Biology Cohort Revisio
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Movement
An action by an organism causing a change in position
Respiration(COL)
Chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules to release energy
Sensitivity
The ability to detect the internal/external environment to make appropriate responses.
Control
The ability to maintain a constant internal environment
Reproduction
The processes that make more of the same kind of organism
Excretion
Removal of waste products of metabolism.
Nutrition
The taking in of materials for energy, growth and development
Growth
A permanent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in cell number/size or both
Why are enzymes called biological catalyst
They increase the rate of reaction, found naturally and remain unchanged after the reaction.
'Lock and Key' model of an enzyme
When a substrate perfectly fits in an enzyme.
How does pH affect enzymes
Each enzyme has their own optimal pH, but change shape at extreme pH
Aerobic respiration
Glucose+Oxygen->Carbon dioxide+water+ATP
Respiration
The release of energy from food, mainly occurring in the Mitochondria
Anaerobic respiration
Glucose->lactic acid(alcohol in yeast)+ATP
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis
Net movement of water molecules from a region of high water potential to a lower water potential through a partially-permeable membrane.
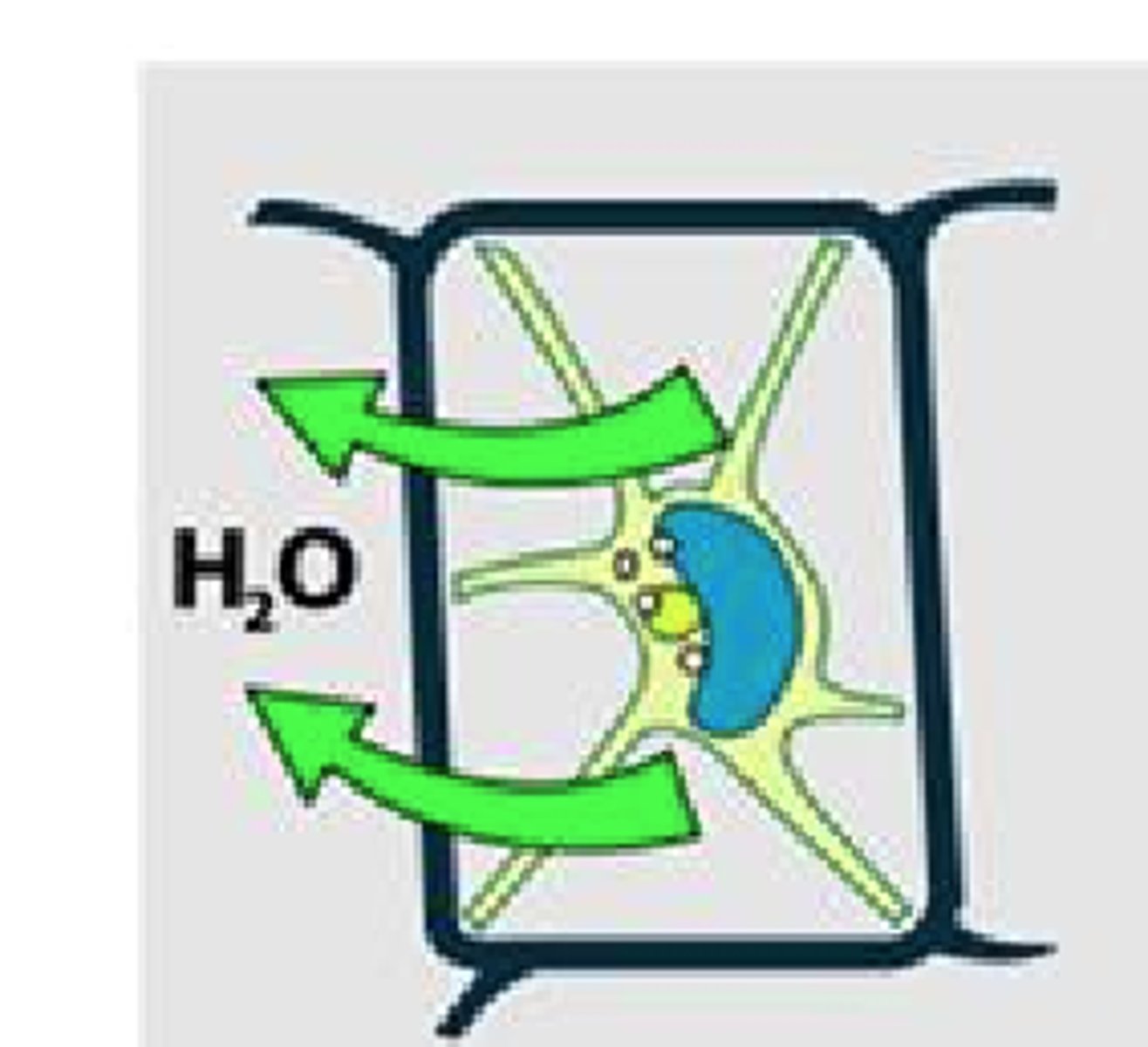
State of cell + surrounding
Plasmolysed, hypertonic
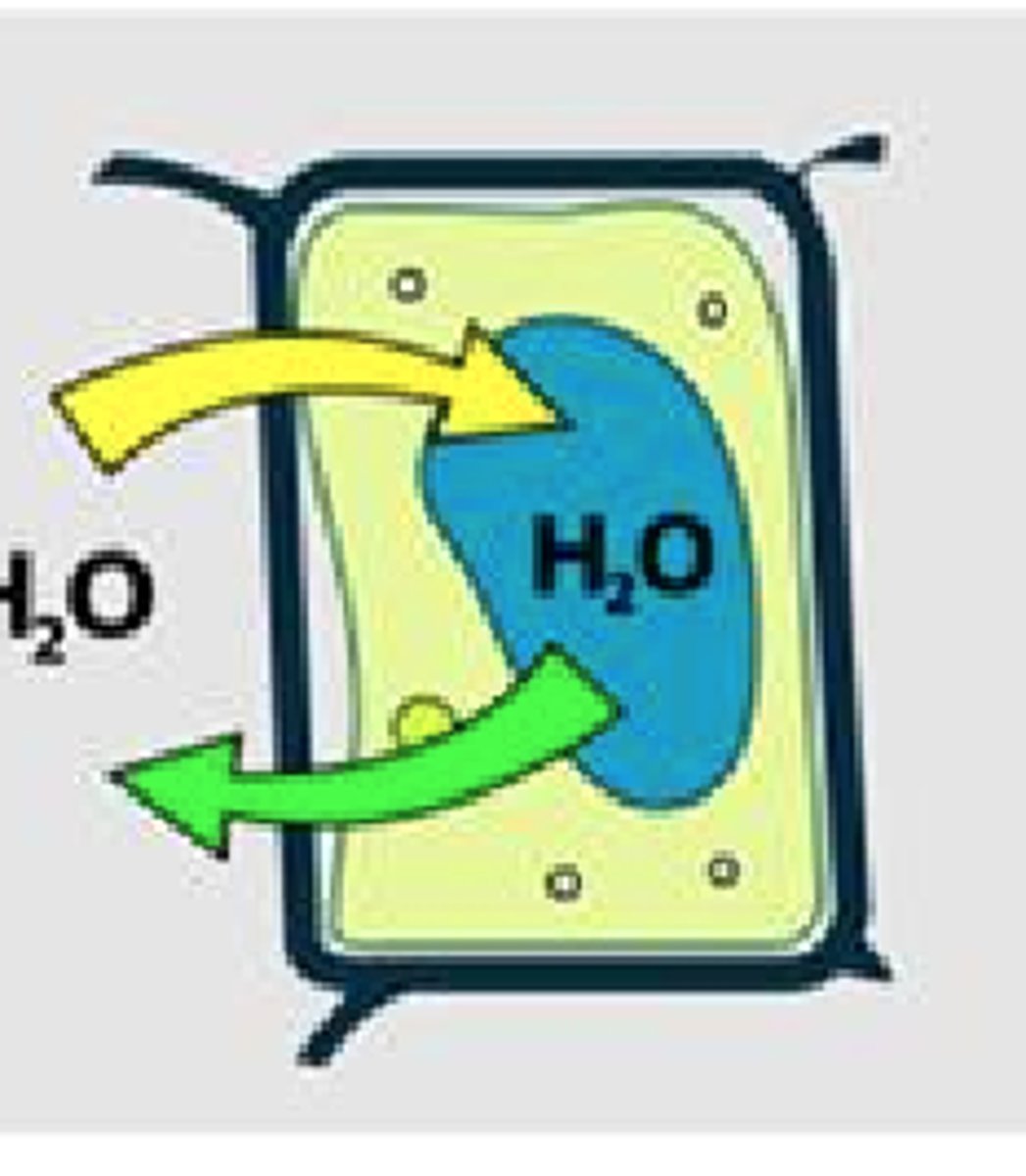
State of cell + surrounding
Flaccid, Isotomic
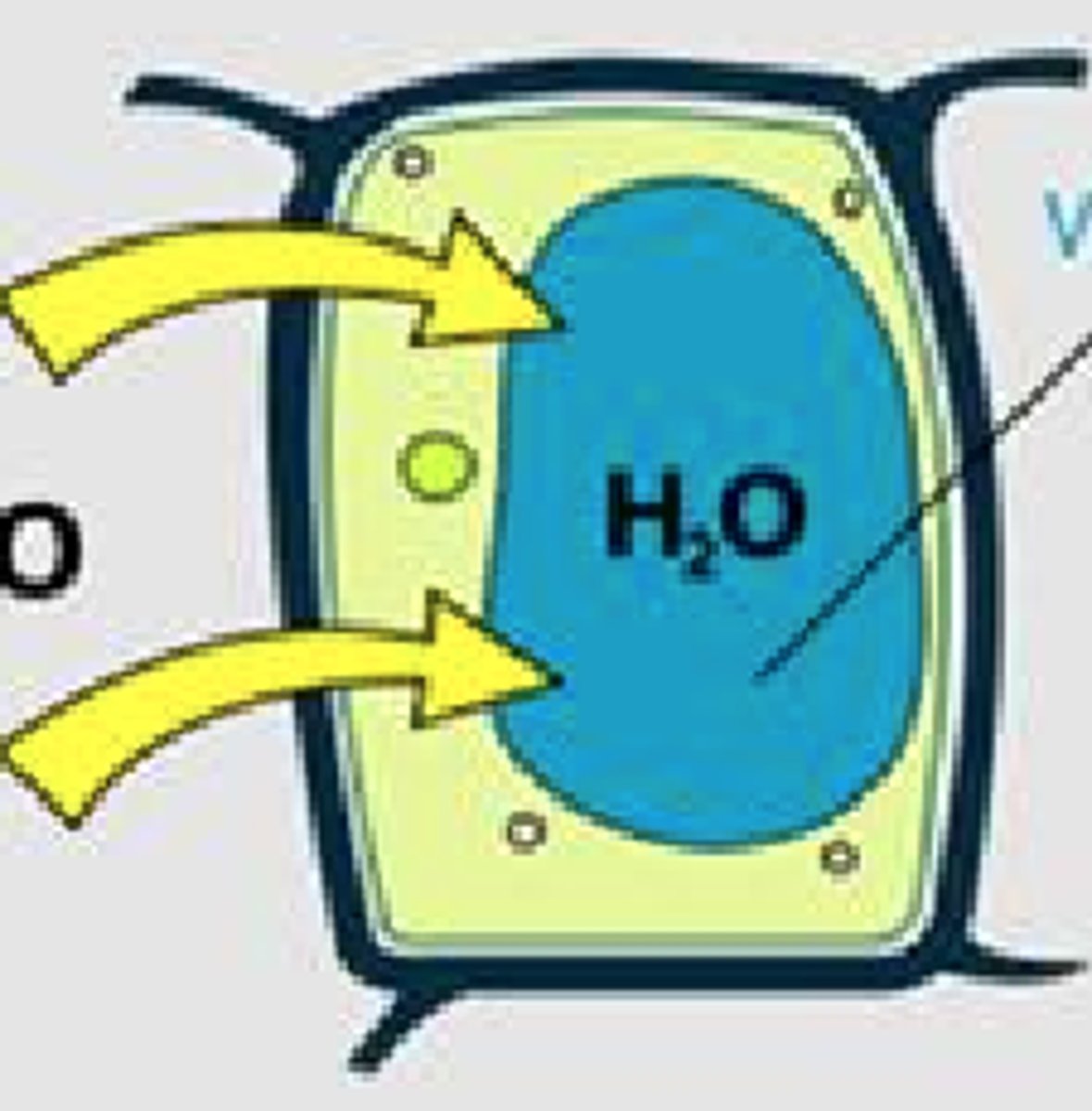
State of cell + surrounding
Turgic, Hypotonic
Levels of organization(in the body)
Organelles, cells, tissues, organs and organ systems.
