Types of Tissues - Anatomy and Physiology
Epithelial tissue
sheets of cells that cover a bodys surface or lines a body cavity; cells fit so close to make continuous sheets; contains nerves but no blood vessels; quick regeneration
Simple
one layer
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Epithelial tissue
sheets of cells that cover a bodys surface or lines a body cavity; cells fit so close to make continuous sheets; contains nerves but no blood vessels; quick regeneration
Simple
one layer
Stratified
more than one layer
squamous
flat shape
cuboidal
square shape
columnar
long shape
Simple squamous epithelial
allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration sites where protection is not important. secretes lubricating substances in serosae
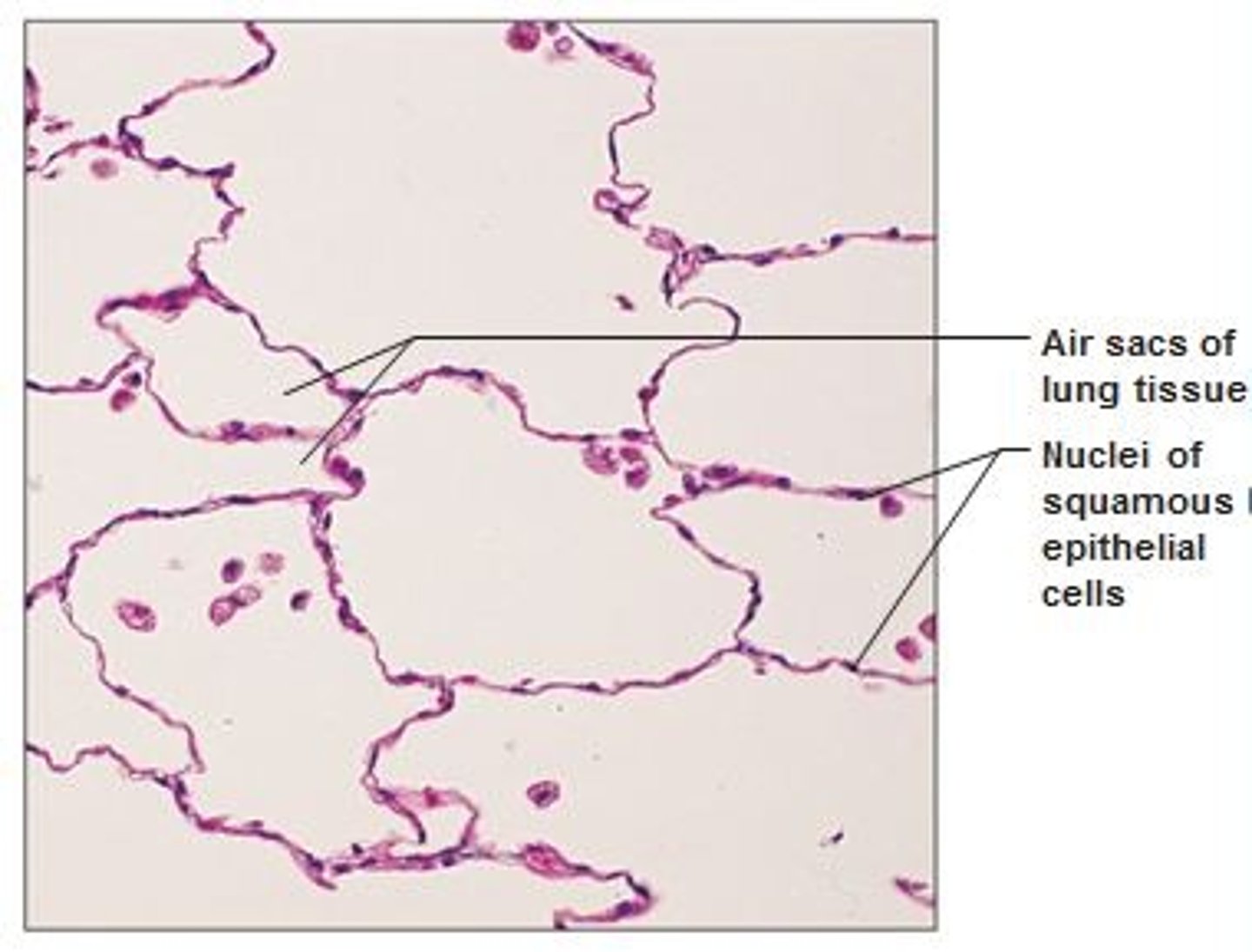
simple squamous epithelial location
kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of hear, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lining of ventral body cavity
simple cuboidal epithelial
secretion and absorption
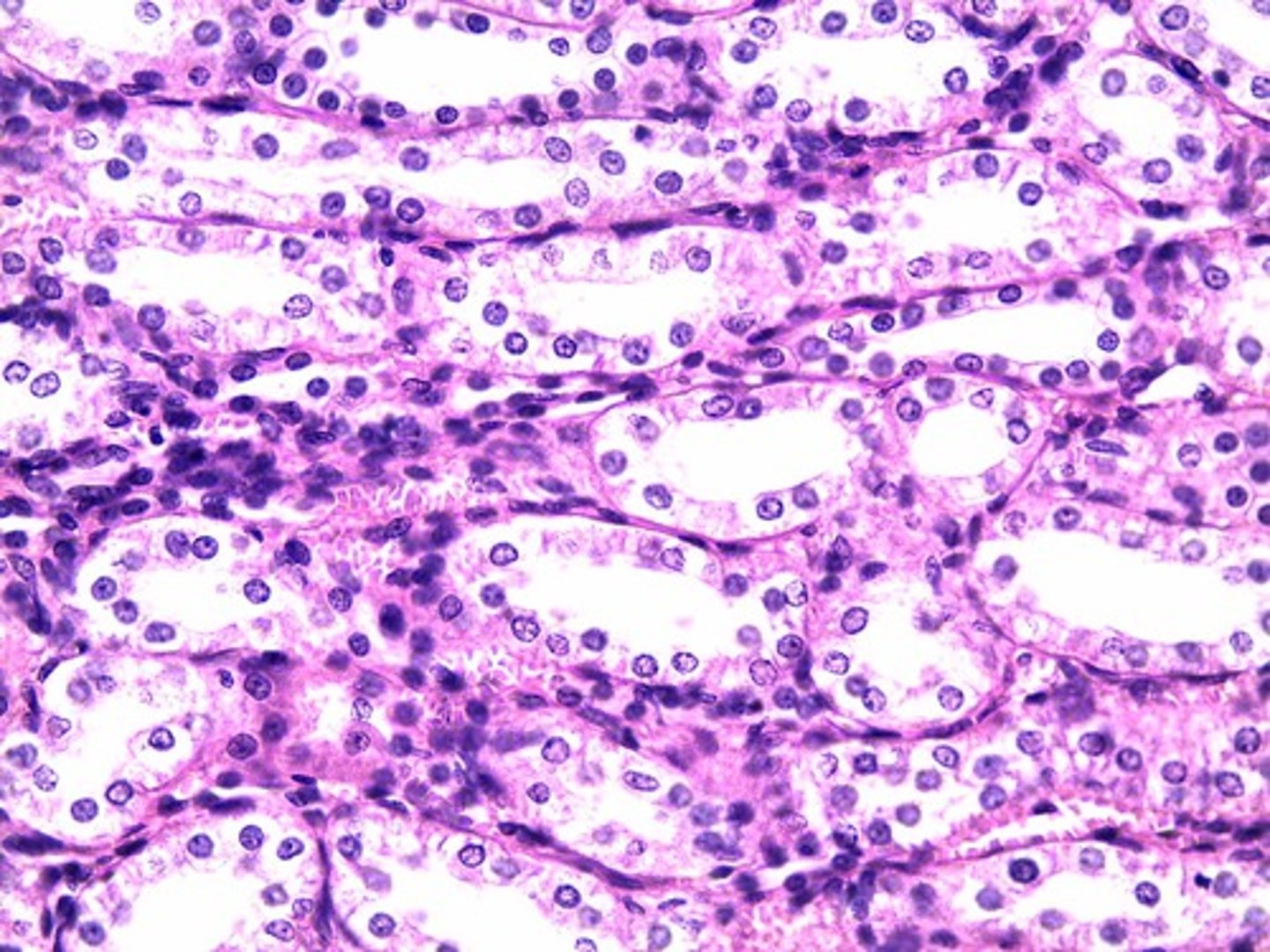
simple cuboidal epithelial location
Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands; ovary surface
simple columnar epithelial
absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliary action
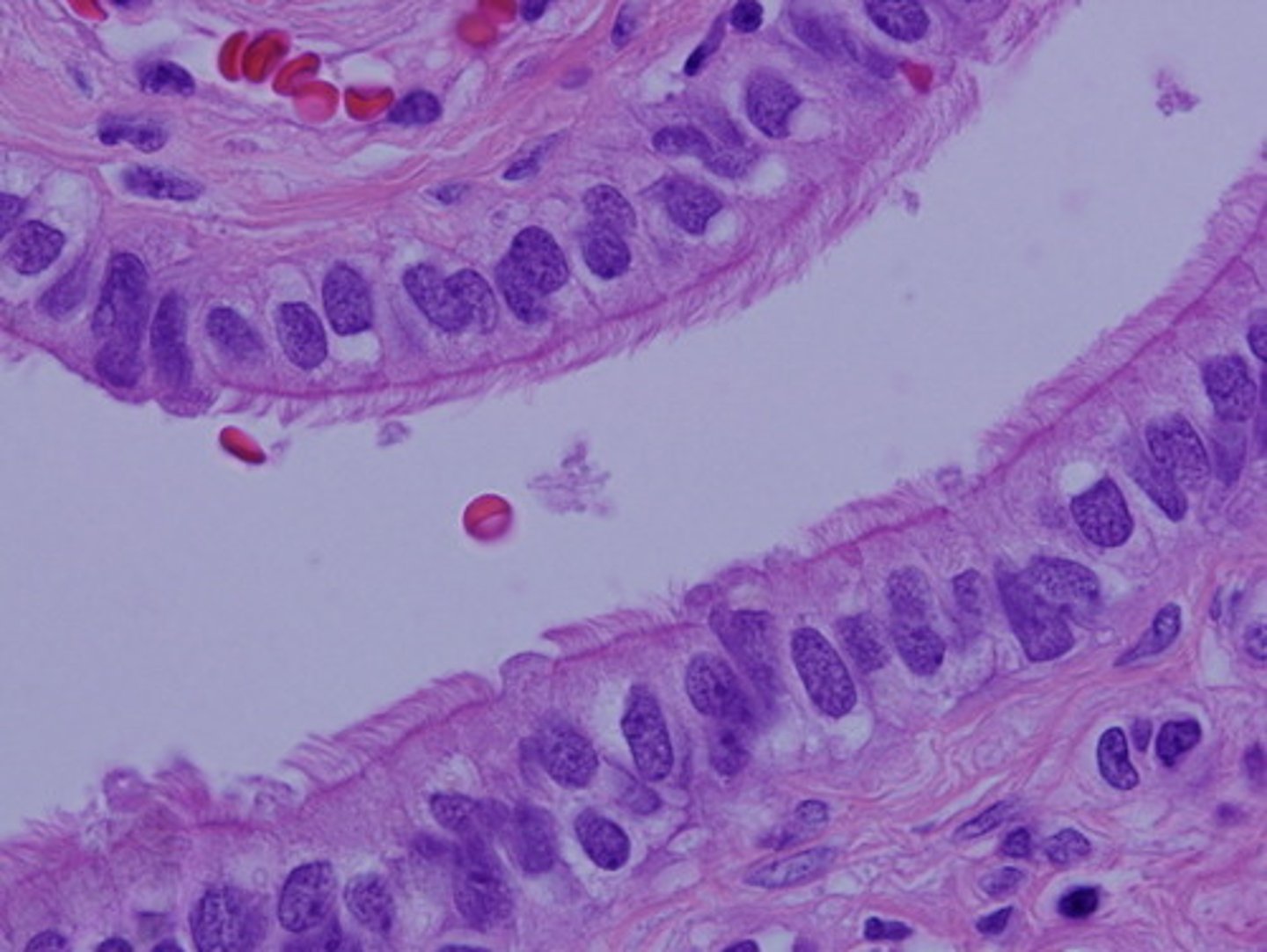
simple columnar epithelial location
nonciliated: digestive tract lining, gallbladder ans excretory ducts
ciliated: small bronchi, uterine tube, and some regions of the uterus
stratified squamous epithelial
protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
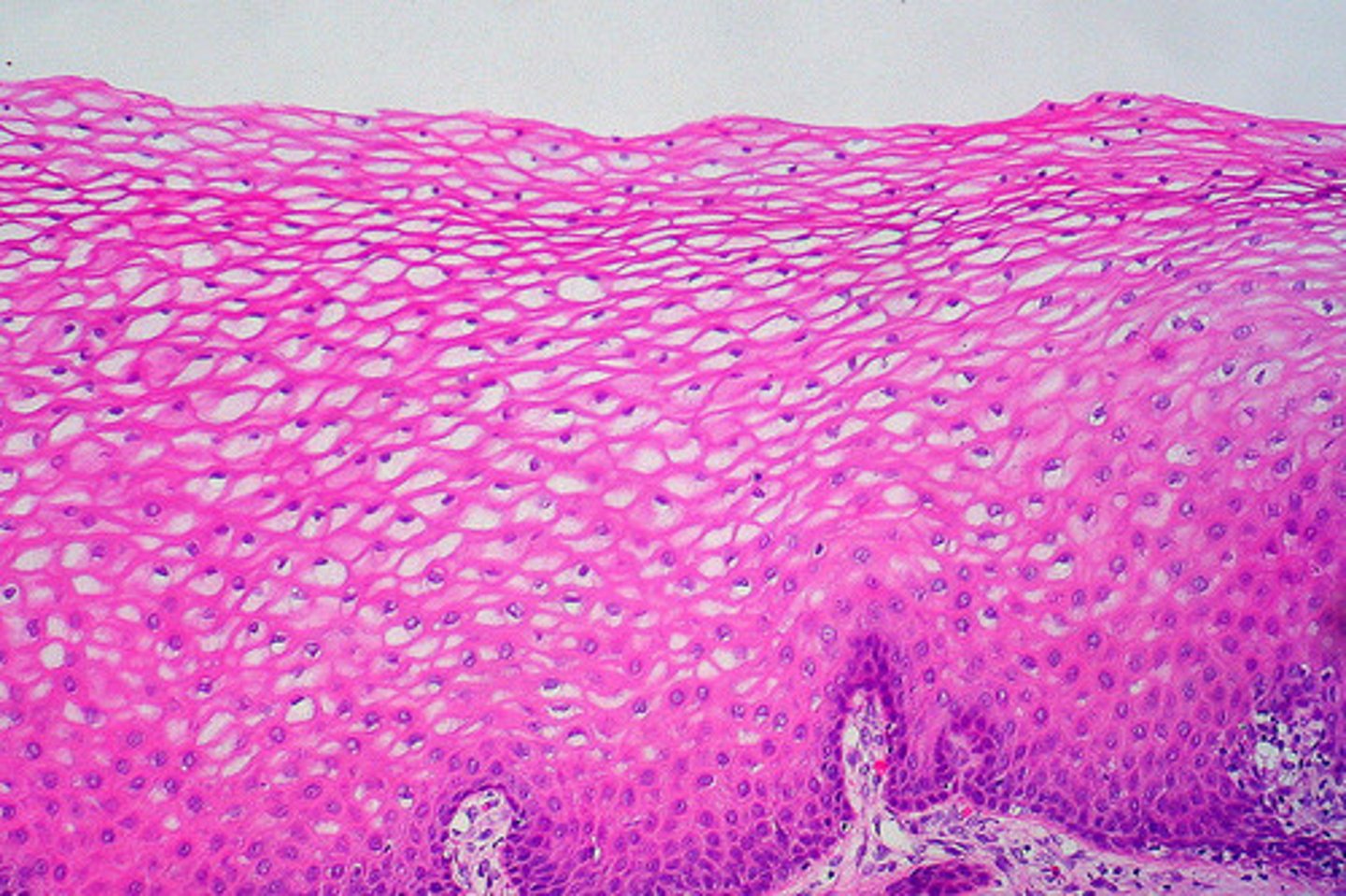
stratified squamous epithelial location
nonkeratinized: forms moist linings of esophagus, mouth and vagina. keratinized: forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane
pseudostratified epithelial
secretion, particularly of mucus, propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
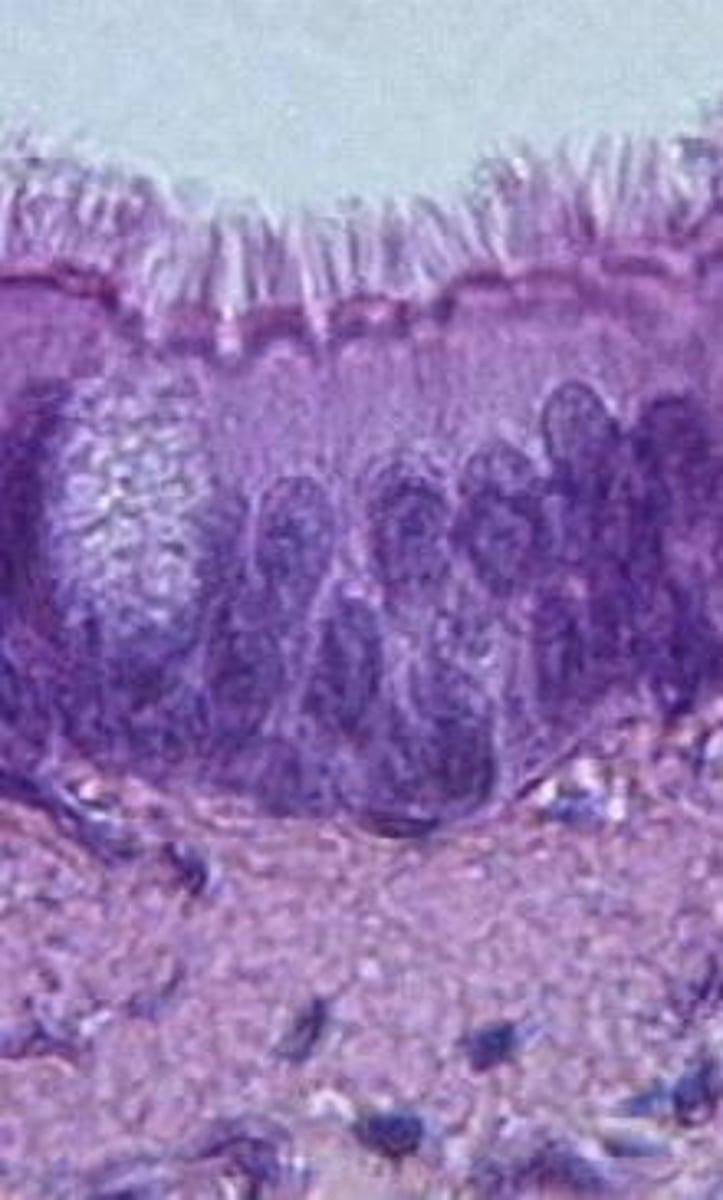
pseudostratified epithelial location
nonciliated: male sperm carrying ducts, ducts of large glands. ciliated: lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract
transitional epithelial
