Anatomy exam 1 JMU
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
cranial/superior
toward the head
caudal/inferior
toward the feet/tail
ventral/anterior
toward the front
dorsal/posterior
toward the back
medial
toward the midline
lateral
toward the side, away from midline
proximal
closer to the trunk of the body (applies to limbs)
distal
further away from the trunk (applies to limbs)
superficial
closer to the surface of the body
deep
closer to the center of the body
sagittal
divides left and right
transverse
superior and inferior
frontal
divides into ventral and dorsal
axial skeleton
vertebral column, ribs, sternum, and skull
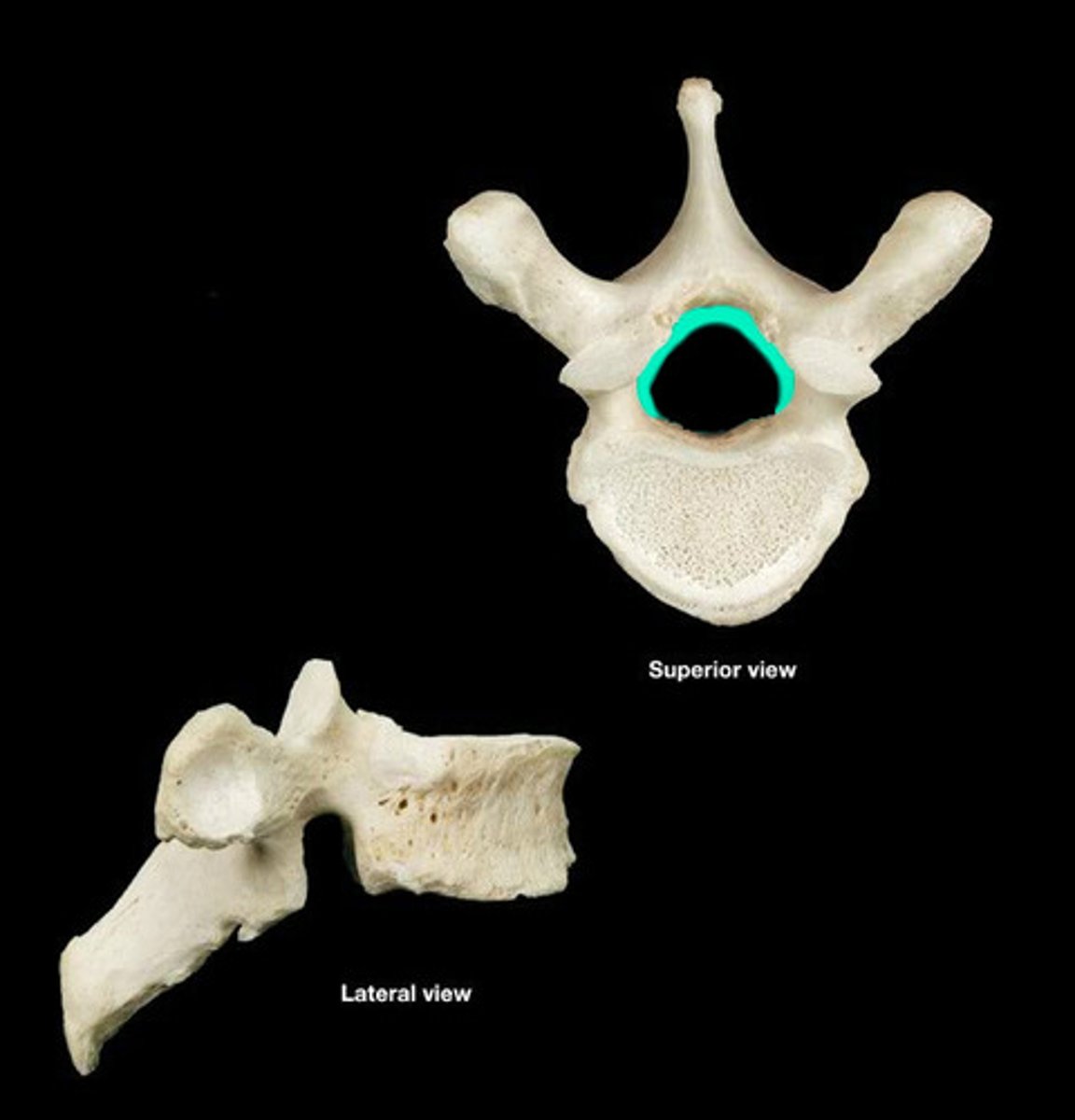
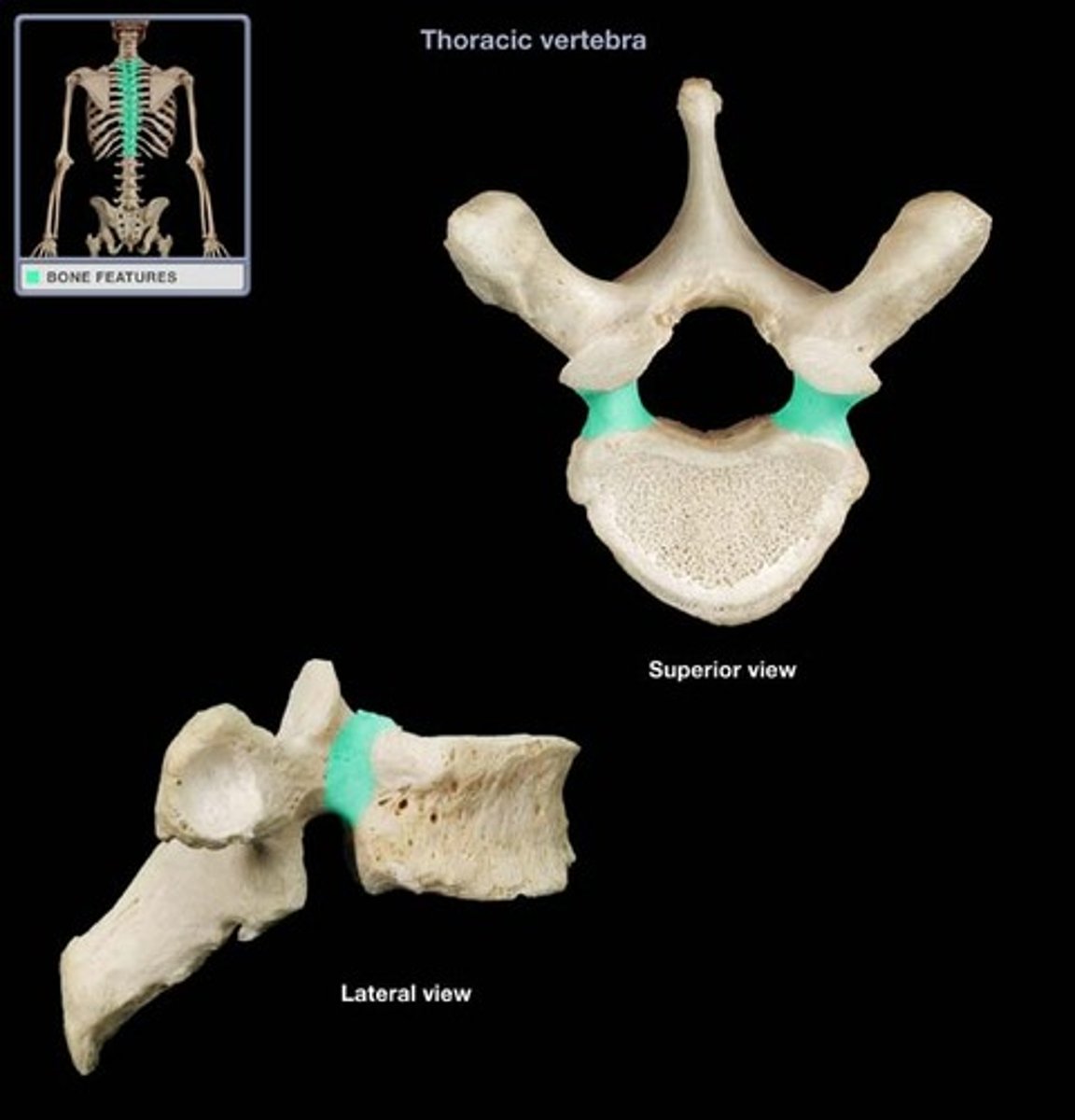
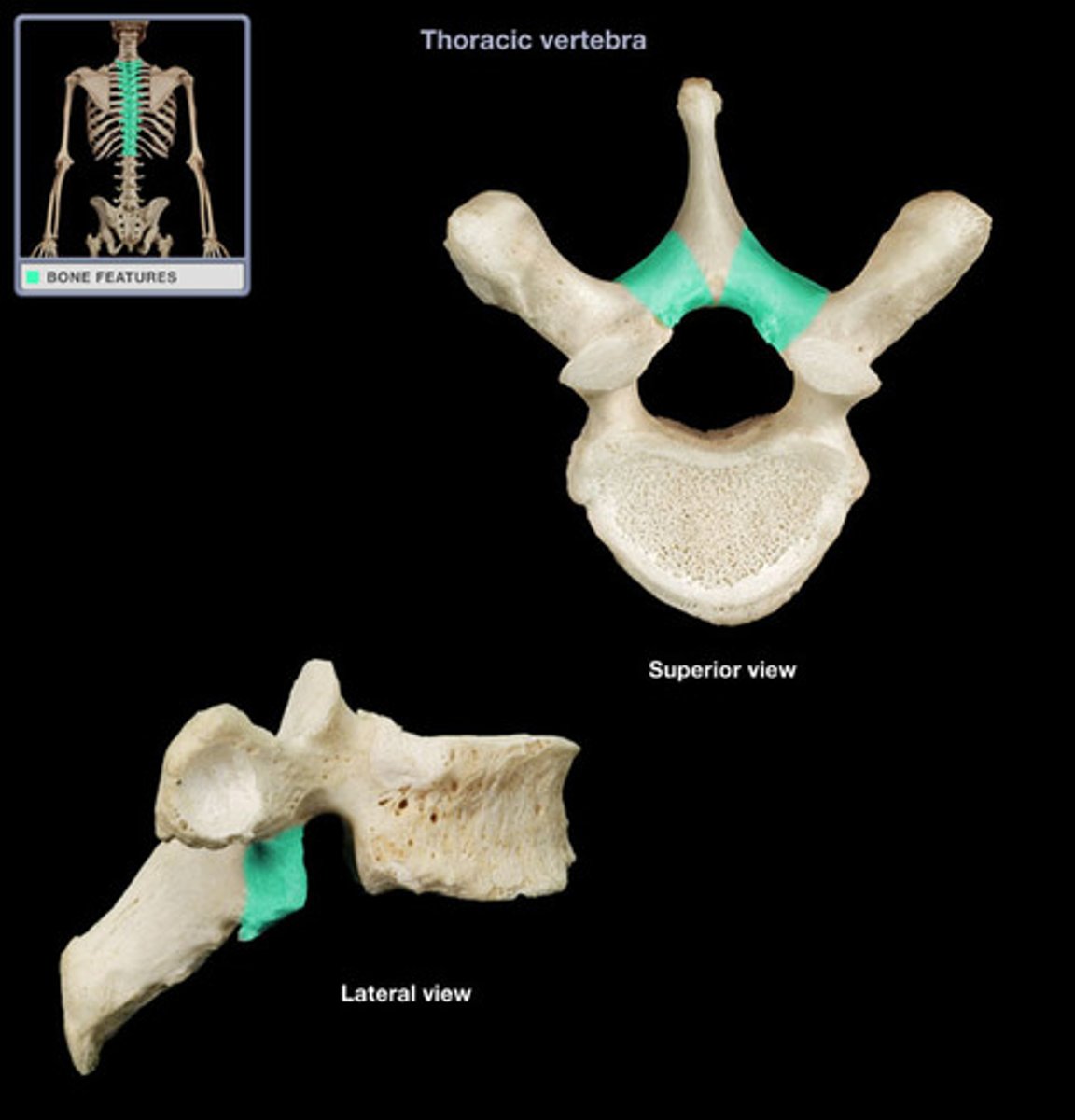
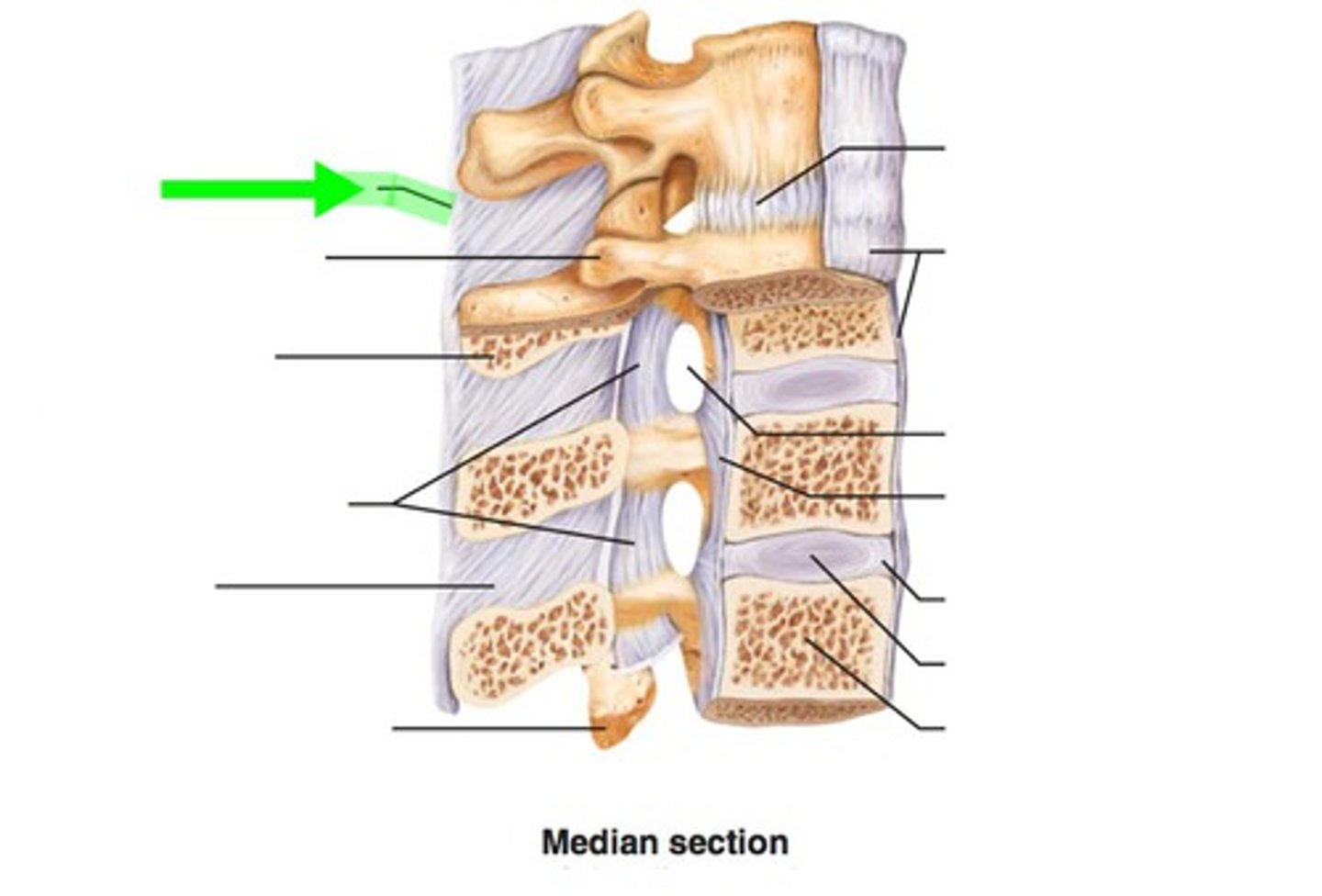
vertebral body
vertebral arch
pedicles
laminae
vertebral foramen
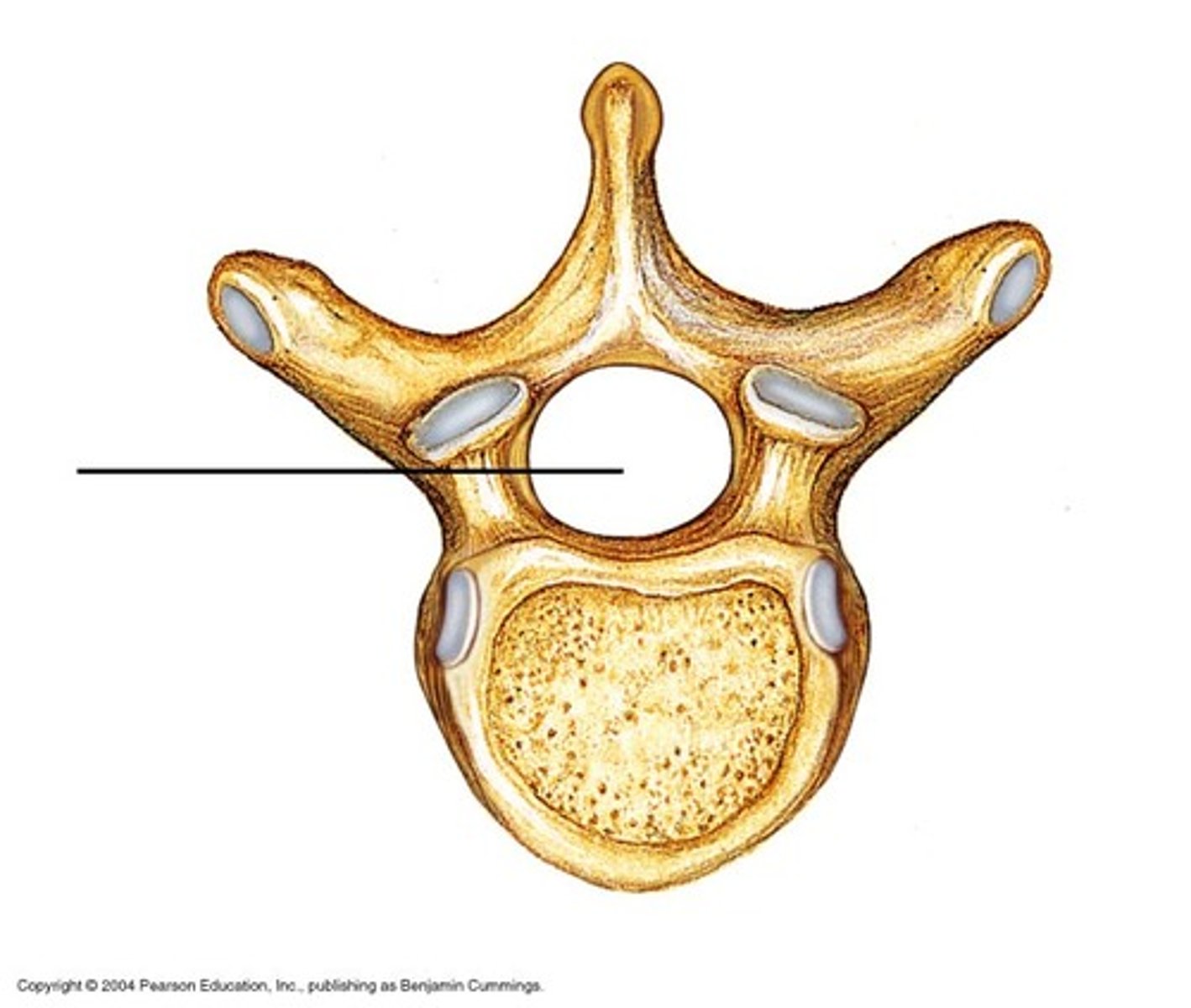
superior articular process
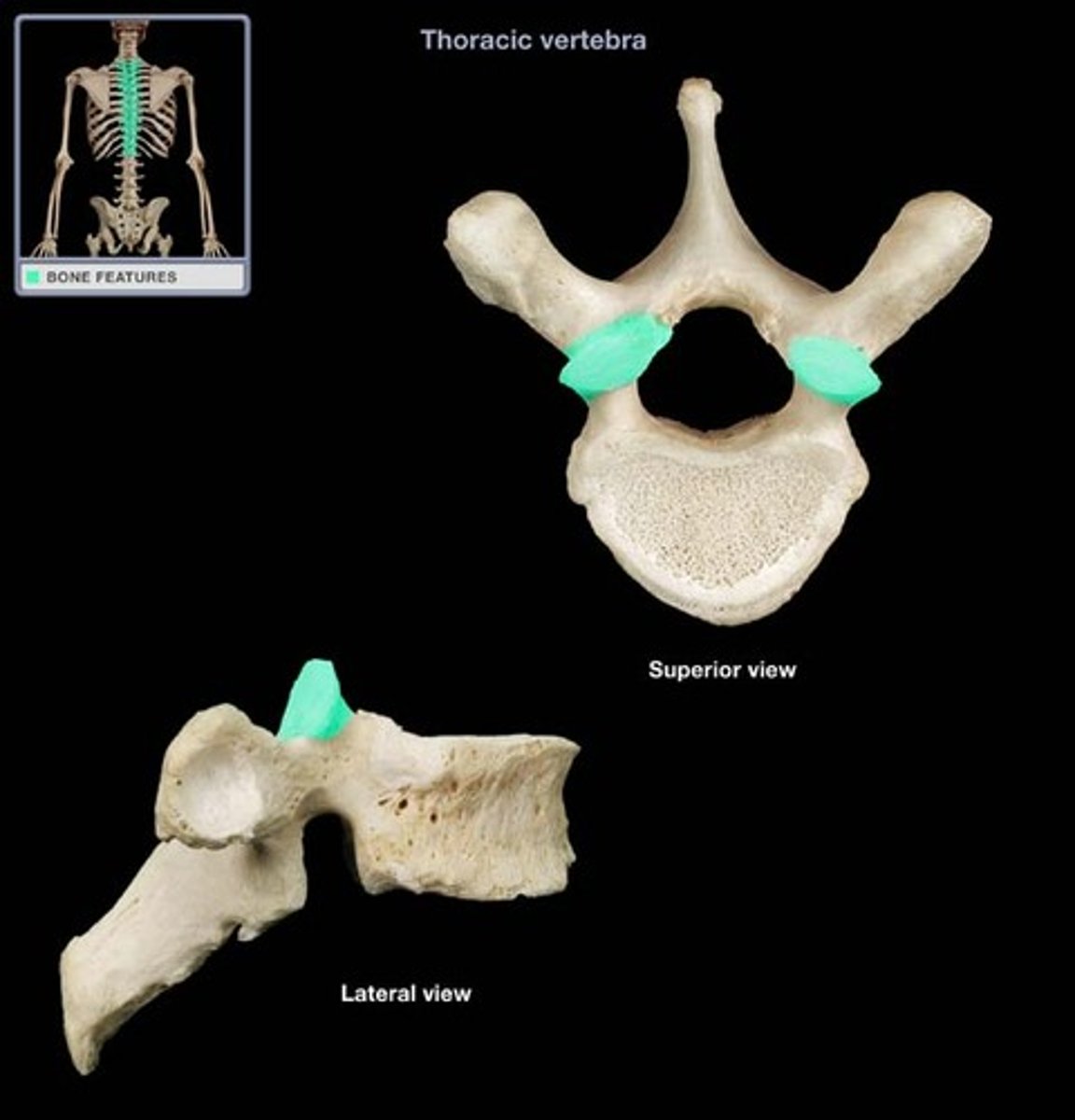
inferior articular process
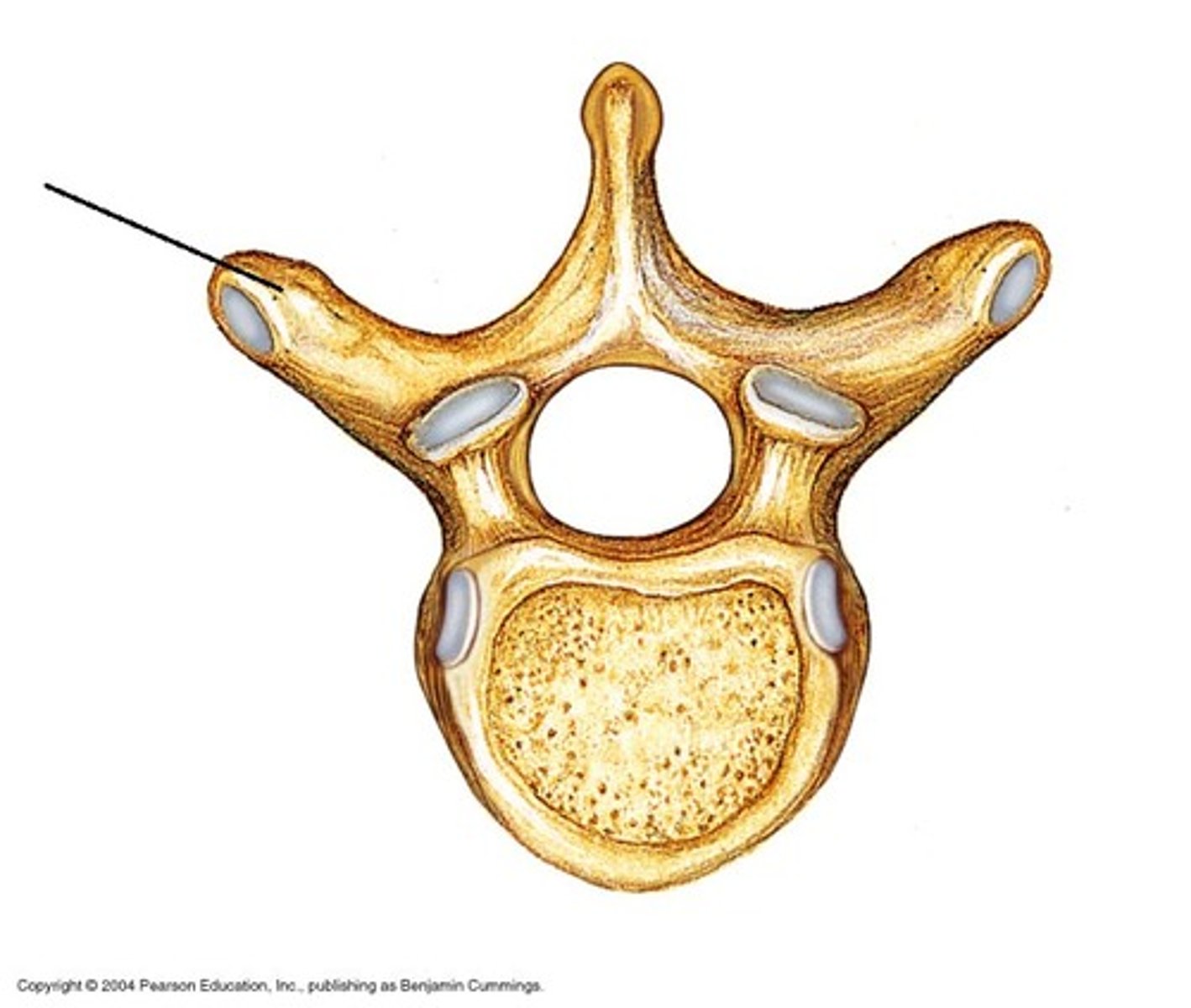
