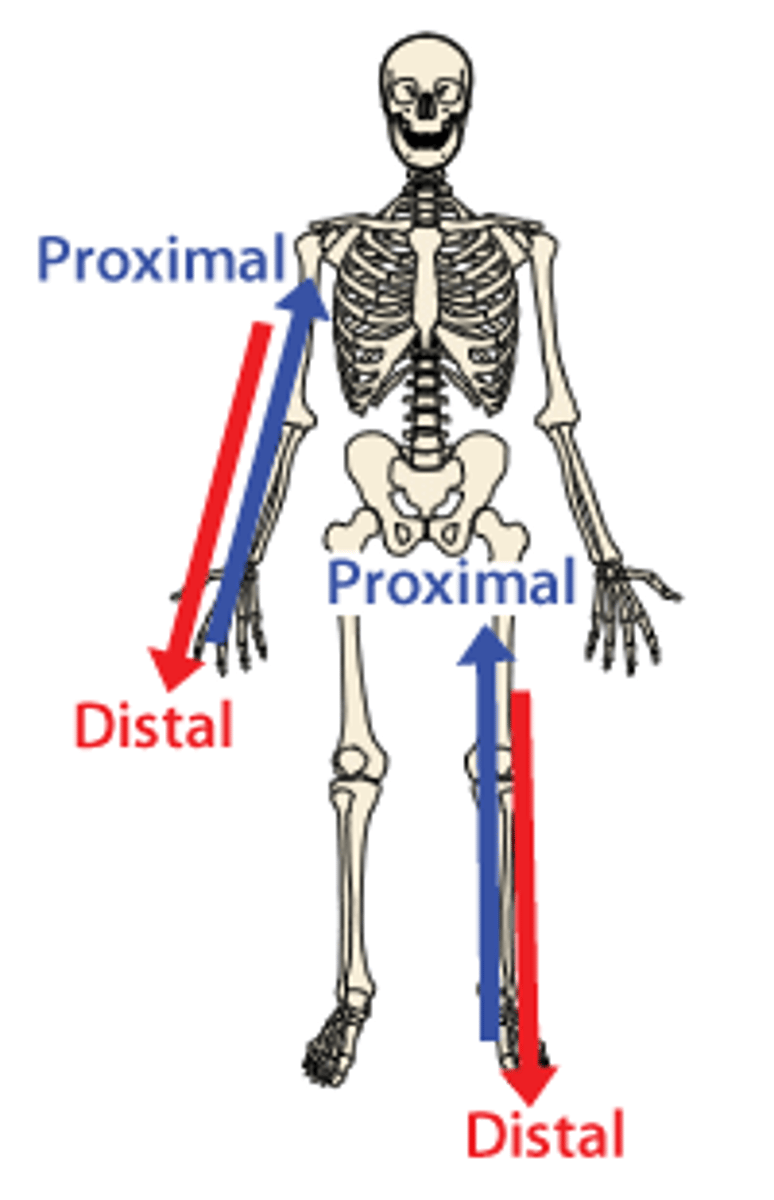
Distal
Away from the joint
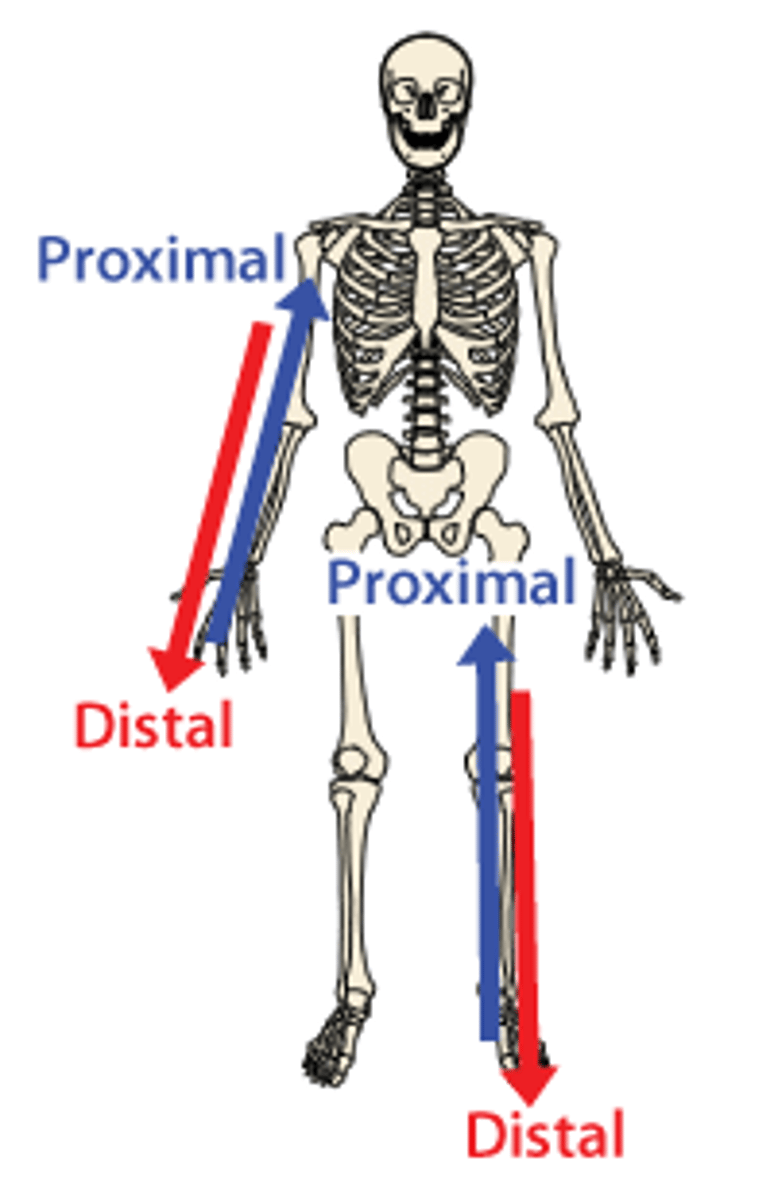
Proximal
Towards the joint
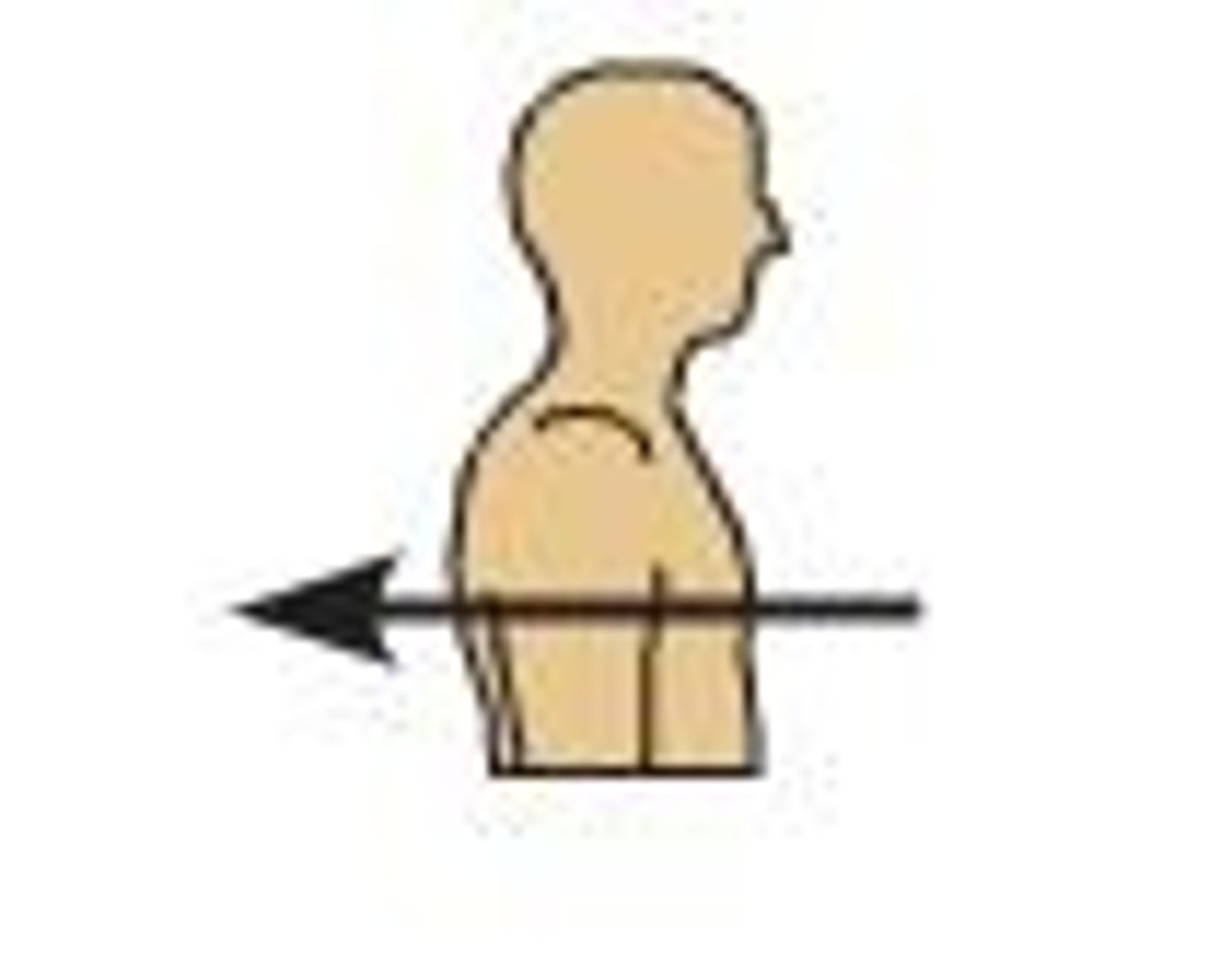
Dorsal
Back of the body
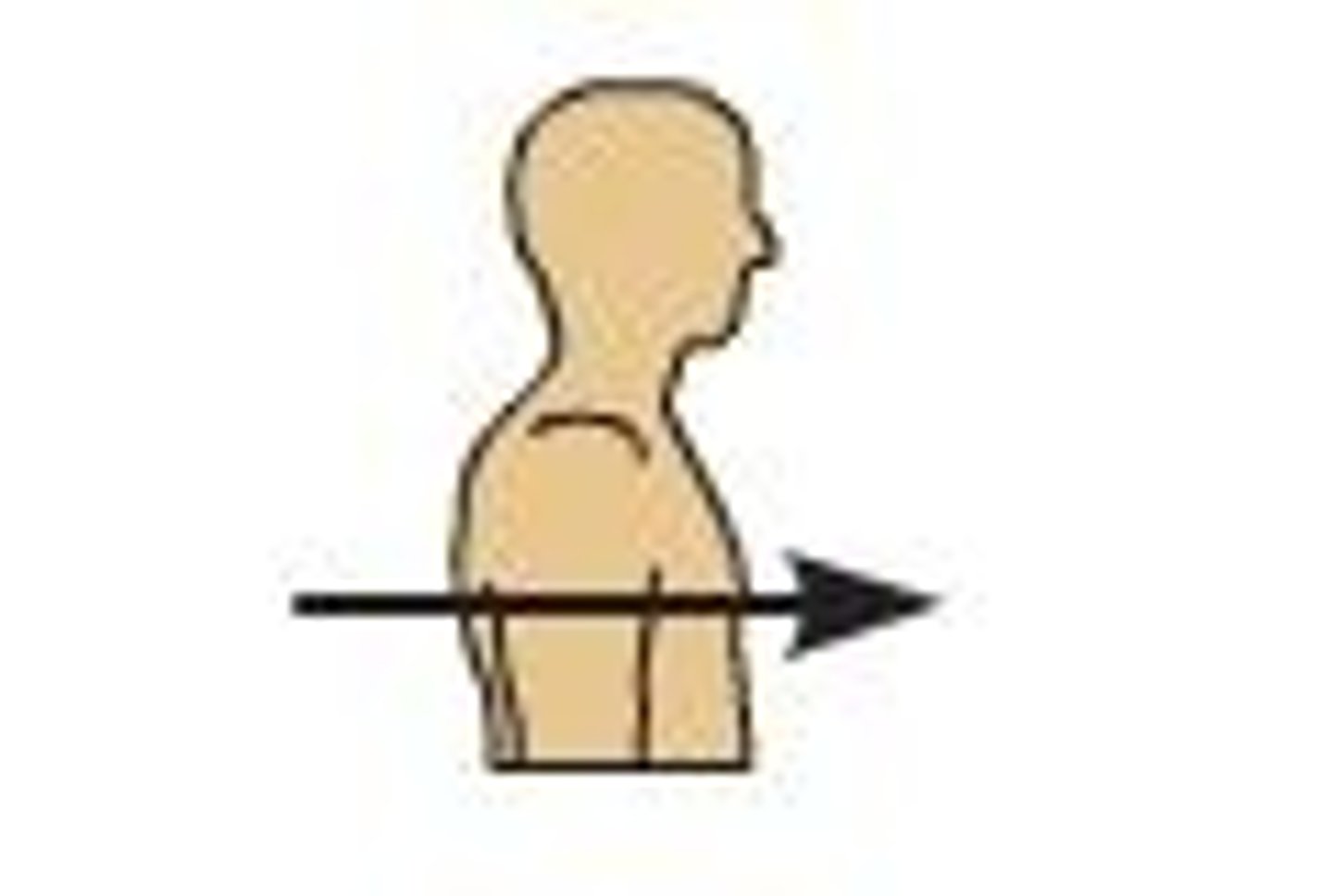
Ventral
Front of the body
Periphreal
away from the center
Central
Near the center of the body
Superficial
Outermost layer of the body
Deep
Deepest layer of the body
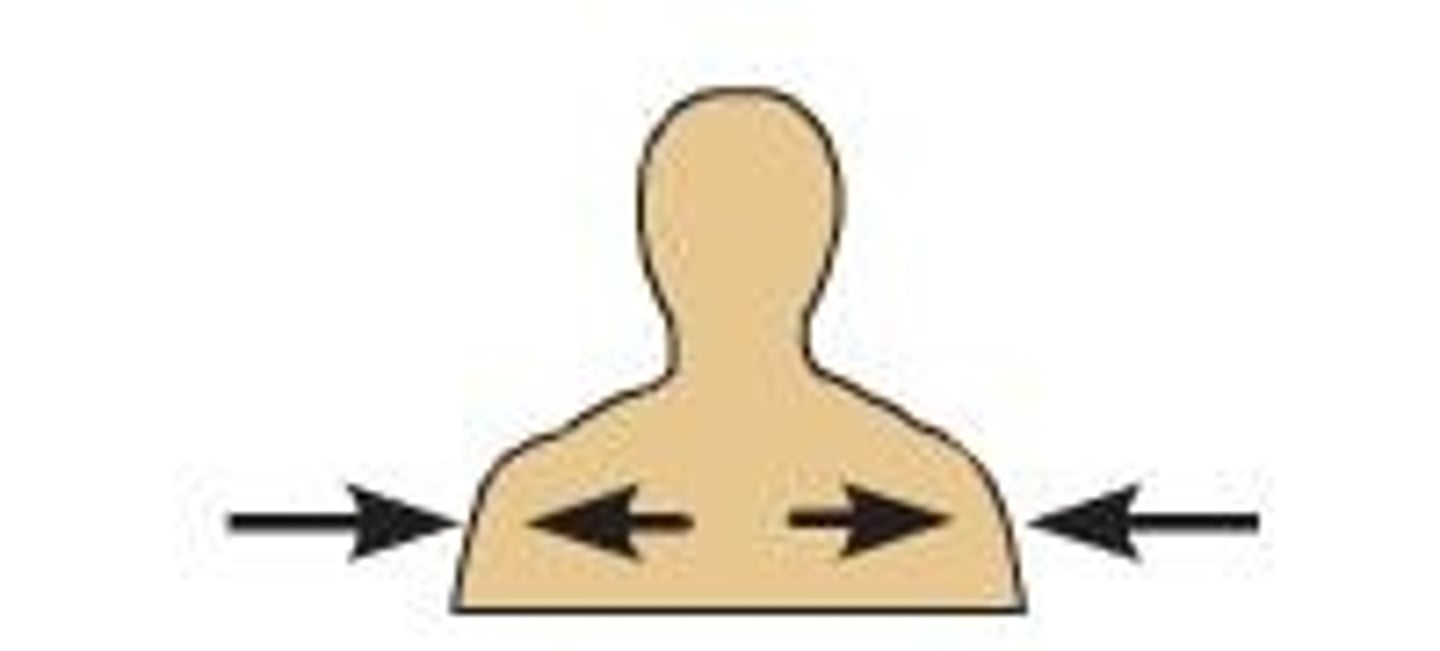
Ipsilateral
Same sides of the body
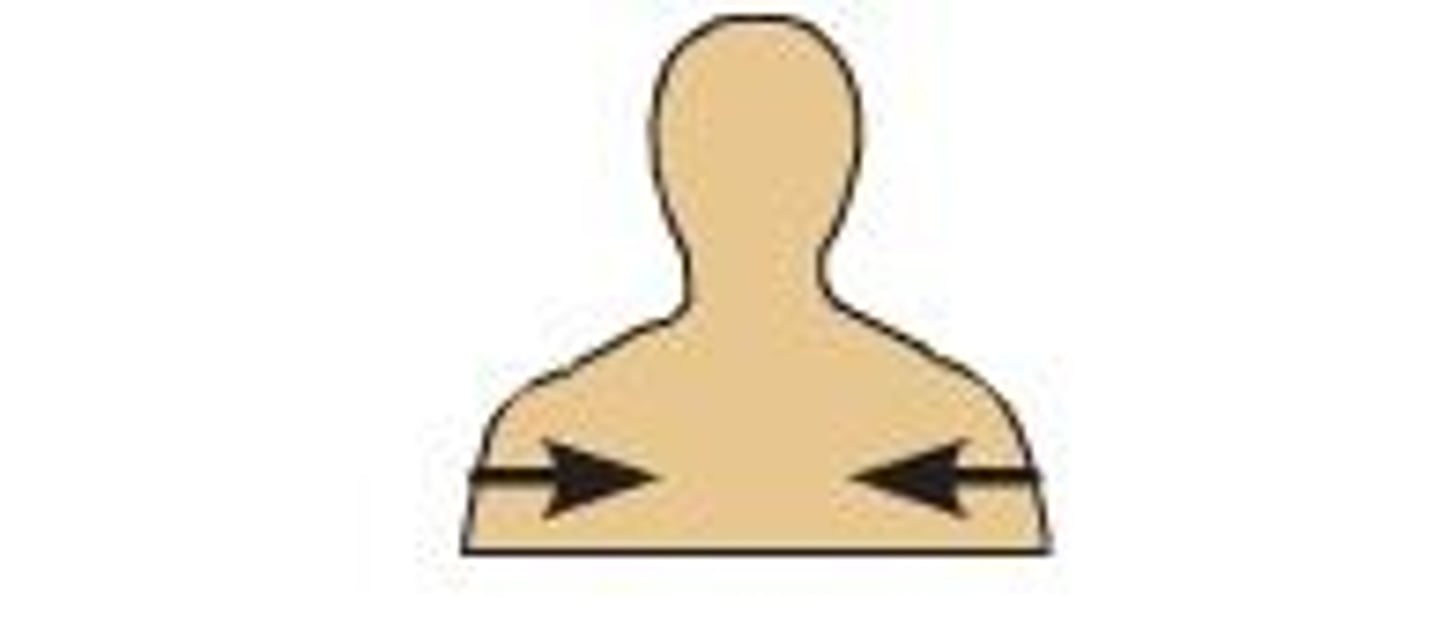
Contralateral
Opposite sides of the body
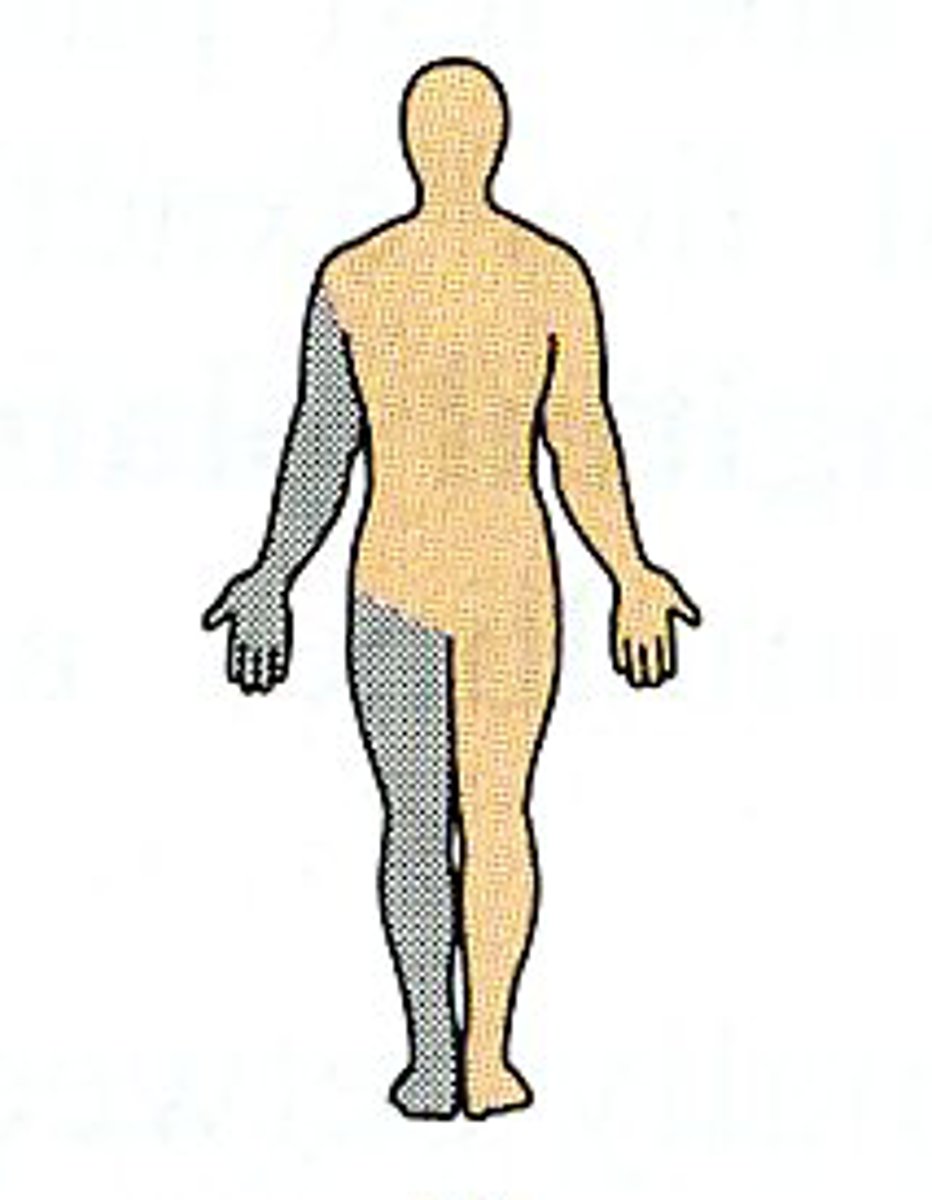