Differentiation
The control of genes to create specialized cells, that carry out particular roles
Mitosis
Cells, such as zygotes, dividing in half to create more cells
What is a species
A group of organisms that share common characteristics and are able to breed with one another, but not able to breed with a different species
Virus
Non living, Can only reproduce in over cells, no cellular structure(Example:HIV,)
Bacteria
Single celled, no nucleus, can carry out photosynthesis but mostly feed on other organisms.(Example:Pneumococcus)
Protoctists
Single celled, some have feature like an animal or plants(Example:Chlorella)
Fungi
diagnosed in mycelium, made from thread-like structures(hyphae), cells wall made of chitin, can't carry out photosynthesis(Example:Mucor)
Animals
Multicellular,no cell wall, stores carbohydrates as glycogen(Example:You, yes you)
Plant
Multi cellular, cells contain chloroplast, cellulose cell wall, stores carbohydrate as sucrose(Example:Corn)
Gas exchange
The process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide through the respiratory system.
Ventilation
The movement of air into and out of the lungs.
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange
a large surface area, thin walls, a moist lining, and a rich blood supply
Carbohydrate
Main energy source
Fats
Energy source, Insulation
Protein
Growth, Repair and Energy
Water
Needed to transport and have chemical reactions
Fibre
Help to move food throug hte gut
Calcium
Makes strong Teeth and Bone
Iron
Needed to make Haemoglobin, the oxygen carrying pigment in blood.
Vitamin A
Needed for good Eyesight
Vitamin C
Needed for connective tissue
Bitamin D
Helps absorb Calcium
Starch food test
food +water+Iodine solution brown->black
Sugar food test
food+water+Benedict's solution, heat the test tube to 90*C. Blue->green, yellow, brick red
Protein food test
food+water+Biuret's solution, blue->purple
Lipids food test
Food+ethanol then water, cloudy white suspension
Amylase
Salivary glands, starch->maltose
Maltase
Small intestine, Maltose->glucose
Pepsin
Stomach,Protein->peptides
Trypsin
Pancreas, Protein->Peptides
Lipase
Pancreas, Lipids to glycerol and fatty acids
Bile
Liver, Fat globules to smaller droplets.
Fats(digestion)
HCO,glycerol+fatty acids
Carbohydrate(digestion)
HCO,glucose or simple sugars
Protein(digestion
HCON, different amino acids
Ingestion
Intake of food by swallowing or absorbing it
Peristalsis
The contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the intestine, creating wave like movements that push the contents forward.
Digestion
Mechanical: Physical break down of food into smaller bits
Chemical:Breakdown of food into smaller soluble molecules by enzymes and other chemical agents.
Absorption
The process which nutrient molecules pass from the digestive system into the blood system.
Assimilation
The process by which absorbed nutrients are taken in by the cells of the body and used for energy, growth and repair.
Egestion
The discharge/expulsion from the digestive tract