transverse process
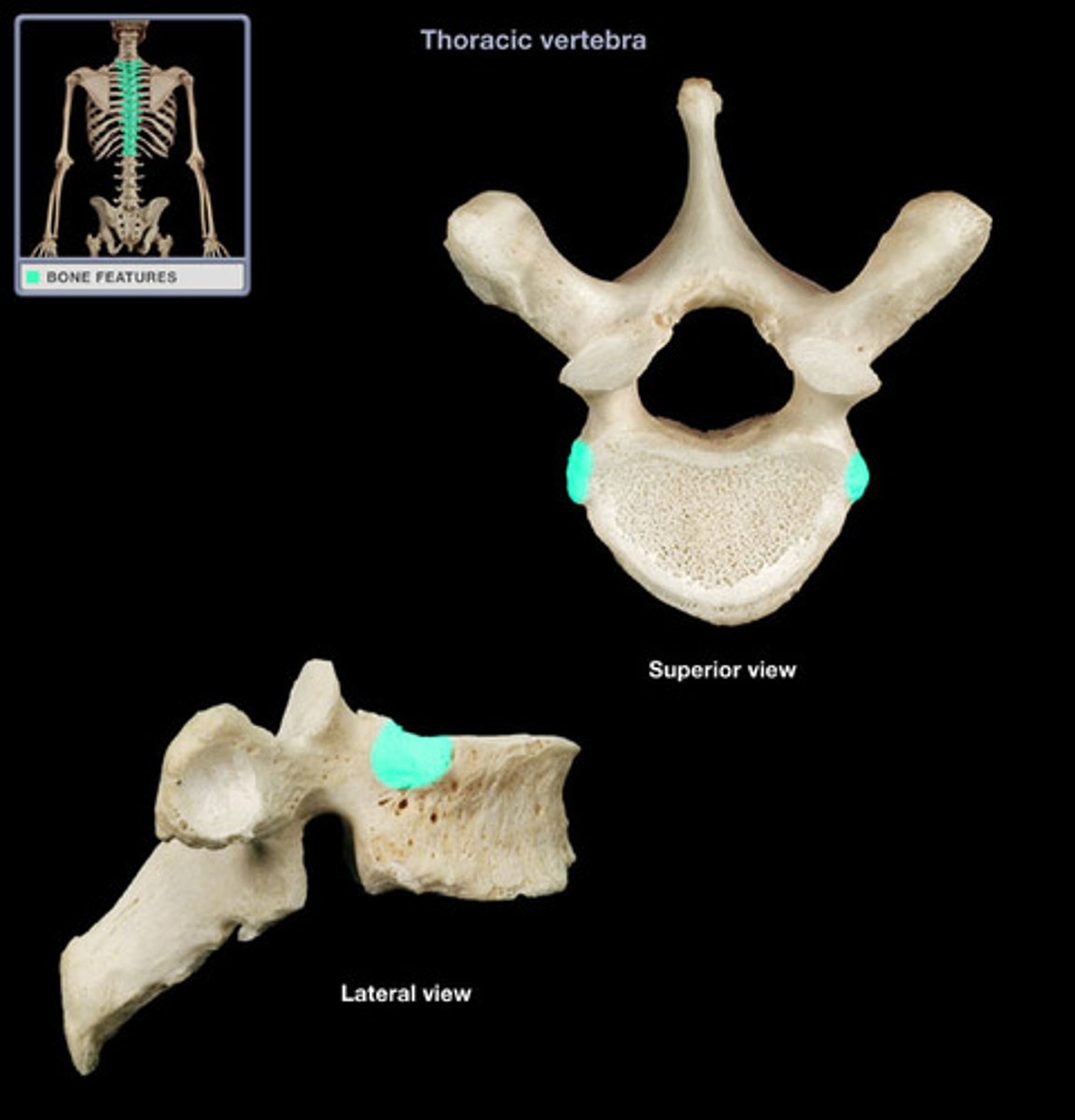
costal facet
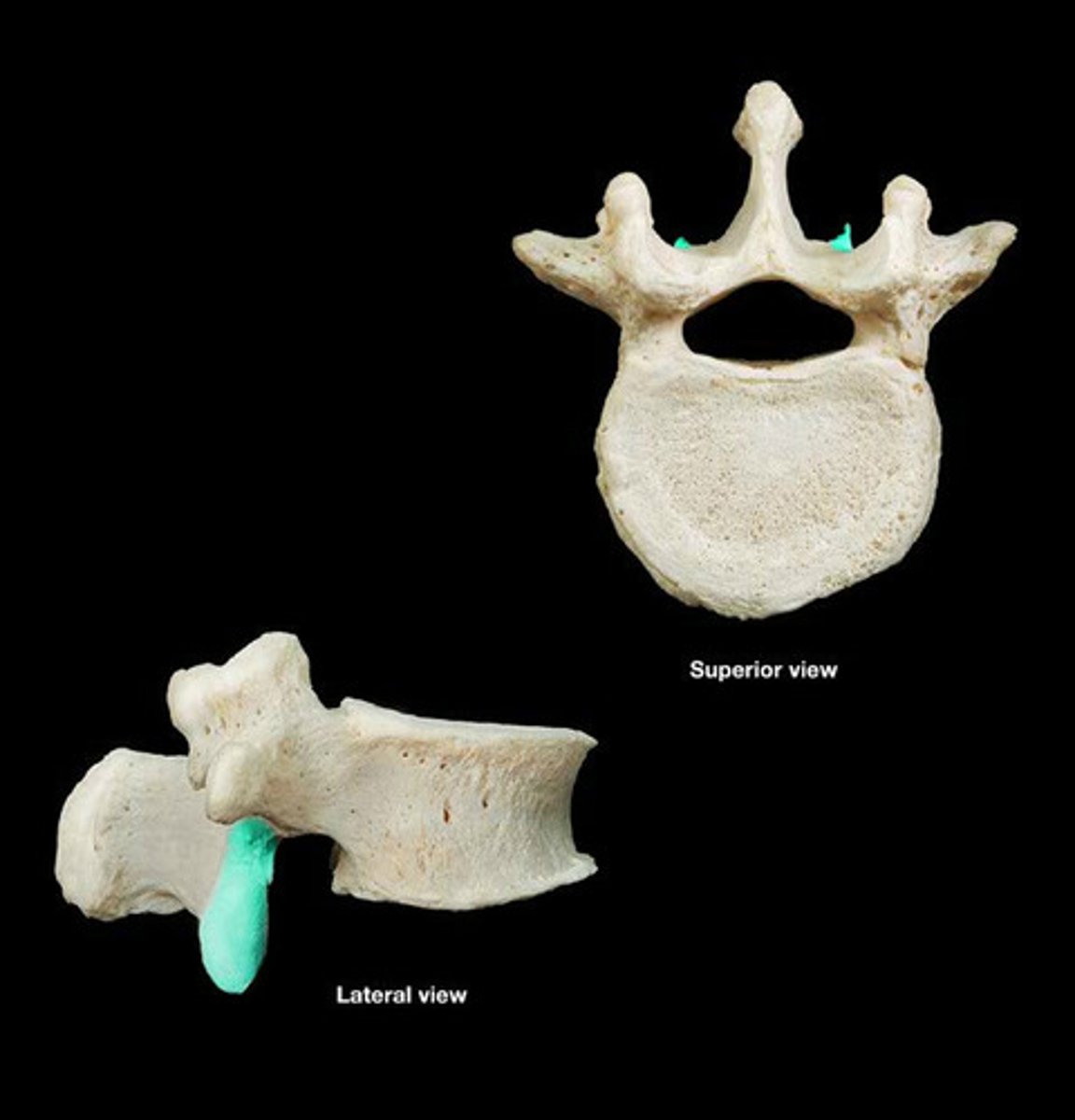
spinous process
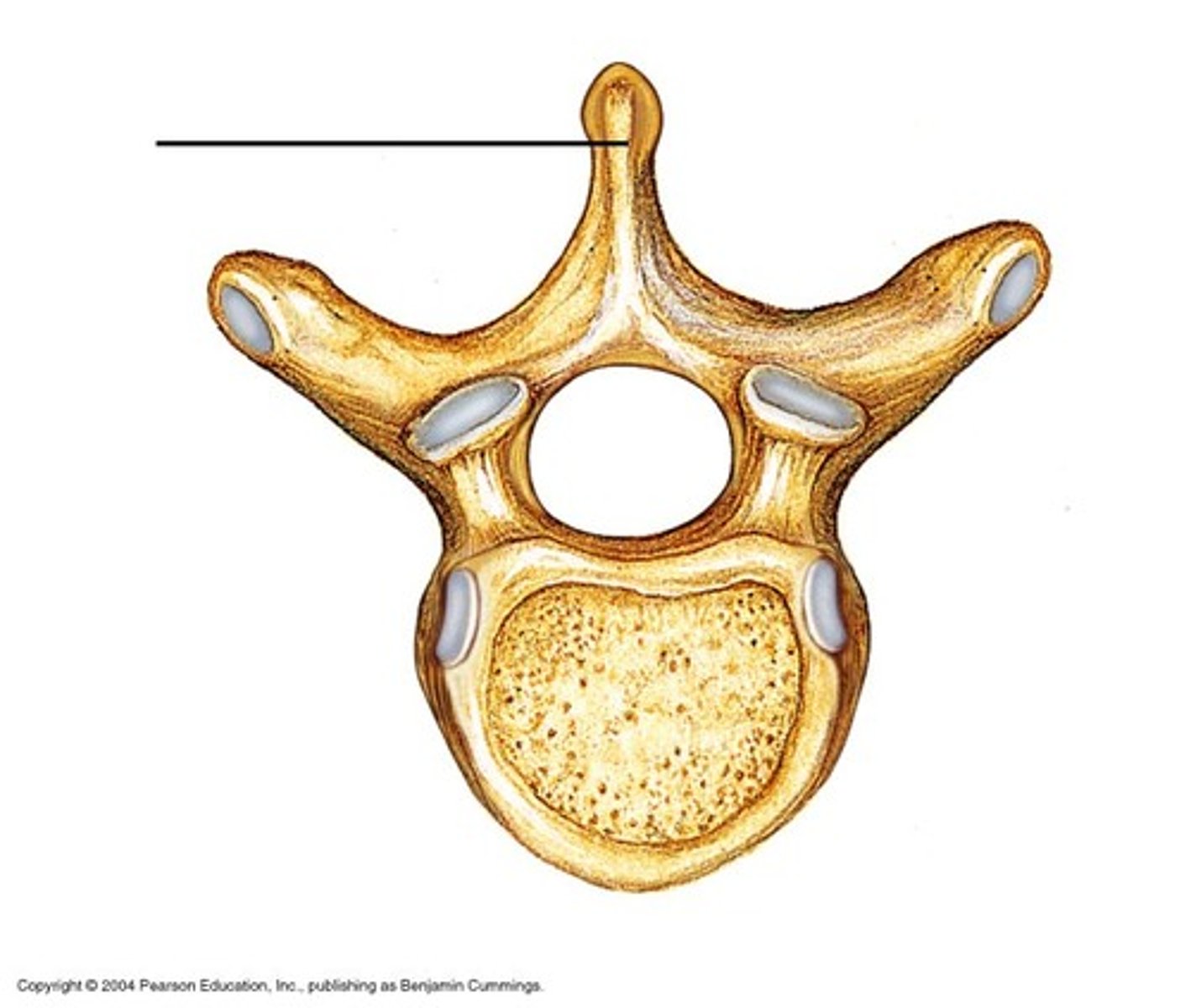
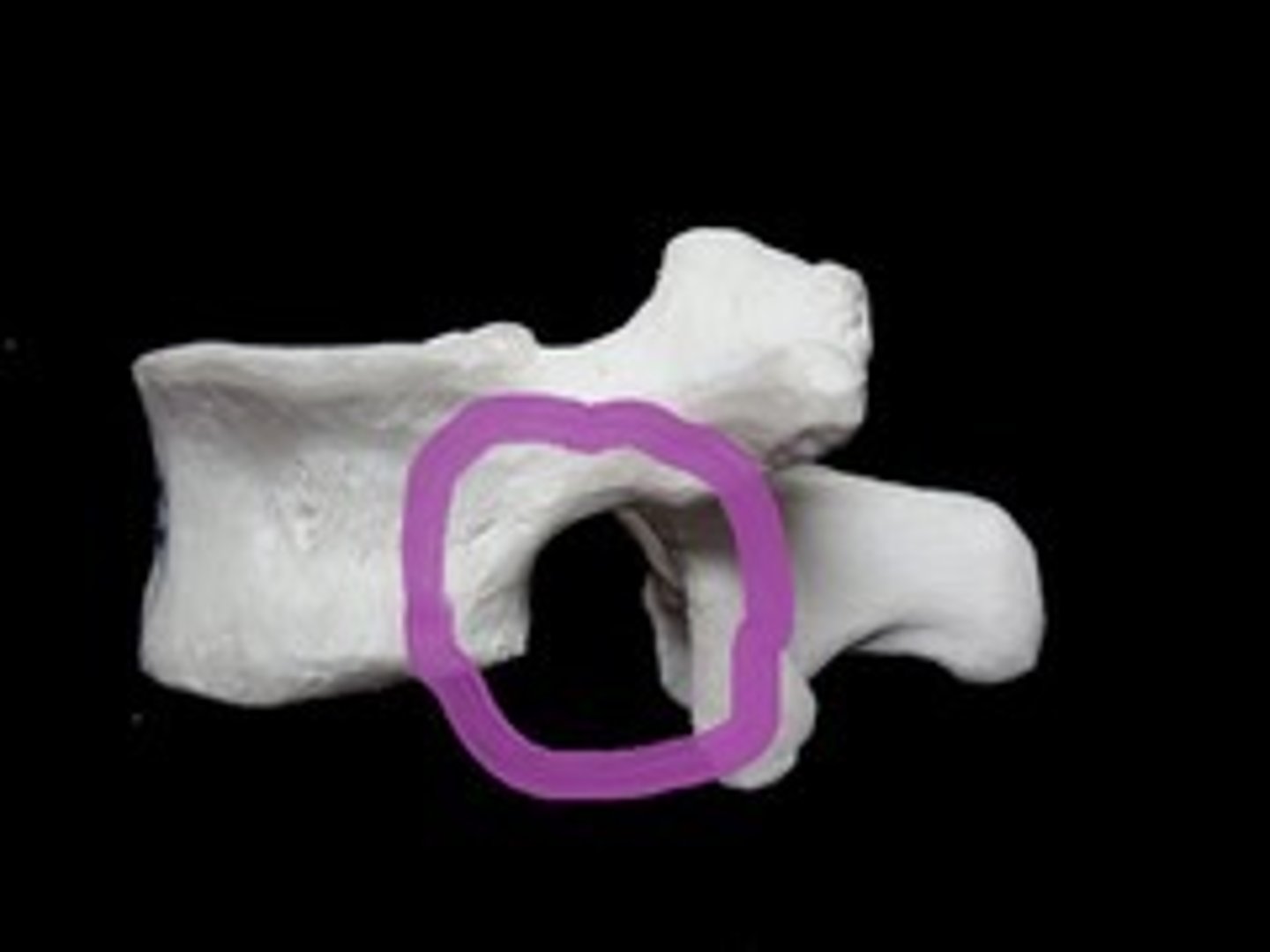
intervertebral foramen
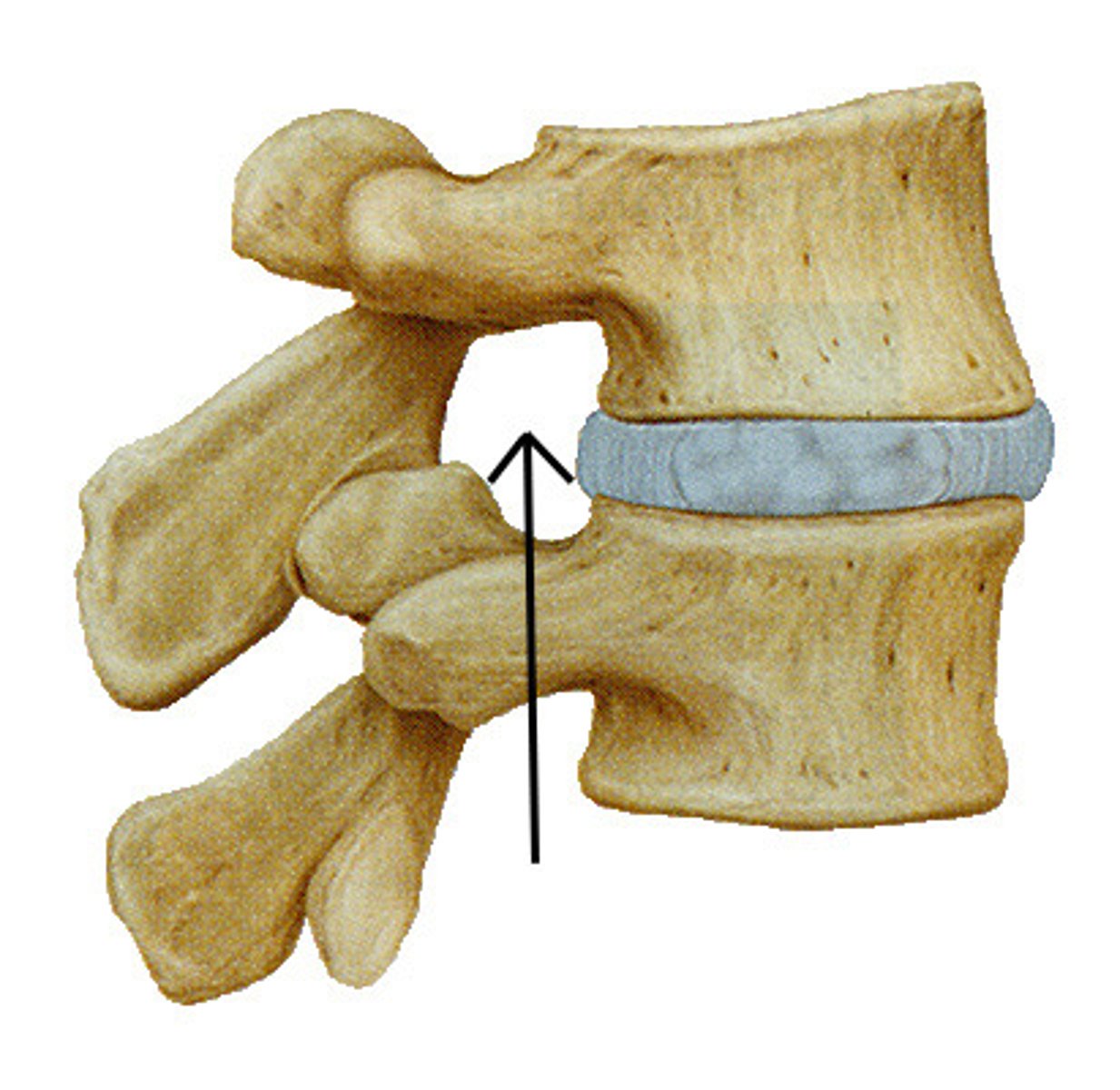
superior vertebral notch
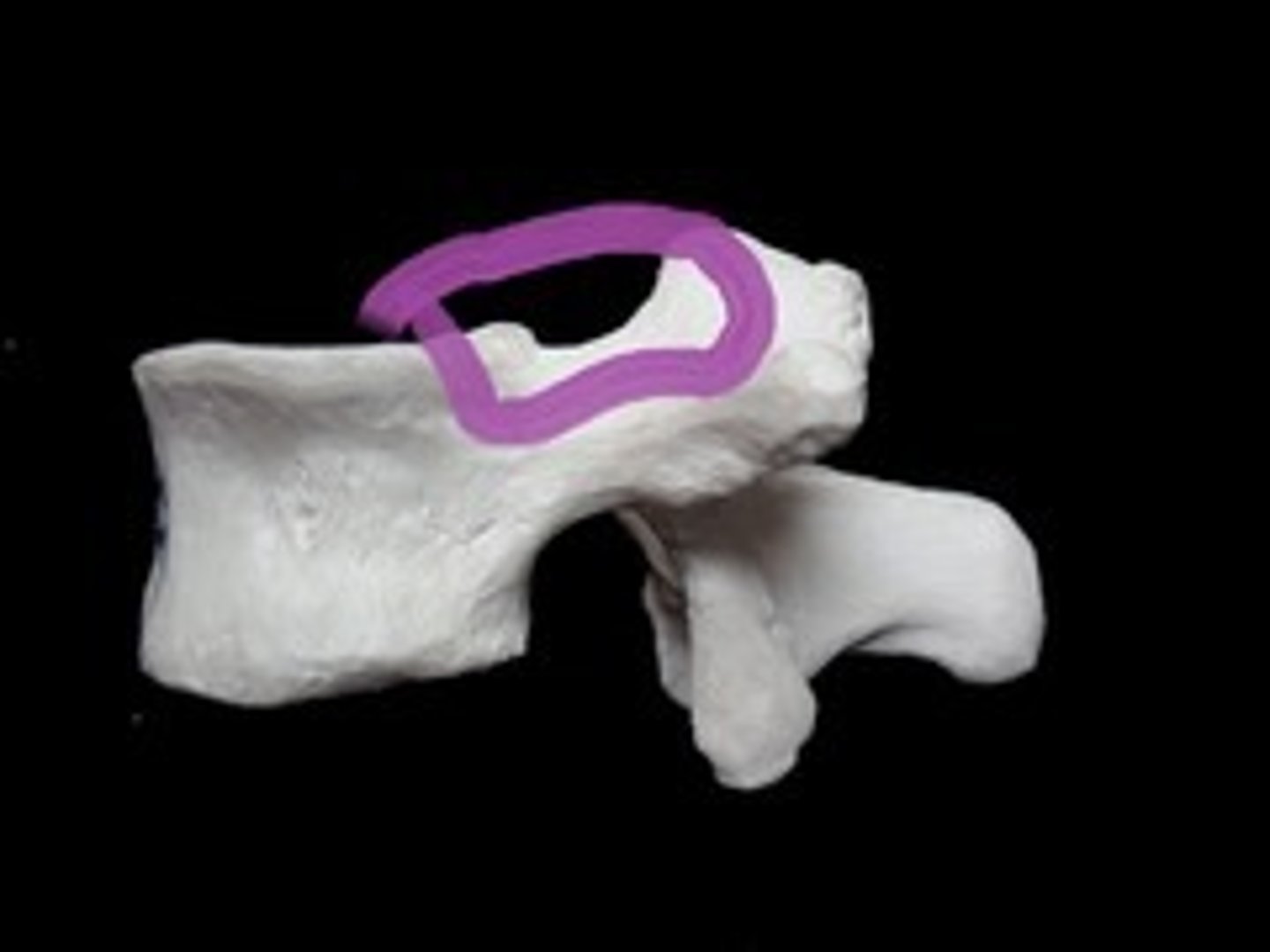
inferior vertebral notch
atlas
no vertebral body
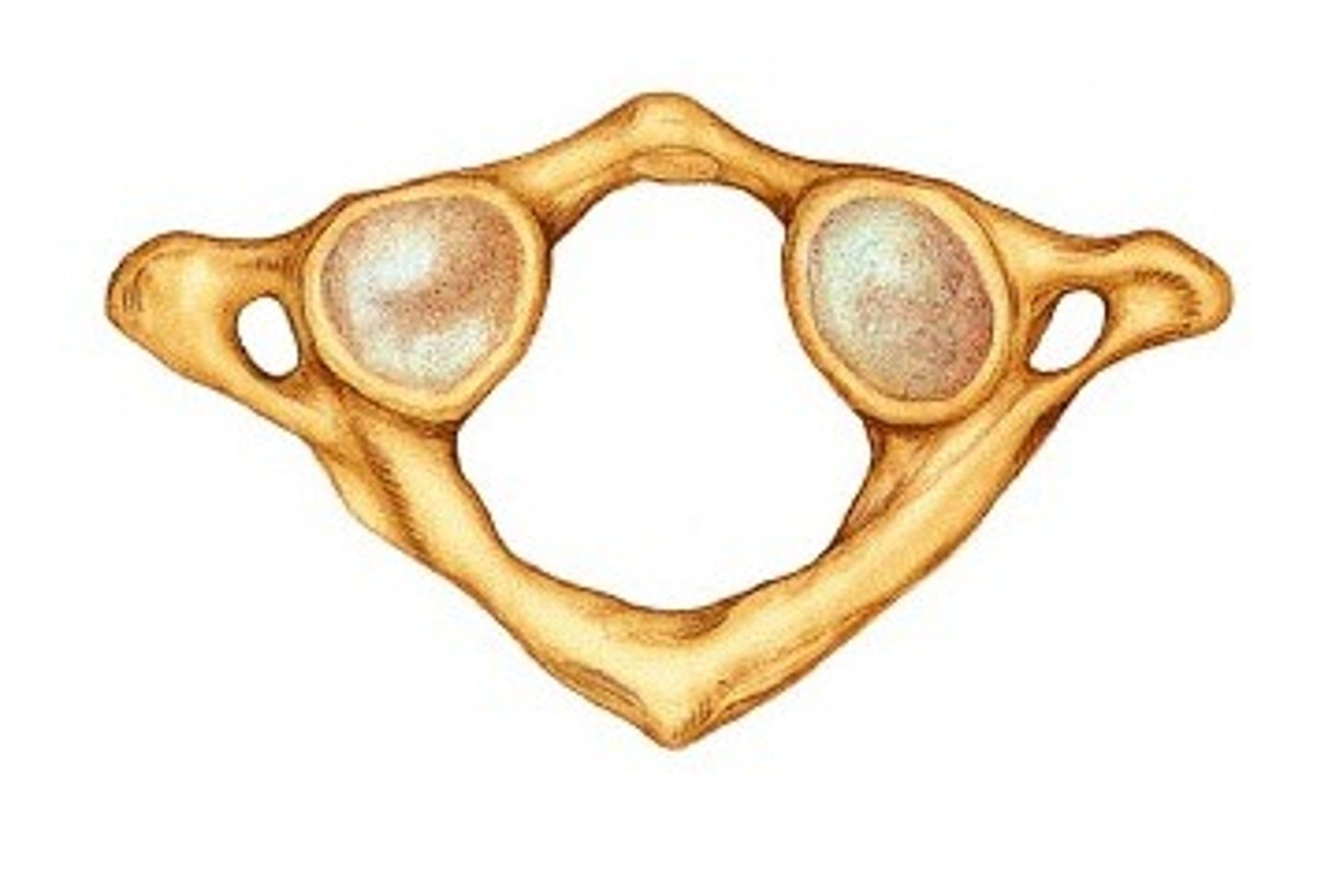
axis
has dens
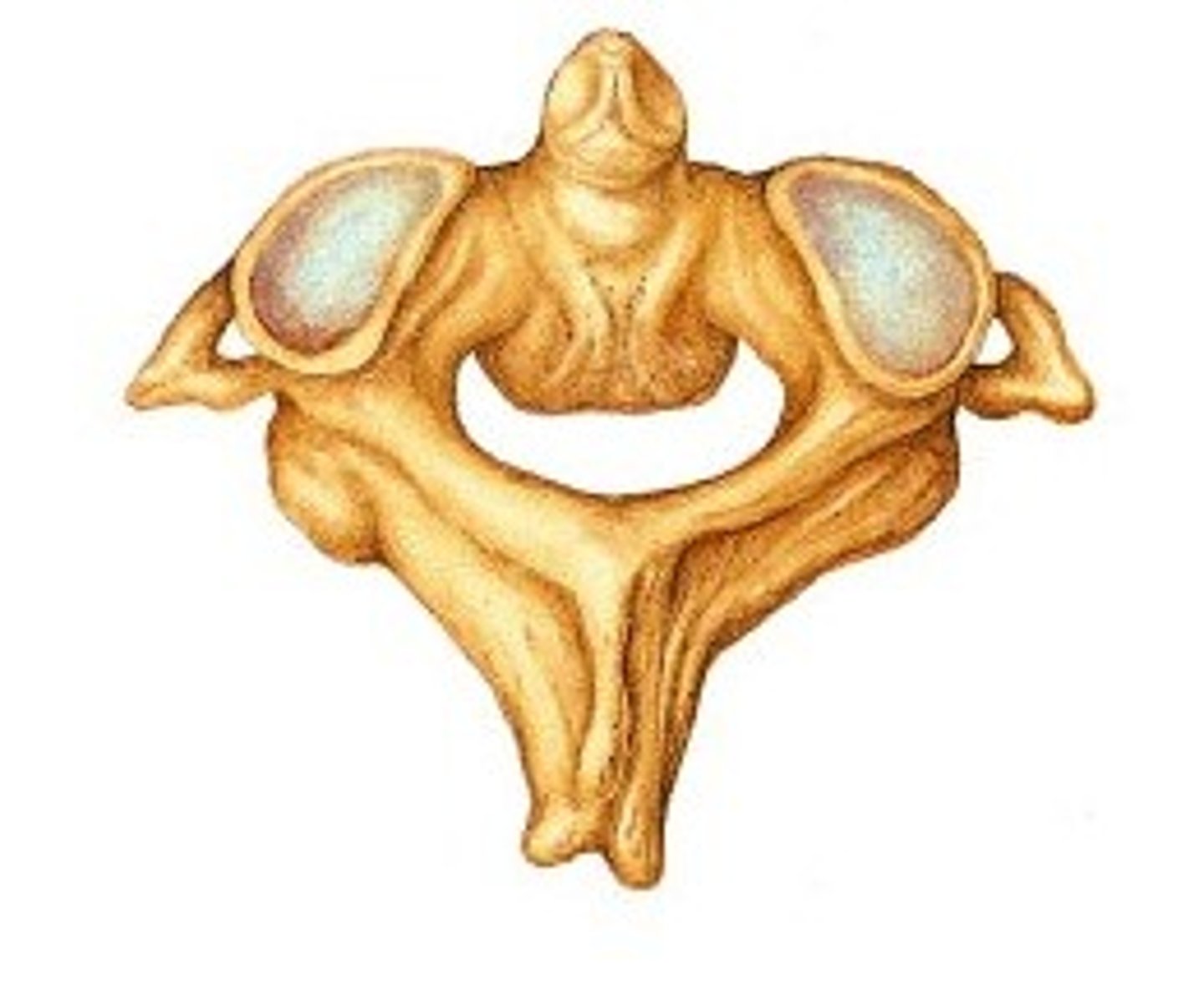
thoracic vertebrae
12
superior costal facets(t2-t9) and inferior costal facets (t1-t8)
costal facets (t1,t10-12)
transverse costal facets(t1-t10)
lumbar vetebrae
5
sacral vertebrae
5 fused vertebrae
coccygeal
3-5 tiny caudal vertebrae
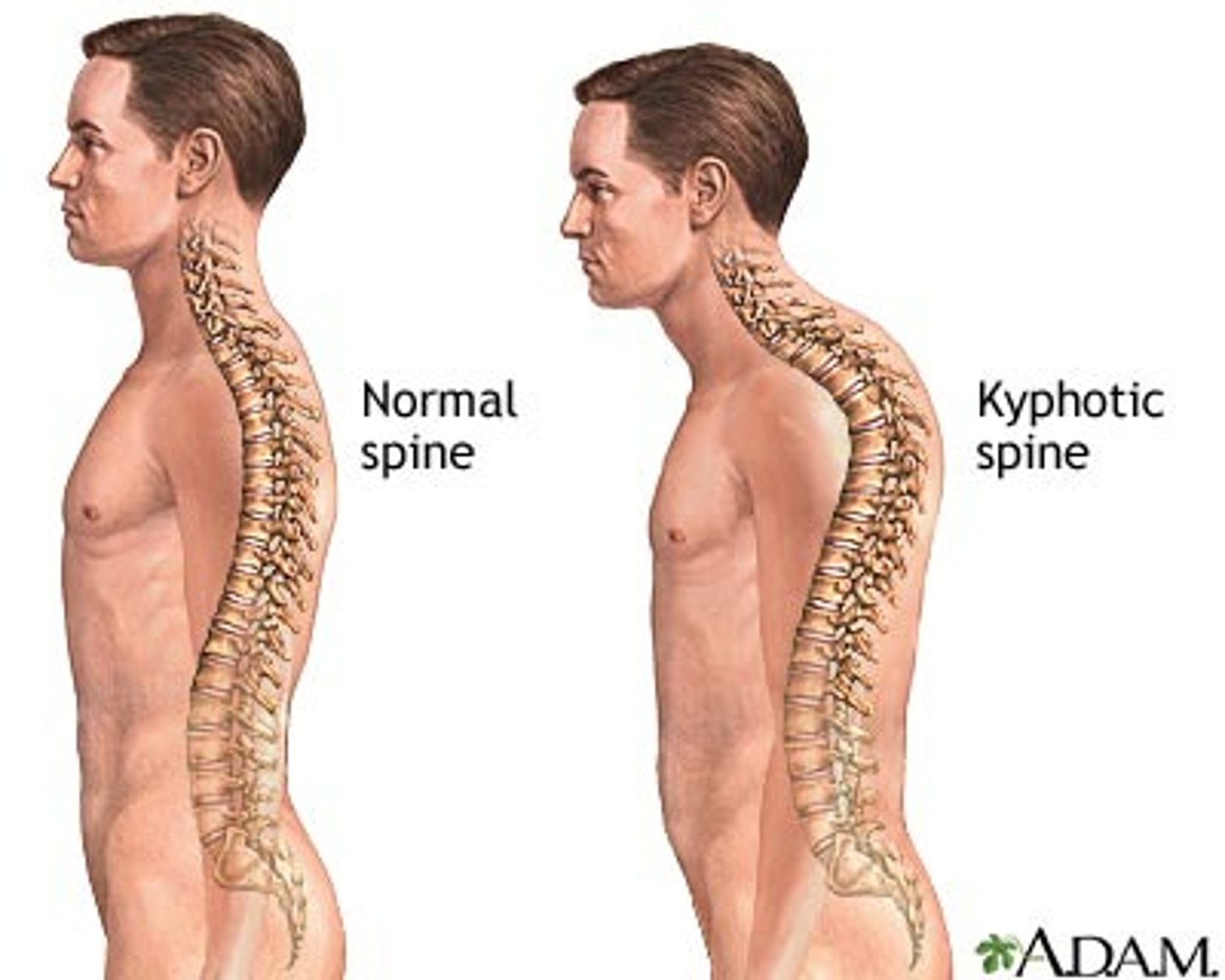
kyphosis
thoracic curvature
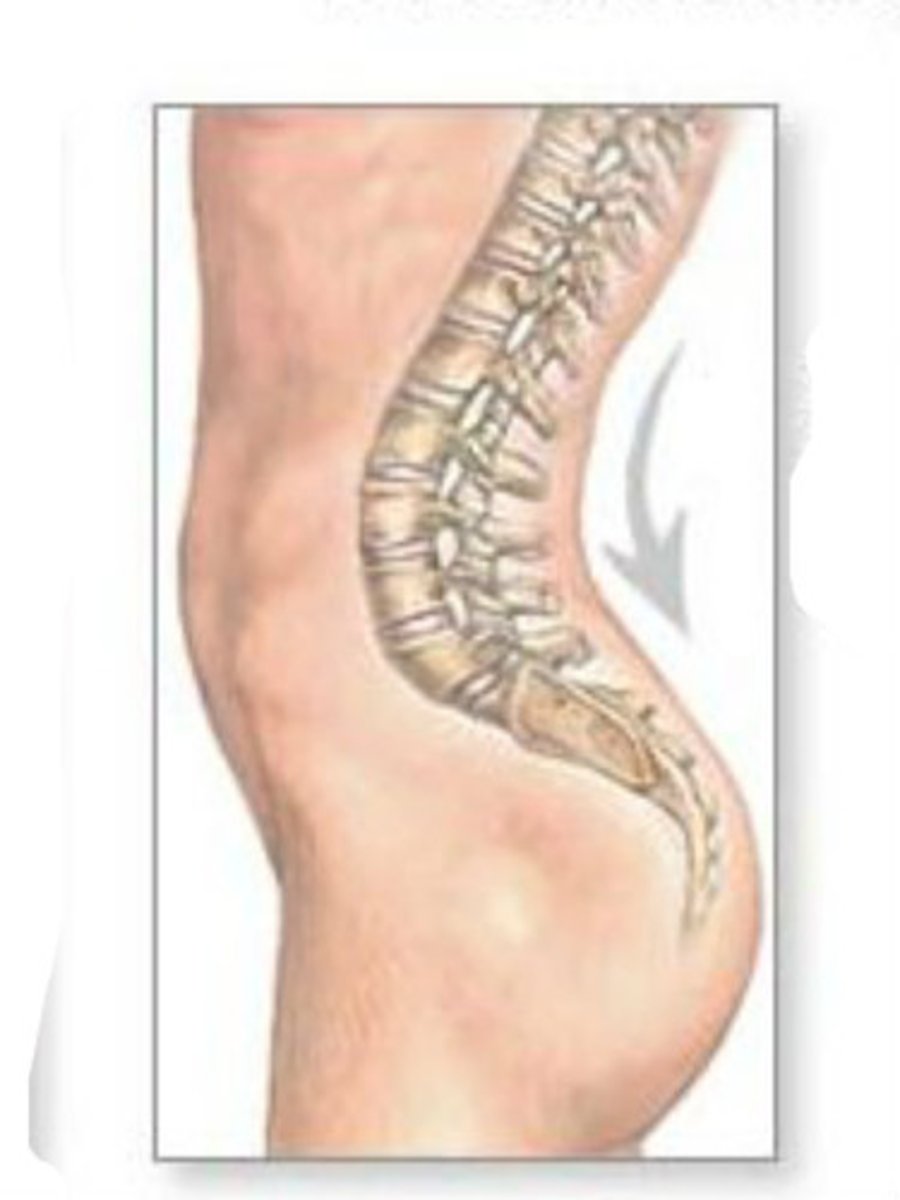
lordosis
lumbar and cervical curvature
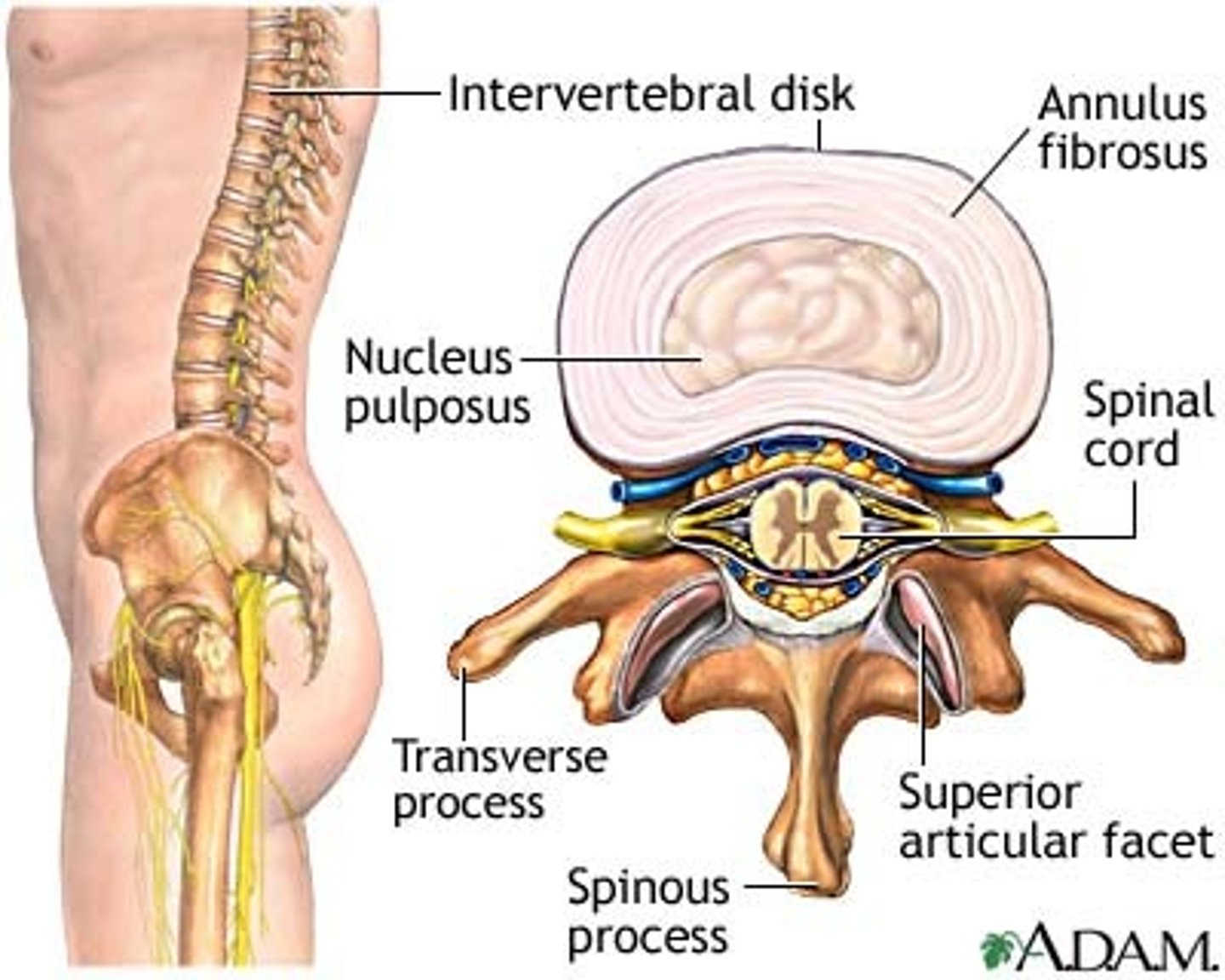
intervertebral disks
joints b/w vertebral bodies and act as shock absorbers for the vertebral column
nucleus pulposus