Bilateral
Two sides
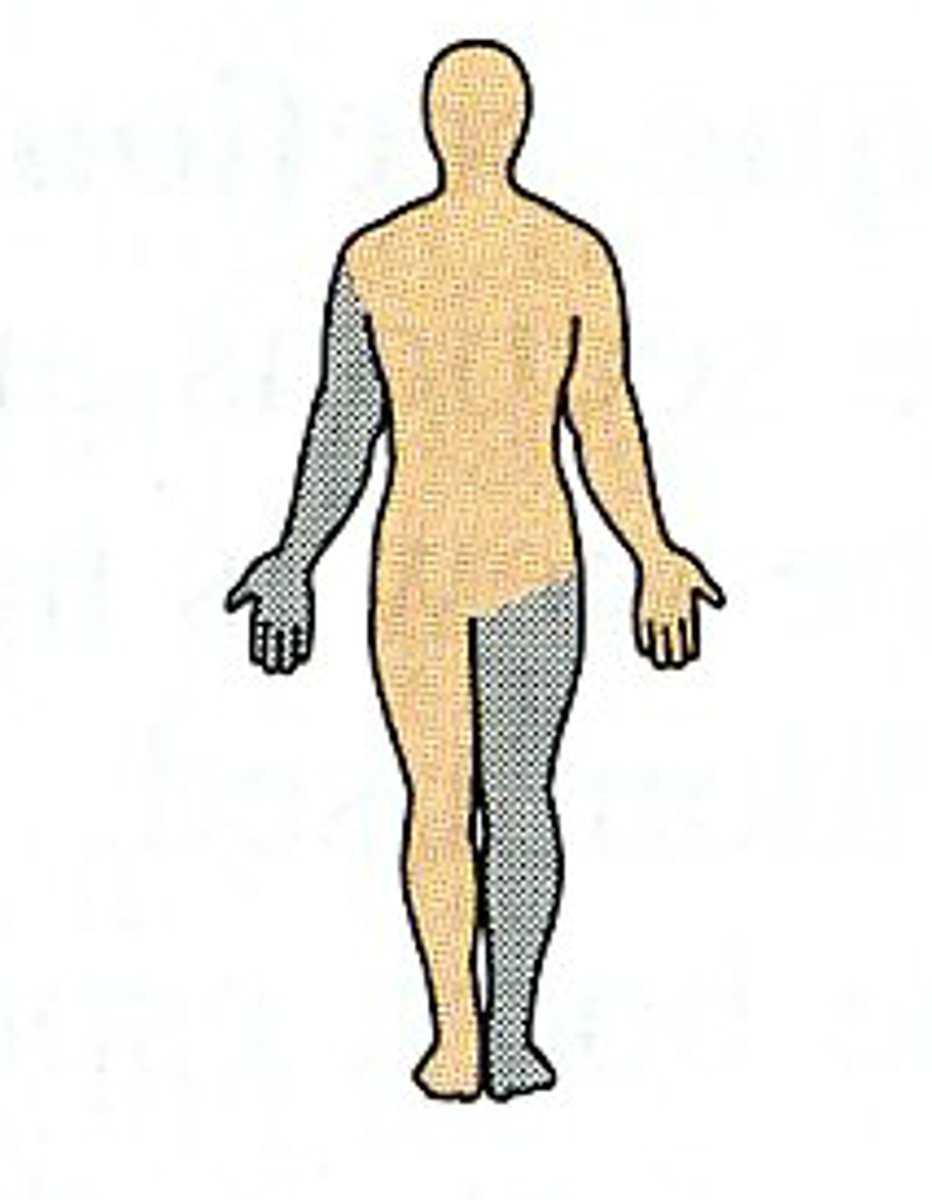
Unilateral
One side
Prone
lying face down
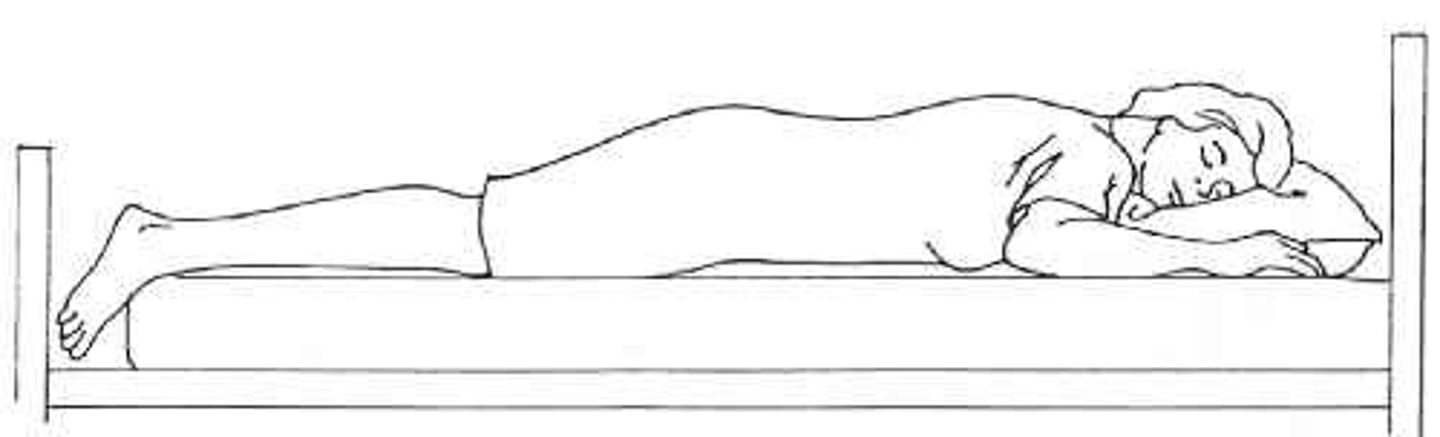
Supine
lying on the back
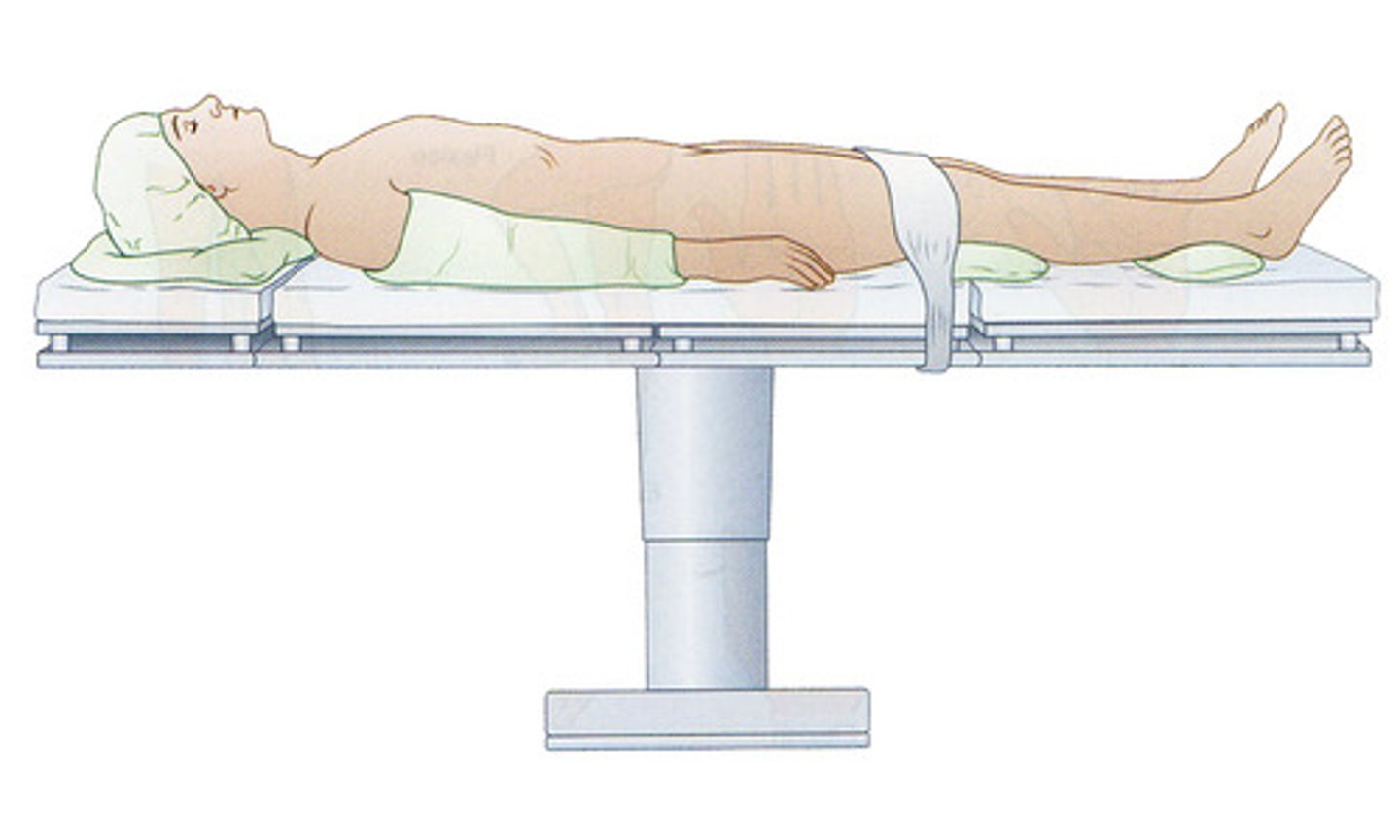
Sagital
divides body into left and right
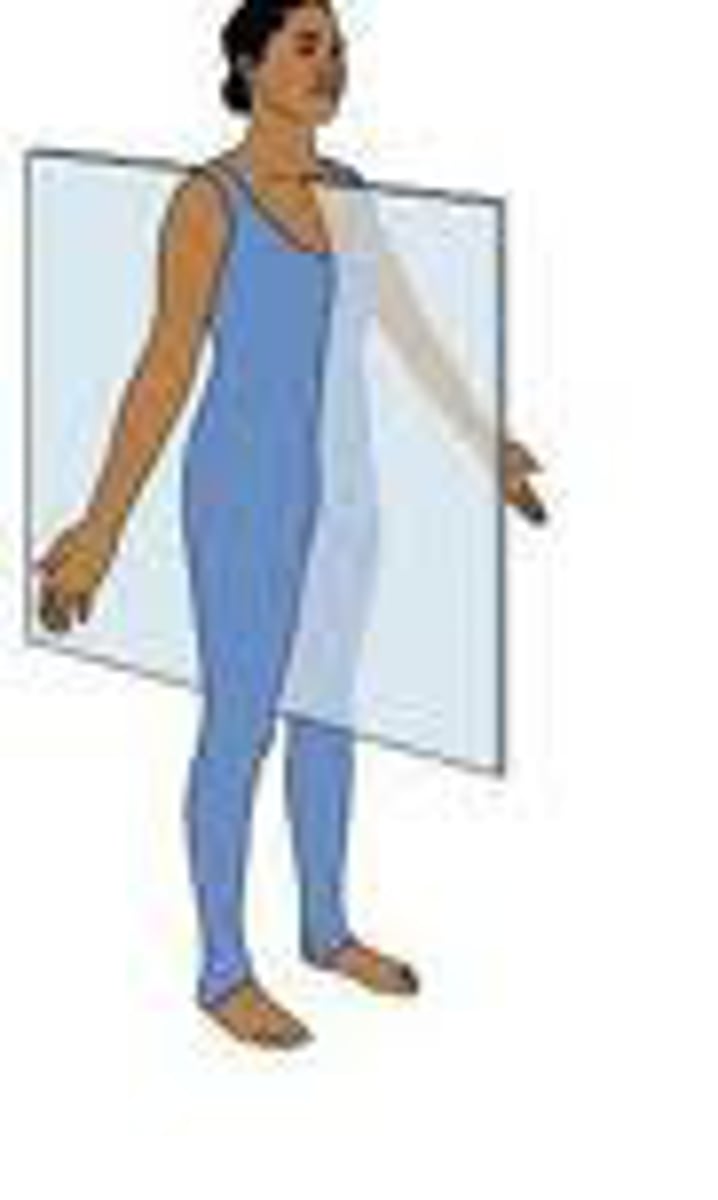
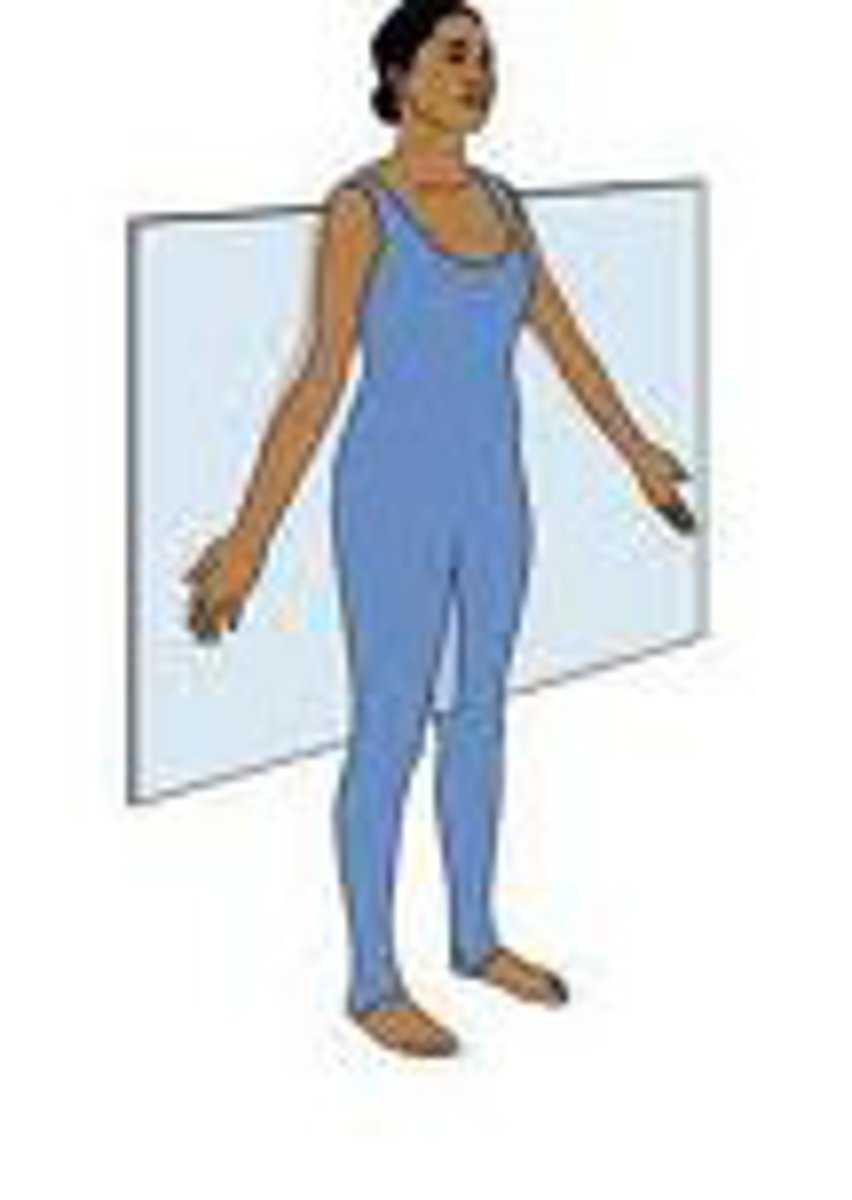
Coronal
divides the body into slices from front to back

Medial
Towards the middle of the body
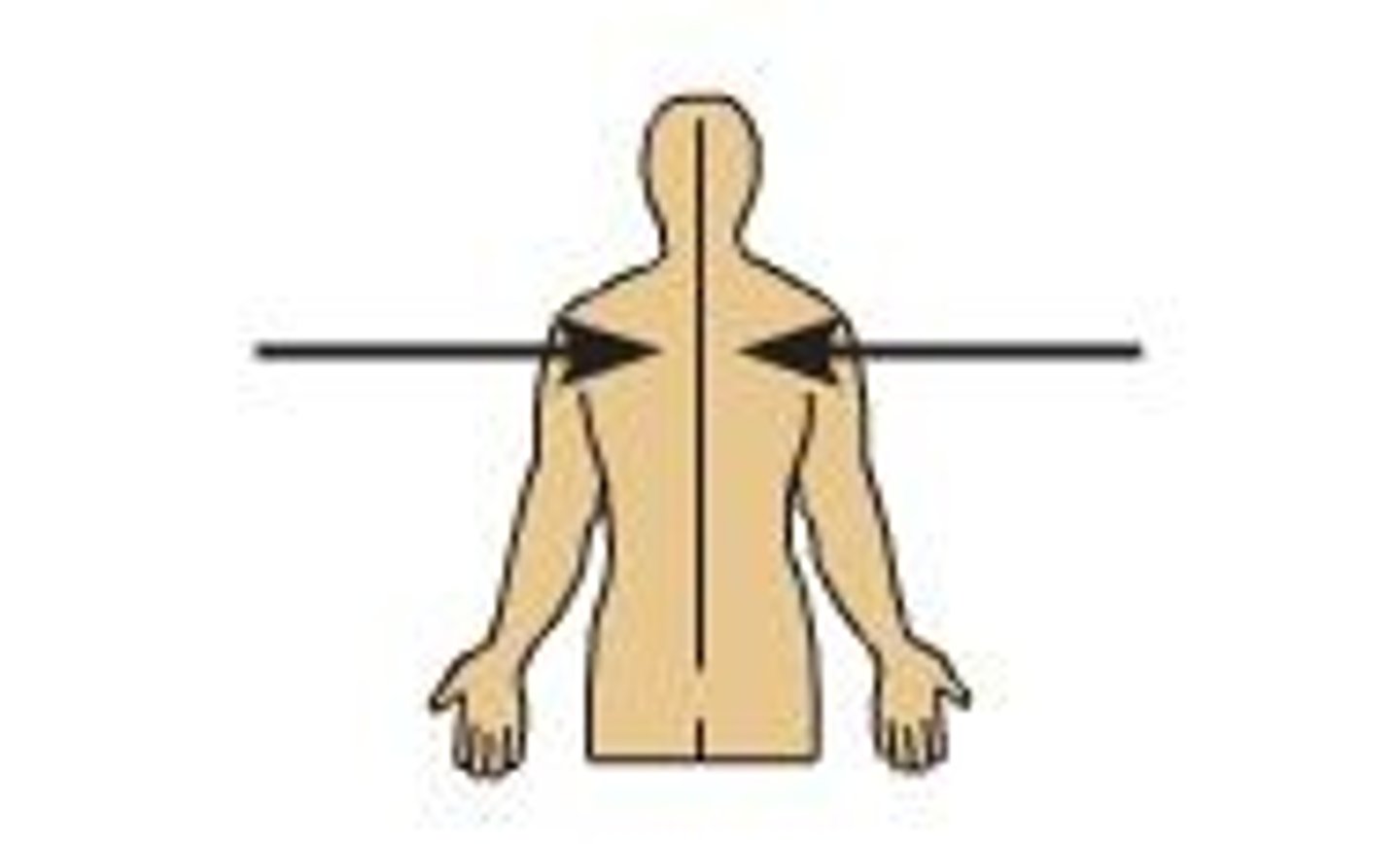
Lateral
Towards the outside of the body
Rostral
toward the nose or mouth
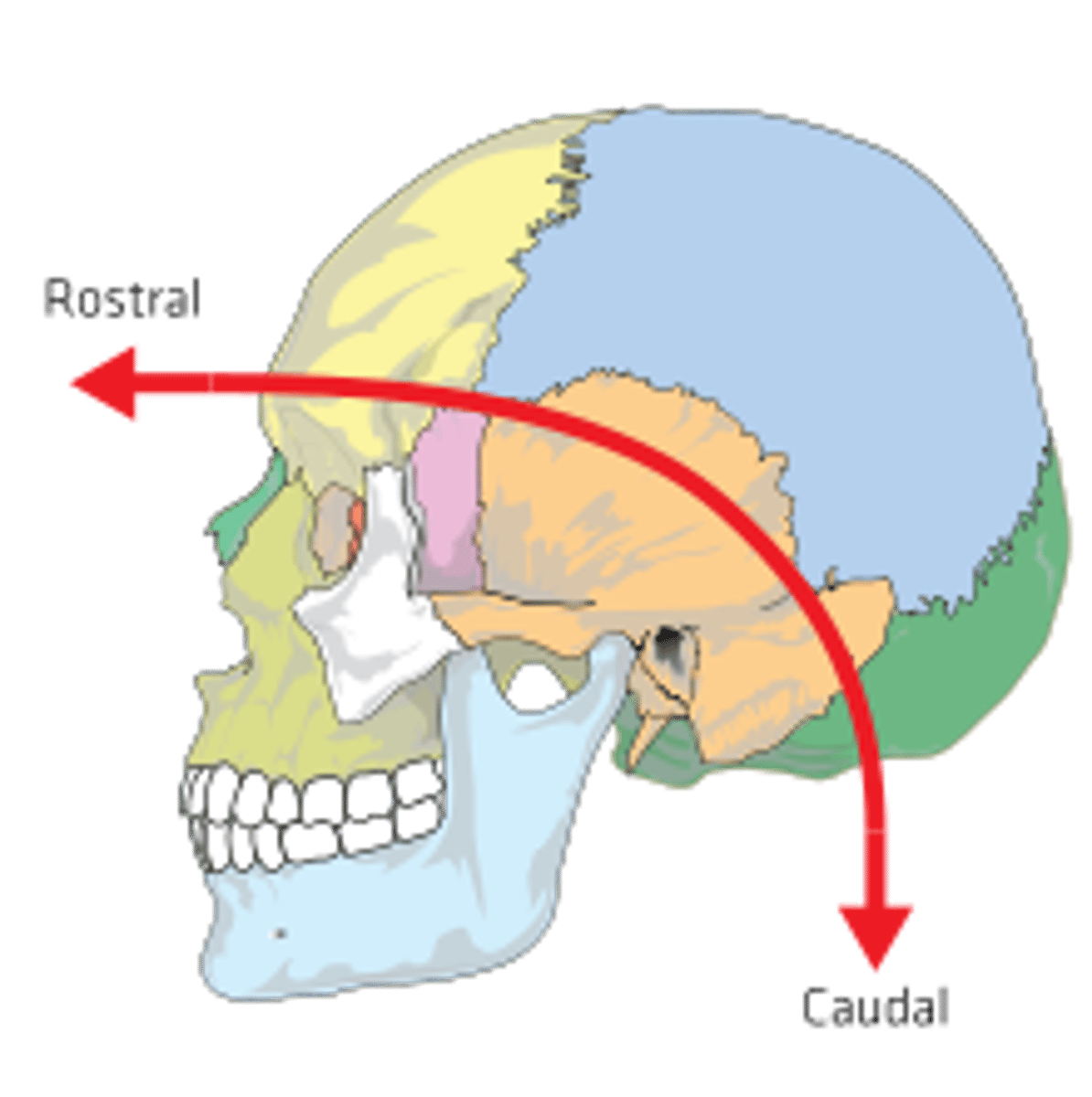