stretches readily and permits dissension or urinary organs by contained urine
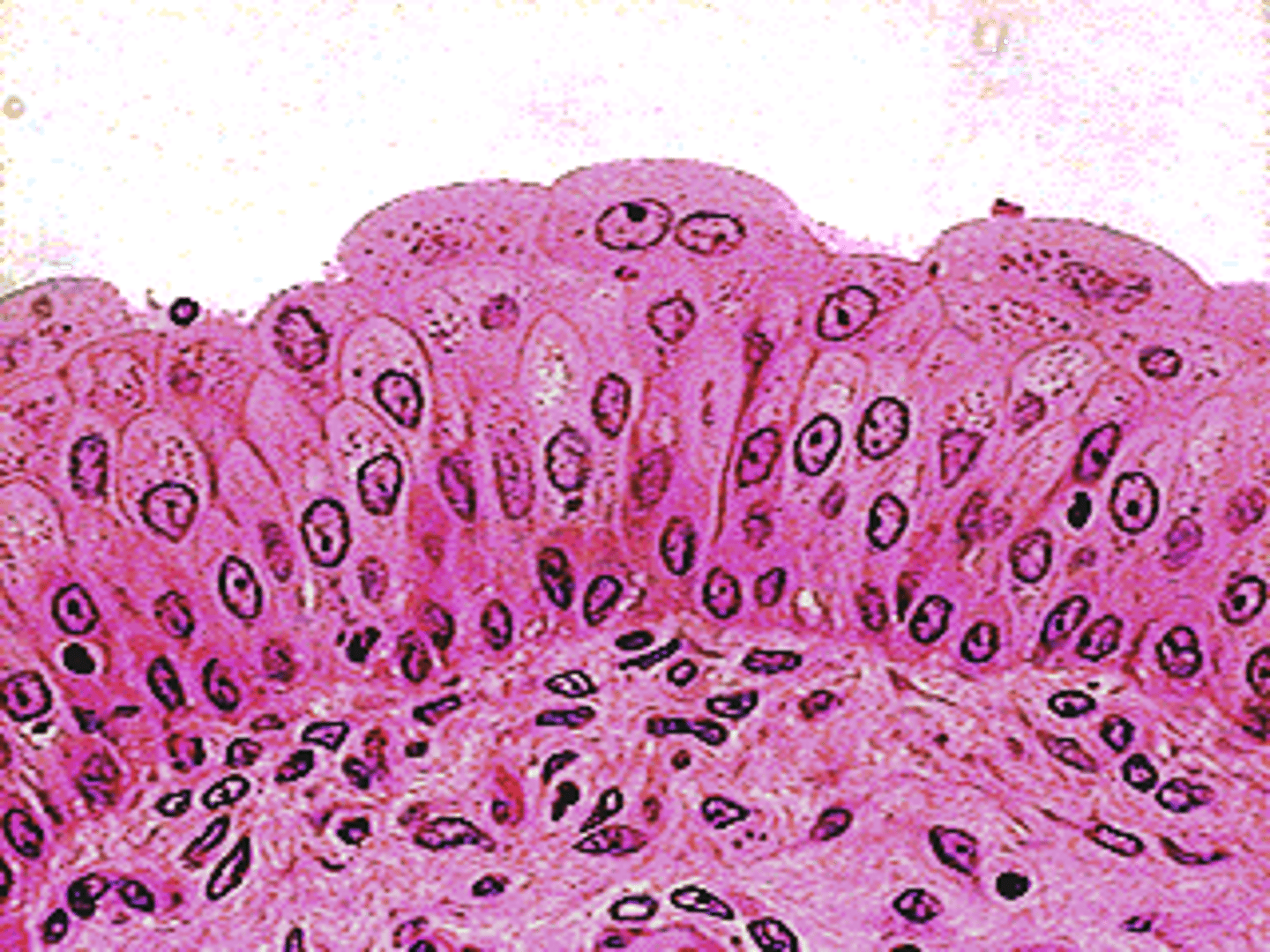
transitional epithelial location
lines the ureters, bladder, and part of the urethra
nervous tissue
transmits messages throughout the body via electrical impulses
neurons
transmit electrical signals from the sensory receptors and to effectors ( muscles and glands) which control their activity
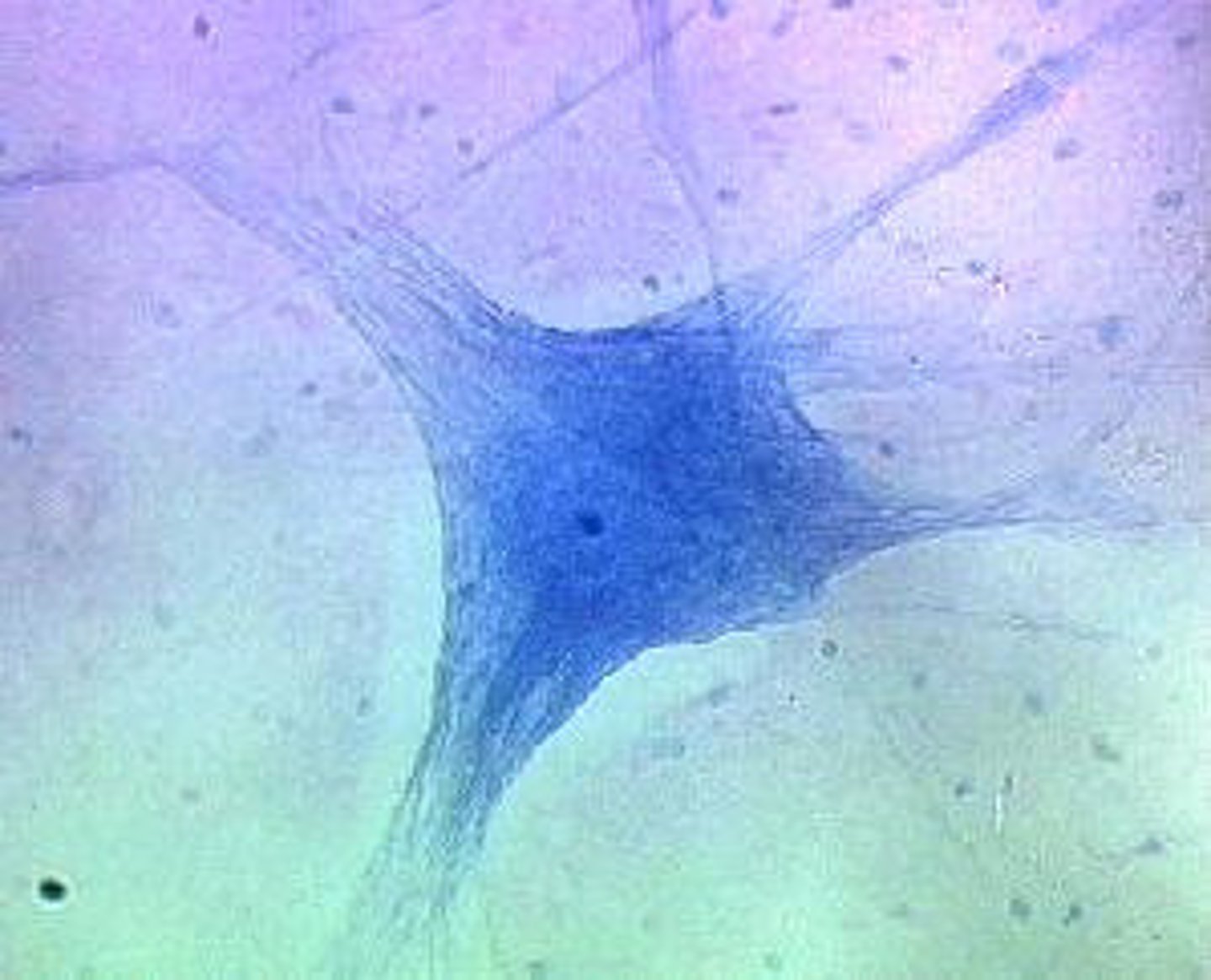
neurons location
brain, spinal cord, and nerves
neuroglia (peripheral)
satelite cells and schwann cells
neuroglia (central)
oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells
connective tissue
most abundant and widely distributed tissue in various degrees
connective tissue functions
binding and support, protection, insulation, transportation
Loose connective tissue, areolar
wraps and cushions organs; its macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid
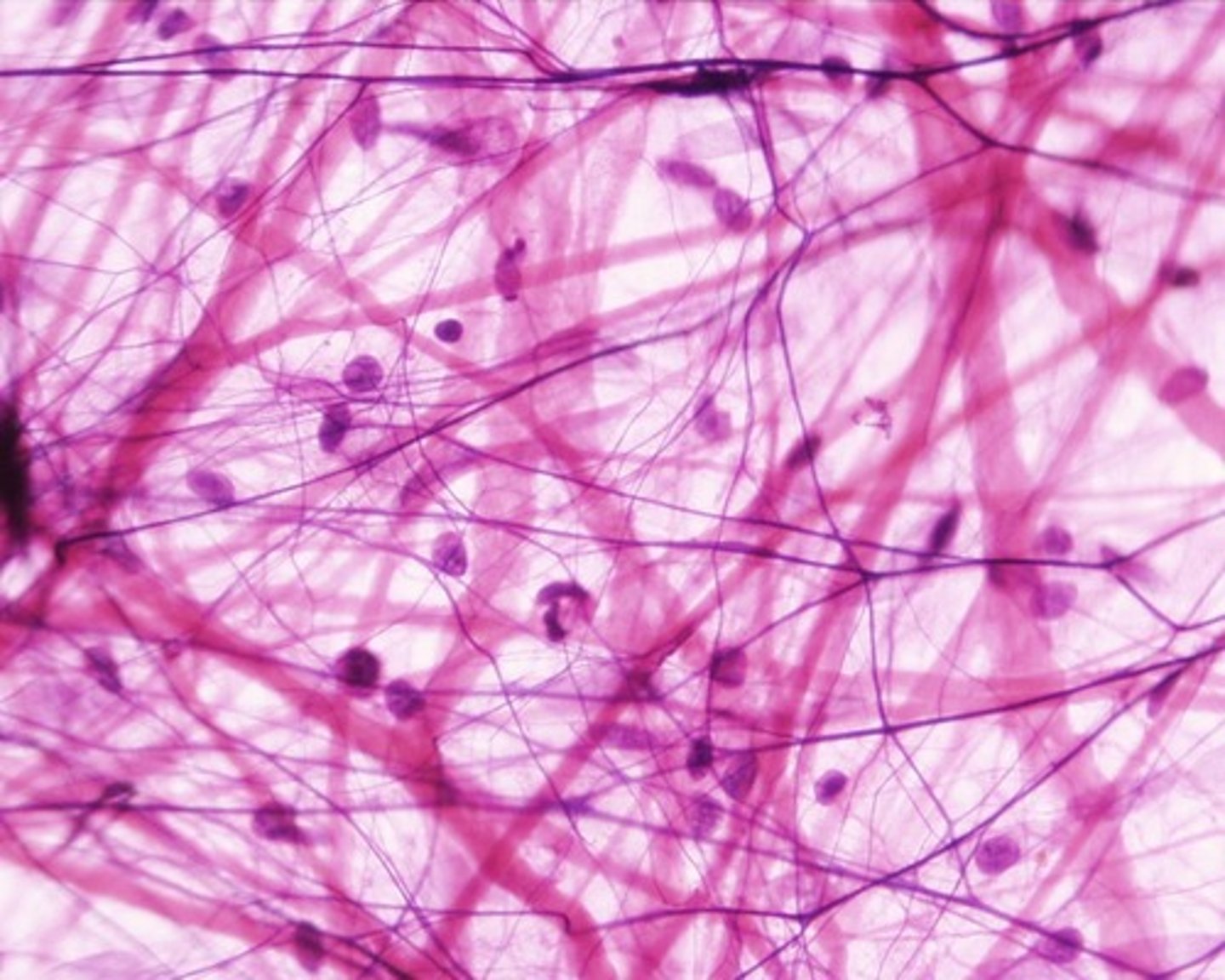
loose connective tissue areolar location
Widely distributed under epithelia of body, e.g., forms lamina propria of mucous membranes; packages organs; surrounds capillaries.