center part of vertebral disk
annulus fibrosus
outer rings of vertebral disk
anterior longitudinal ligament
attaches to the anterior vertebral body another anterior vertebral body
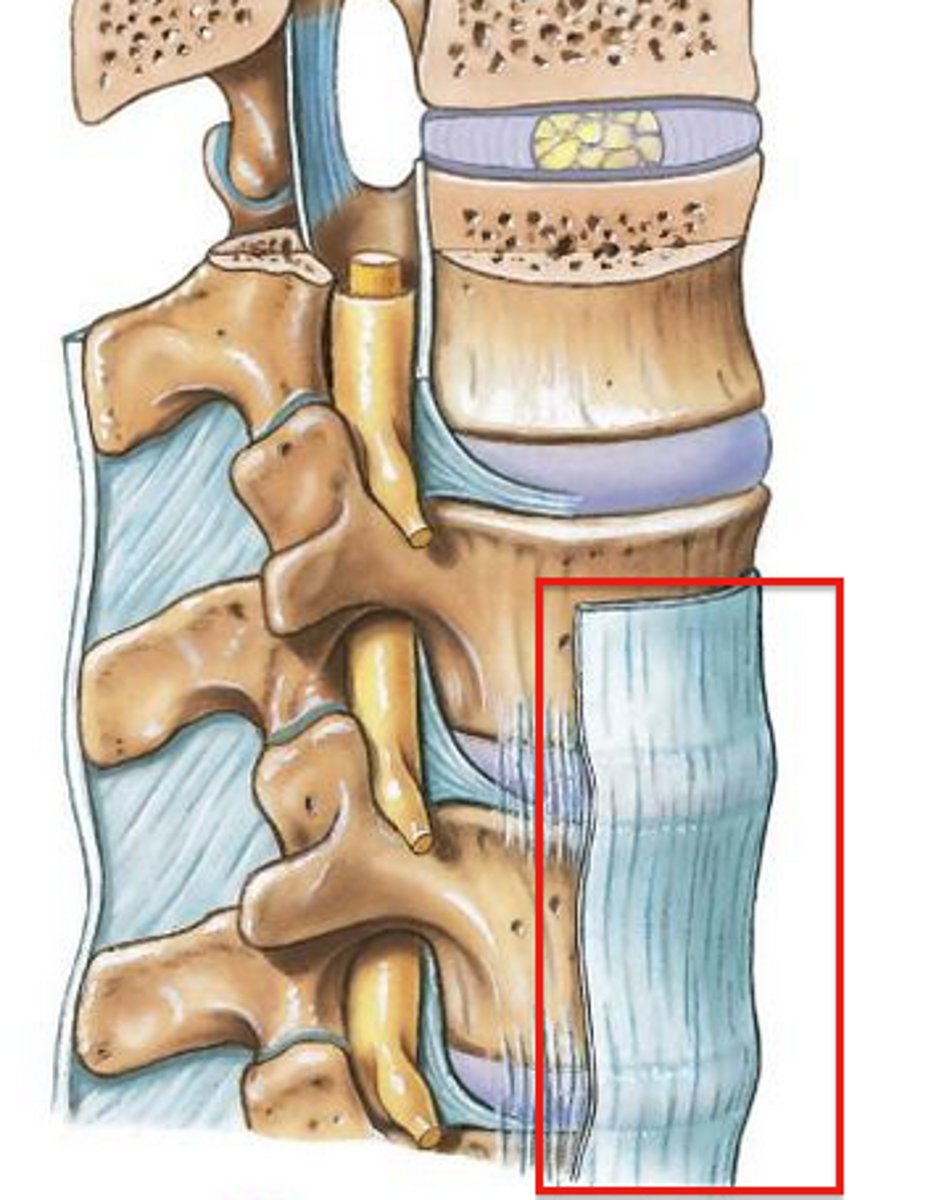
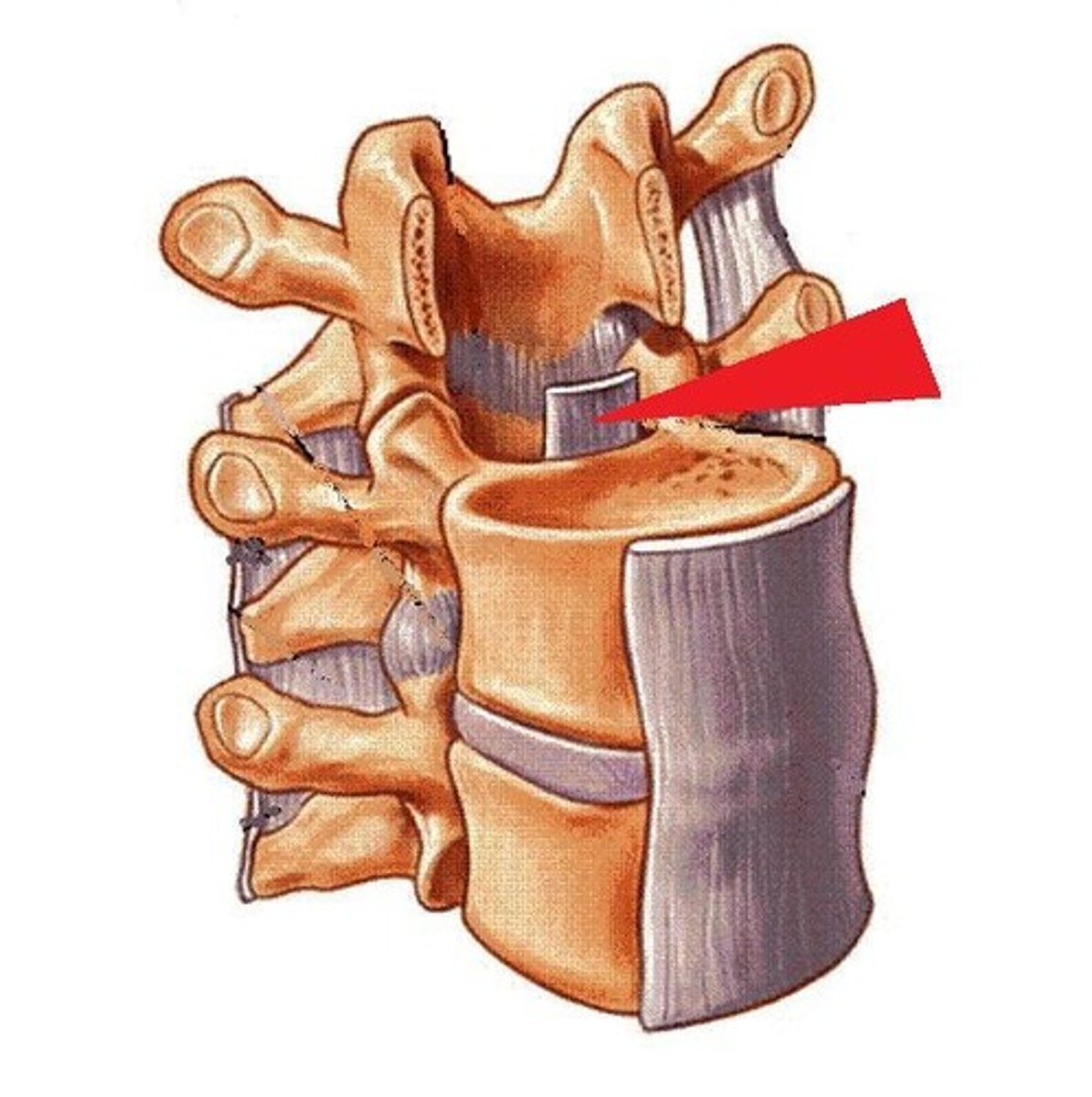
posterior longitudinal ligament
attaches to the posterior vertebral body another posterior vertebral body
ligamentum flavum
attaches from lamina to lamina
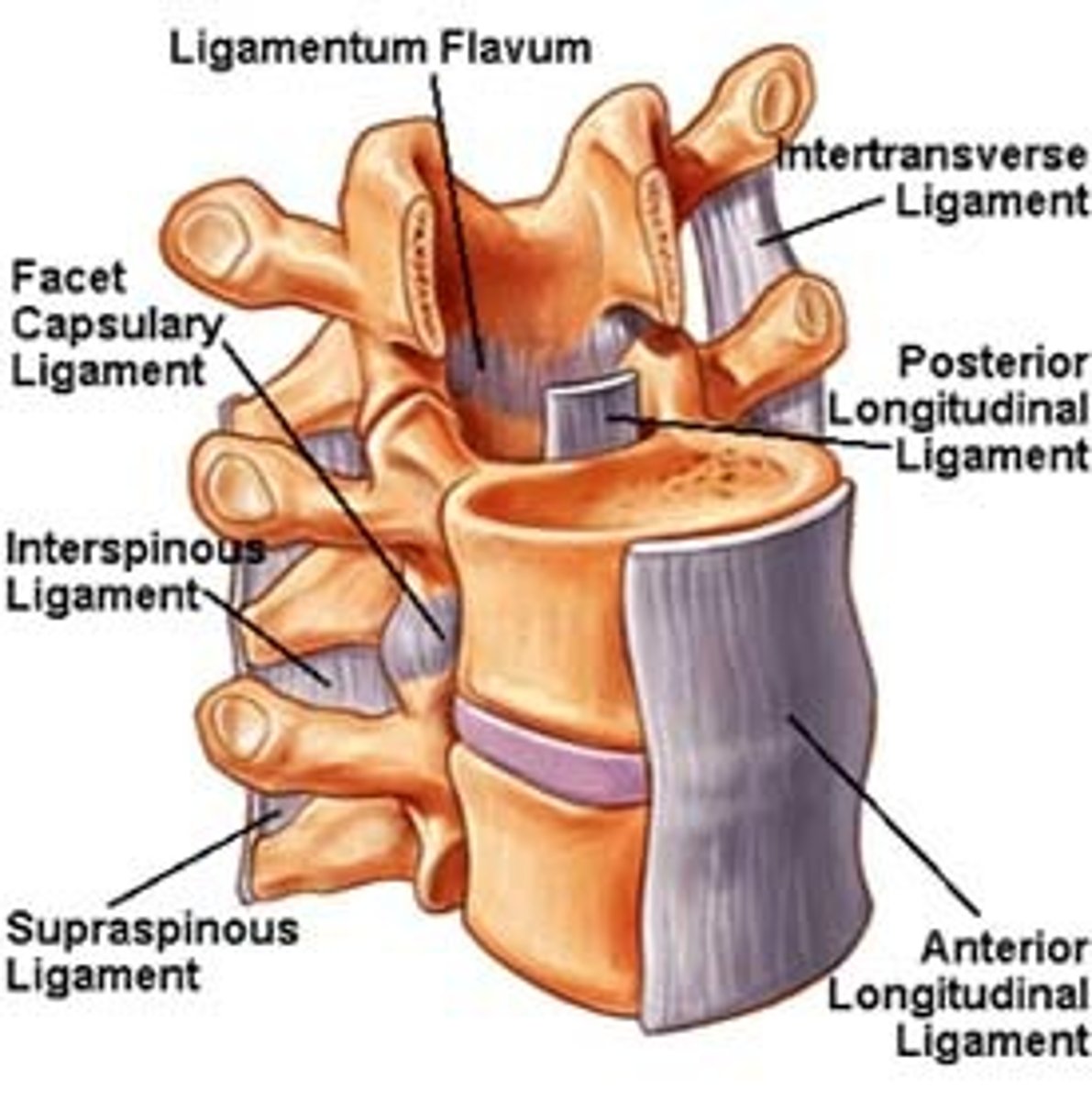
intertransverse ligament
attaches from transverse process to transverse process
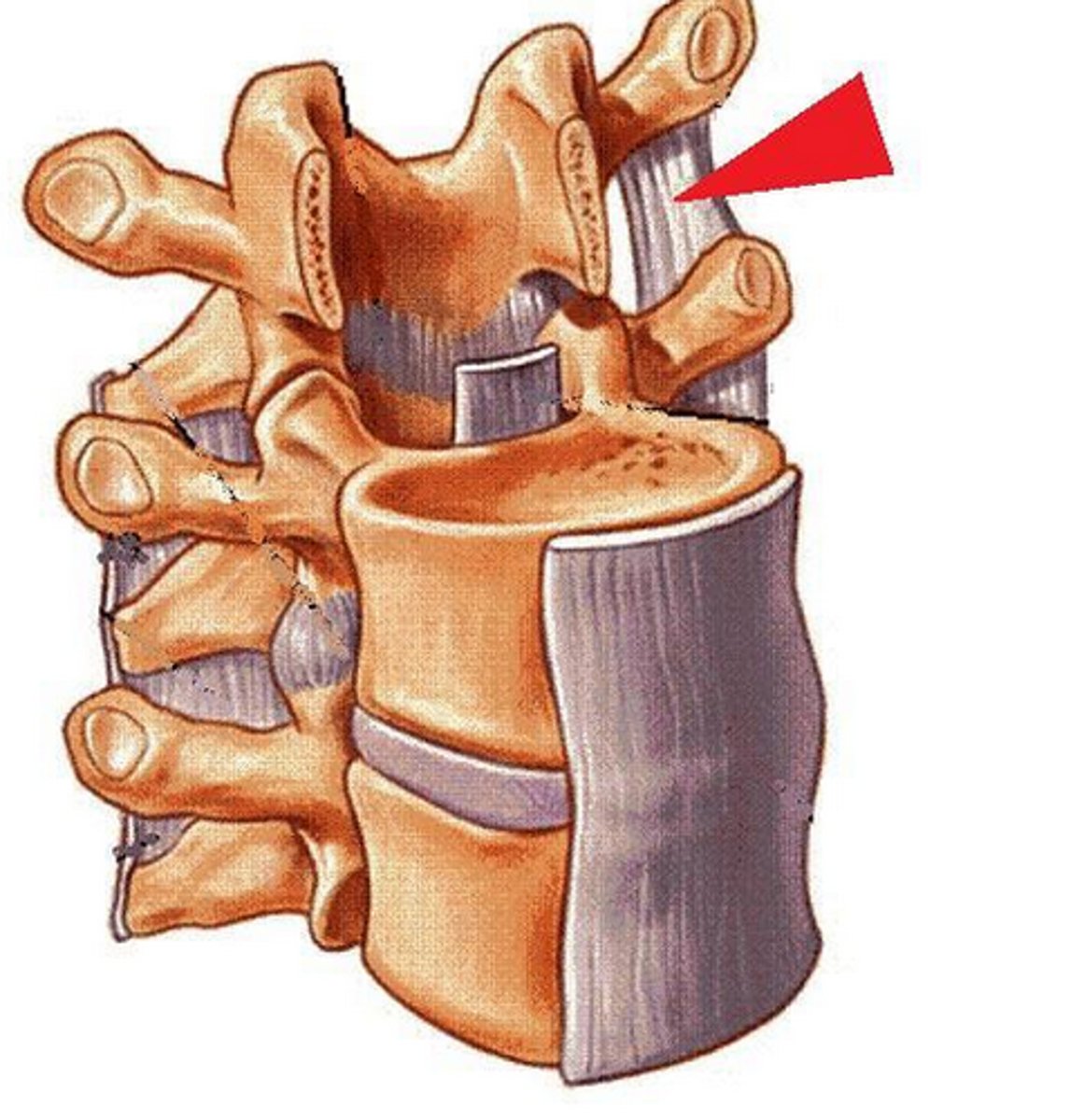
interspinous ligament
attaches from spinous process to spinous process
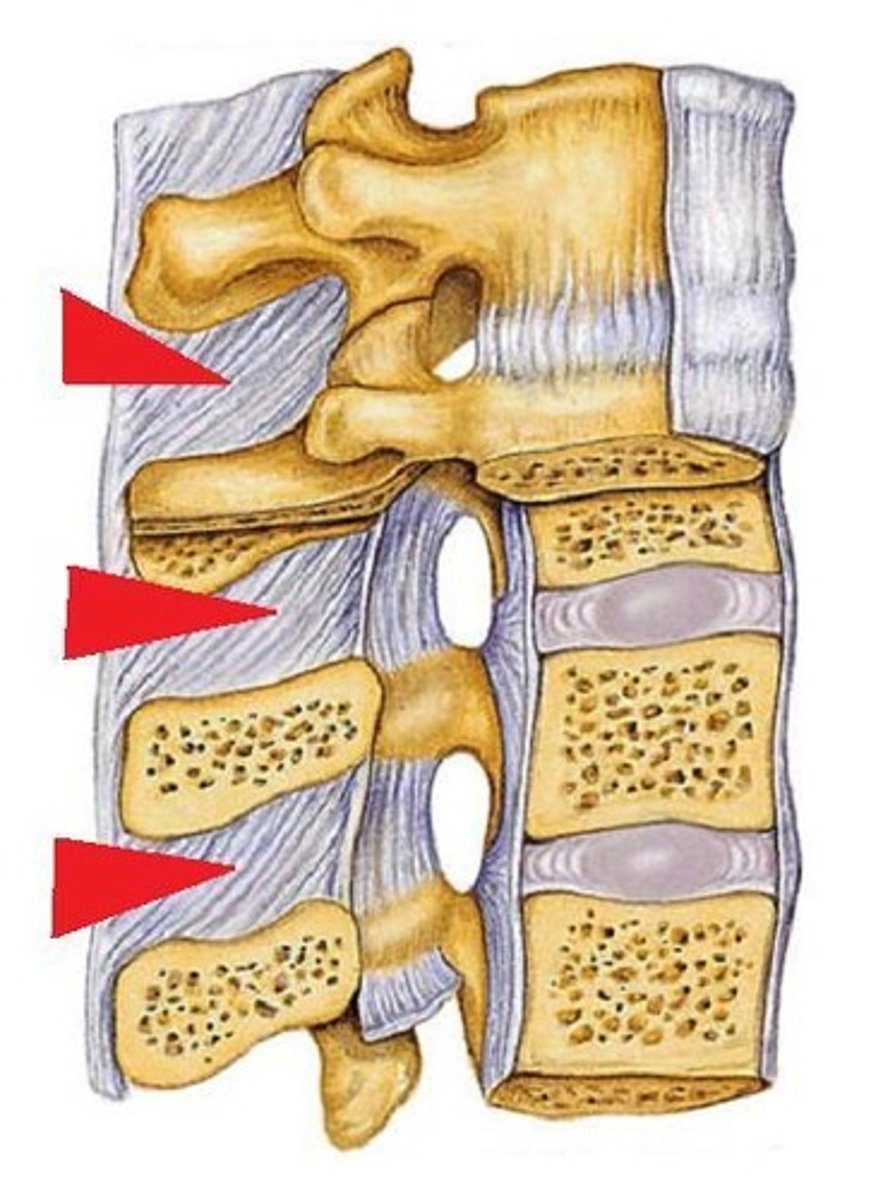
supraspinous ligament
attaches from posterior spinous process to another posterior spinous process
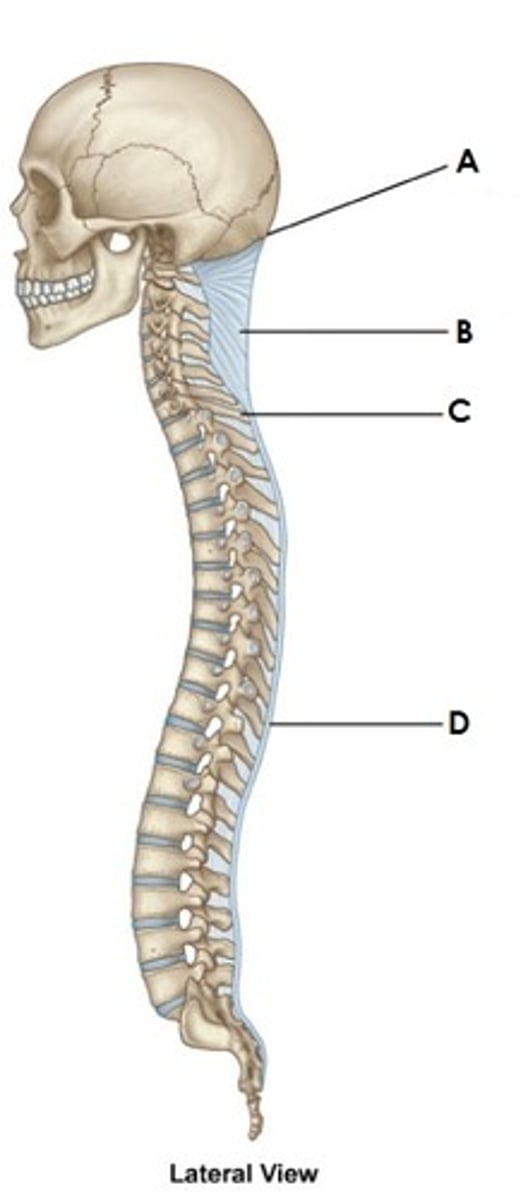
nuchal ligament
attaches from the skull to cervical spinous processes
true ribs
first 7 pairs of thoracic ribs that connect directly to the sternum via costal cartilages
false ribs