Transverse (axial)
Divides the body into top and bottom
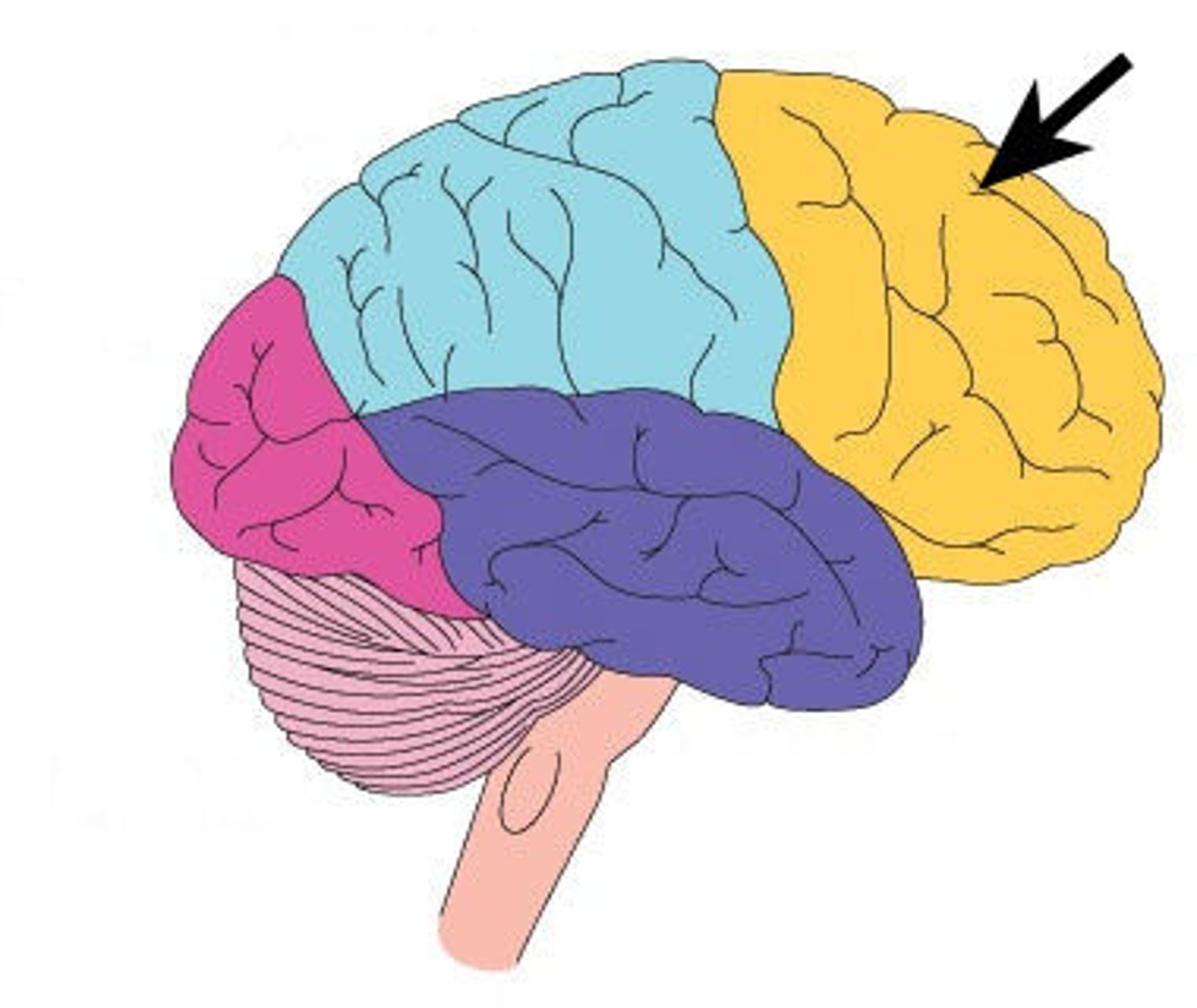
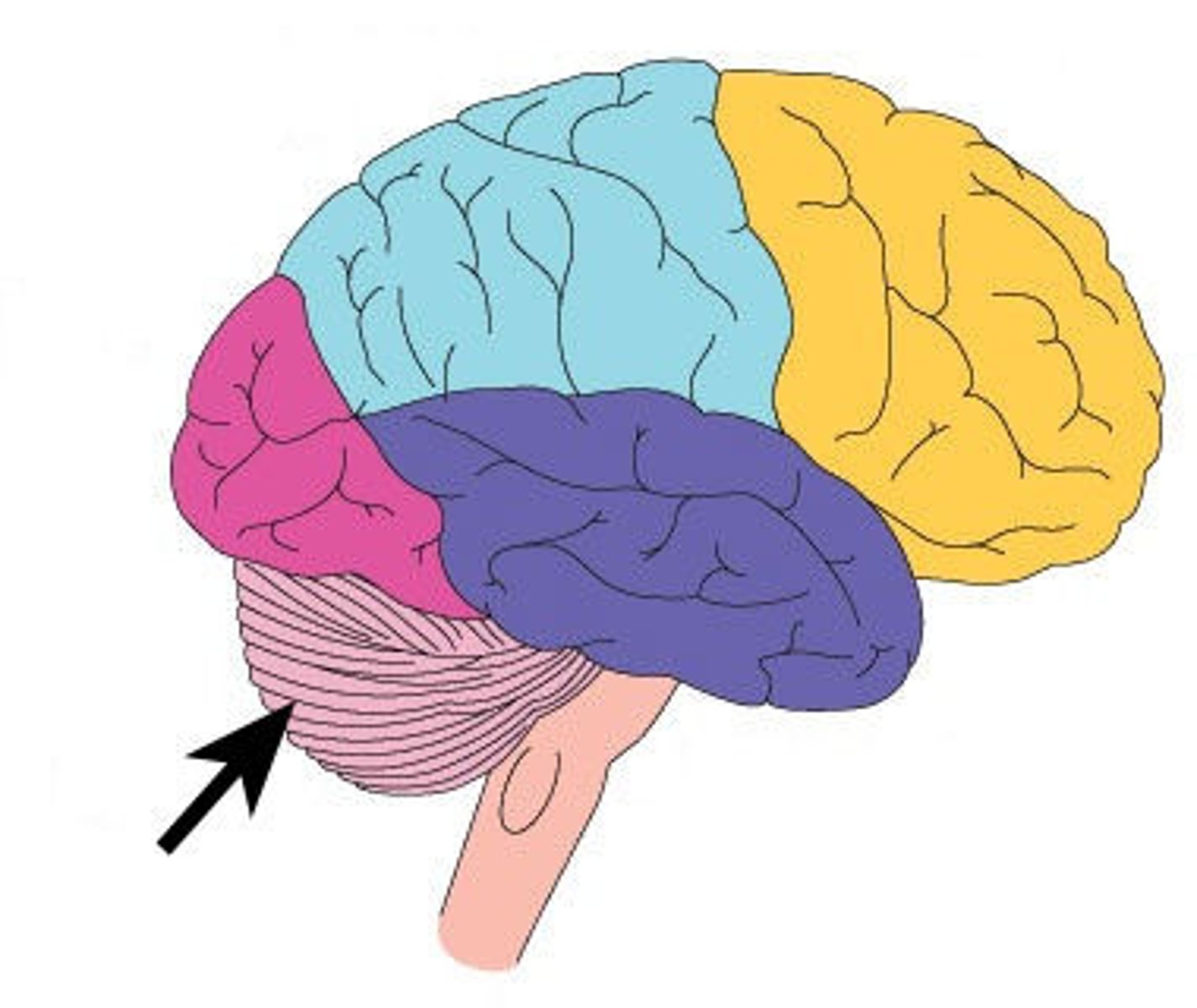
Frontal Lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
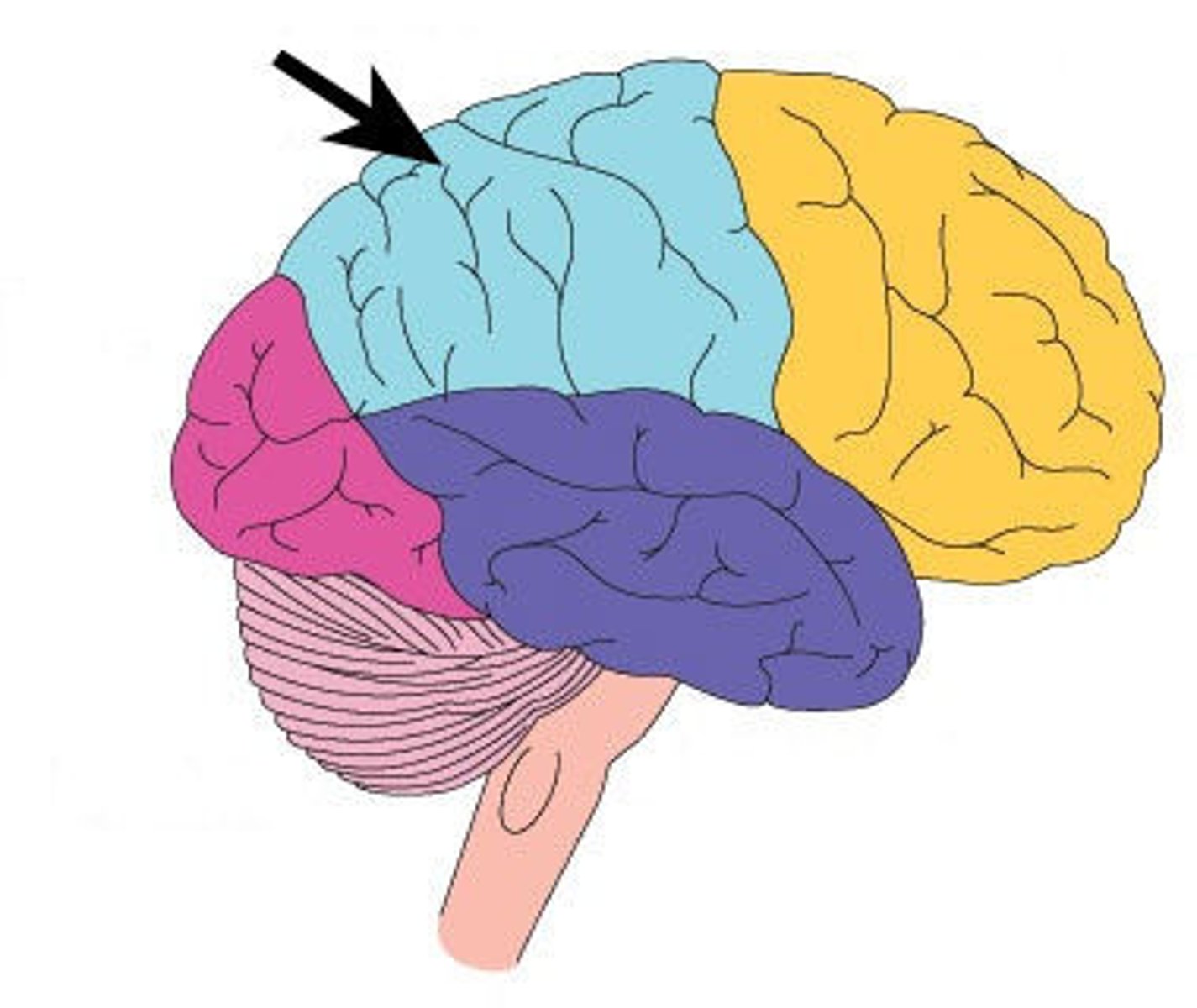
Parietal Lobe
receives sensory input for touch and body position
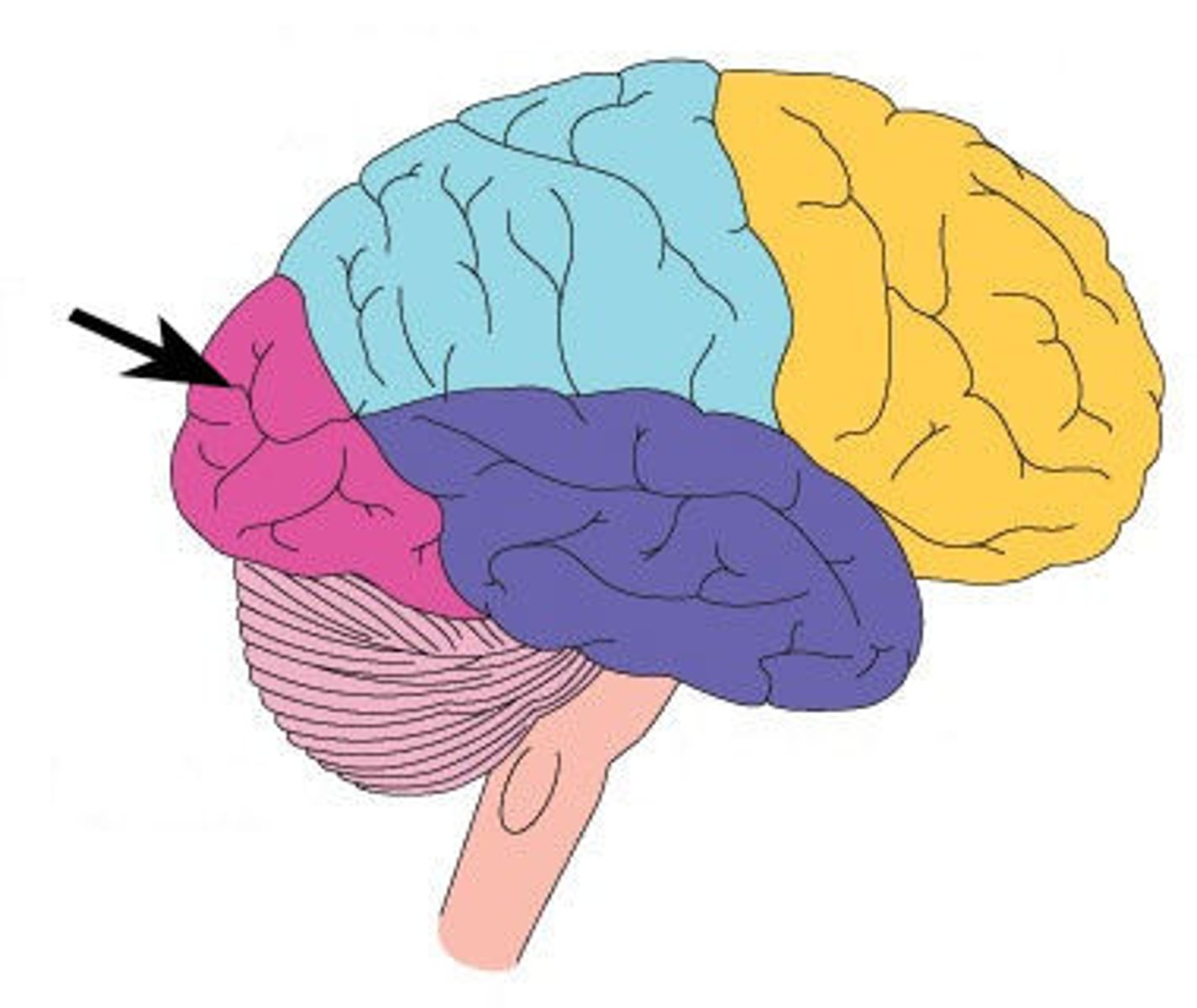
Occipital Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
Temporal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
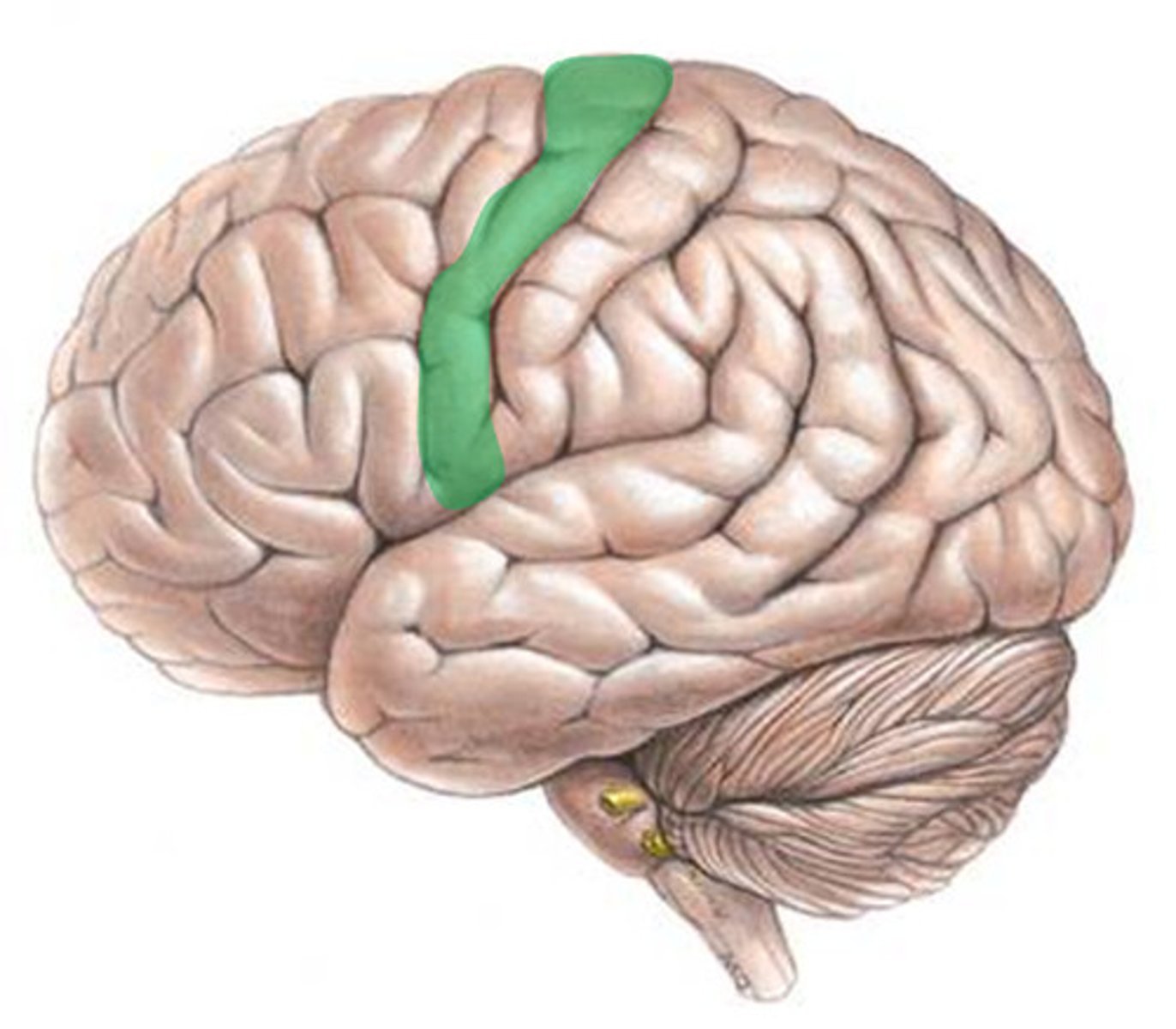
Precentral Gyrus
the strip of frontal cortex, just in front of the central sulcus, that controls voluntary movement