loose connective, adipose
provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
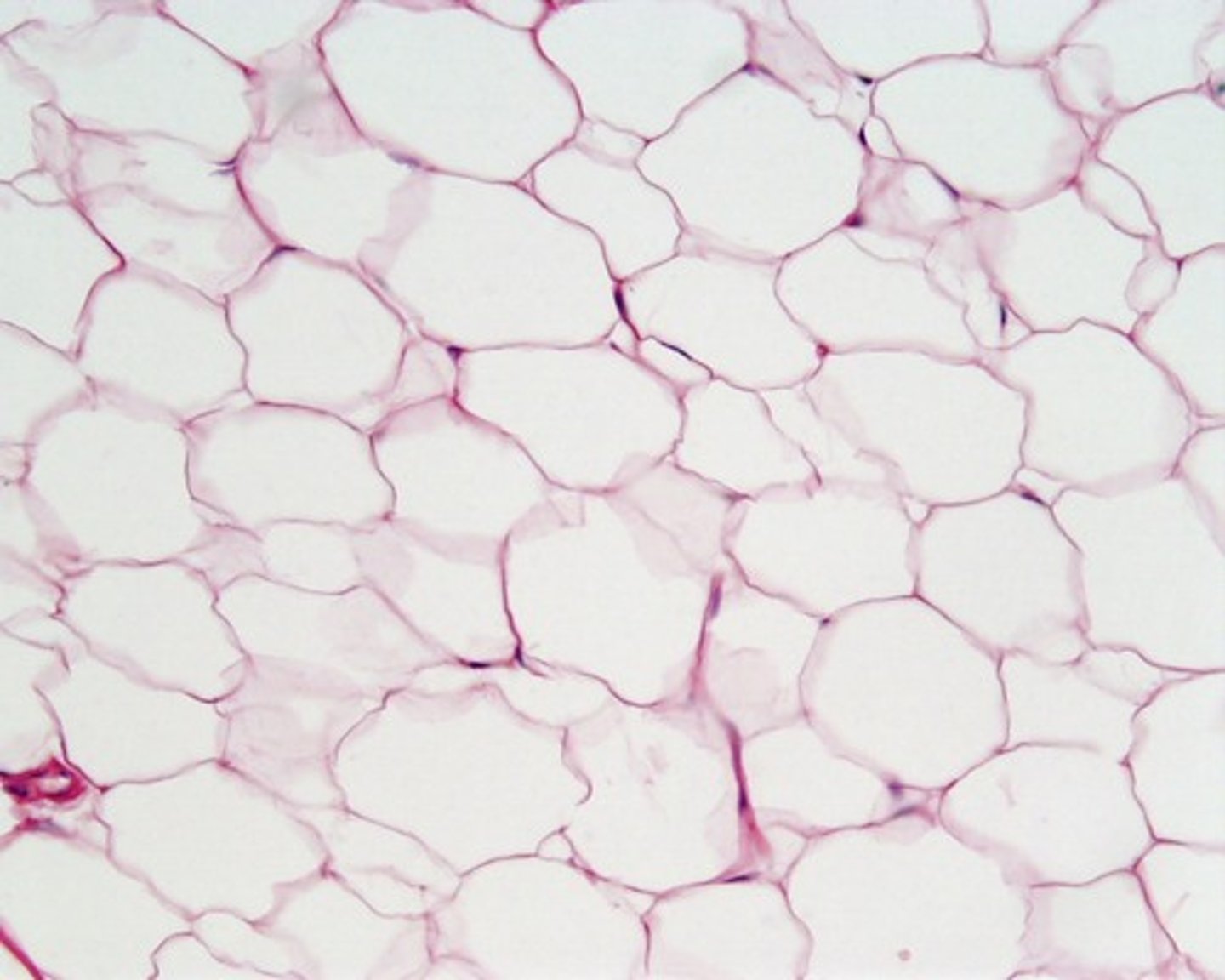
loose connective adipose location
under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, in breasts
loose connective, reticular
fibers form a soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
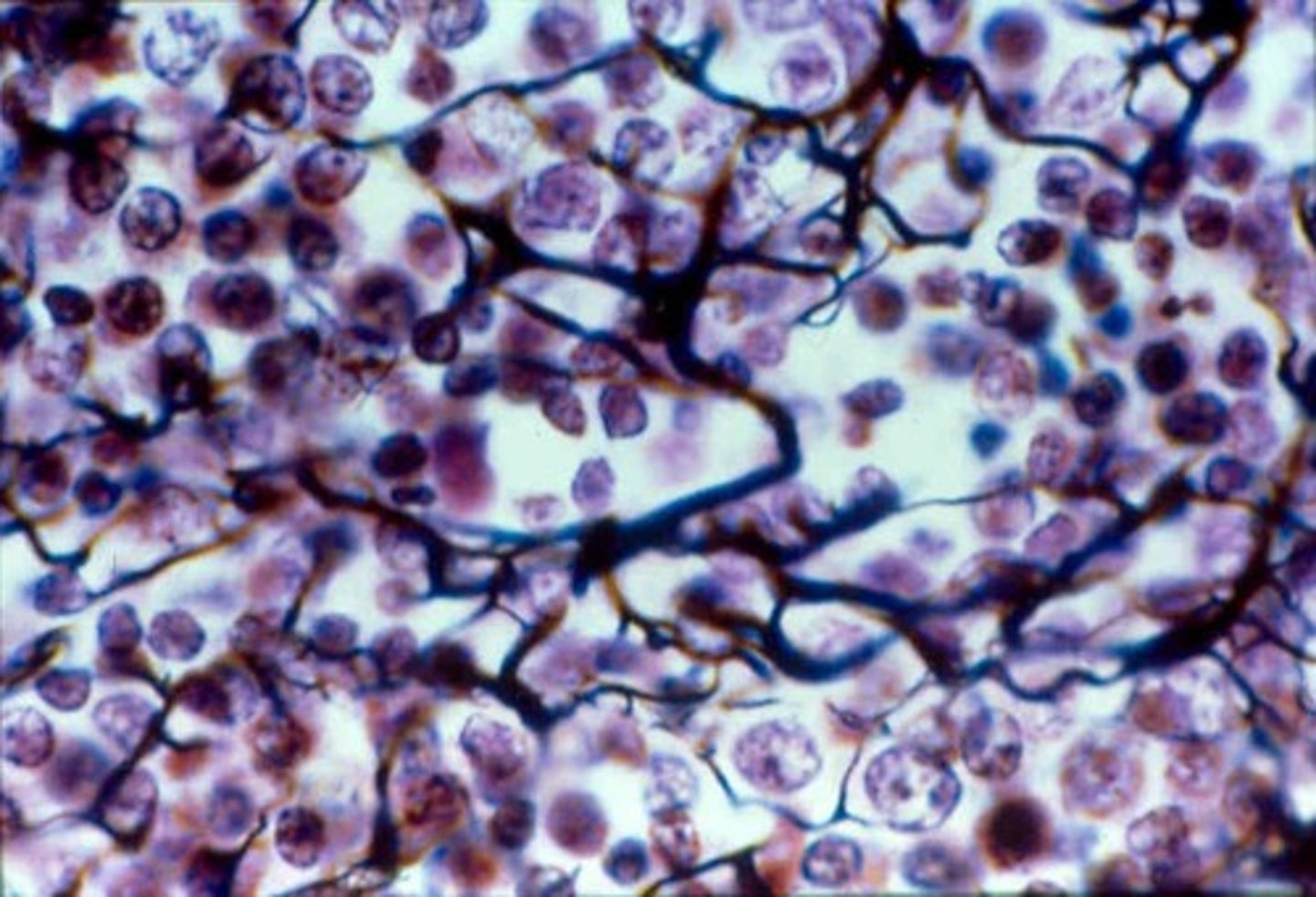
loose connective reticular location
lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
dense connective regular
attaches muscles to bones; bones to muscles; bones to bones. withstanding great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction.