ribs 8 to 10 attach indirectly to the sternum via costal cartilages of the more superior ribs
floating ribs
ribs 11 and 12, dont attach to the sternum or to the cartilages of other ribs
appendicular skeleton
limbs
acetabulum
joint surface for femur located at fusion of ilium, ischium, and pubis
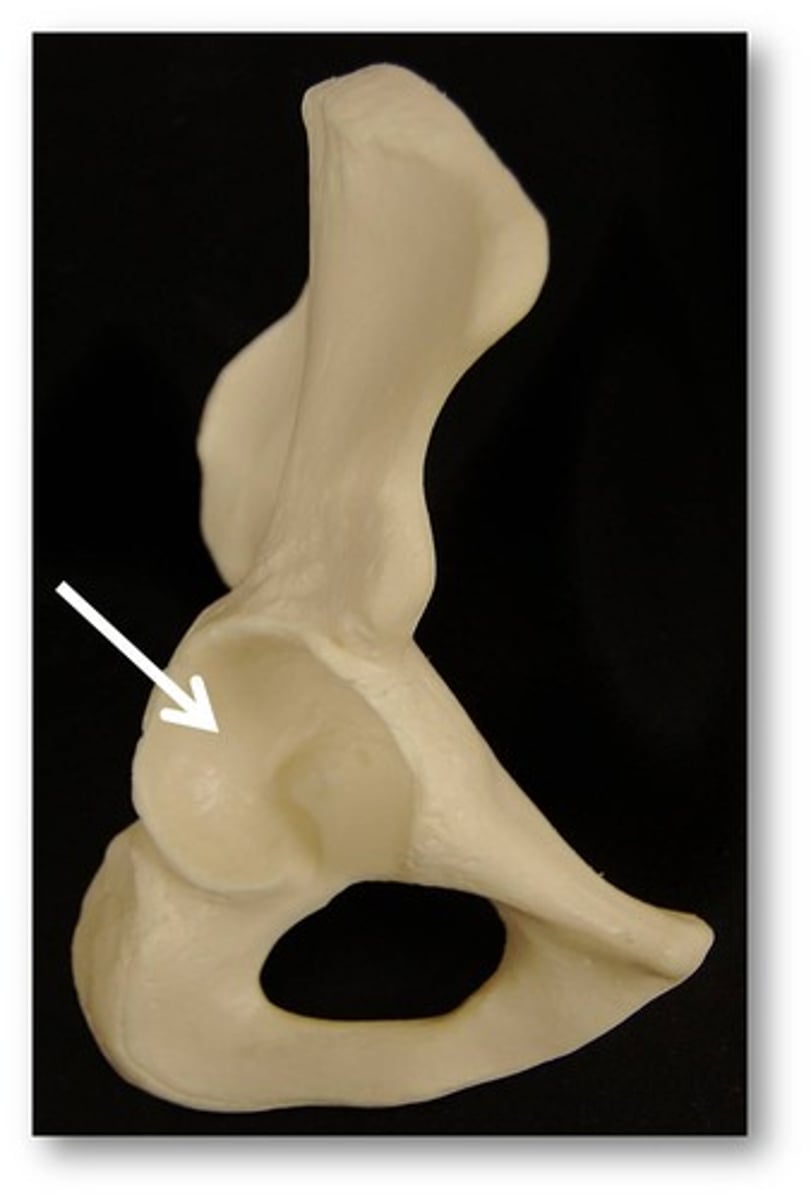
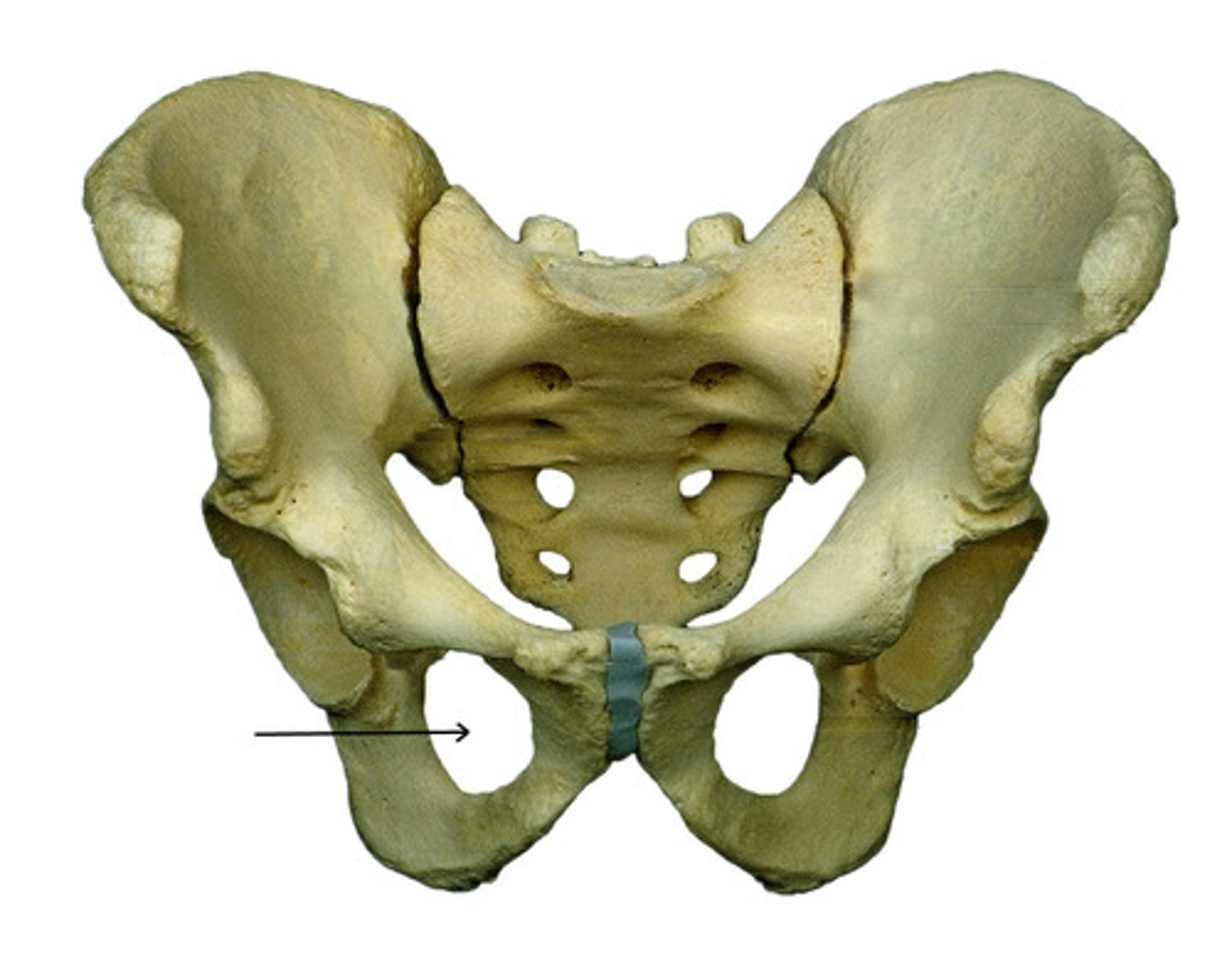
obturator foramen
located between ischium and pubis
sacroiliac attaches
sacrum <-> ilium
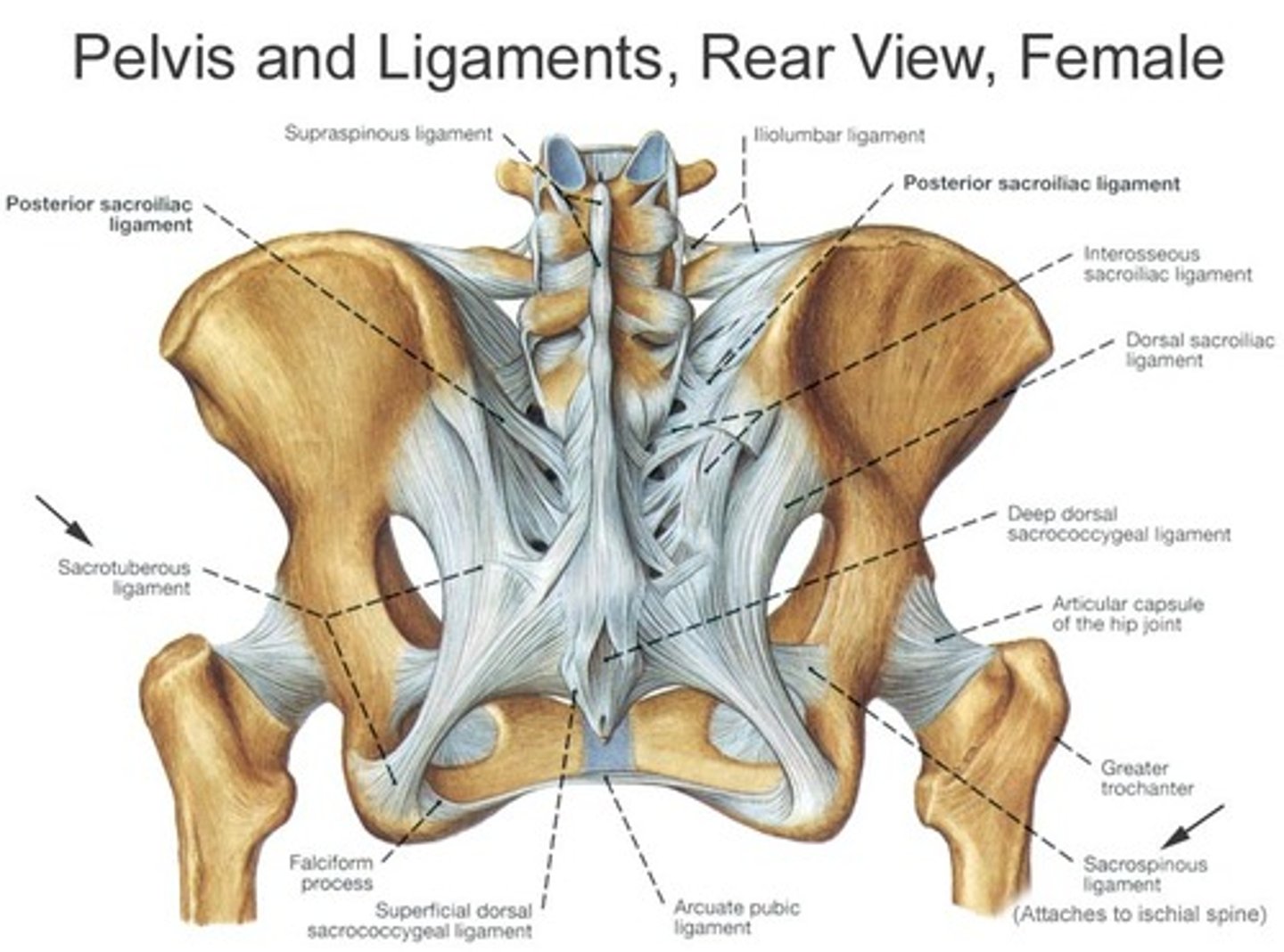
sacrotuberous attaches
sacrum <-> ischial tuberosity
forms lesser sciatic foramen by closing of the open border of the lesser sciatic notch
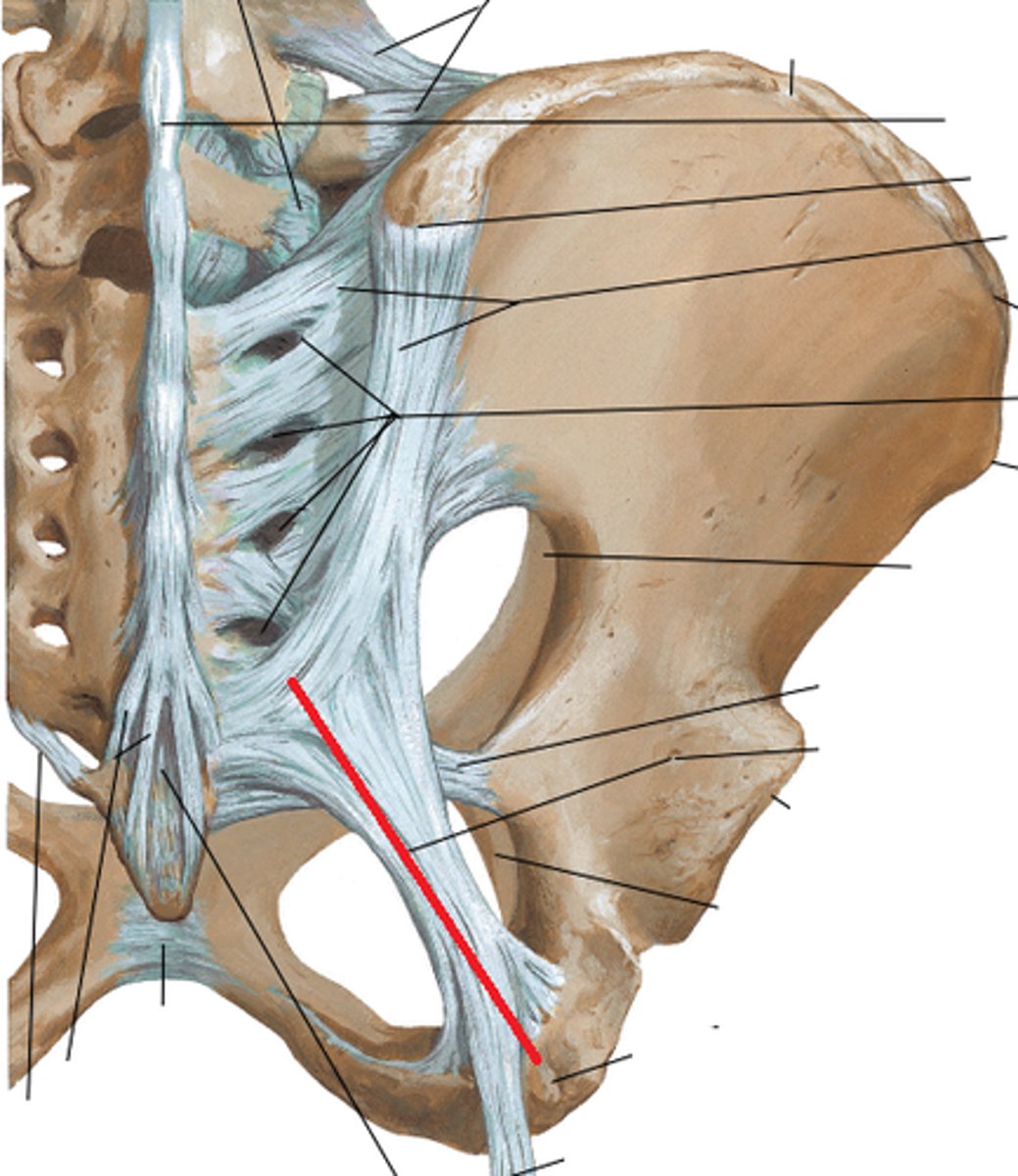
sacrospinous attaches
sacrum <-> ischial spine
form the greater sciatic foramen by closing off the open boarder of the greater sciatic notch
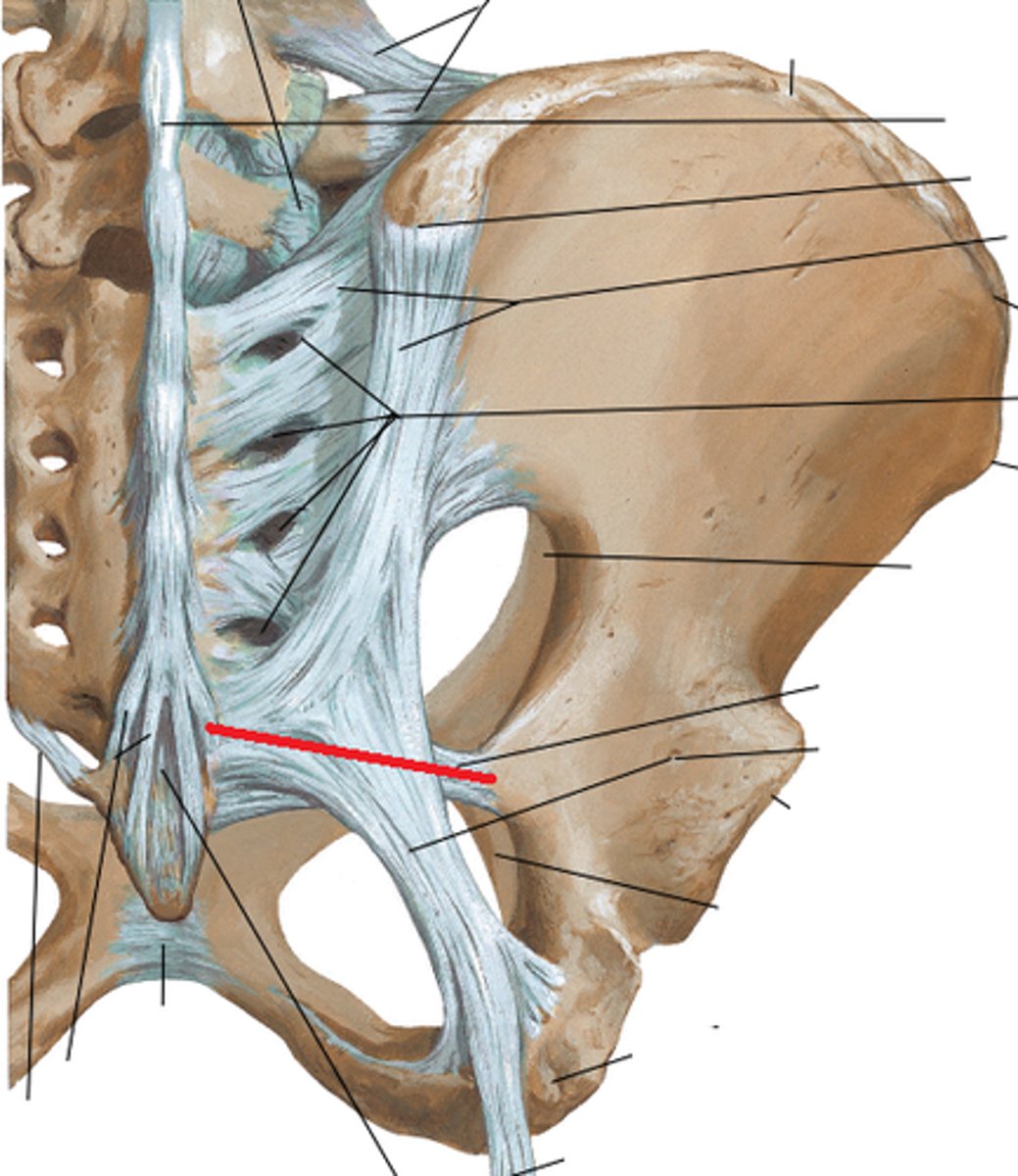
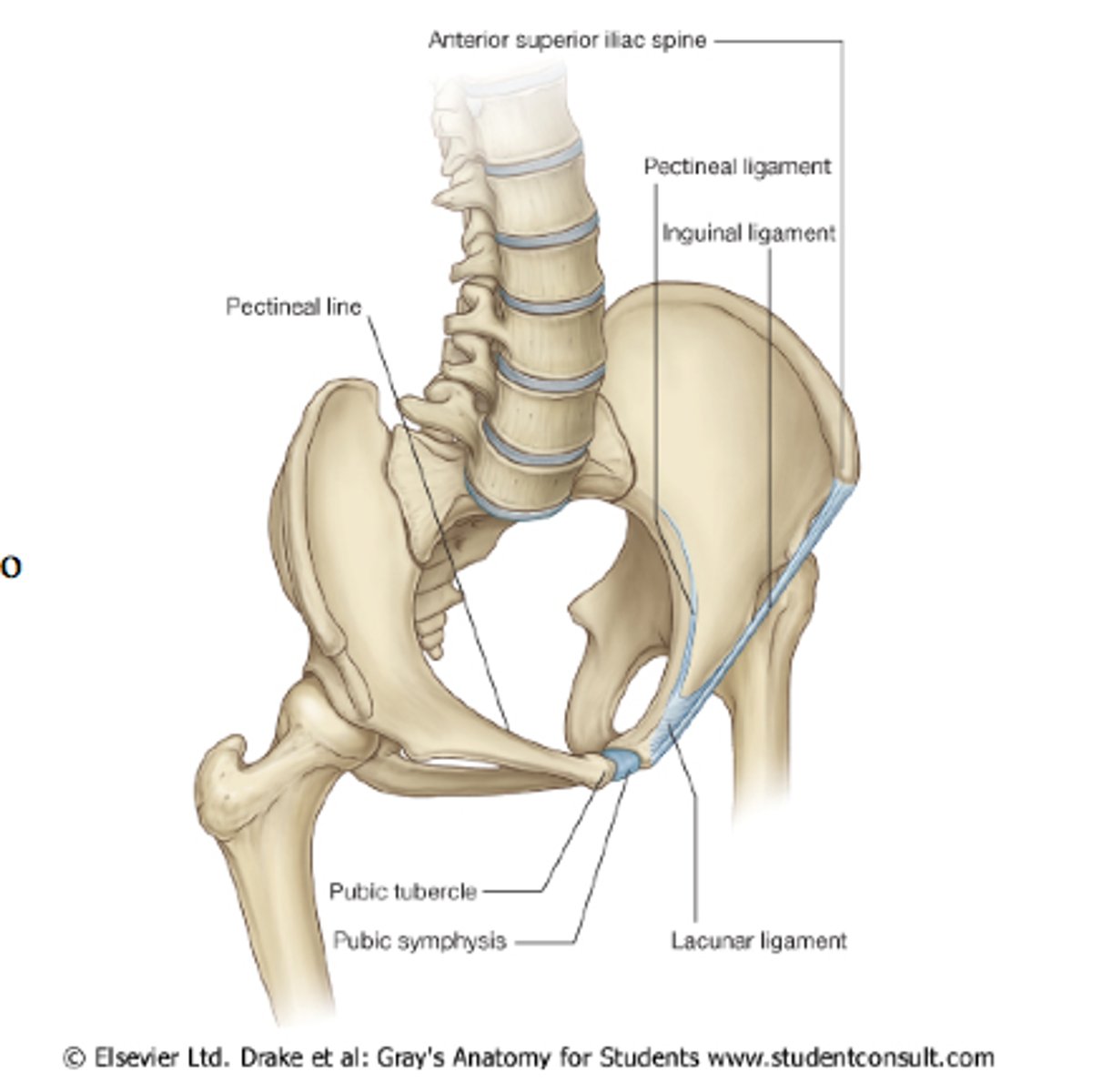
inguinal ligament attaches
anterior superior iliac spine <-> pubic tubercle
inferior tendinous boarder of an abdominal body wall muscle
extension