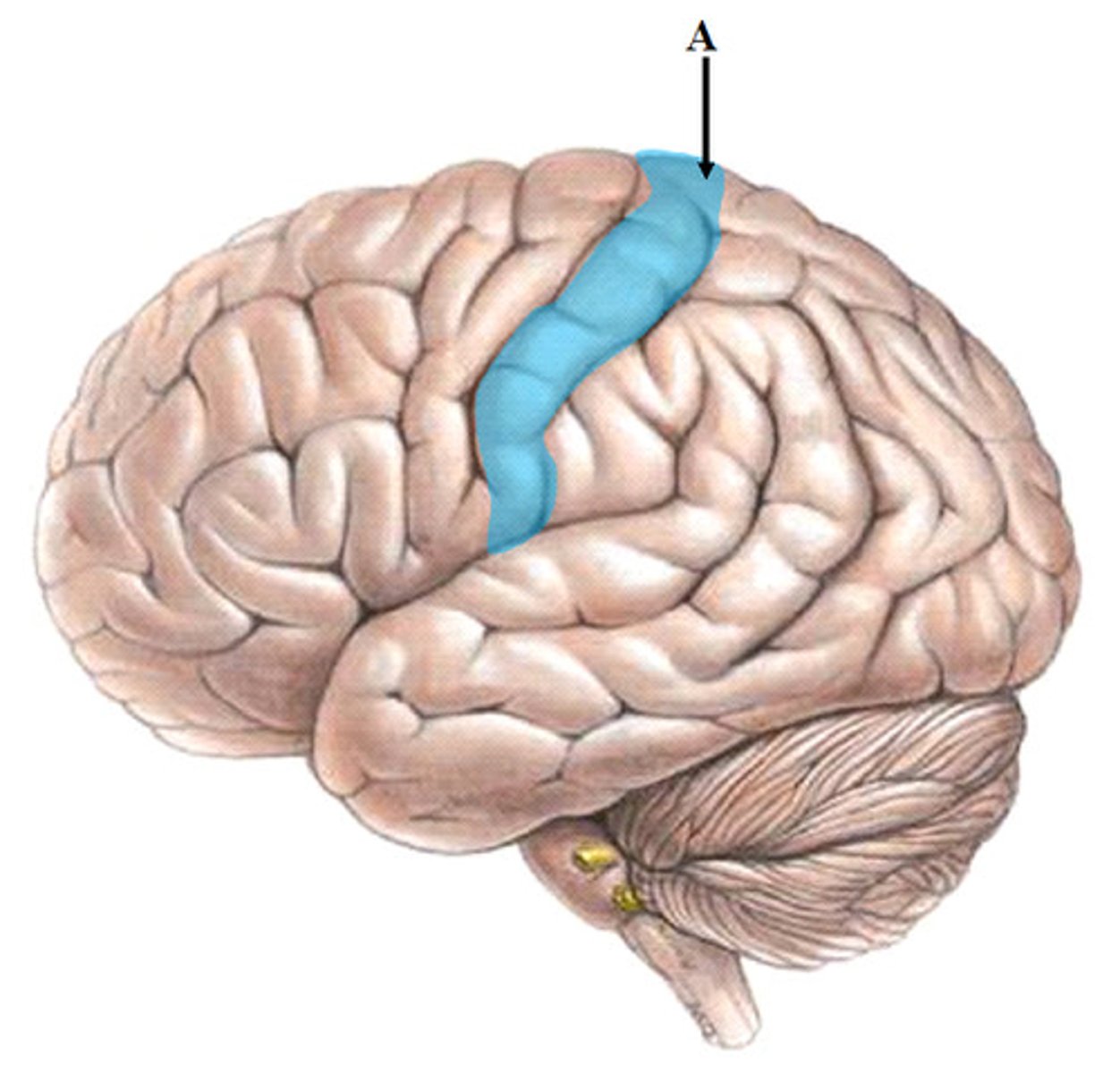
Postcentral Gyrus
the strip of parietal cortex, just behind the central sulcus, that helps perceive general sensations (touch and pain)
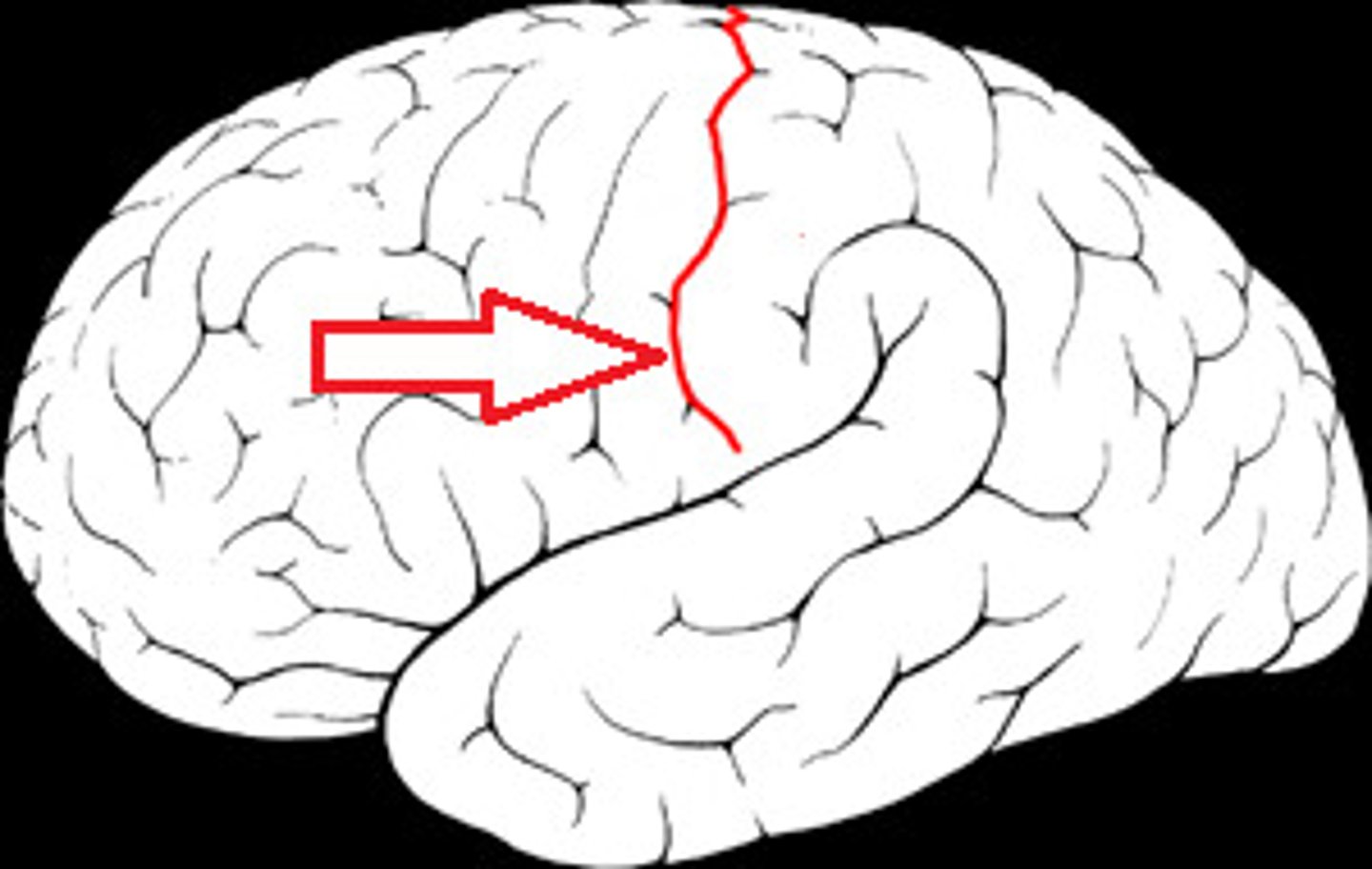
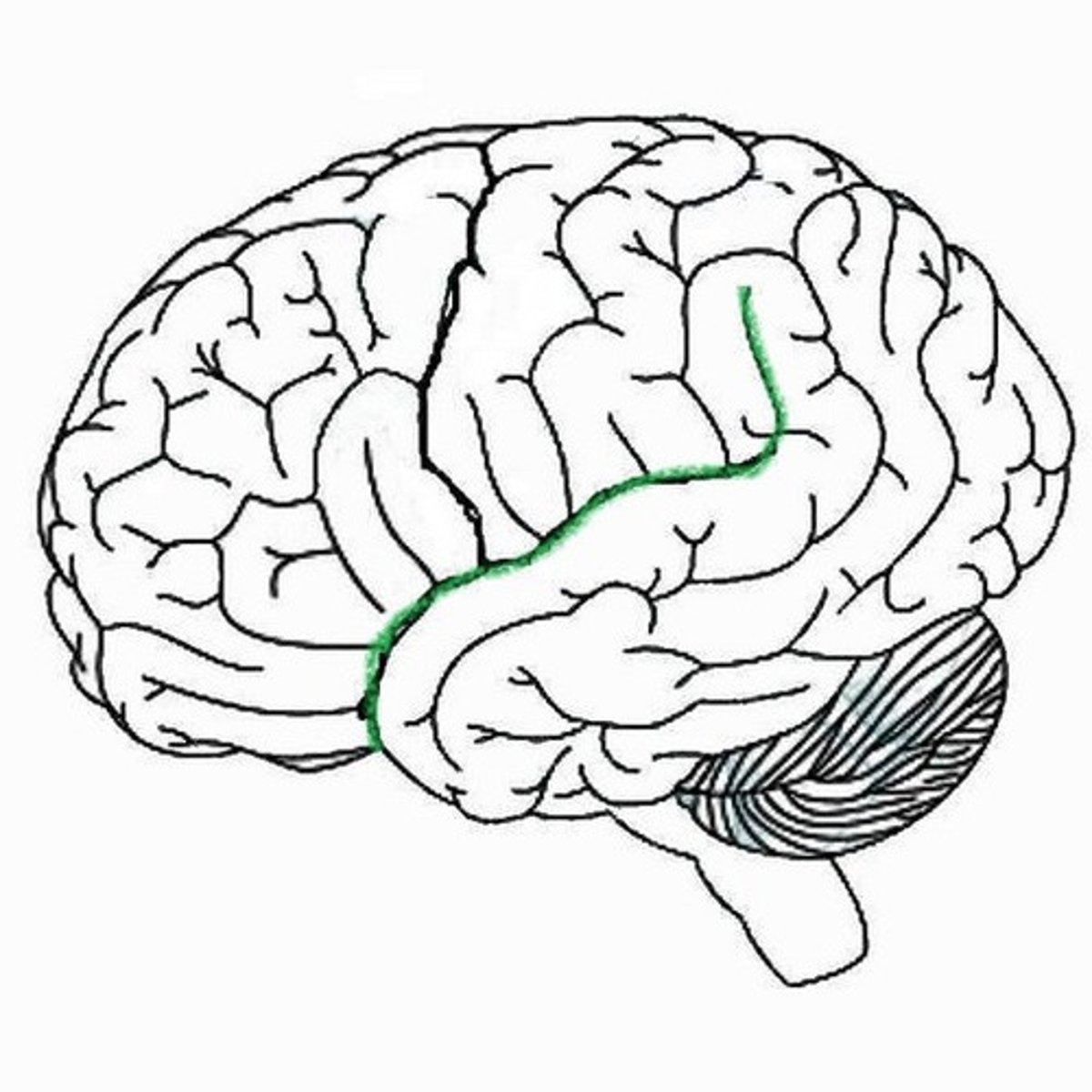
Central Sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
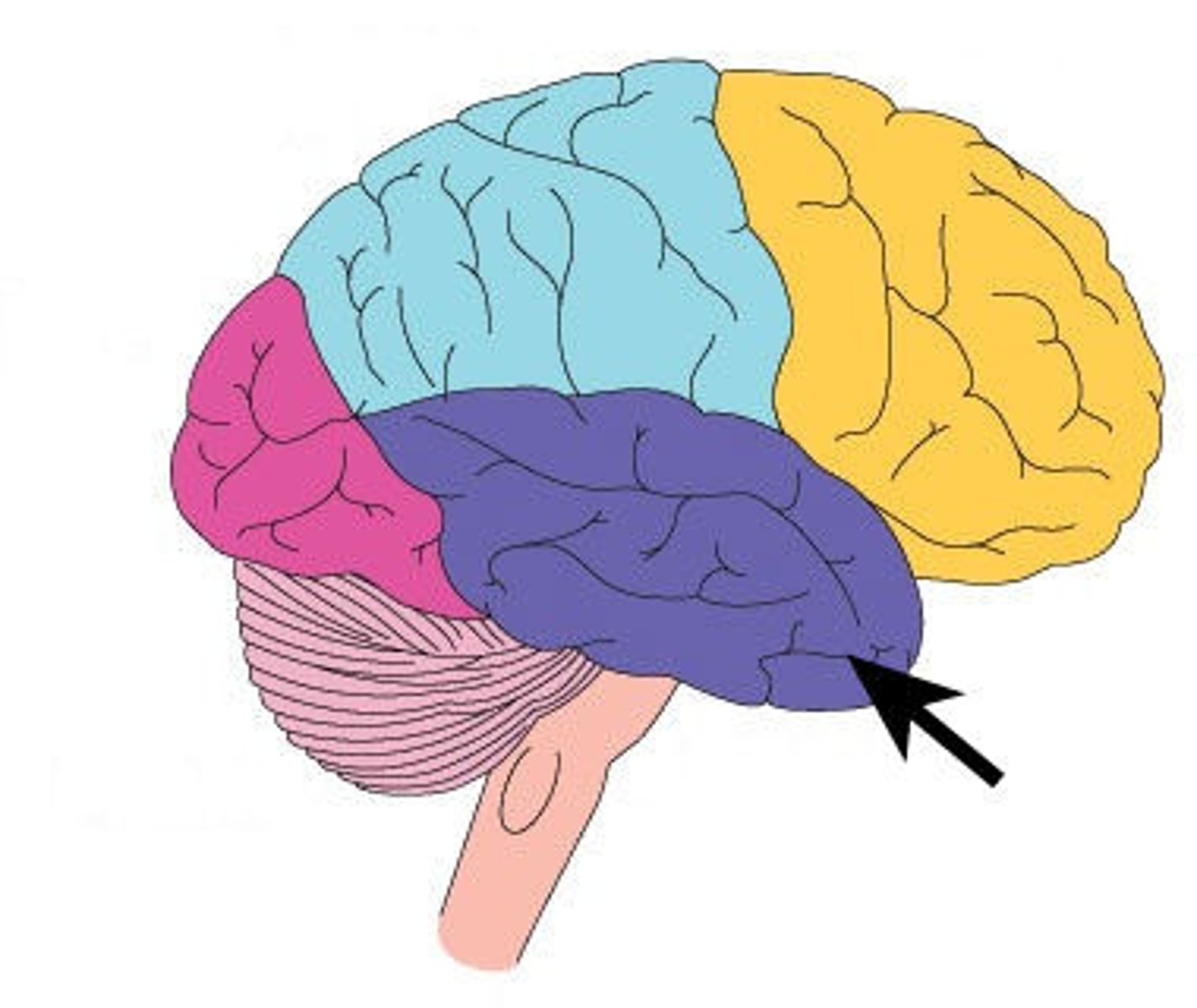
Sylvian Fissure
Separates the temporal from the frontal lobe, and the temporal from the parietal lobe
Cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that processes motor coordination, balance, and movement.