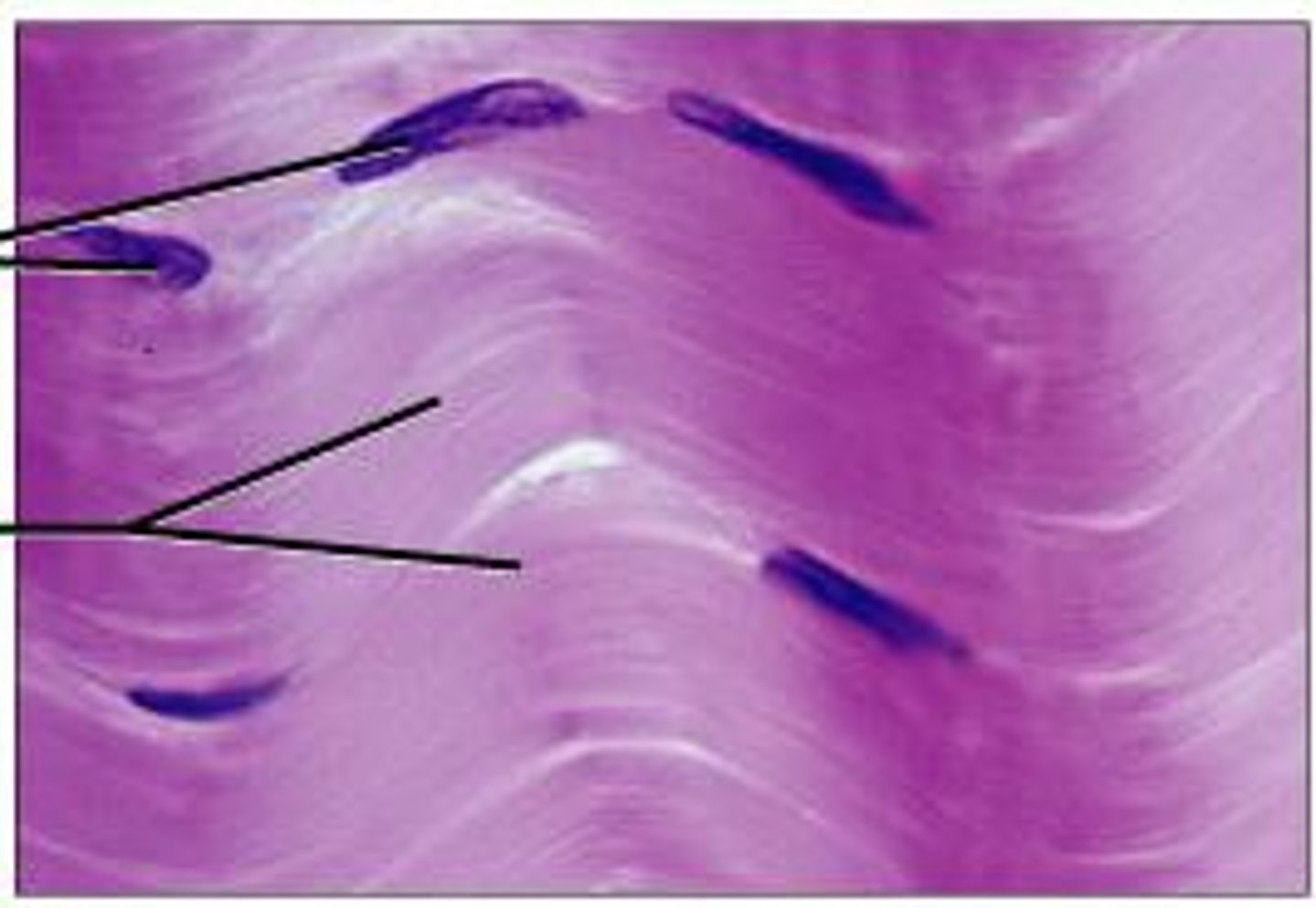
dense connective regular location
tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
dense connective irregular
able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength
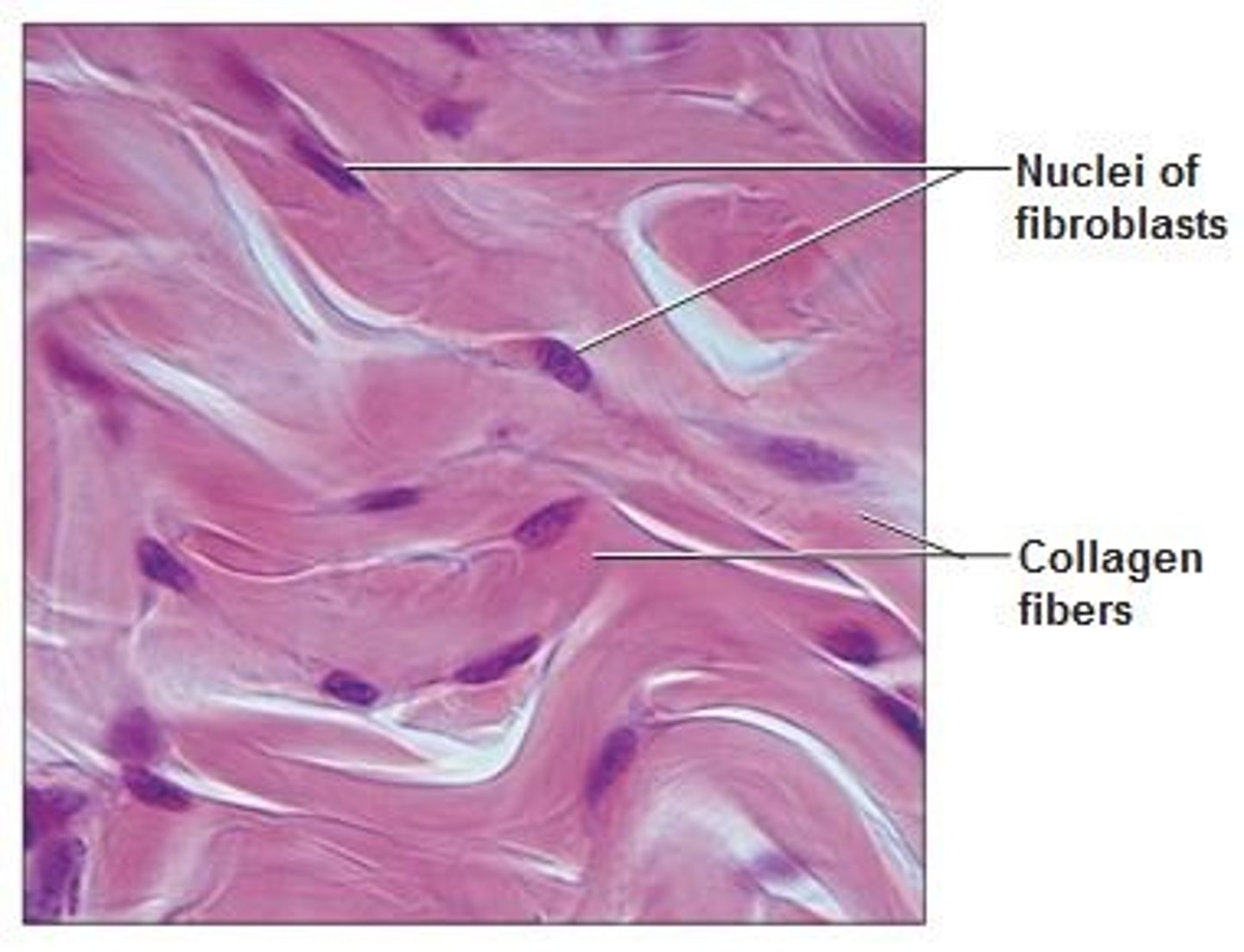
dense connective irregular location
dermis of the skin, submucosa of digestive tract, fibrous capsules of organs and joints.