epaxial muscles on both sides of the vertebral column contracting pulling the trunk, neck, and head into an upright position
lateral flexion
epaxial muscles on one side of the vertebral column contract and the trunk, neck, and head are moved laterally to that same side
splenius origin
cervical and thoracic spinous processes and nuchal ligament
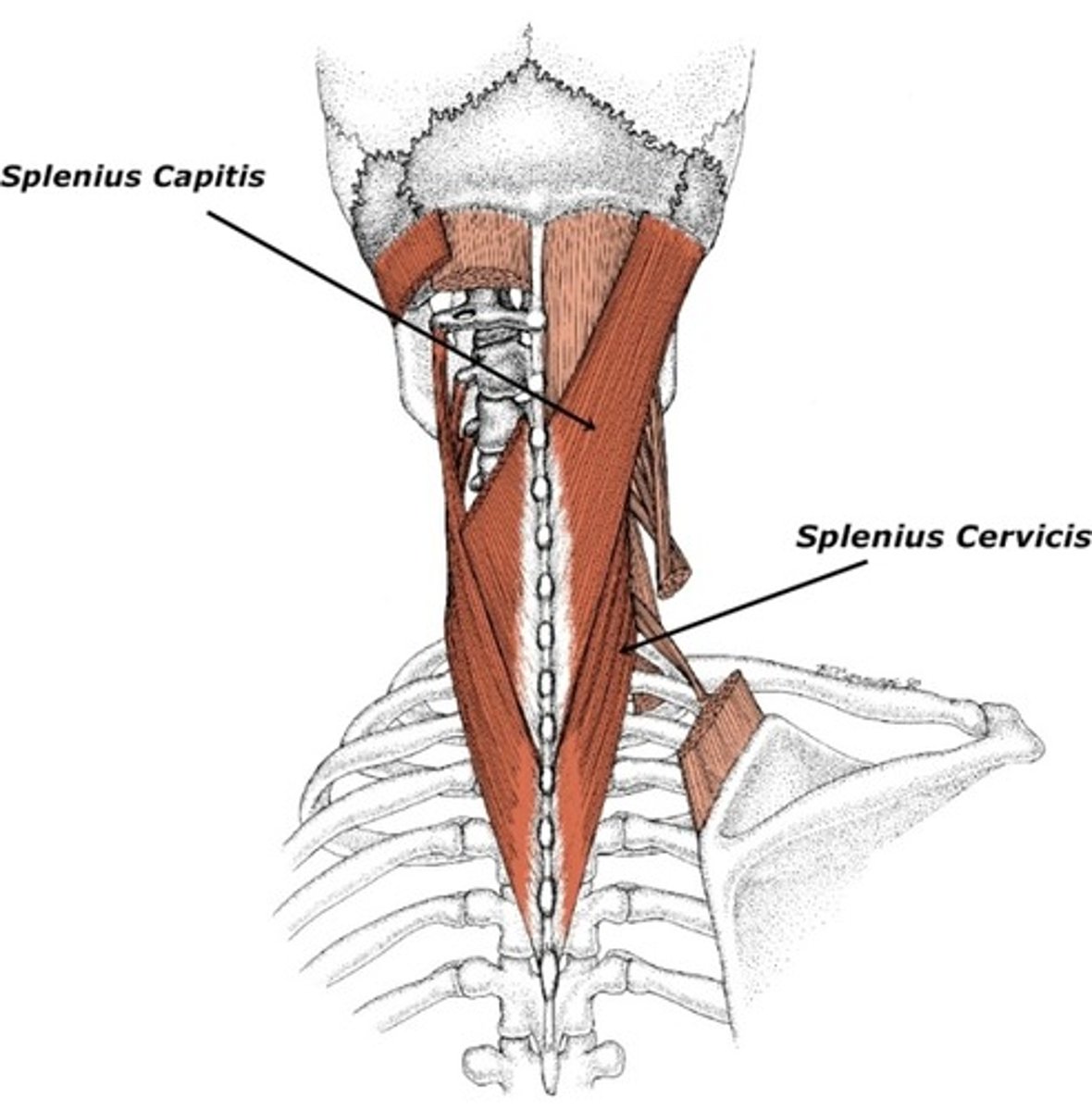
splenius insertion
cervical transverse processes, occipital bone, mastiod process
splenius action
bilateral: extend head and neck
unilateral: laterally flex and rotate head and neck
splenius innervation
cervical dorsal rami
iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis origin
posterior sacrum, iliac crest, sacrospinous ligament, and spinous processes of lumbar and sacral vertebrae
iliocostalis insertion
cervical transverse processes and angles of the ribs
iliocostalis and spinalis action
bilateral: extend vertebral column
unilateral: laterally flex vertebral column
iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis innervation