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
Medulla Oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that helps with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake cycles, alertness, and temperature regulation
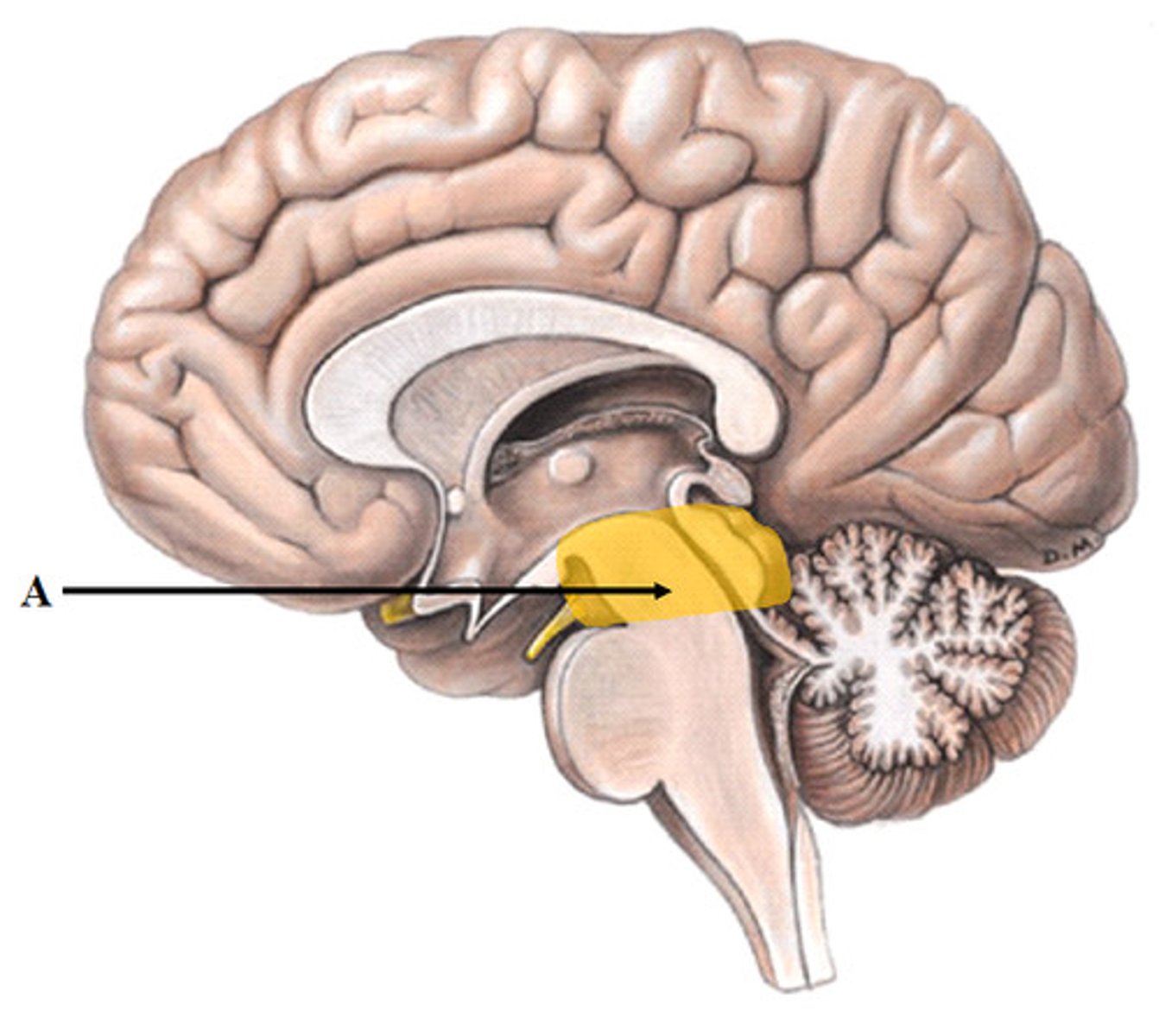
Thalumus
the structure of the brain that relays sensory information
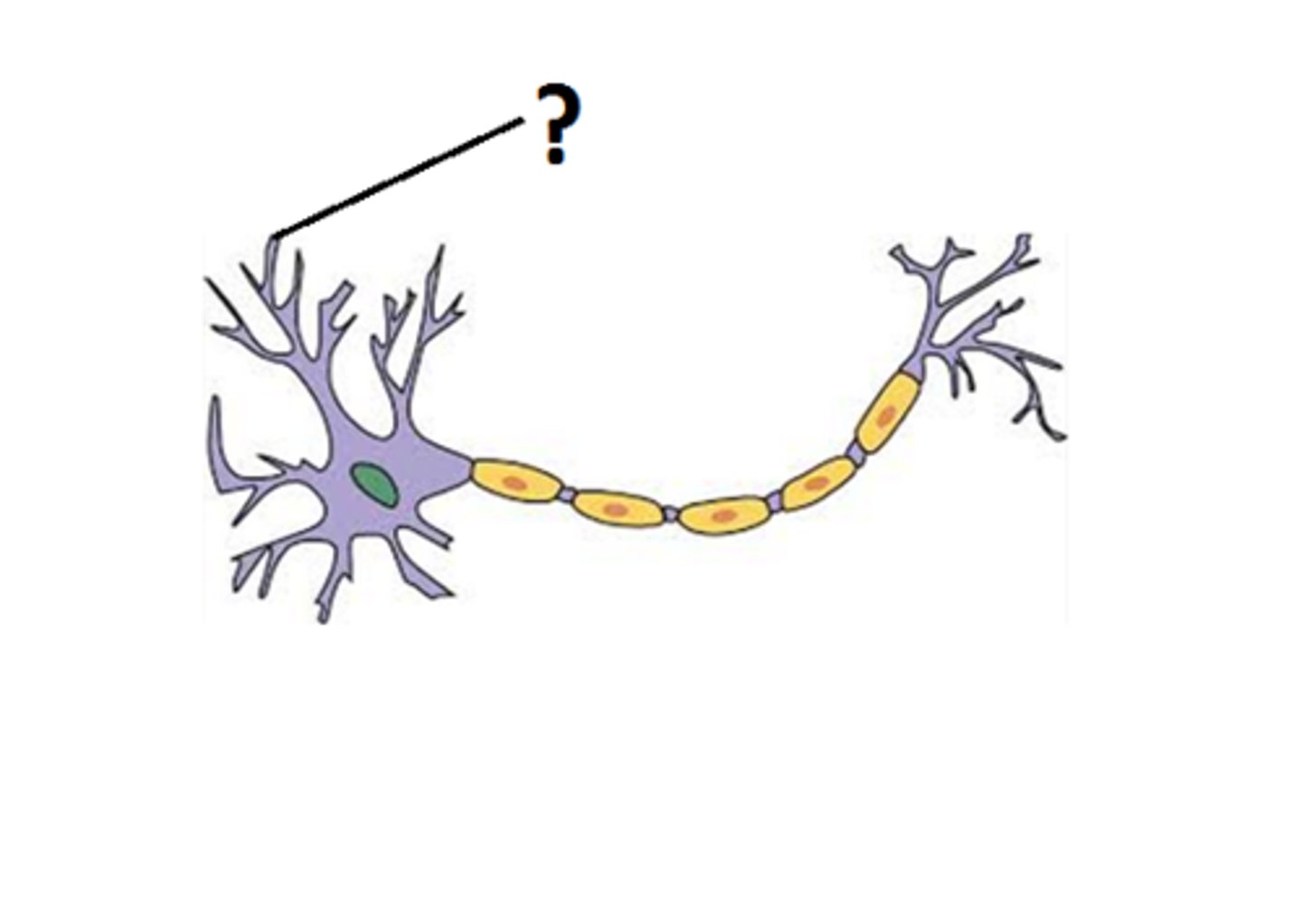
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
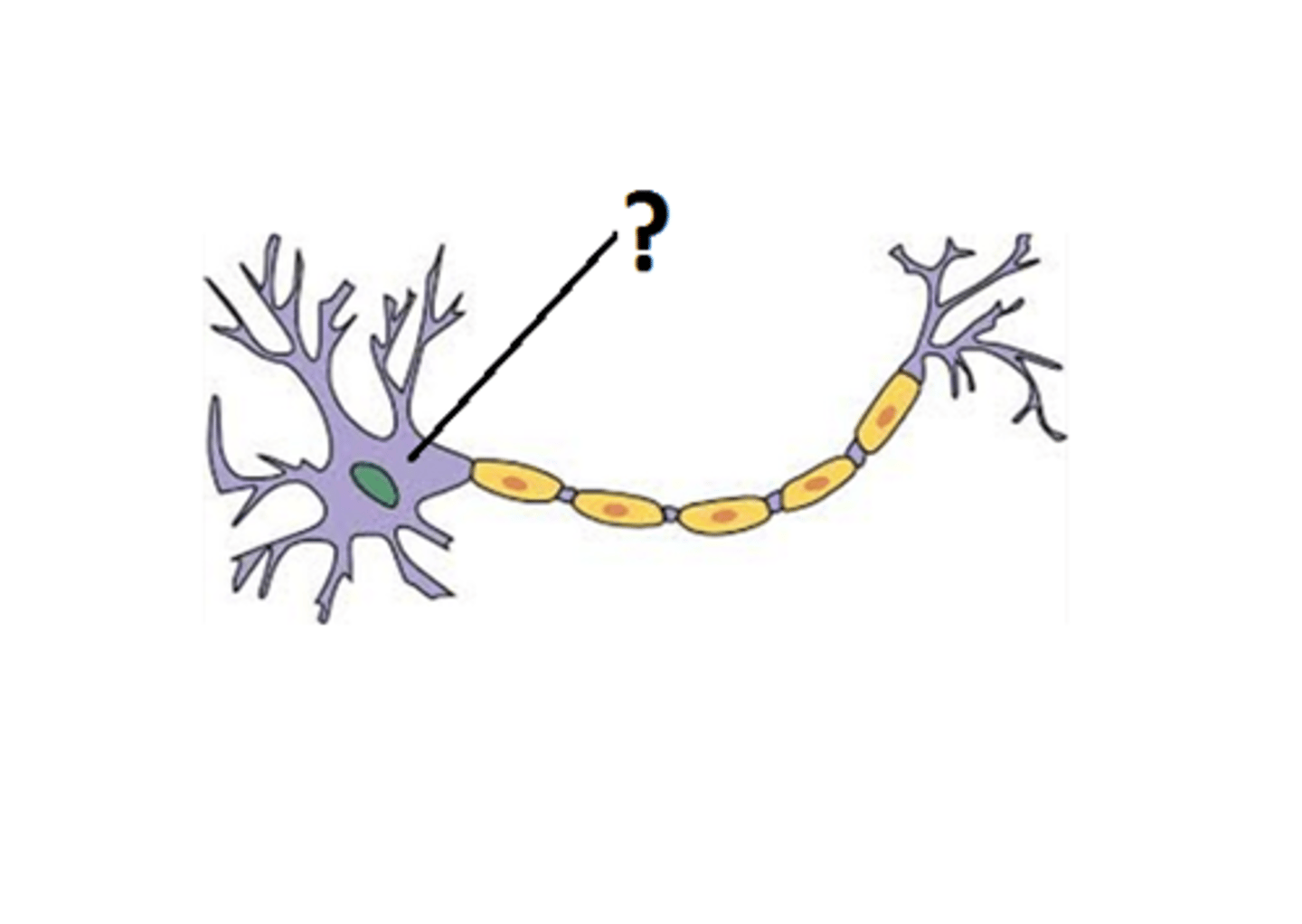
Soma
cell body of a neuron
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
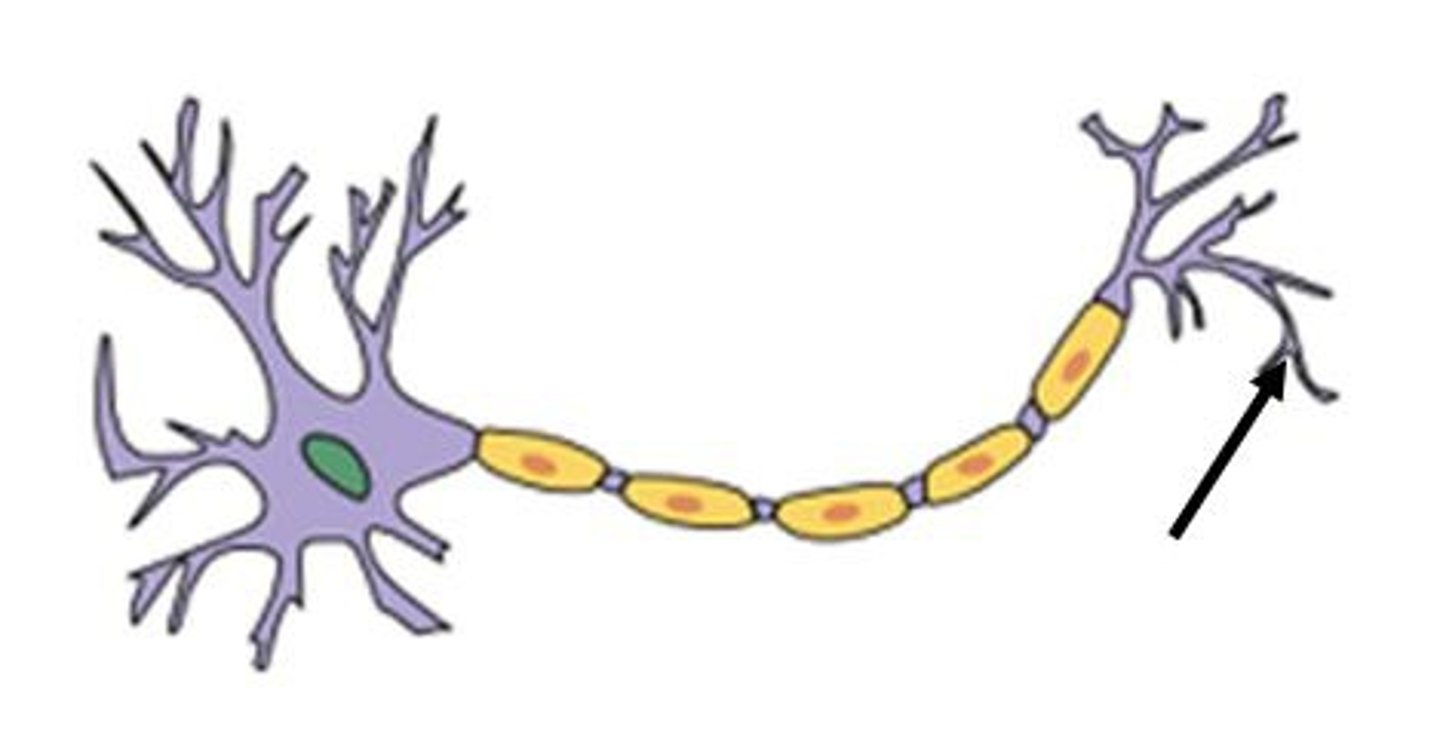
Axon Terminals
branches at the end of the axon
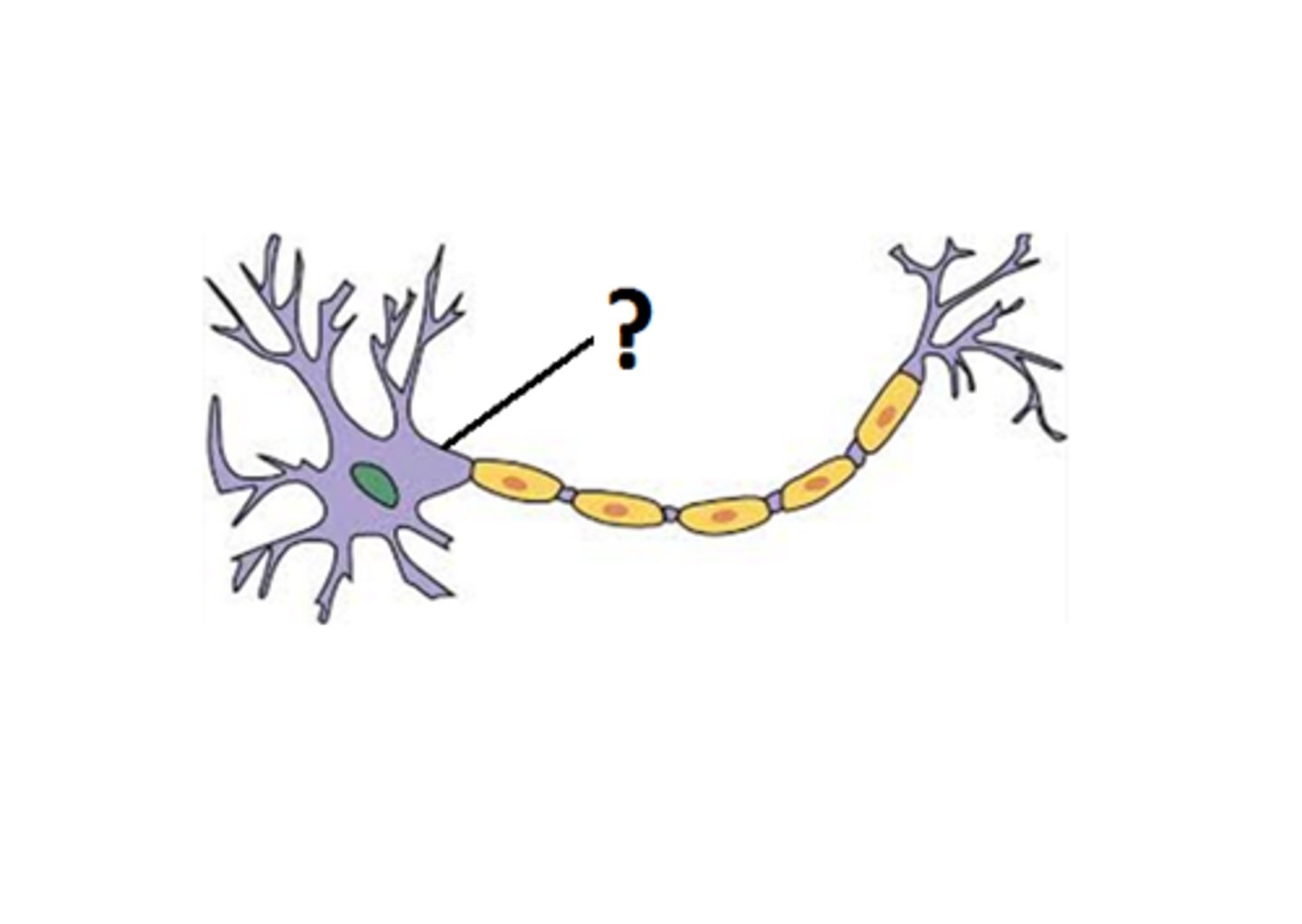
Axon Hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body.
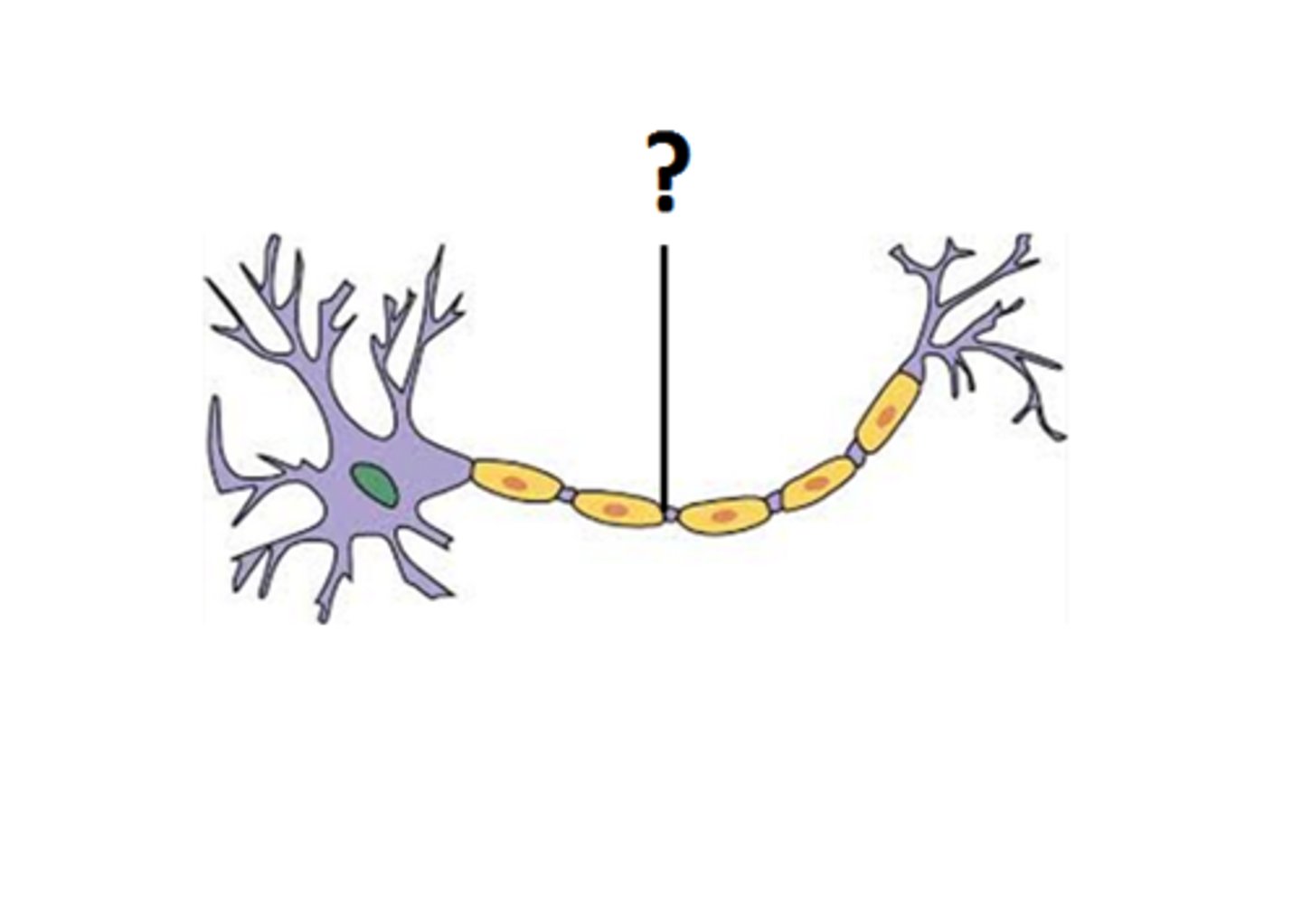
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
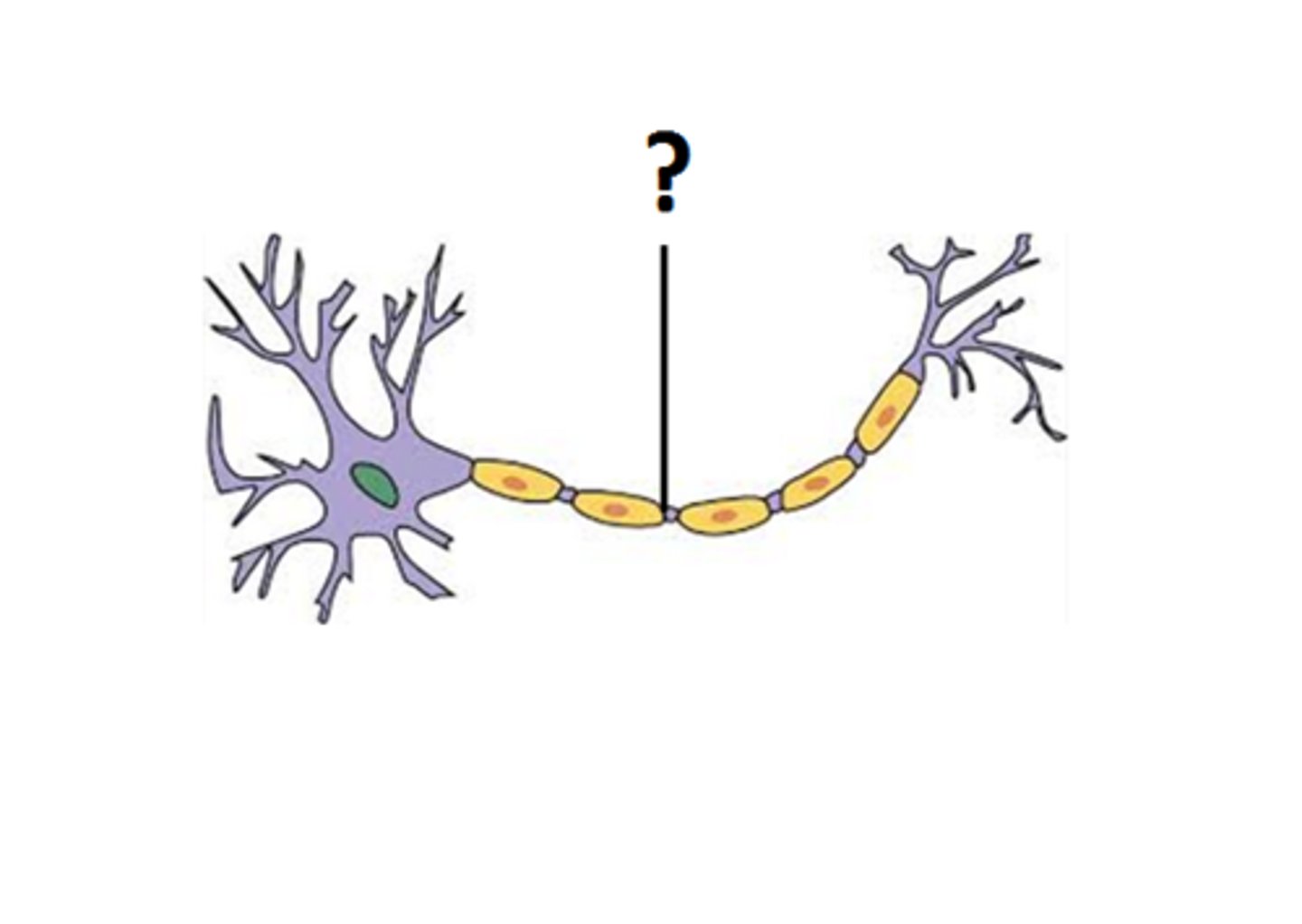
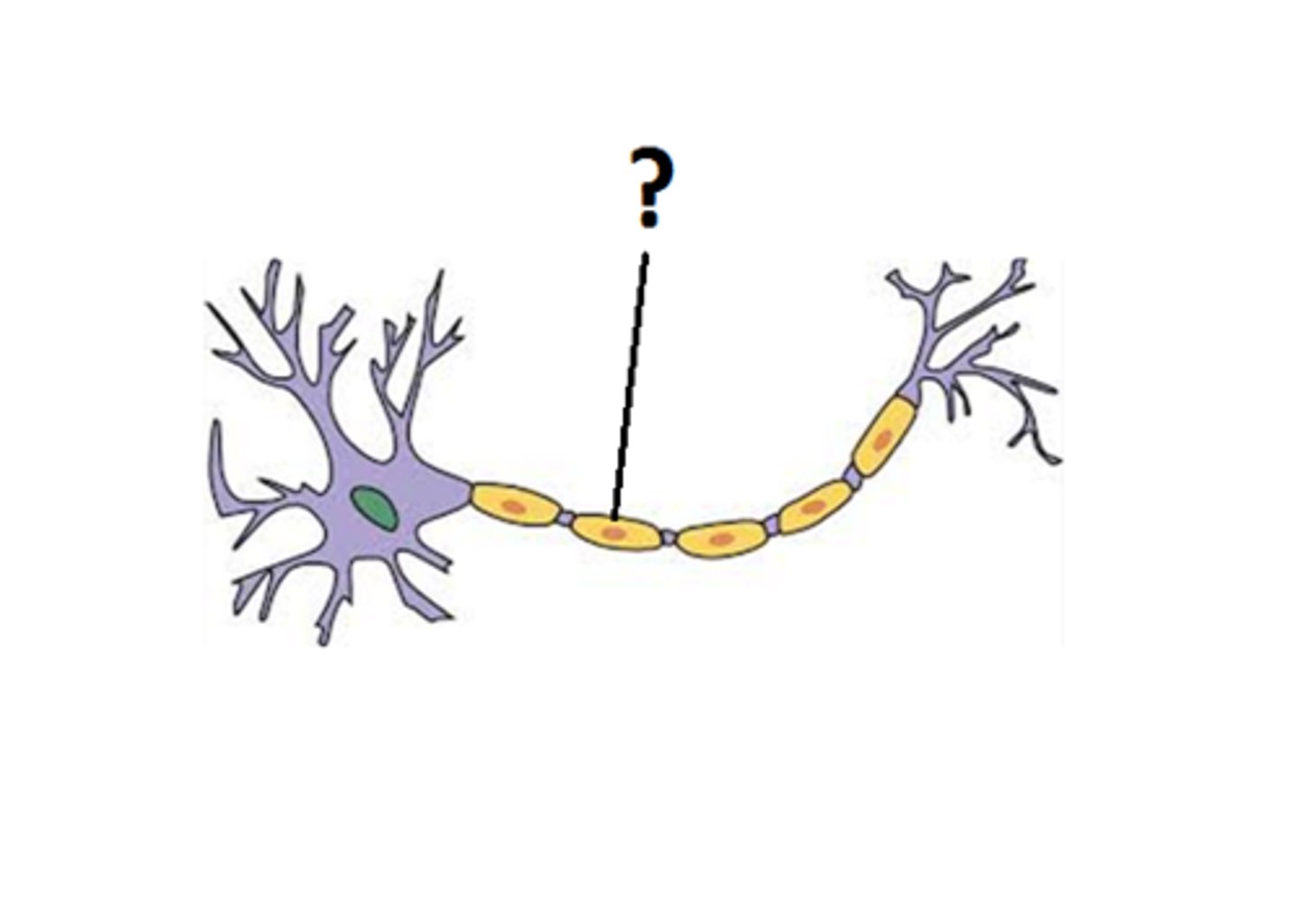
Myelin (part of a neuron)
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
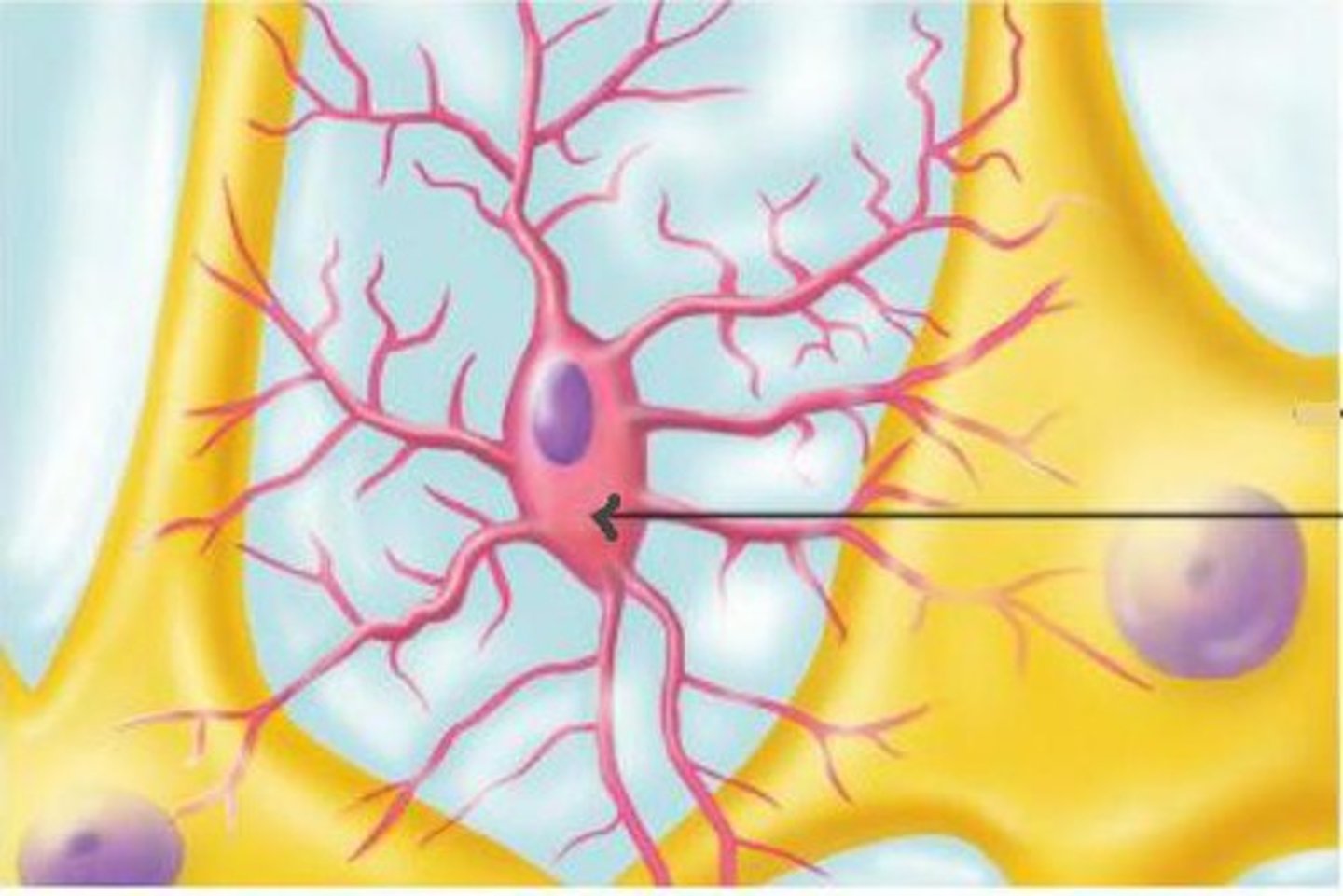
Microglial Cells
Recyclers
- Clean up damaged tissue and waste in the extracellular space
- Recycles excess neurotransmitters after and action potential
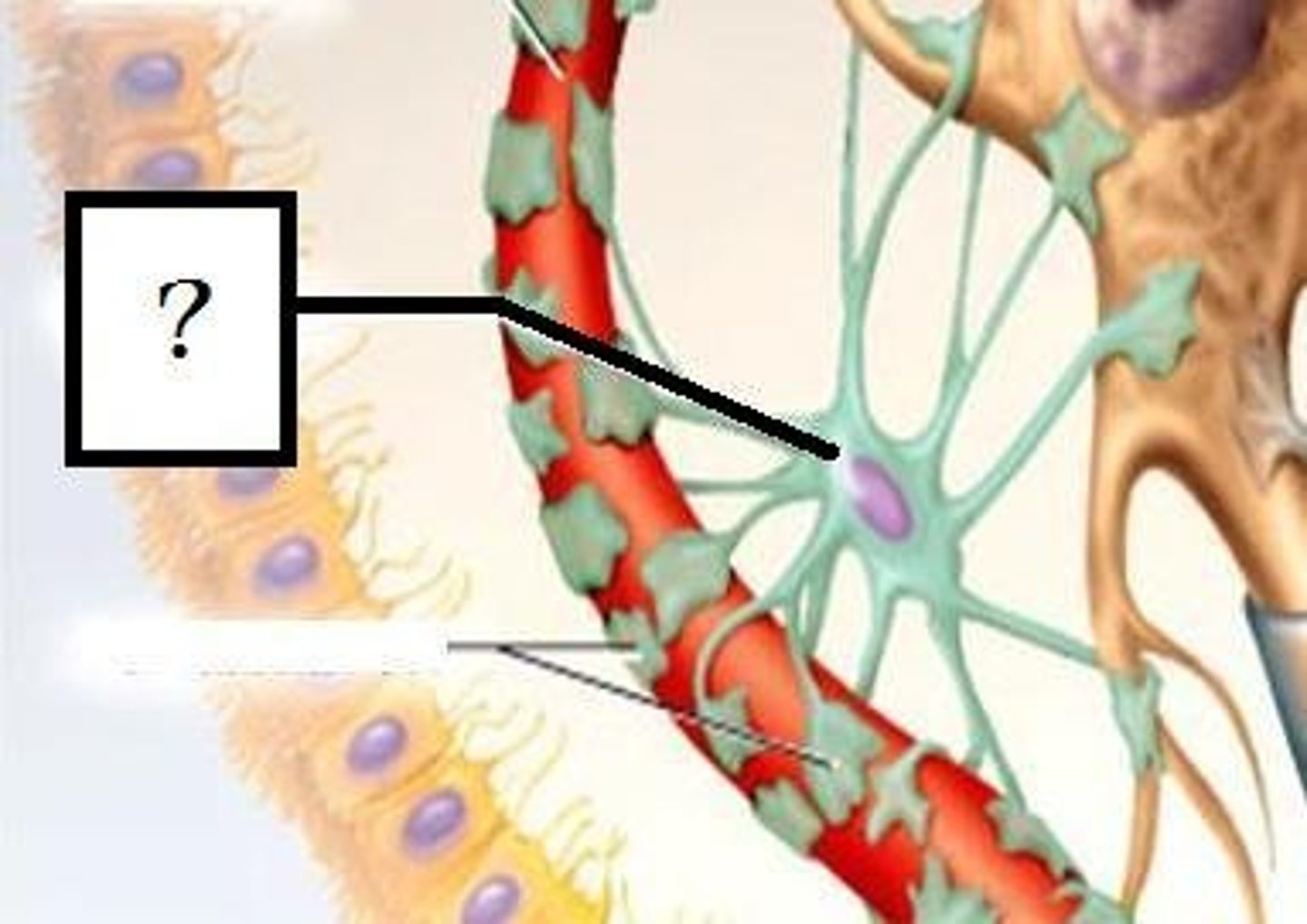
Astrocytes
- Star shaped support cells
- Transports nutrients to neurons
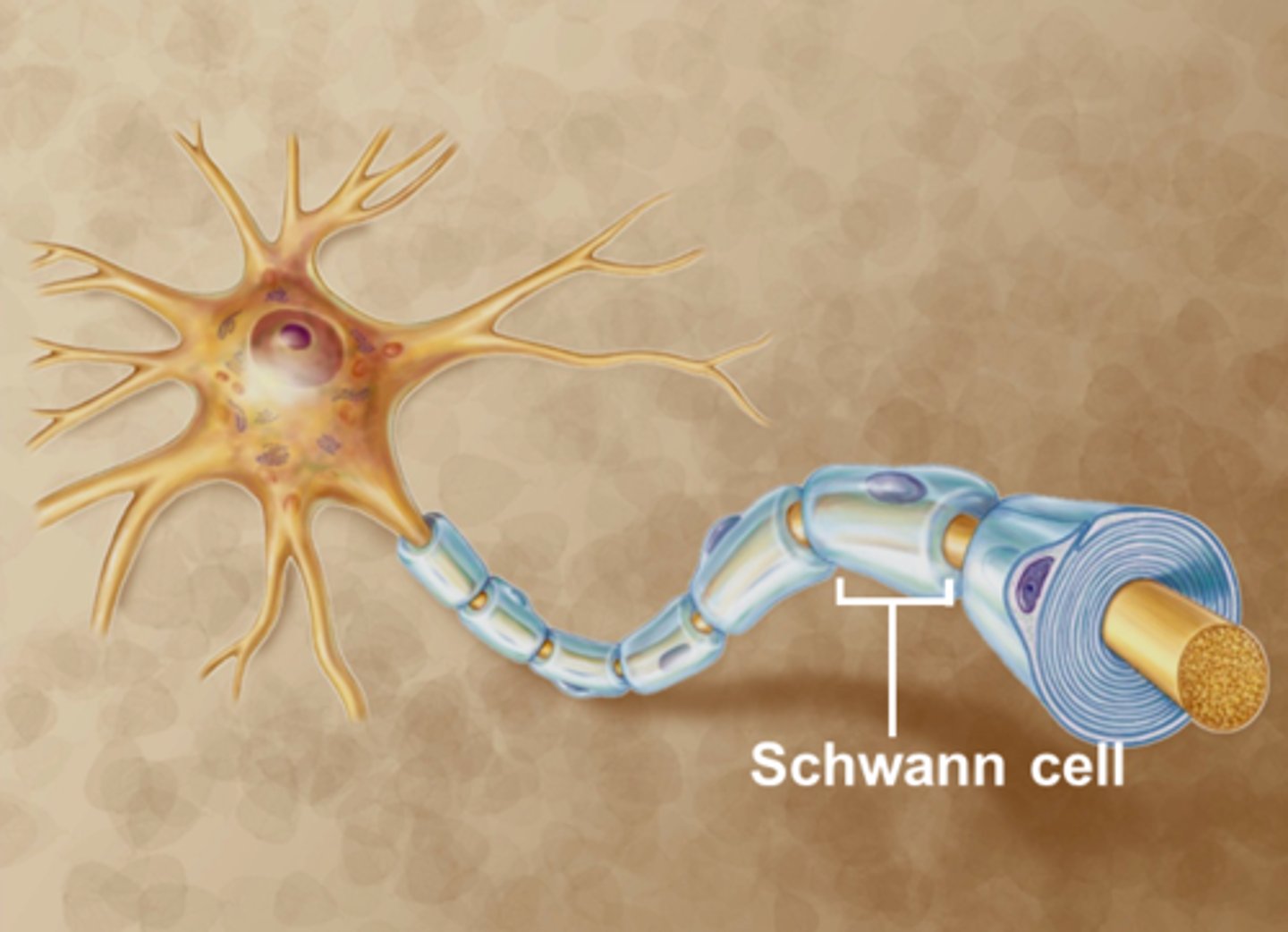
Myelin (cell)
- Schwann cells (PNS) and oligodendroglia (CNS)
3 Functions:
- Protect
- Speed transmission of signals
- Reduce signal loss
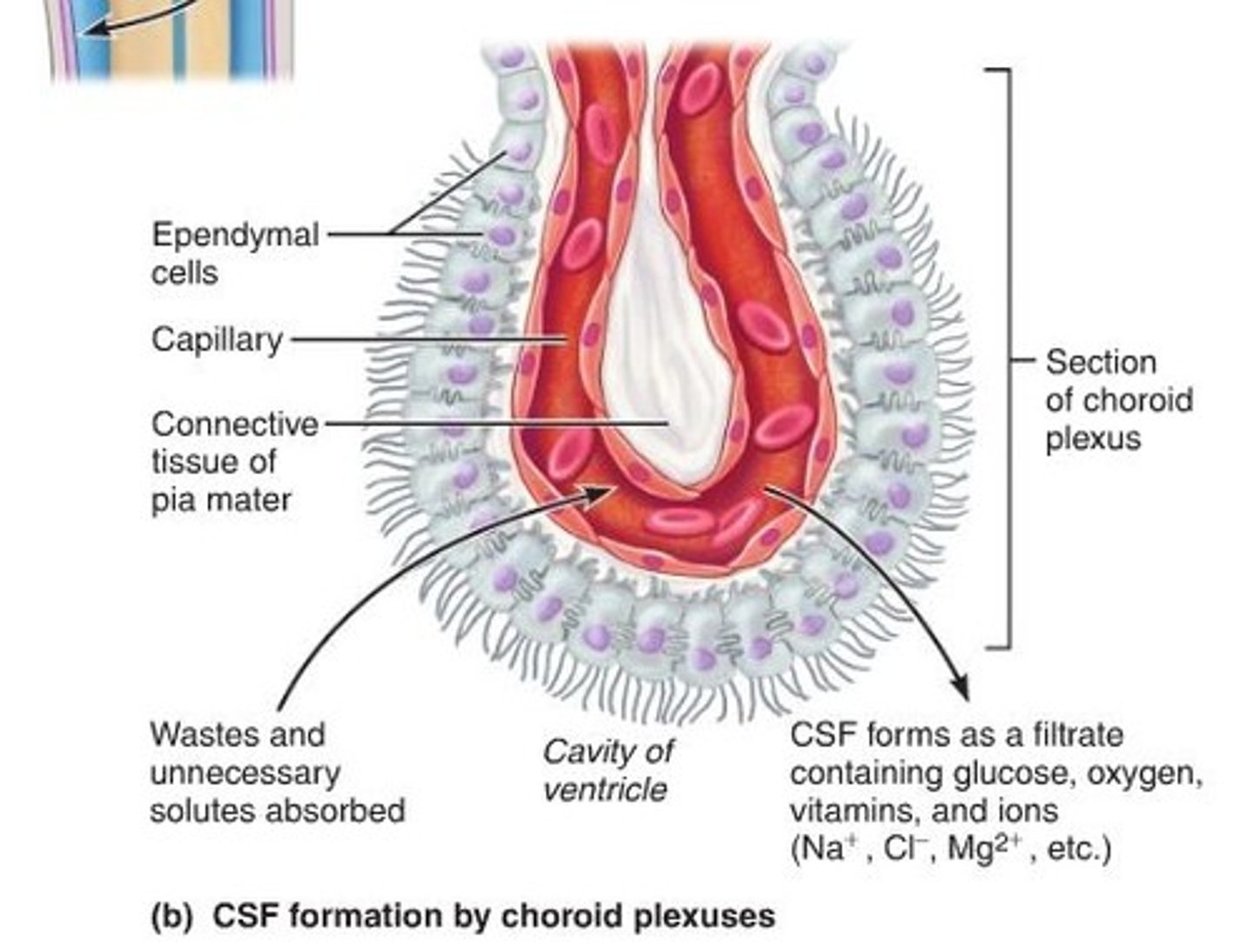
Ependymal Cells
- Found within the choroid plexus
- Produces cerebrospinal fluid
- Serves as a cushion to the brain
- Transports nutrients to the brain
-Removes wastes
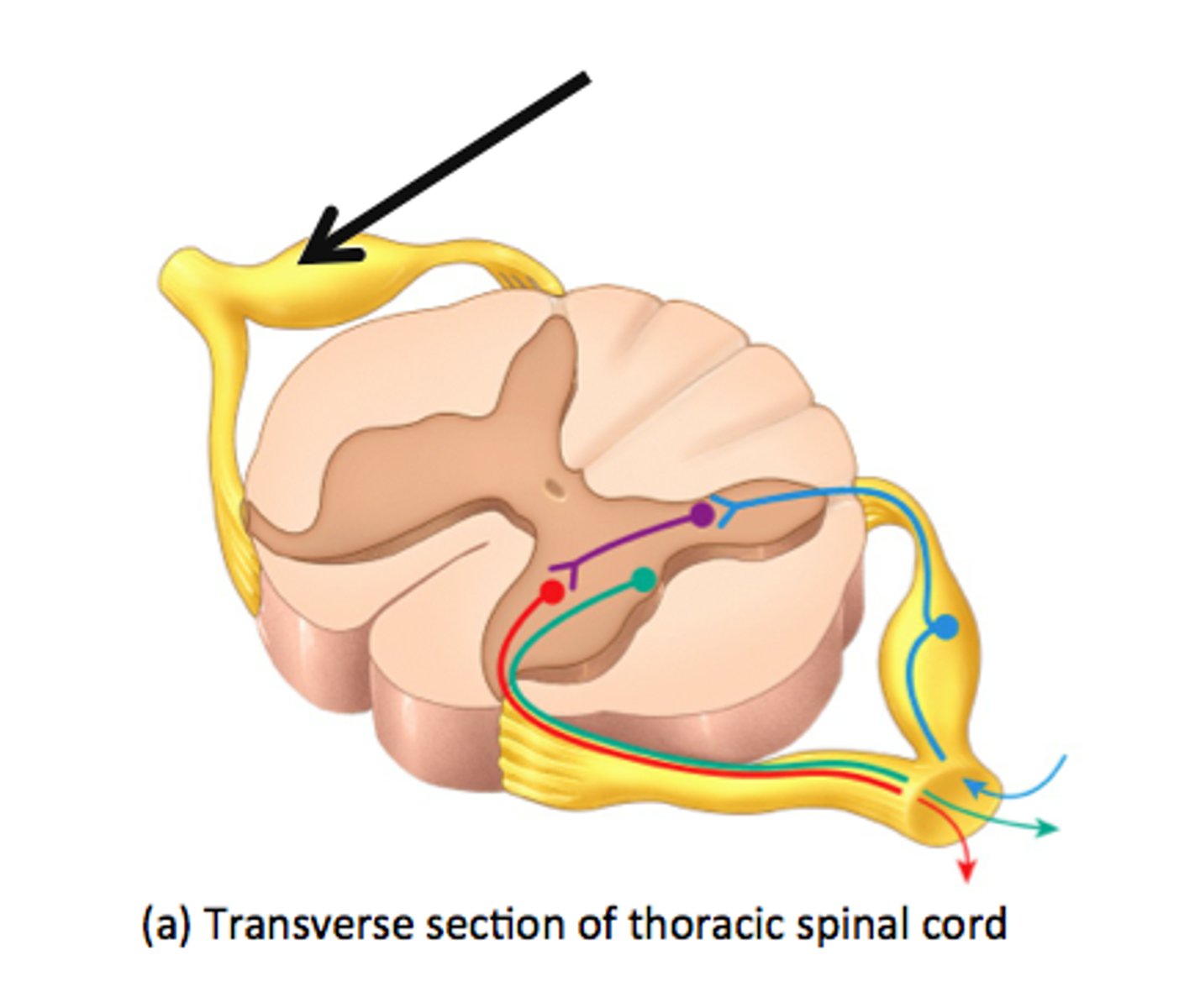
Dorsal root
contains axons of sensory neurons
Dura mater
Thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
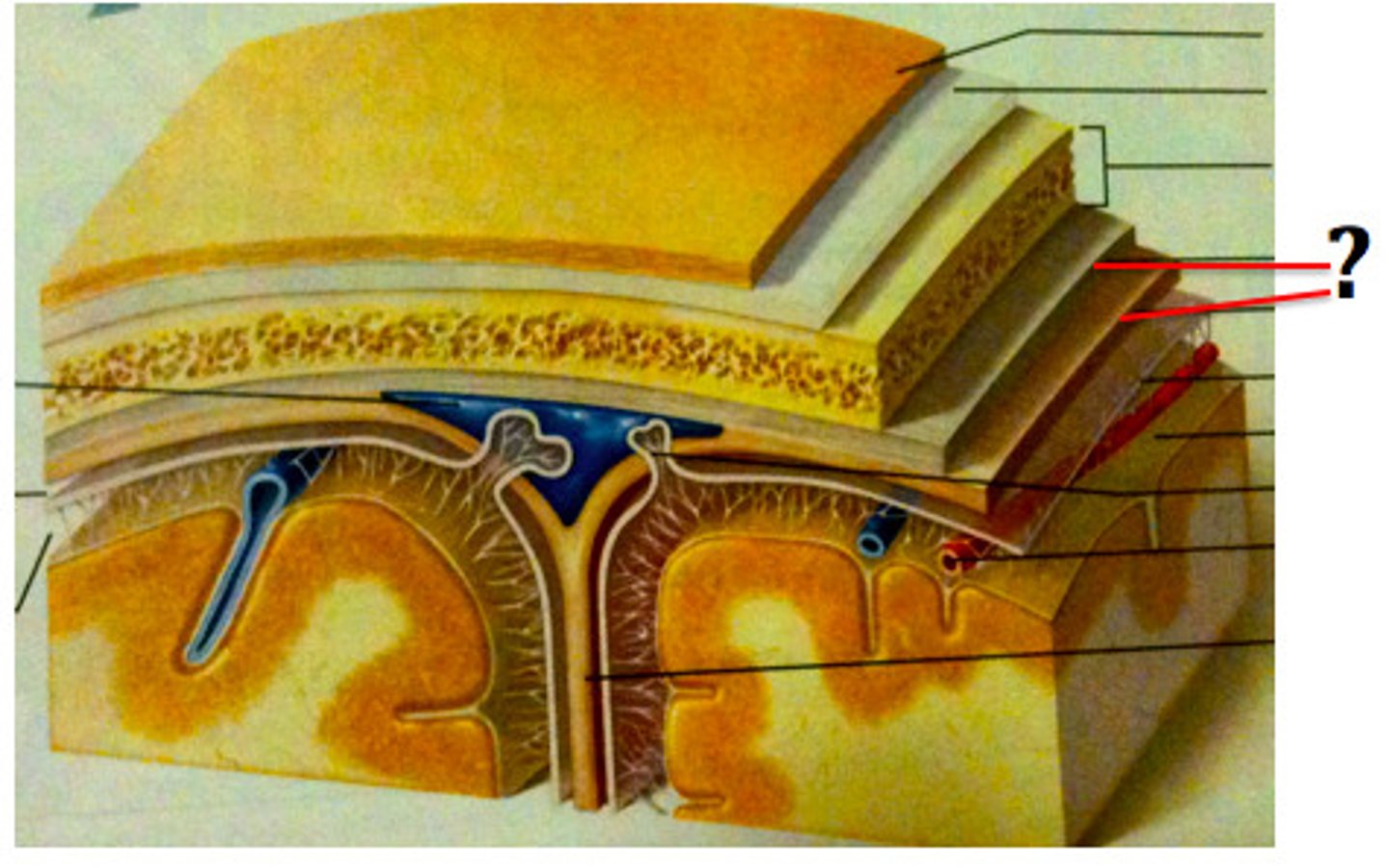
Arachnoid mater
Weblike middle layer of the three meninges
Pia mater
Thin and permeable
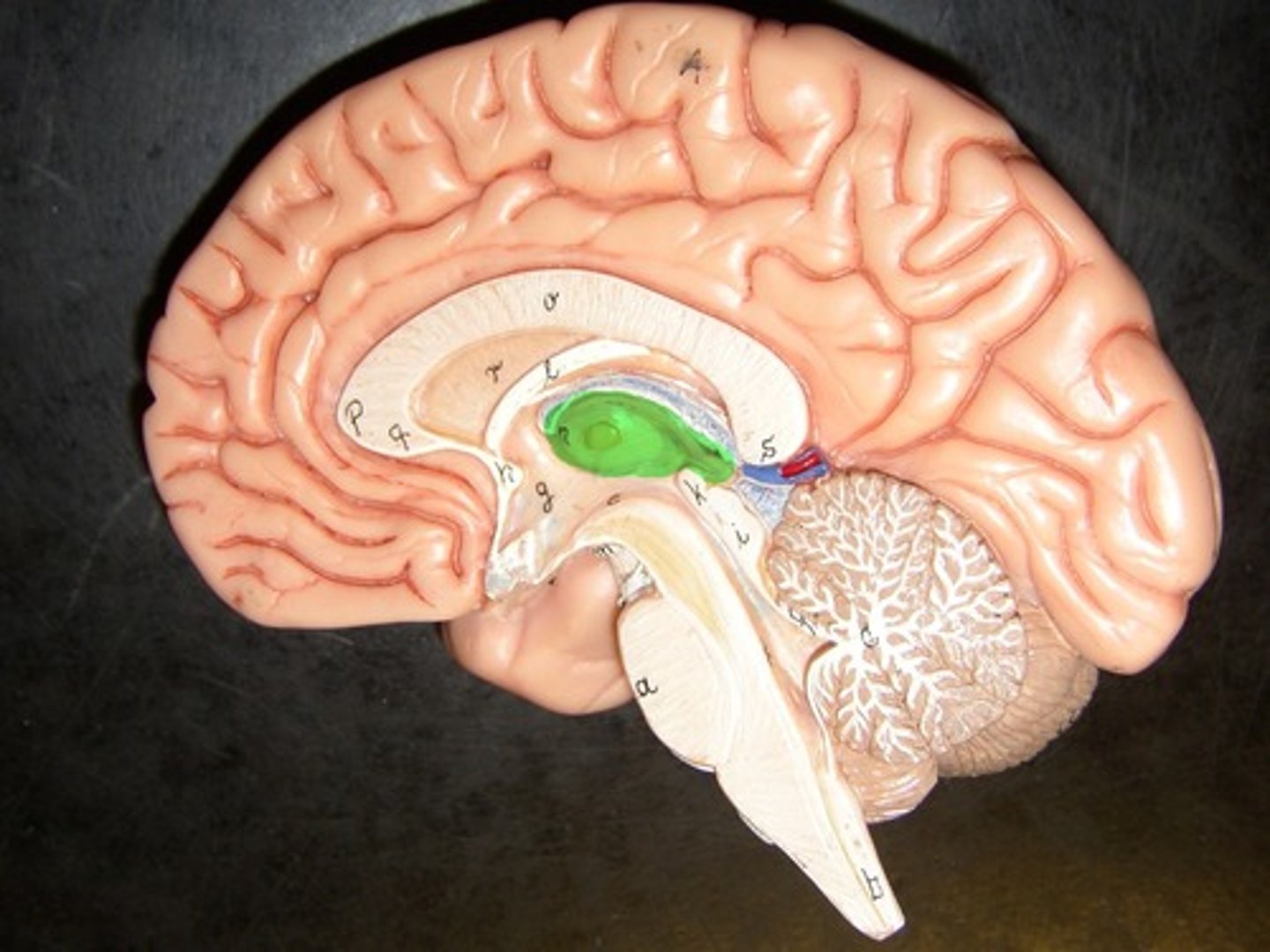
Lateral ventricle
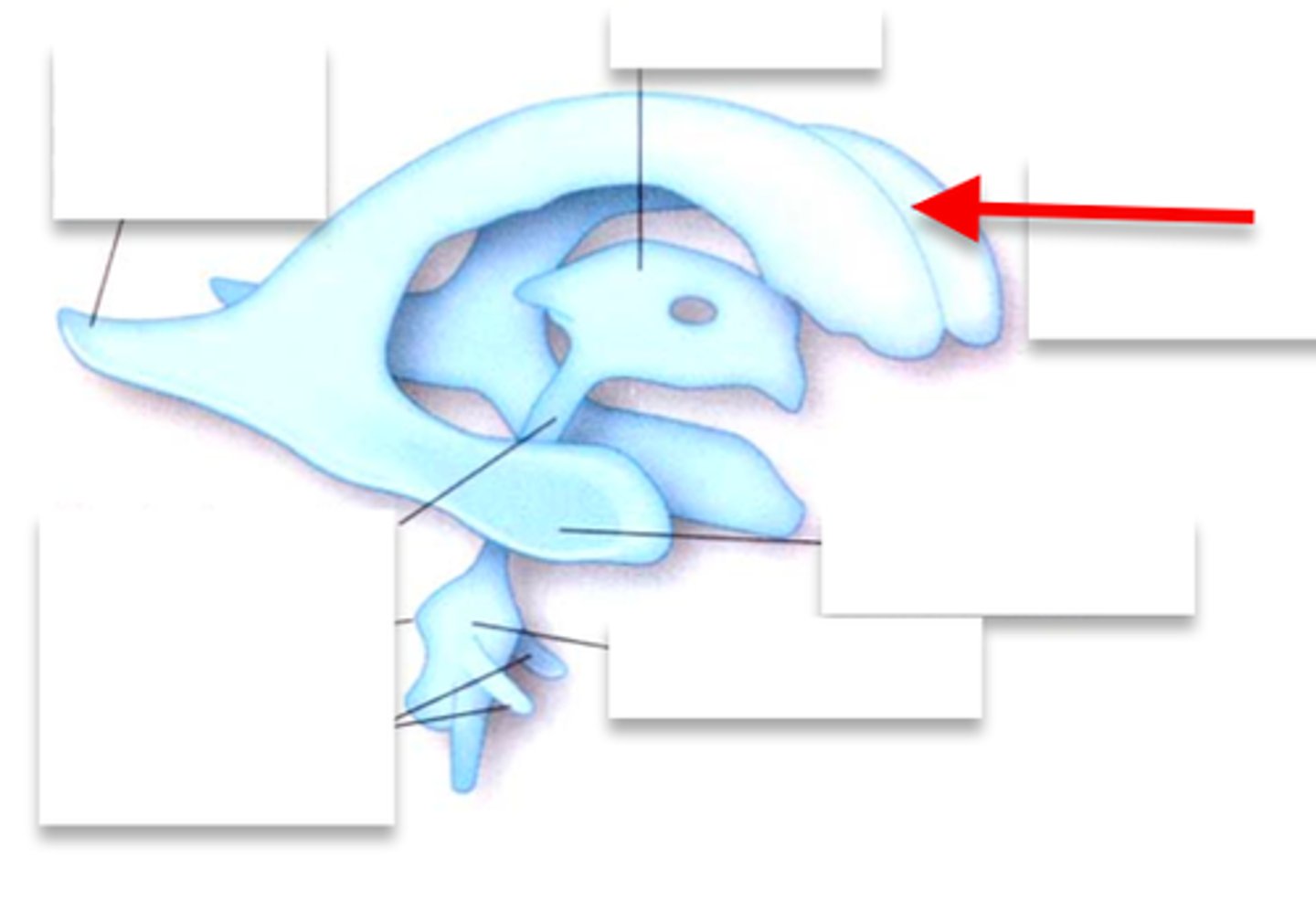
Choroid plexus
produces CSF
Third ventricle
Fourth ventricle
Central canal
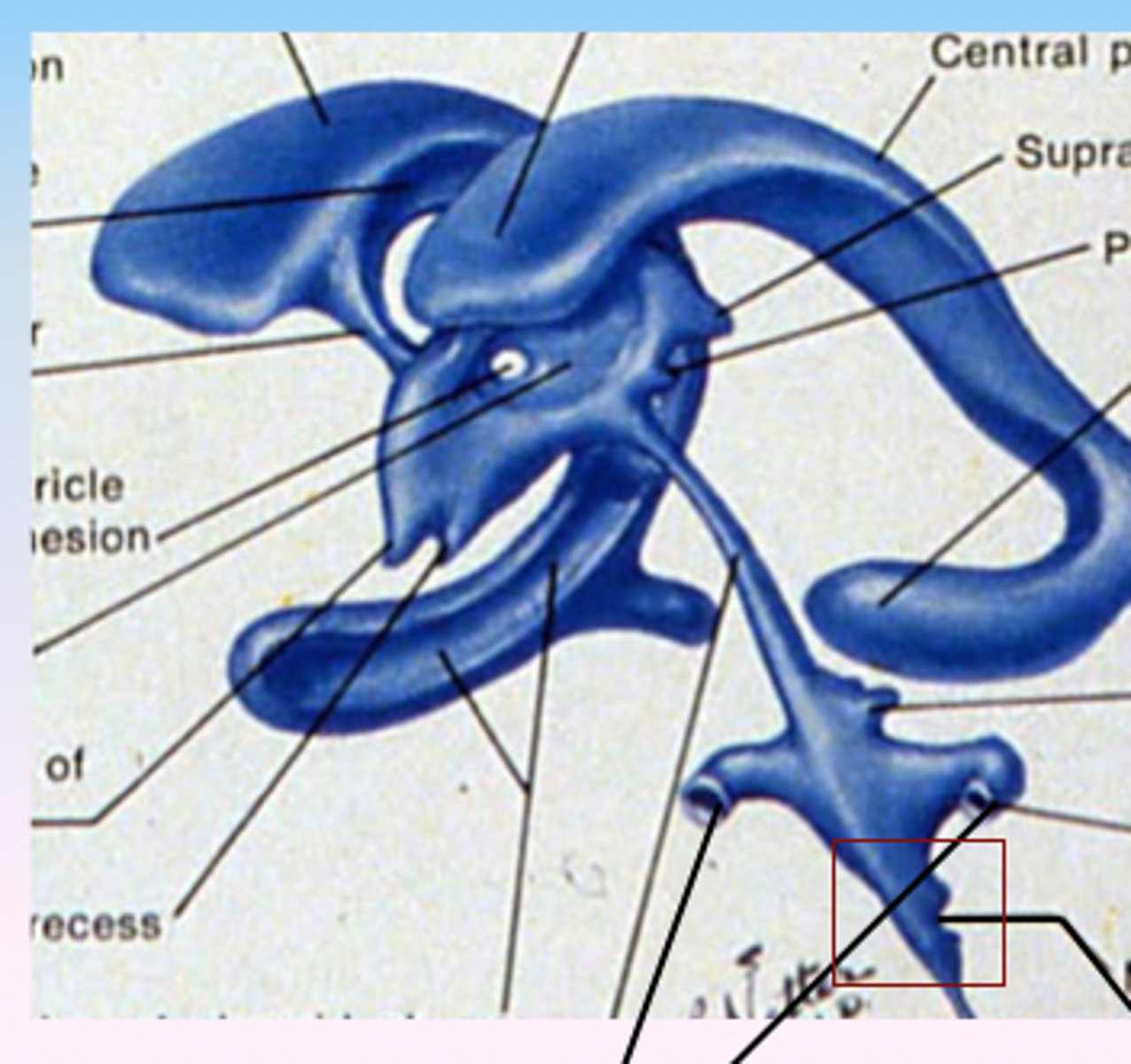
CSF function
1. Mechanical support (cushioning for the brain and spinal cord)
2. Spatial buffering (Intracranial pressure)
Regulation of extracellular environment (transports nutrients to the brain).
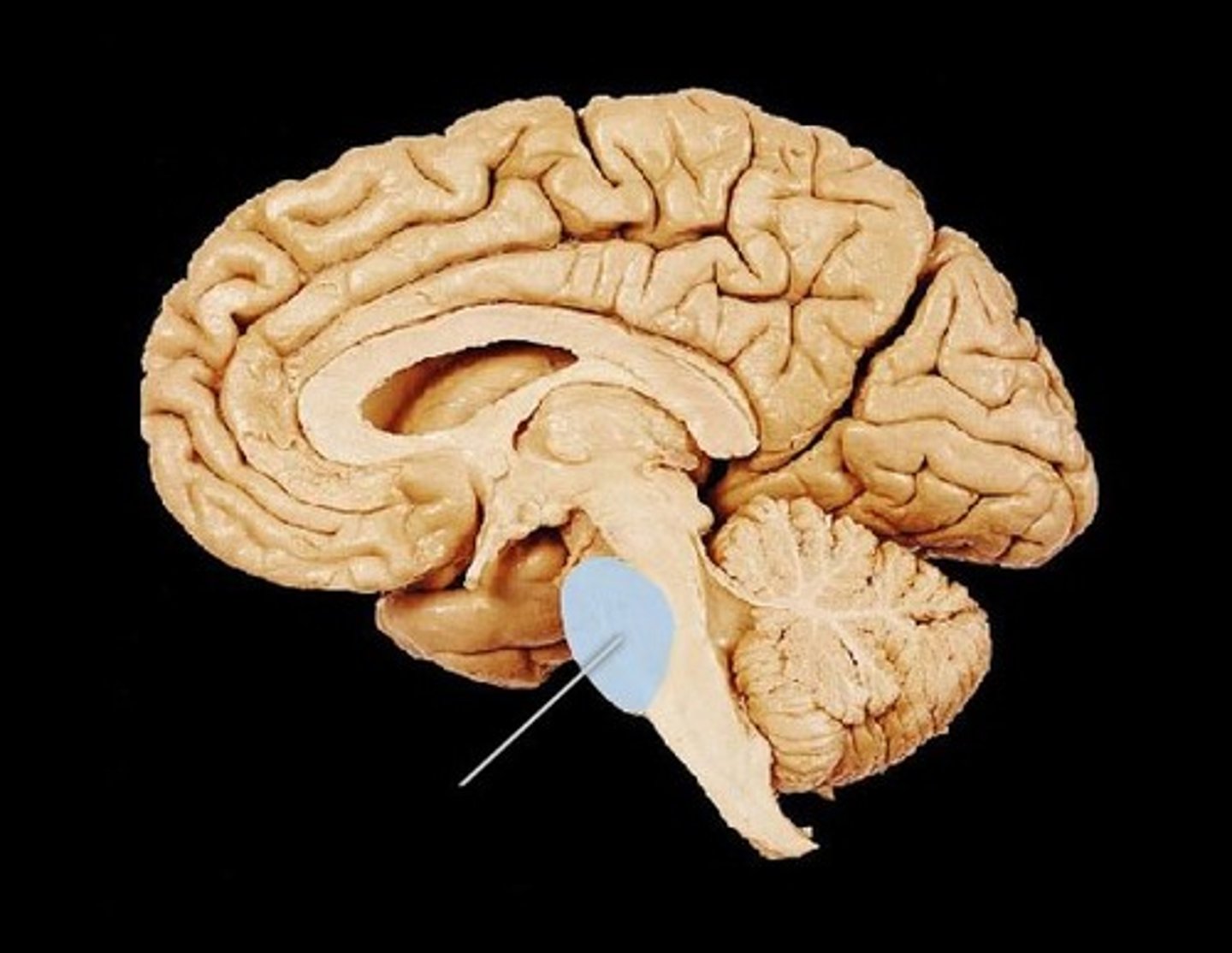
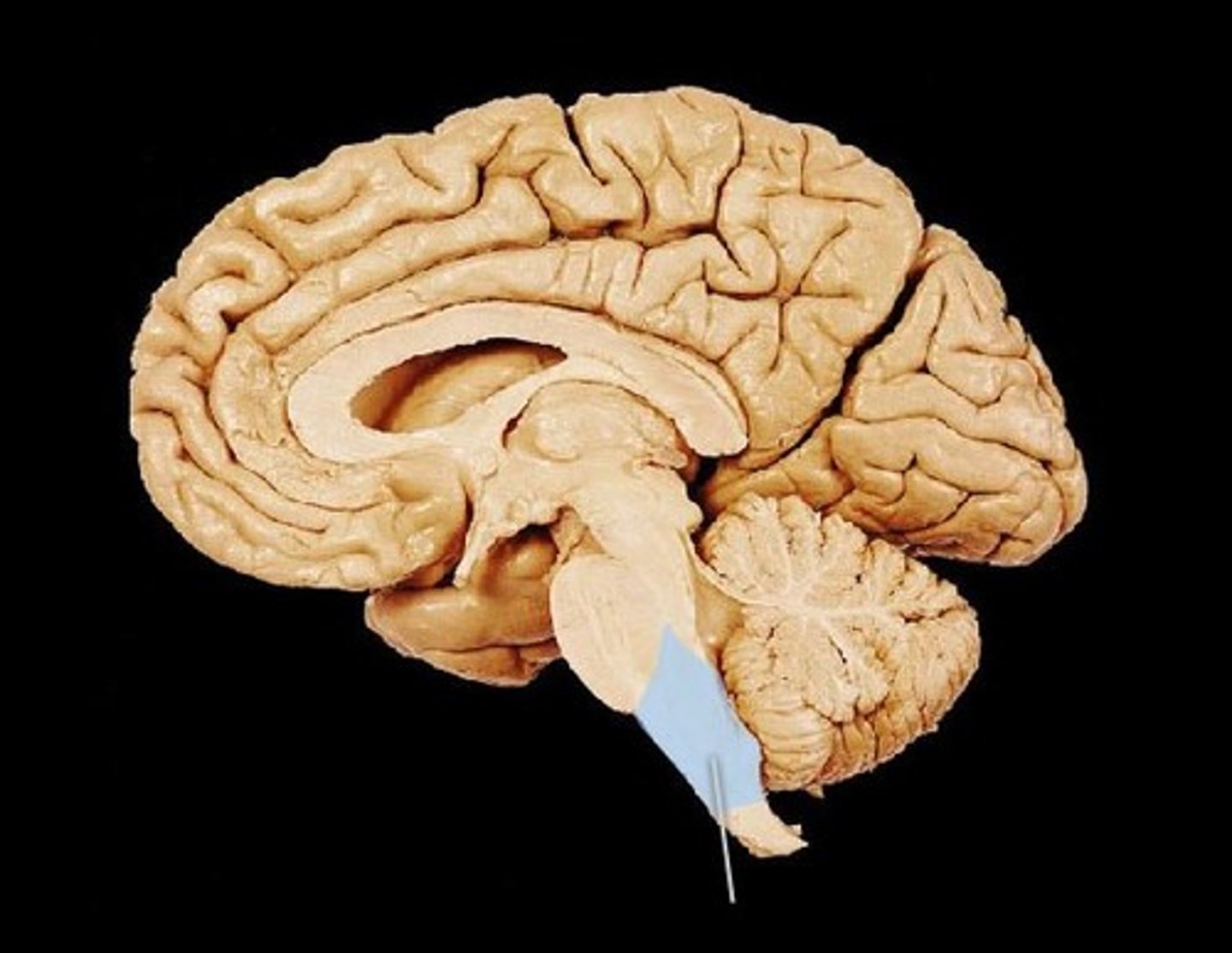
Cerebellum
Balance, motor movement and procedural memory
Alzheimer’s disease
A common cause of widespread cortical atrophy that leads to receding tissue surrounding ventricles.
What can happen when there is a blockage of flow of CSF fluid? What is it called?
The brain tissue is compressed. noncommunicating or communicating Hydrocephalus
Flow of CSF
CSF fluid circulates all around the external surface of the brain, between the hemispheres of the brain, around the cerebellum, around the brain stem, and down the spinal cord.
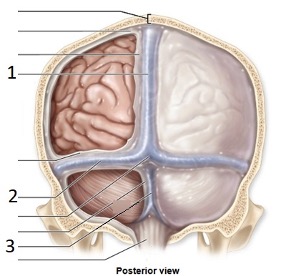
Meningeal extension Number 1
Falx Cerebri
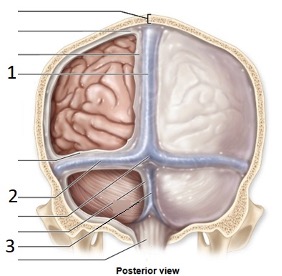
Meningeal extension Number 2
Tentorium cerebelli
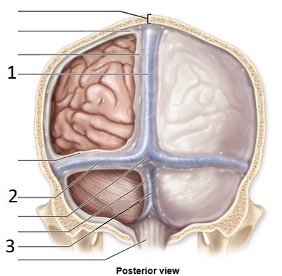
Meningeal extension Number 3
Falx cerebelli
Meningeal extension functions
Provides structural support for brain and separates the different parts of the brain
Meningeal extension inflammation
Meningitis
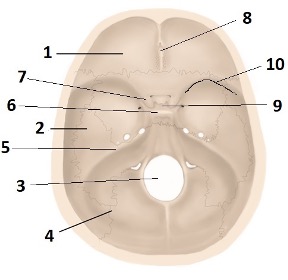
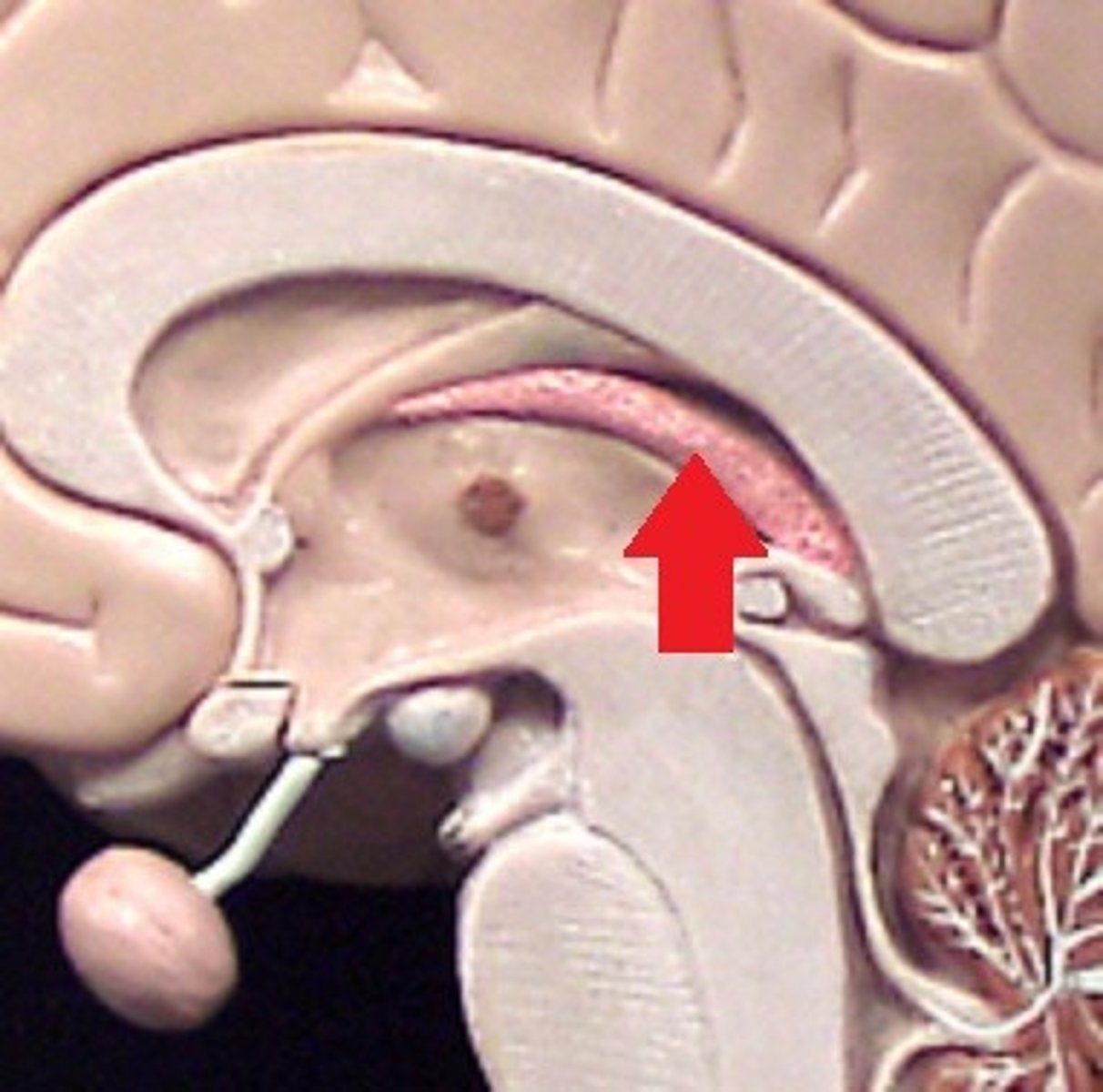
Depression indicated by #9
Pituitary gland
Ridge indicated by #10
Sphenoid ridge
CT scan
It uses radiation to measure attenuation. It detects hypodense areas in the brain that might indicate swelling or bleeding. Bony structures are highly visible
MRI
Uses contrast to detect any abnormalities within the soft tissue of the brain. Soft tissue is highly visible
Ischemia in a CT scan
Darkened area in a CT scan
Hemorrhage in a CT scan
Brighter white area in a CT scan
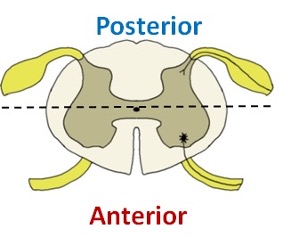
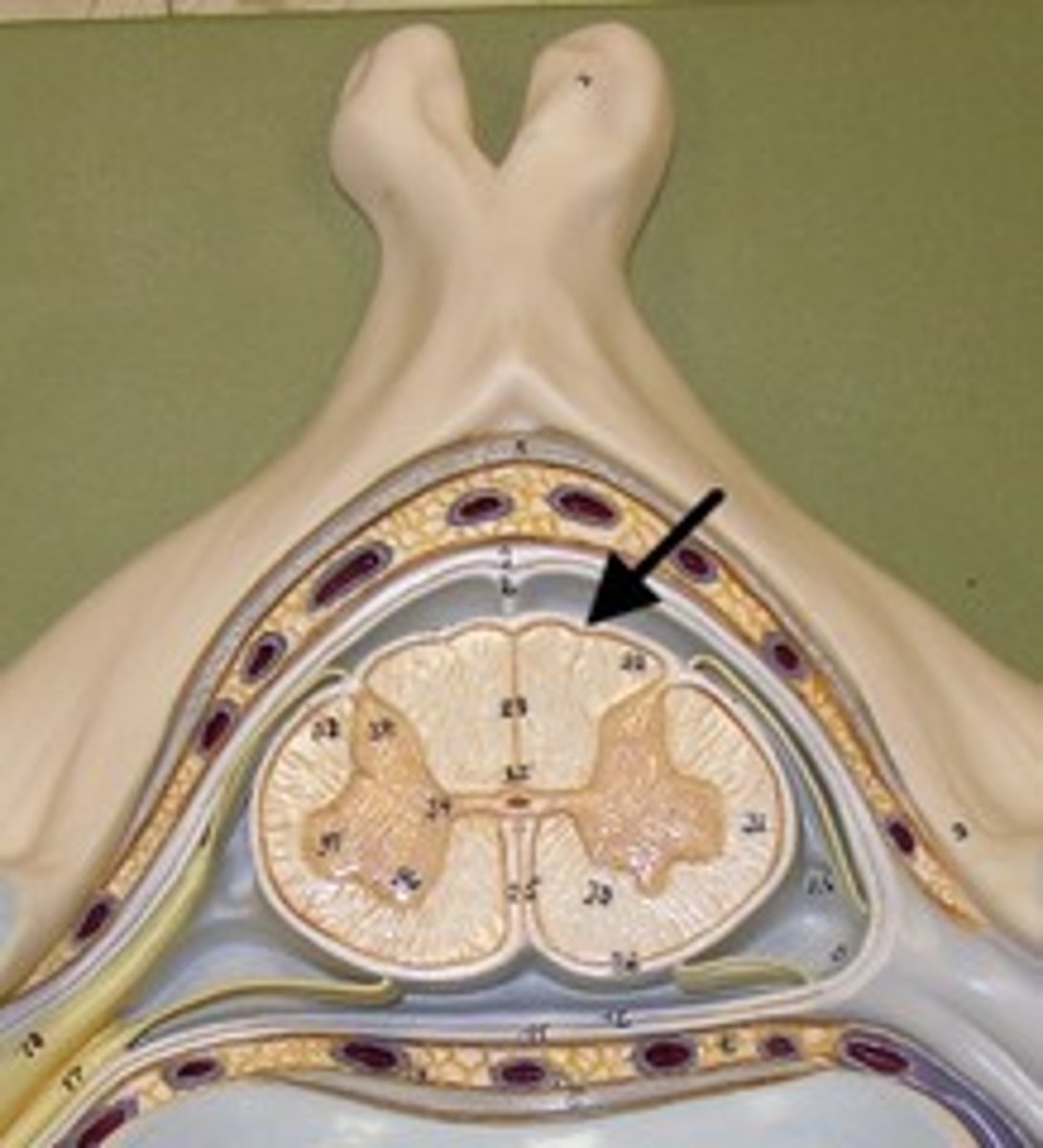
Which part of spinal cord is motor and which is sensory?
The posterior part is sensory, and the anterior part is motor. The dorsal root indicates the posterior section.
Discuss how the organization of the cerebrum parallels the spinal cord organization
Both structures consist of white matter and gray matter with the interior and exterior portions being reverse for these two structures (ie. Grey matter inside and white matter outside for the spinal cord and vice versa for the cerebrum).
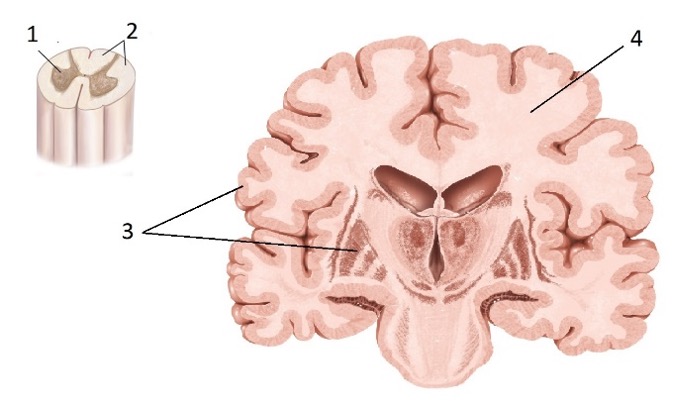
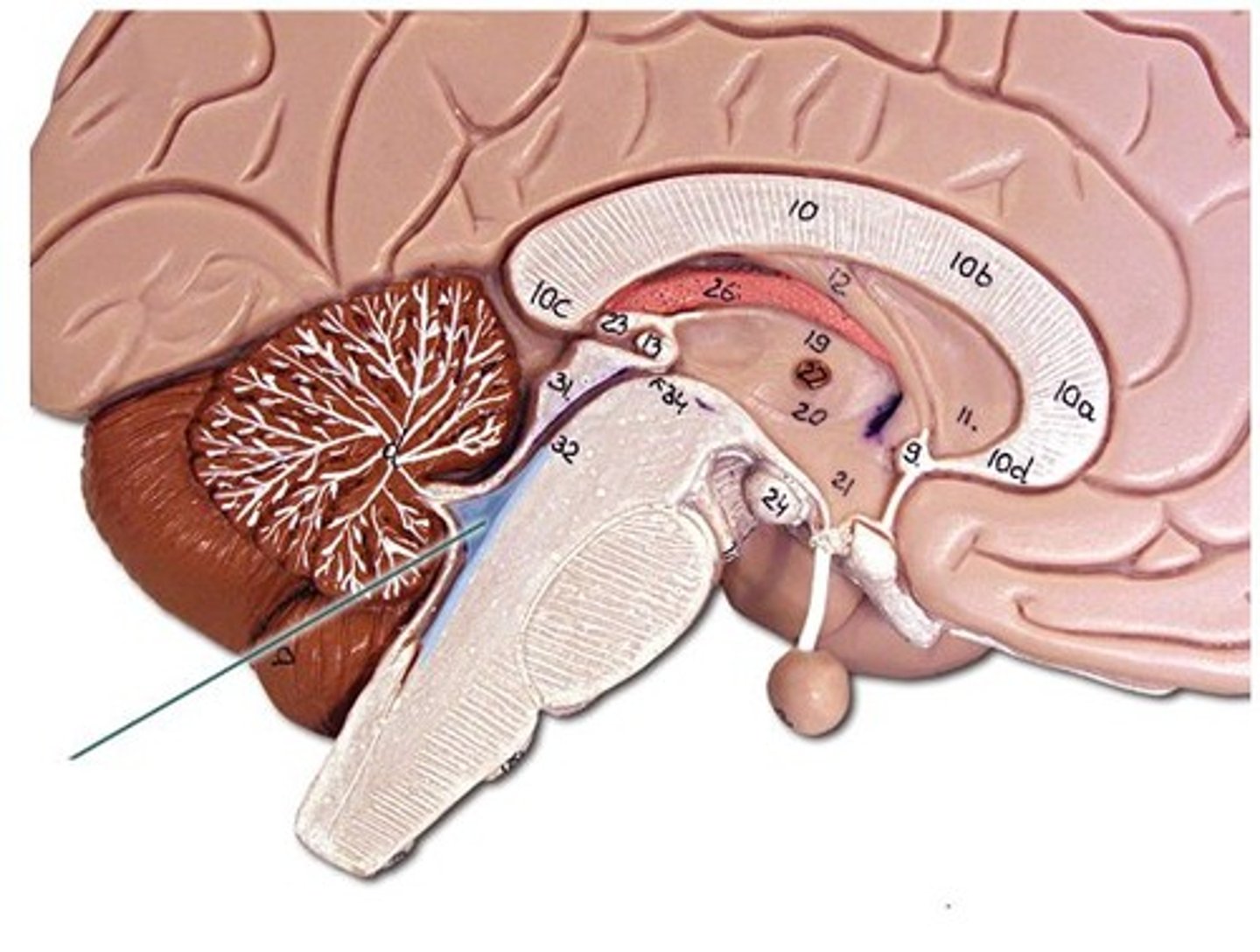
Gray matter vs White matter
Gray Matter: 1 and 3
White Matter: 2 and 4