cartilage connective tissue
supports and reinforces, has resilient cushioning properties, resists compressive stress
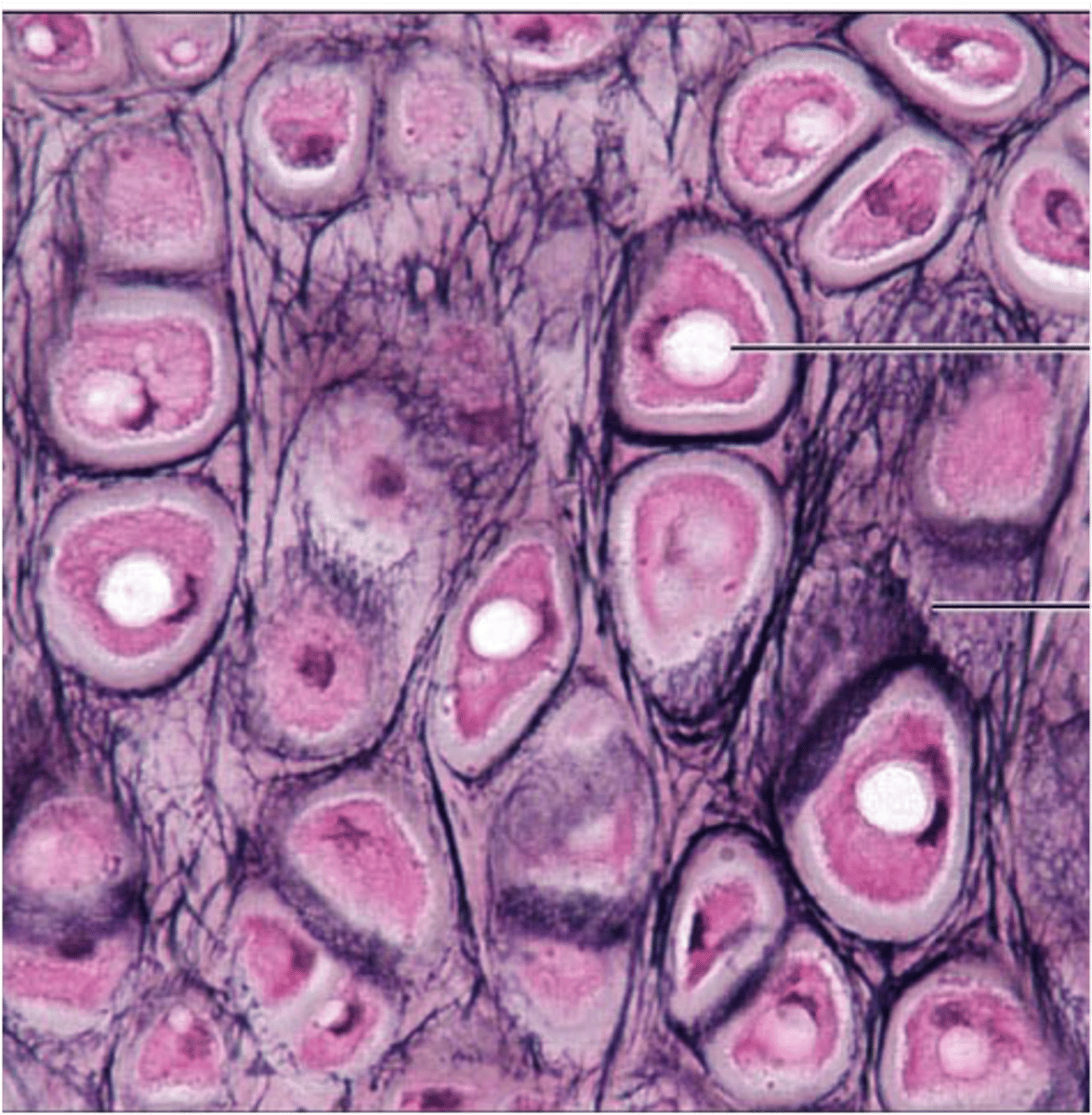
cartilage connective tissue location
forms most of the embryonic skeleton, covers the ends of the long bone in joint cavities, forms costal cartilage of the ribs, cartilage of the nose, trachea and larynx
bone connective tissue
bone support and protect (by enclosing); provided levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
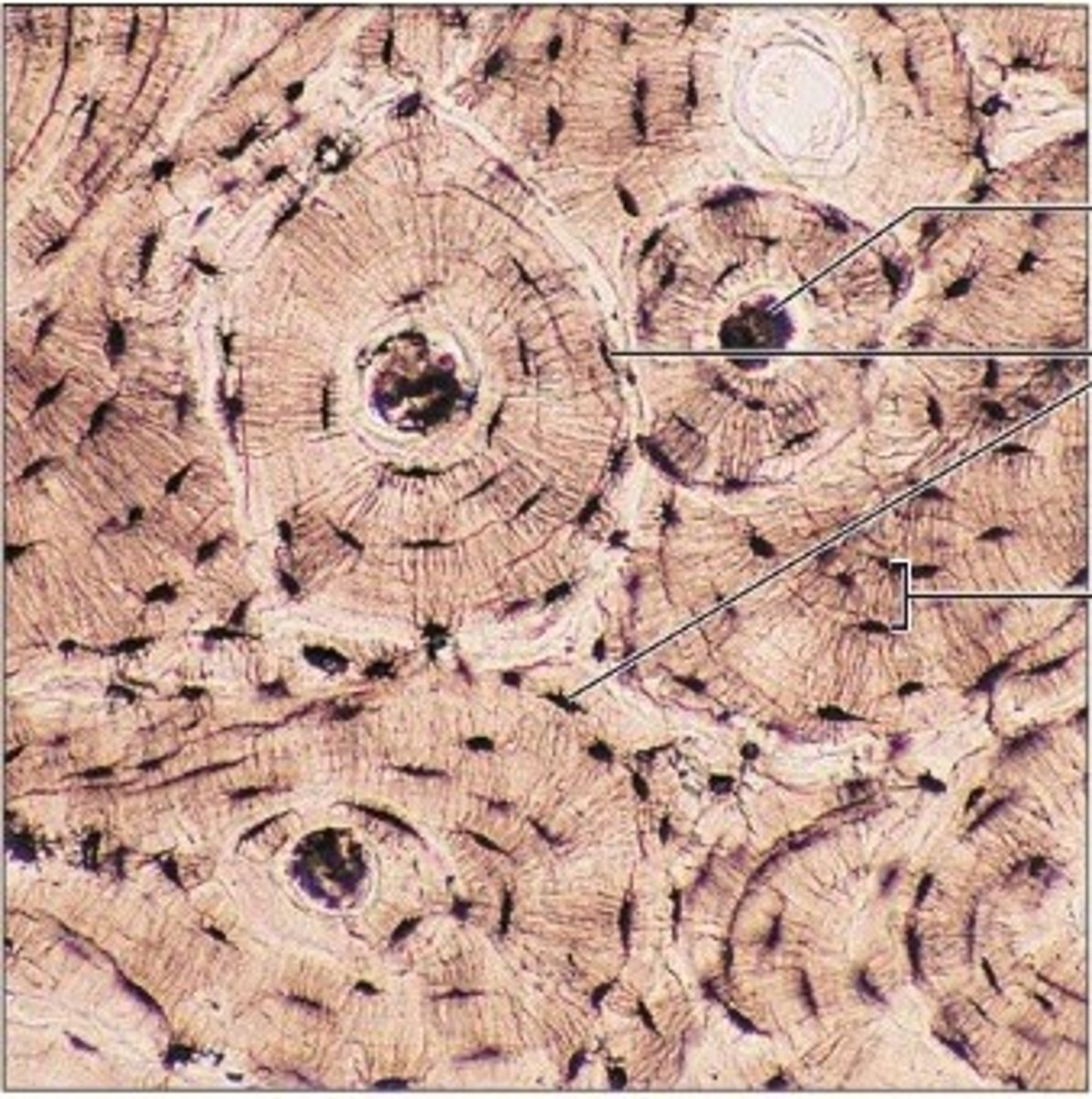