dorsal rami (all levels)
longissimus insertion
cevical and thoracic transverse processes and mastoid process
longissimus action
bilateral: extend vertebral column and head
unilateral: laterally flex vertebral column and head
spinalis insertion
cervical and thoracic spinous processes
semispinalis origin
transverse processes of cervical and thoracic vertebra
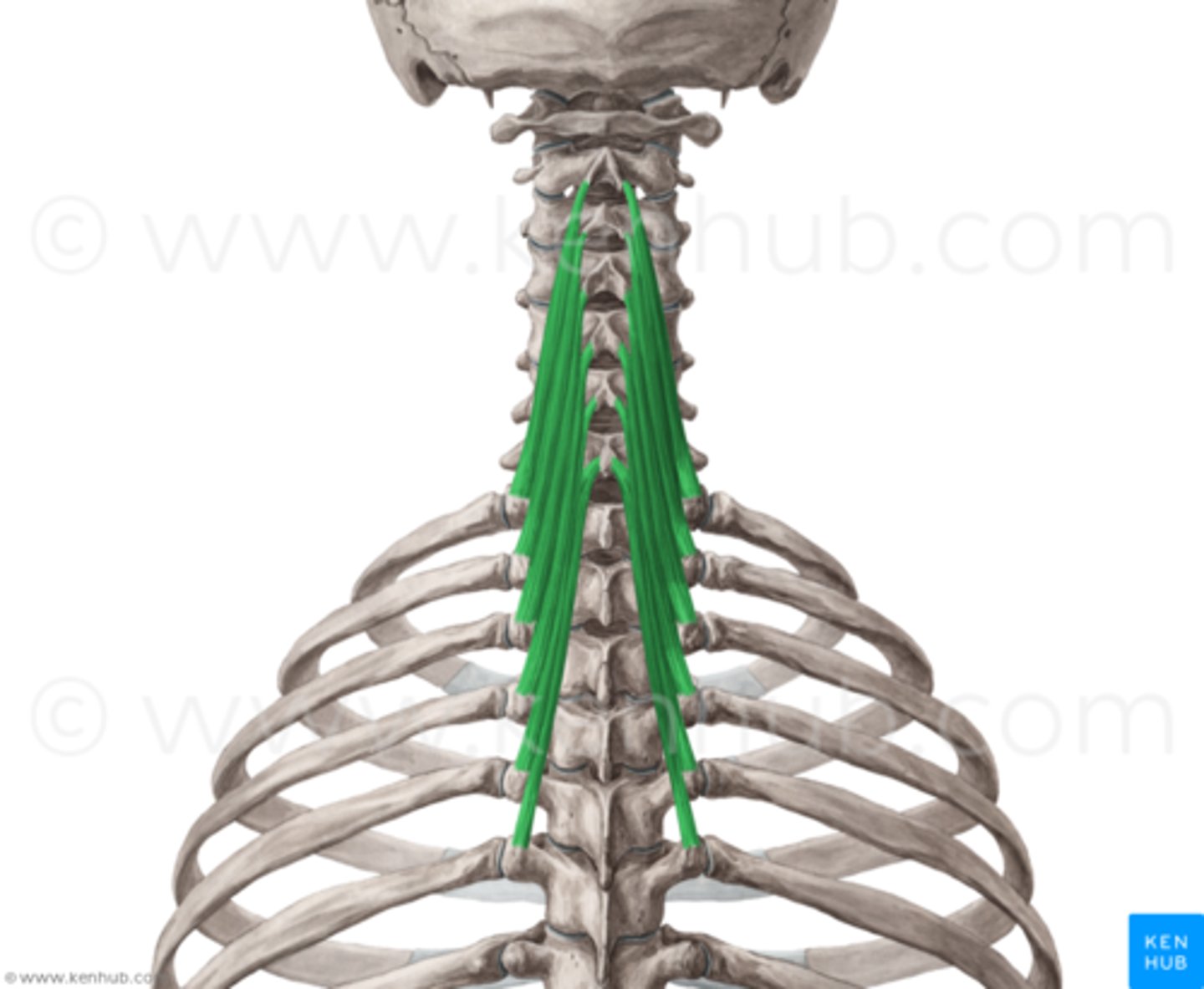
semispinalis insertion
spinous processes 6-7 segments superior to origin and occipital bone
semispinalis action
bilateral: extend vertebral column and head
unilateral: laterally flex vertebral column and head
semispinalis inervation
cervical and thoracic dorsal rami
multifidus origin
tansverse processes of all vertebrae
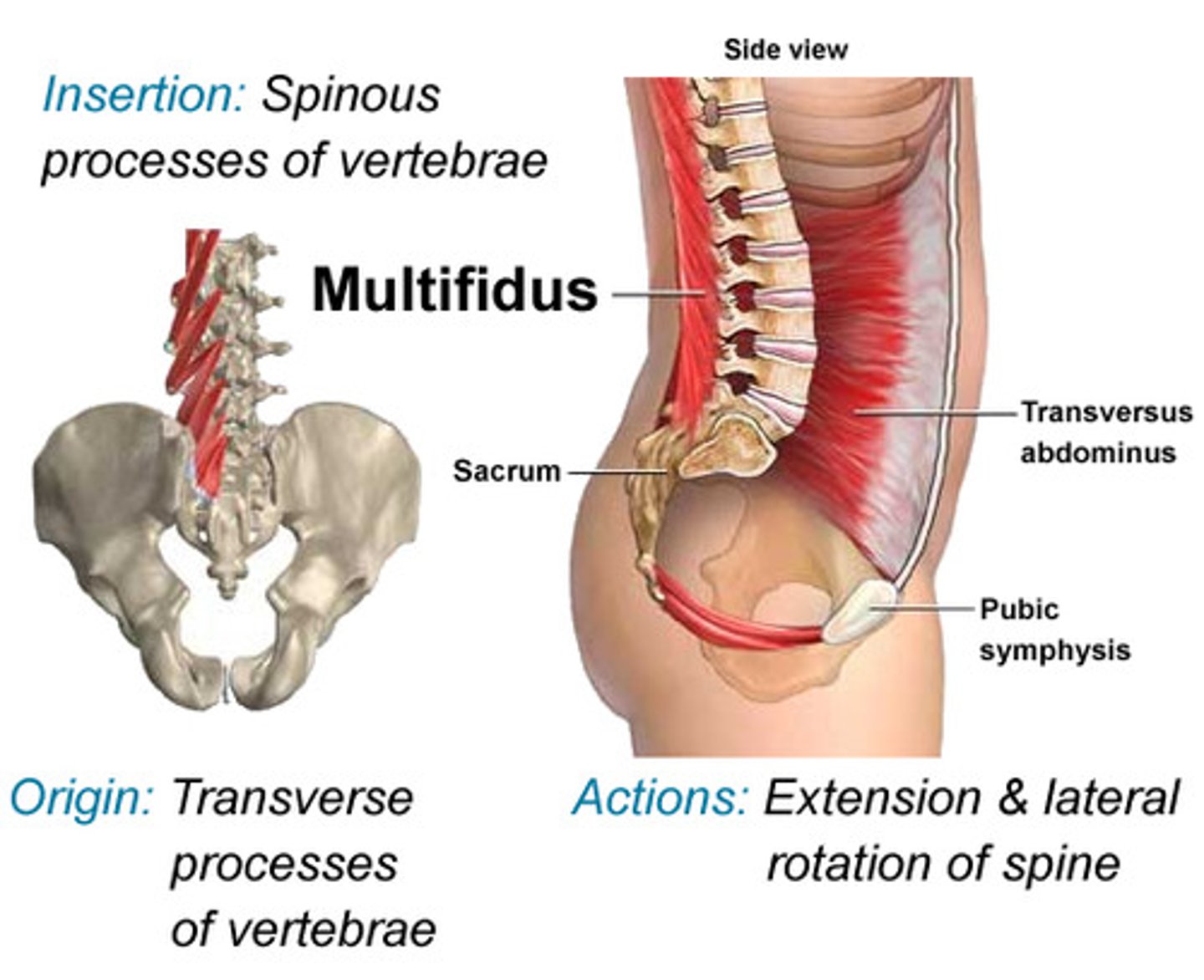
mutifidus insertion
spinous processes 2-4 segments superior to origin
multifidus action
bilateral: extend vertebral column
unilateral: laterally flex and rotate vertebral column
multifidus innervation
dorsal rami (all levels)
external intercostal origin and insertion
lower margin of the superior rib to upper margin of the inferior rib (obliquely downward from vertebra towards sternum)
external intercostal action
elevates ribs during inspiration; stabilizes thoracic wall
external, internal, innermost intercostal and tranversis thoracis innervation
intercostal nn. (thoracic ventral rami)
internal intercostal and innermost intercostal origin
lower margin of superior rib to upper margin of inferior rib (obliquely downward from sternum towards vertebra)
internal and innermost innercostal action
depresses ribs during expiration; stabilizes thoracic wall
tranversus thoracis origin
body and xiphoid process of sternum (internal surface)
transversus thoracis insertion
costal cartilages 2-6 (internal surface)
transversus thoracis action
depresses ribs during expiration
rectus sheath
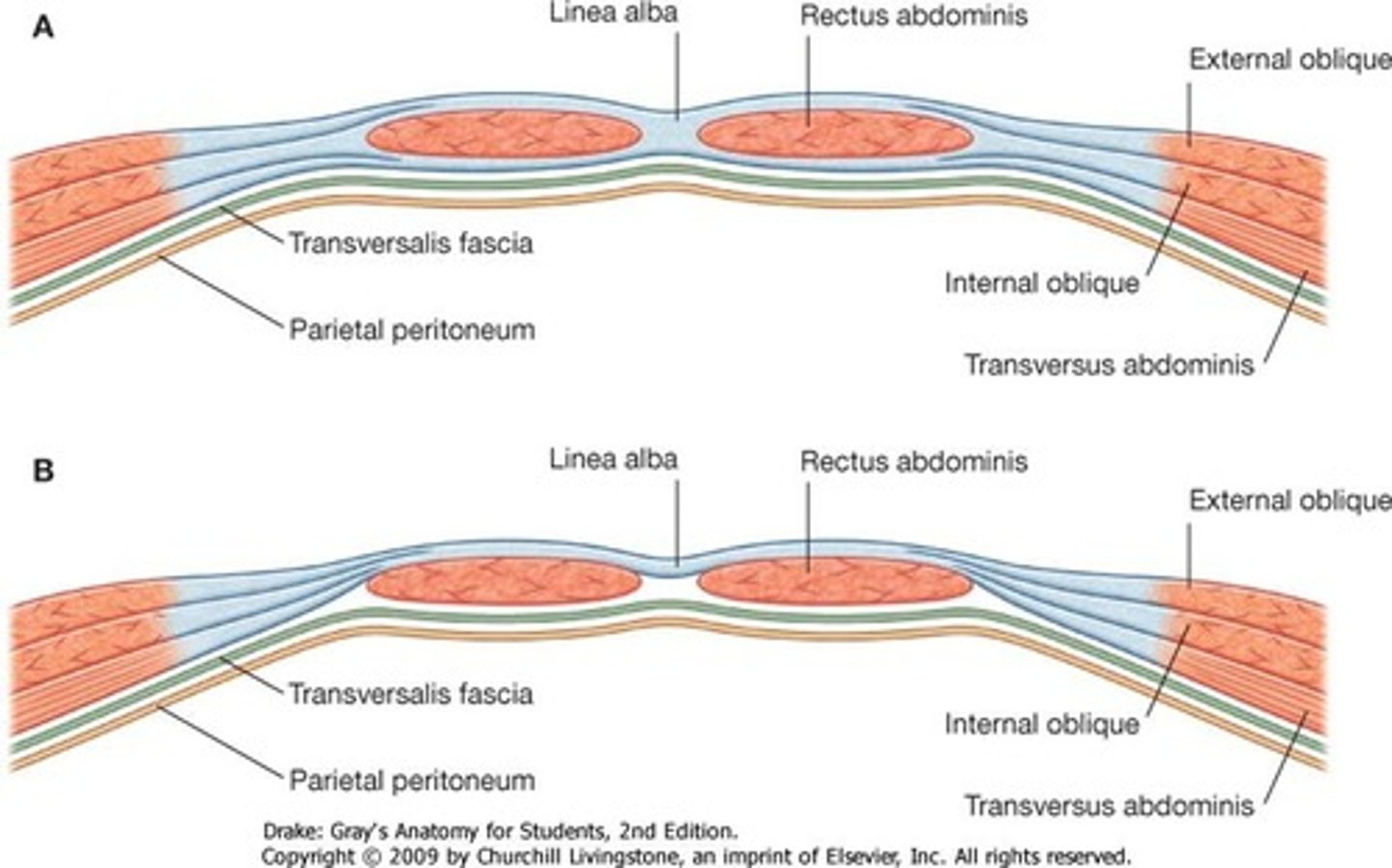
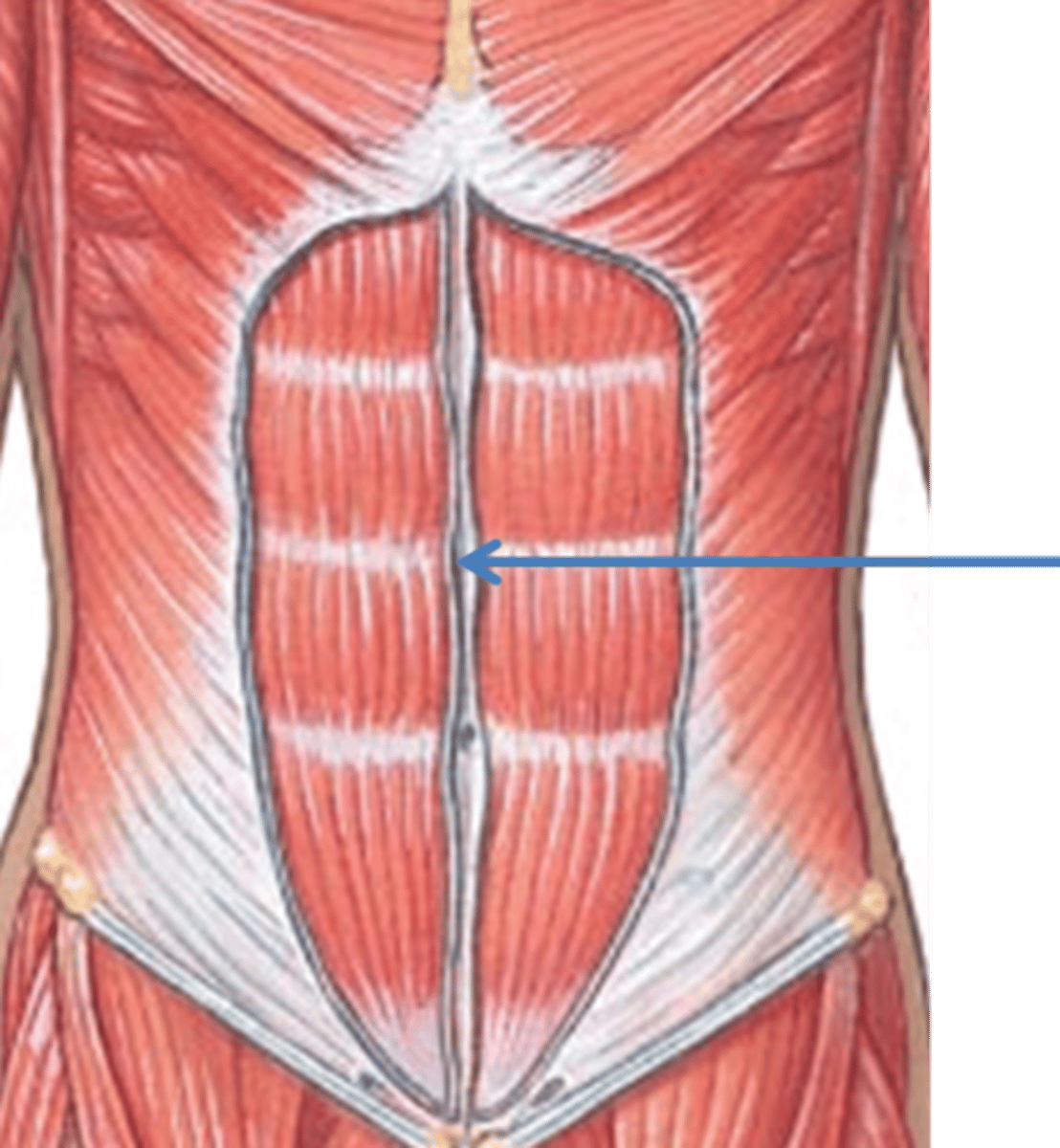
linea alba
white line down center of abdomen
external oblique origin
outer surfaces of lower ribs
external oblique insertion
linea alba, pubic tubercle, iliac crest
external and internal oblique action
unilateral: laterally flexes and rotates trunk
bilateral: flexes trunk and compresses abdomen
external oblique innervation
inferior thoracic ventral rami
internal oblique origin
thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament
internal oblique insertion
lower ribs and linea alba
internal oblique and transversus abdominis innervation
inferior thoracic and L1 ventral rami
transversus abdominis origin
costal cartilages of lower ribs, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament
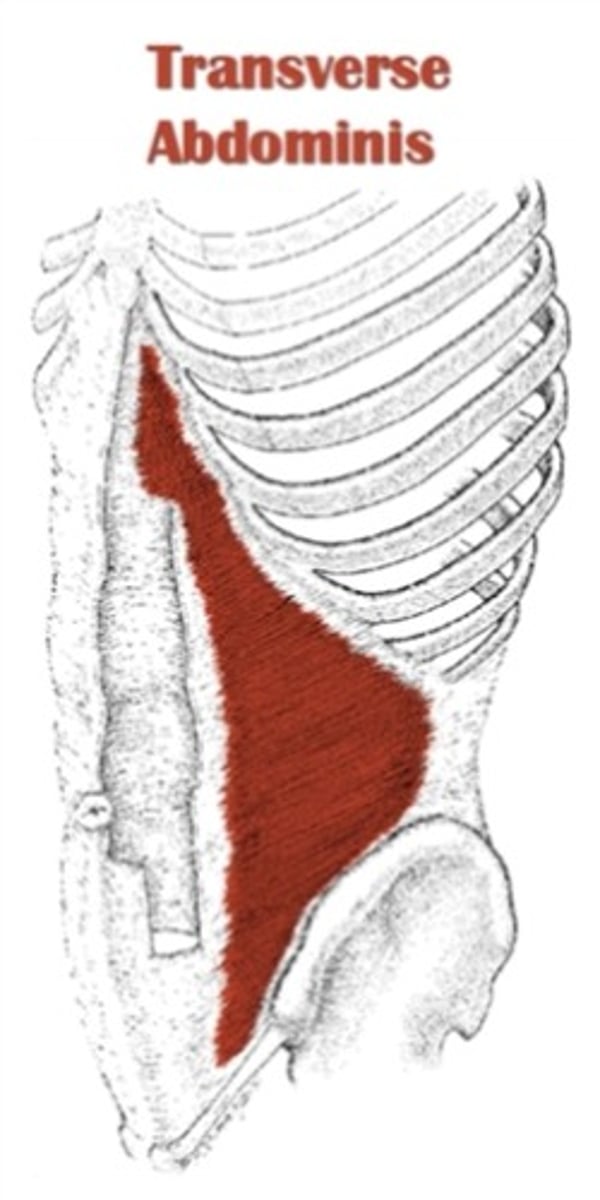
transversus abdominis insertion
linea alba and pubic bone
transversus abdominis action
unilateral: rotate trunk to same side
bilateral: compress abdomen and support viscera
rectus abdominis origin
pubic tubercle
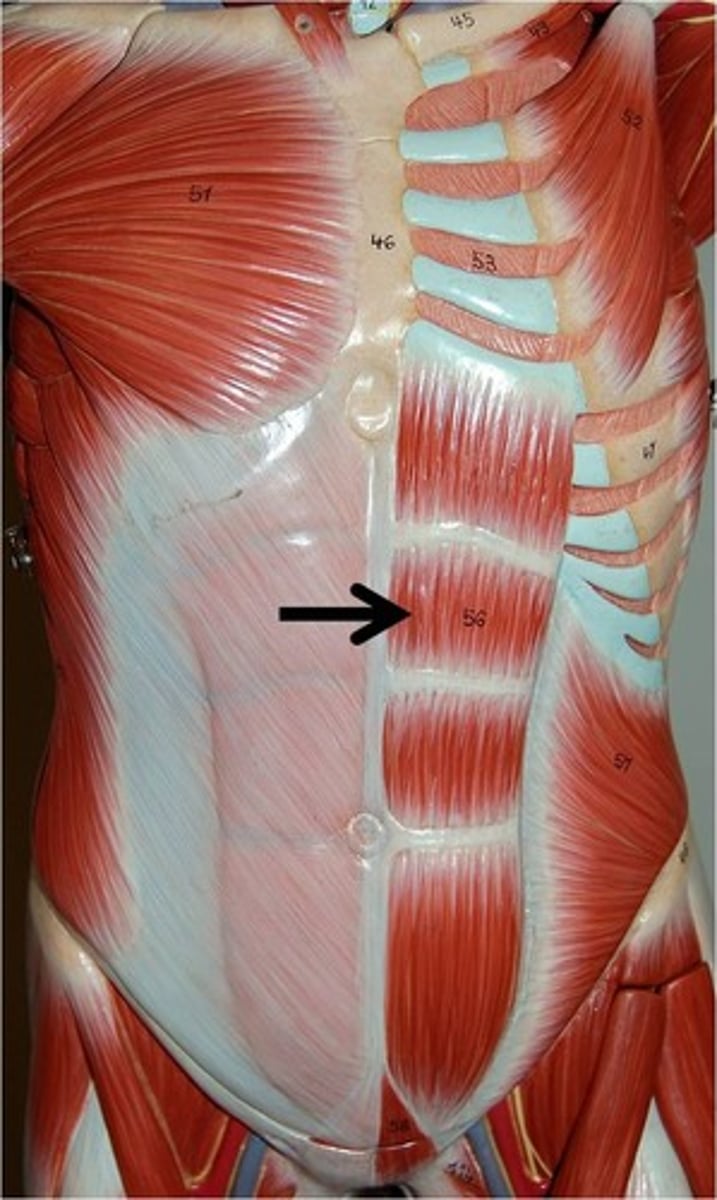
rectus abdominis insertion
lower costal cartilages and xiphoid process
rectus abdominis action
flex trunk and compresses abdomen
rectus abdominis innervation
inferior thoracic ventral rami