bone connective tissue location
bones
blood connective
transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
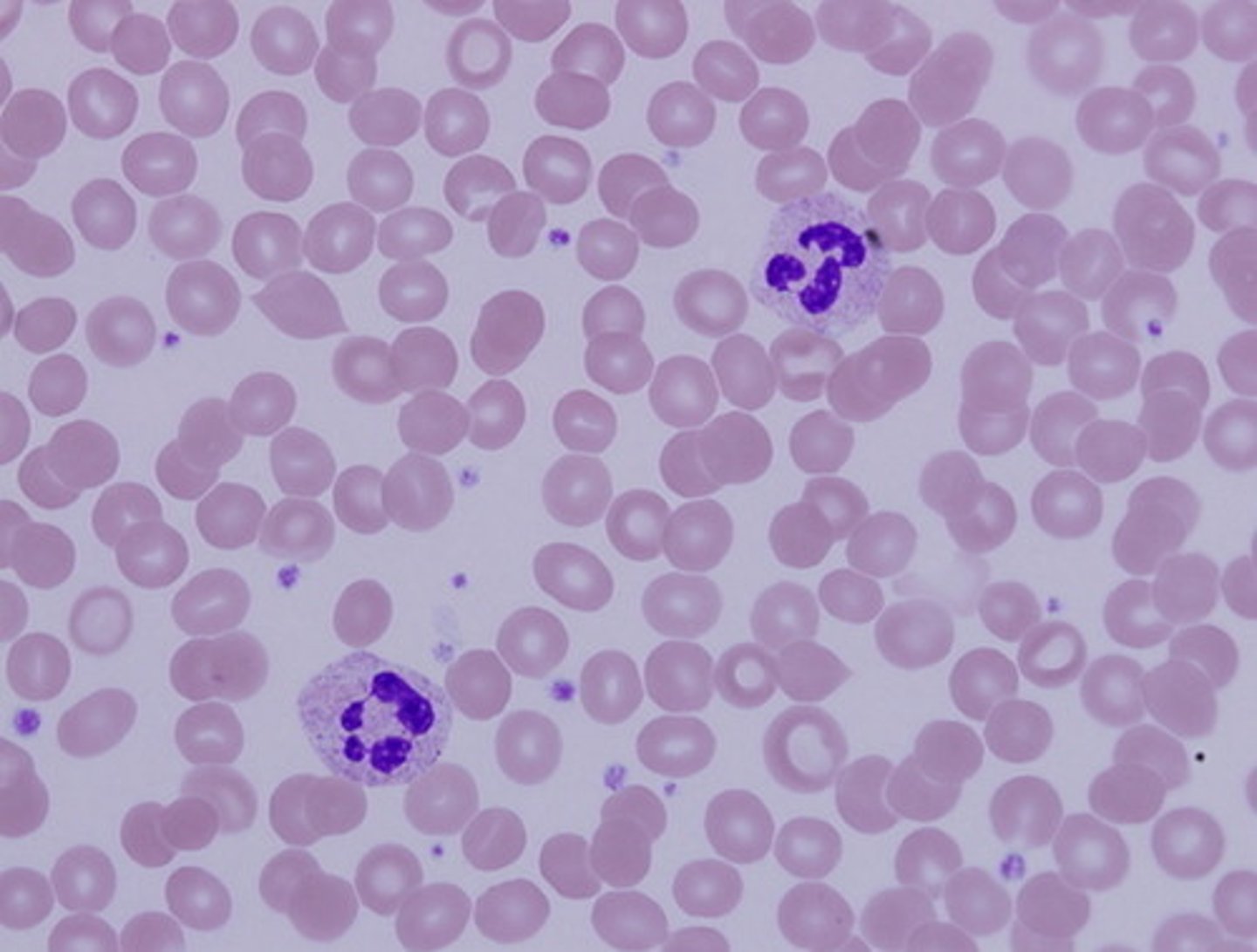
blood connective location
contained within blood vessels
smooth muscle
fibers are thin and tapered, no striations, single nuclei, produces involuntary movement
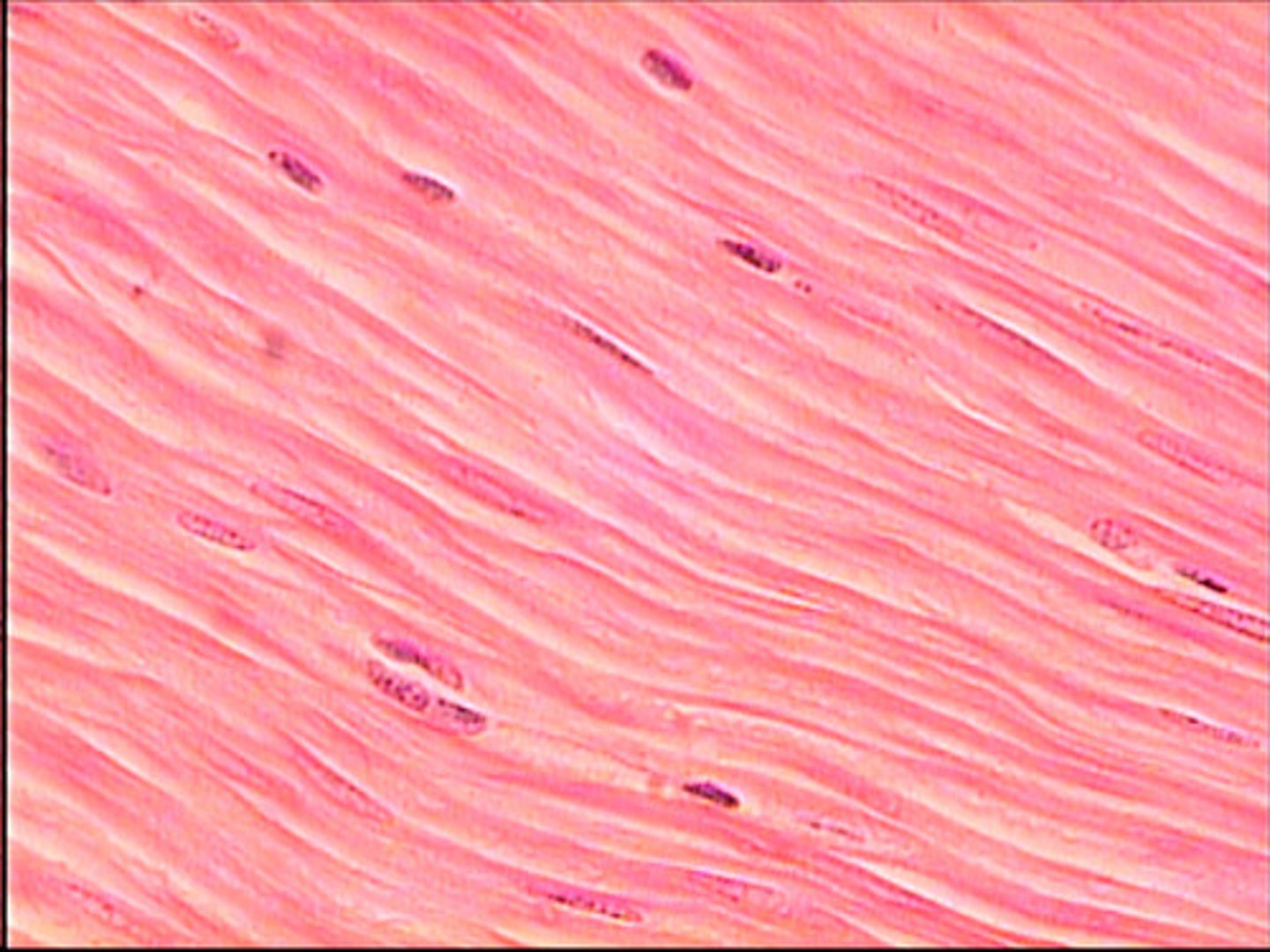
smooth muscle location
organs
skeletal muscle
multinucleated, striated, resembles salmon meat, produces voluntary movement
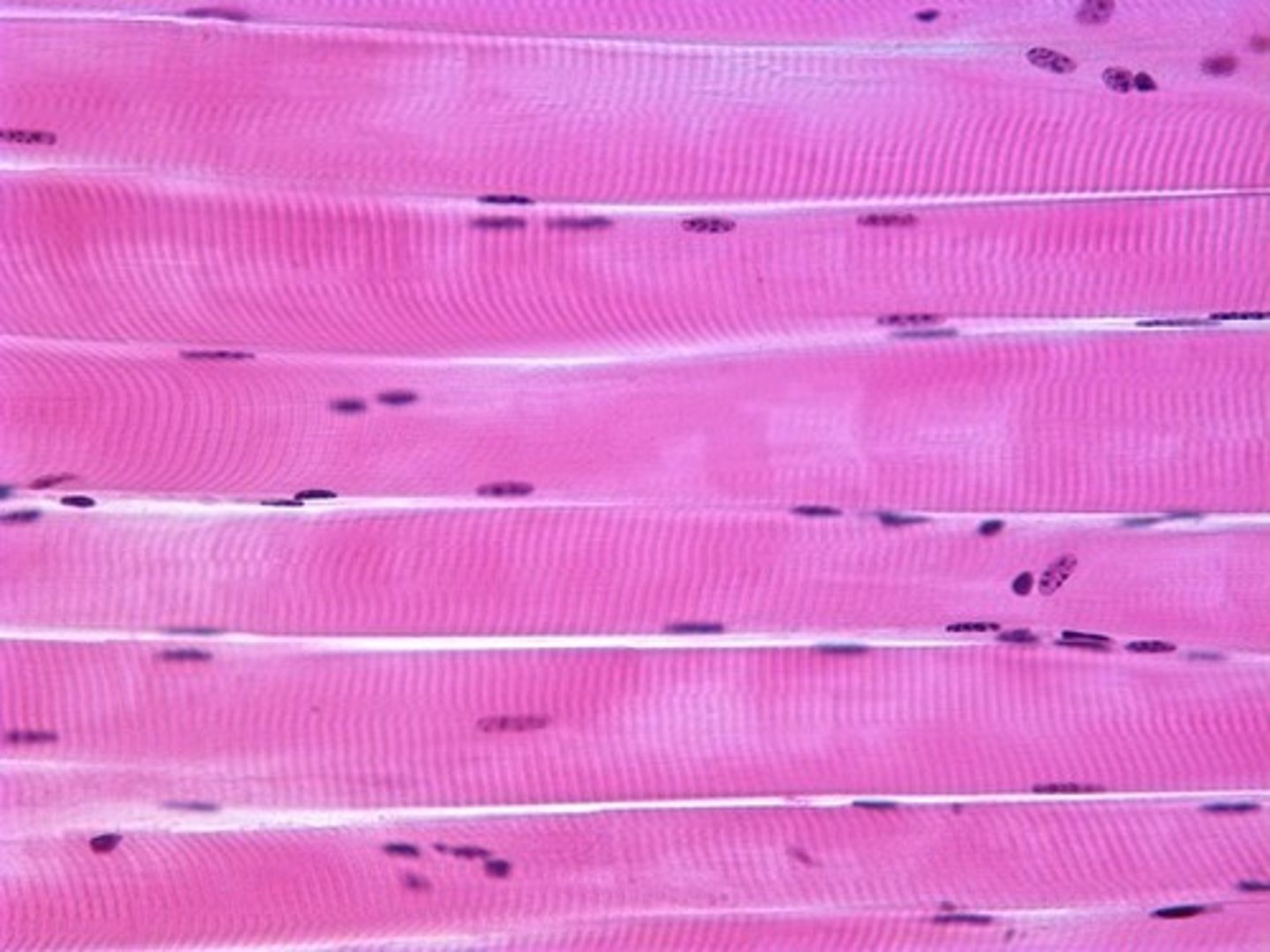
skeletal muscle location
attached to the skeleton
cardiac muscle
Striated, involuntary muscle, thick chunky ribbon shaped cells
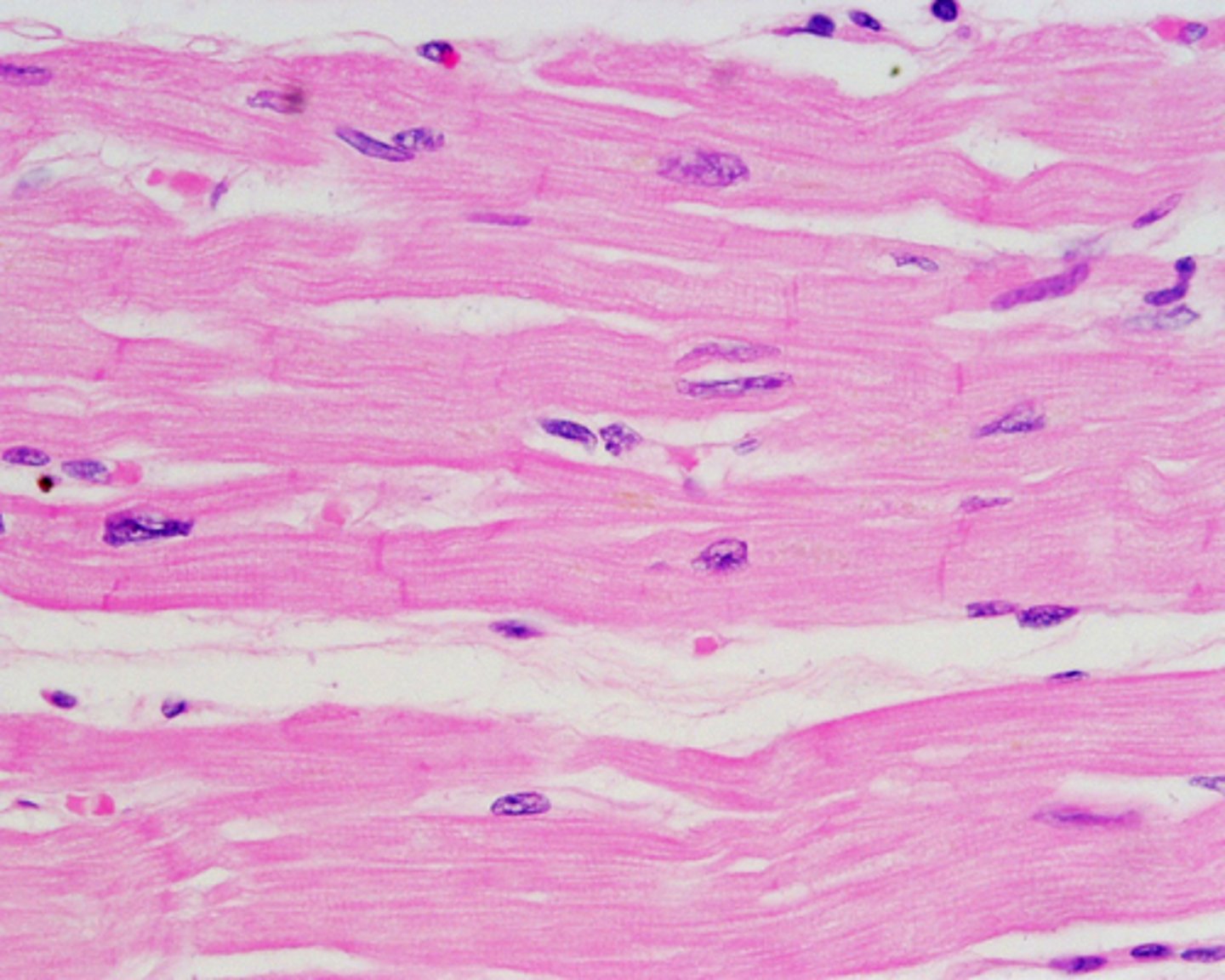
cardiac muscle location
only in the heart
elastic cartilage
maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
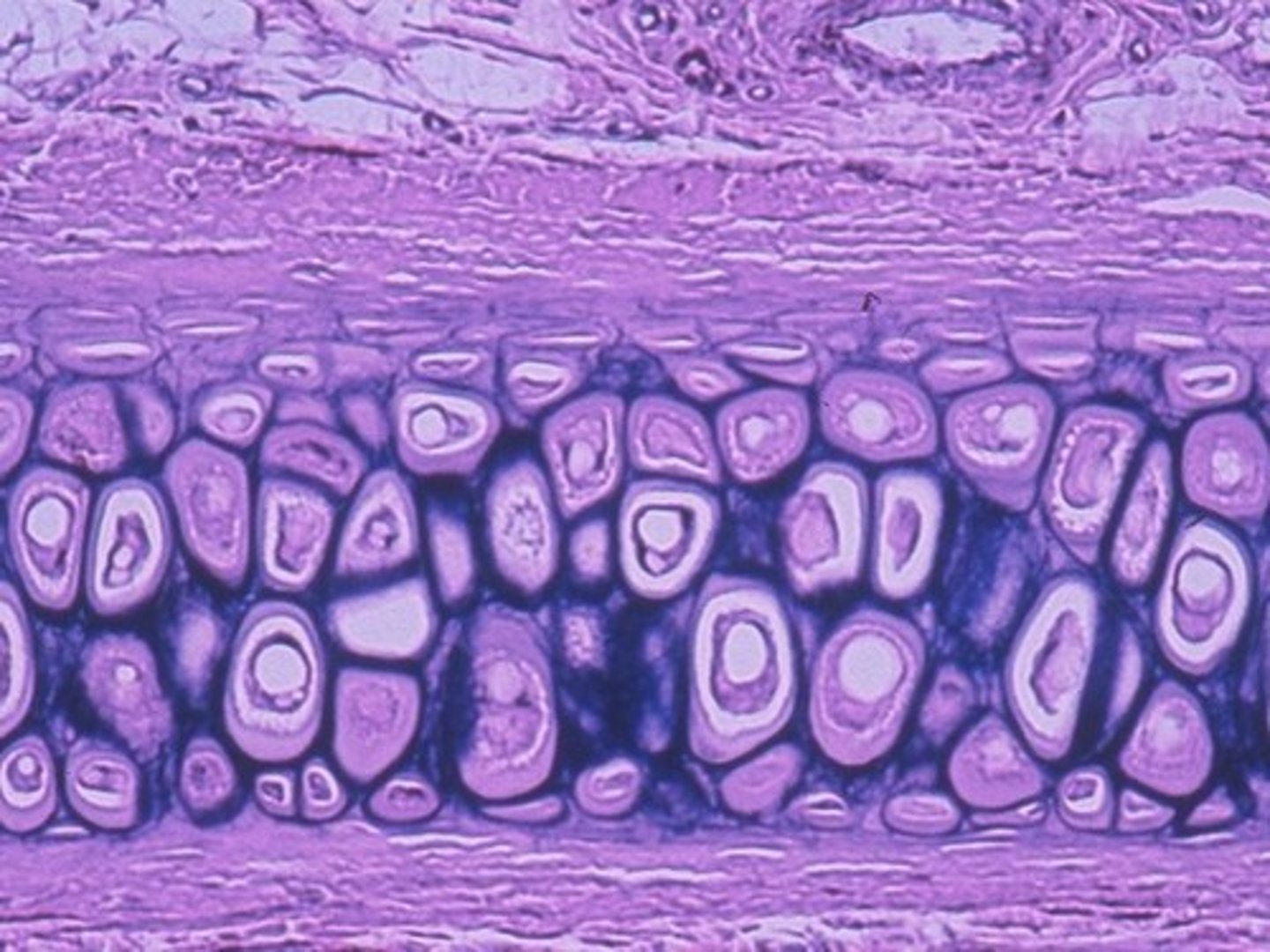
elastic cartilage location
supports the external ear (pinna); epiglottis
fibrocartilage
tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
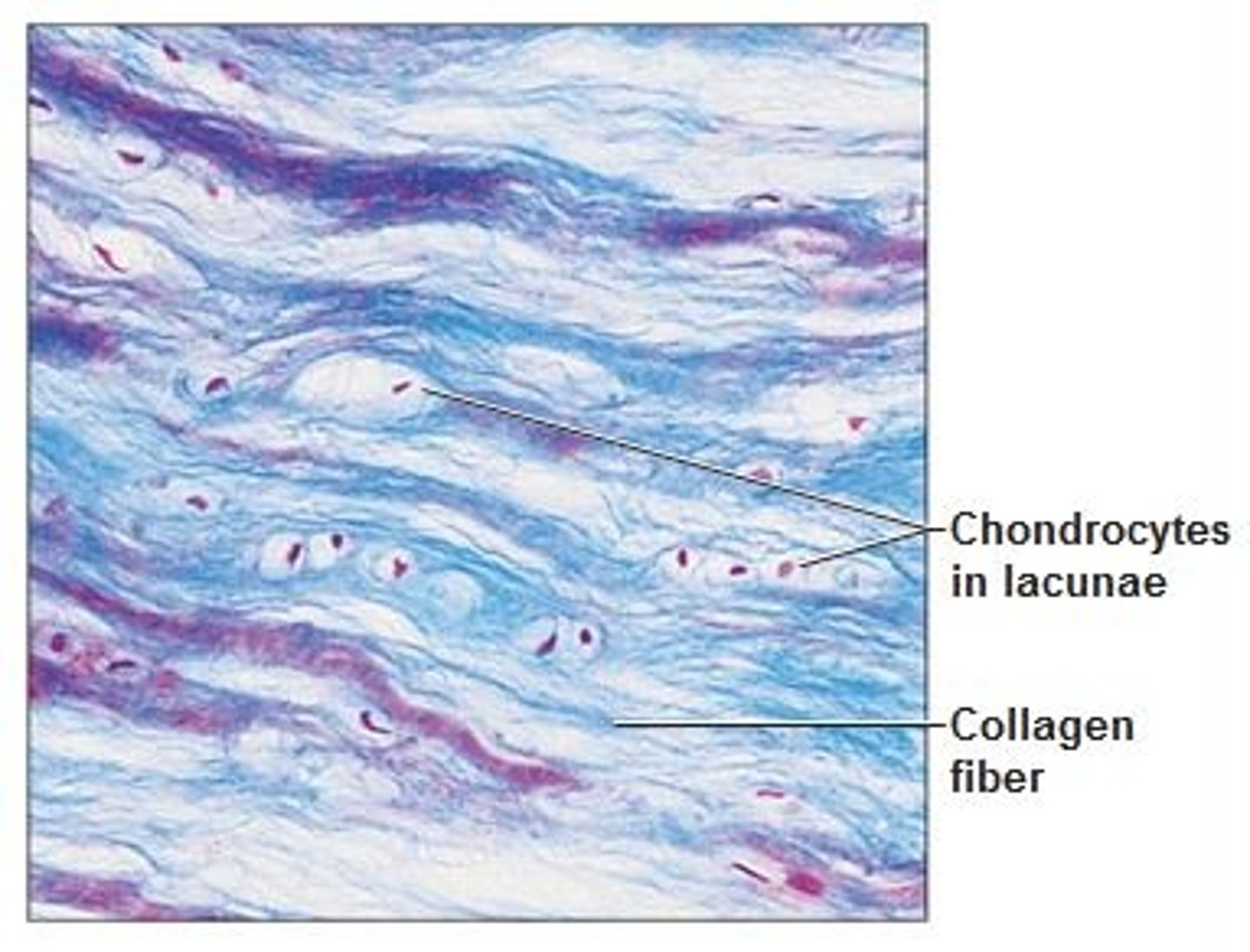
fibrocartilage location
intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint