Coasts and Landscapes
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA A-level Geography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Define: System
A type of model which simplify the world for better study, an assemblage of interrelated parts that work together.
Define: coastal landscape
A section of coastline that includes a range of coastal landforms resulting from erosional and depositional processes.
What distinguishes a closed system from an open system in coastal geography?
A closed system has no inputs or outputs except for energy while an open system can receive inputs and transfer outputs to other systems.
What is the difference between high energy and low energy coastal environments?
High energy coastal environments are dominated by erosional features, whereas low energy coastal environments are characterized by depositional features.
What are the main zones of a coastline?
Backshore, foreshore, nearshore, inshore, and offshore.
Define: Backshore
The area between high water mark and the landward limit of marine activity. Changes take place only during storm activity.
Define: Foreshore
The are between high water mark and low water mark. Most important for marine processes not influence by storm activities.
Define: Nearshore
The area extending seaward from the high water mark to the area where waves begin to break. It includes the swash zone, surf zone, and the breaker zone.
Define: Inshore
The area between the low water mark and position where waves cease to have an influence on the beach.
Define: Offshore
The area beyond the point the waves cease to have influence on the beach and cease to impact upon the seabed. The activity is limited to deposition of sediment.
The energy to drive the coastal system is provided by w____, w___, t____, and c_______.
waves, wind, tides, and currents
Define: Wind
The movement of air caused by uneven heating of the Earth which creates different pressures.
What causes waves to form?
By the transfer of energy from wind blowing over the sea surface.
Define: Fetch
The distance over which wind blows uninterrupted across water, affecting the energy and magnitude of waves.
Constructive waves characteristics
low wave height
long wavelength (often 100m)
low frequency (6-8/min)
strong swash
weak backwash
moves material slowly up the beach
shallow beach profiles
Destructive waves characteristics
high wave height
high frequency (10-14/min)
weak swash
strong backwash
material is pulled down the beach
steep beach profiles
Define: Wave refraction
The change in direction of waves as they move between materials with different properties. The topography of the coastline is crucial in determining the effects of the wave action.
How does longshore drift work?
The process where waves approach the shore at an angle, transporting sediment along the coast through swash and backwash.
________ are the permanent or seasonal movement of surface water in the seas and oceans.
Currents
Define: Longshore Currents
Occurs as most waves do not hit the coastline '“head on” but at an angle. This moves water along the surf zone and transports sediment parallel to the shoreline.
Define: Rip Currents
Strong currents moving away from the shoreline. Seawater builds up against the coastline by incoming waves and as it moves back out it forms a rip which is hazardous.
Where are rip currents most common?
Around low areas, breaks in offshore sandbars, and near structures such as jetties or piers.
Define: Upwelling
The upward movement of cold, nutrient-rich water from the ocean depths to replace warmer surface water, contributing to global circulation currents.
Tides are the ________ rise and fall in the level of the sea.
Periodic
What forces act upon tides?
Gravitational pull of the sun and moon, centrifugal force, rotational spin causes the change to be daily.
Define: Spring Tides
Twice in a lunar month, the sun and moon are in alignment causing the rise to be the strongest.
Define: Neap tides
Twice a month, the sun and moon are perpendicular to each other in relation to Earth. This causes the lowest monthly tidal range. High and low tide are between 10-30% lower than average.
The __________ phenomenon refers to the abnormal rise in seawater levels caused by storms.
Tidal surge
What are sediment cells?
Areas where the movement of sediment along the coast is largely self-contained, creating dynamic equilibrium.
A ________ ______ is the balance between changes in the volume of sediment held within the system and the volume of sediment entering or exiting the system.
Sediment Budget
Define: Sub-Aerial Processes
Processes that gradually break down the coastline in-situ, such as weathering, mass movement, and run-off, affecting its shape and enabling more sudden erosion.
Define: Marine Processes
These operate upon a coastline and are connected with the sea, such as waves, tides, and longshore-drift.
__________ is the impact on rocks of the sheer force of the water without debris.
Hydraulic action
How does cavitation erode rocks?
The force of water compresses air into any gap creating pressure within the joint, as the water pulls back there is an explosion effect as the pressure is released. This weakens the cliff face.
What is abrasion/ corrasion?
When material carried in waves wears away rock faces.
What is the process by which rocks slowly are broken down, getting smaller and rounder?
Attrition
_______ is the dissolving of calcium-based rocks.
Solution (erosion)
What factors affect erosion rates on coastlines?
Factors include wave steepness, fetch, sea depth, coastal configuration, beach presence, bathymetry, and human activity.
What is meant by bathymetry of the sea bed?
The submarine topography, the depth of water.
Define: differential erosion
The varying rates of erosion experienced by different types of rock, influencing coastal landforms.
What is marine transportation?
The movement of sediment through processes such as traction, saltation, suspension, and solution.
Define: Traction
Large stones and boulders are rolled and slide along the seabed by moving seawater.
Define: Saltation
Small stones bounce, leapfrog along the seabed and beach, dislodging other particles causing more saltation.
Define: Suspension
Very small particles of sand and slit are carried along by moving water.
Define: Solution (marine transportation)
Dissolved materials that are transported within the mass of moving water.
What is the difference between marine and aeolian deposition?
Marine deposition involves sediment transported and deposited by water, while aeolian deposition concerns sediment carried and deposited by wind.
What is surface creep?
A process similar to traction, where wind rolls or slides sand grains along the surface.
What is saltation? (Aeolian deposition)
Where the wind is strong enough to temporarily lift the grains into the airflow for 20-30 metres.
Define: mass movements
The downward movement of weathered materials under the influence of gravity, including rockfall, landslides, and mudflows.
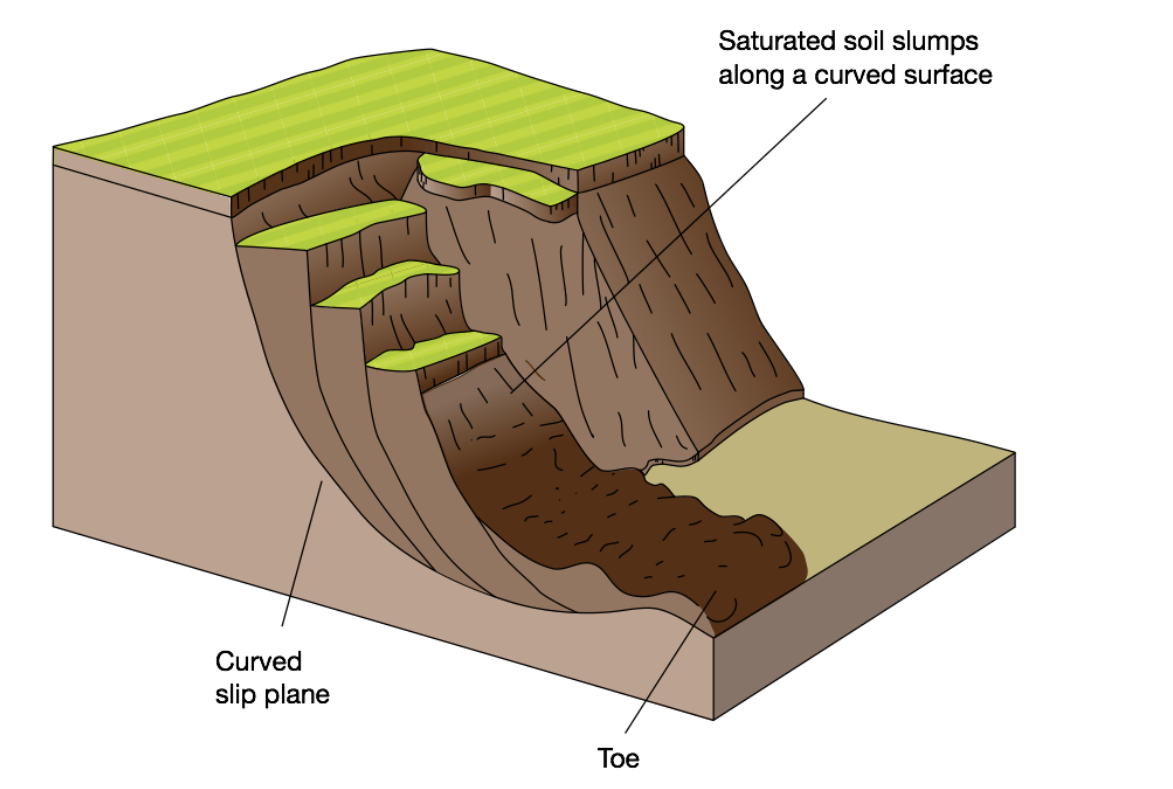
What mass movement is this?
Slumping/Rotational Slip
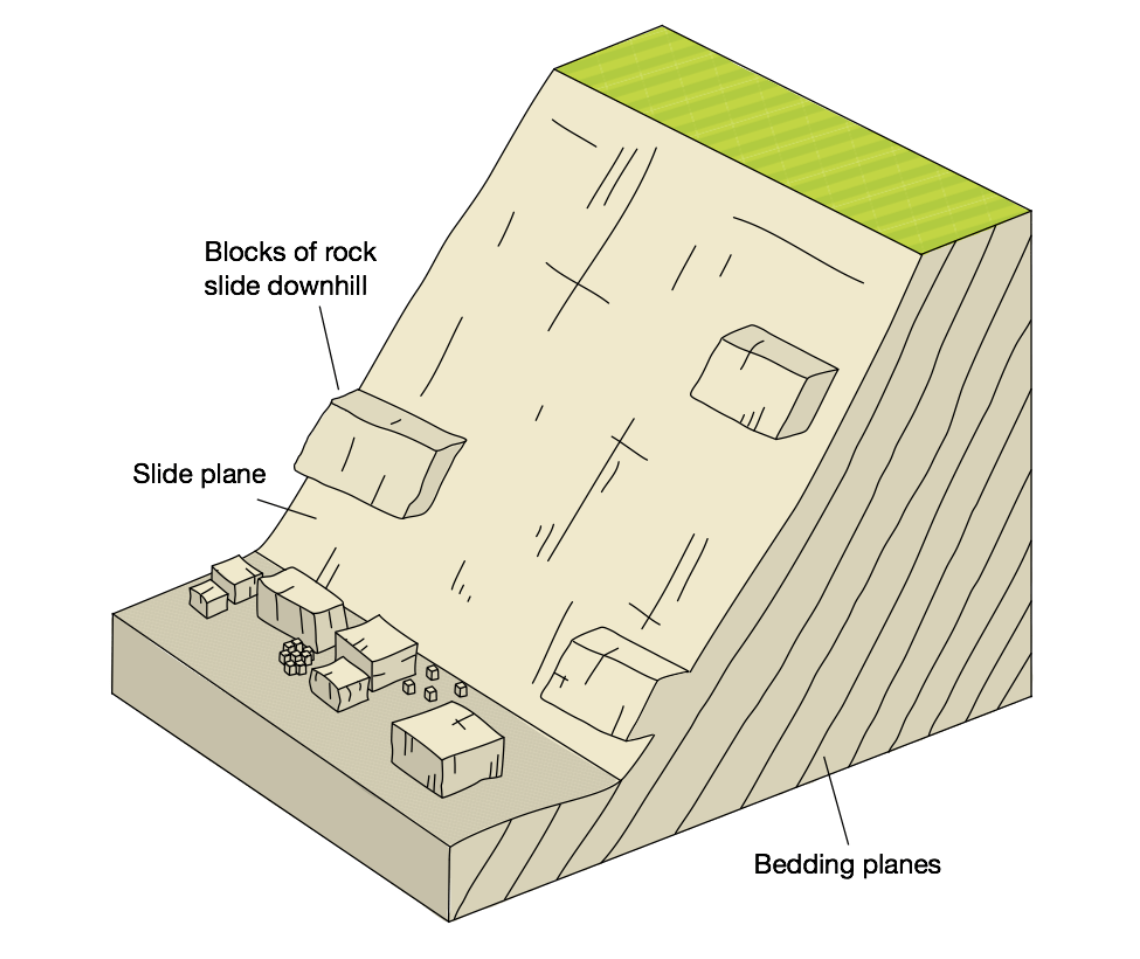
What mass movement is this?
Landslide
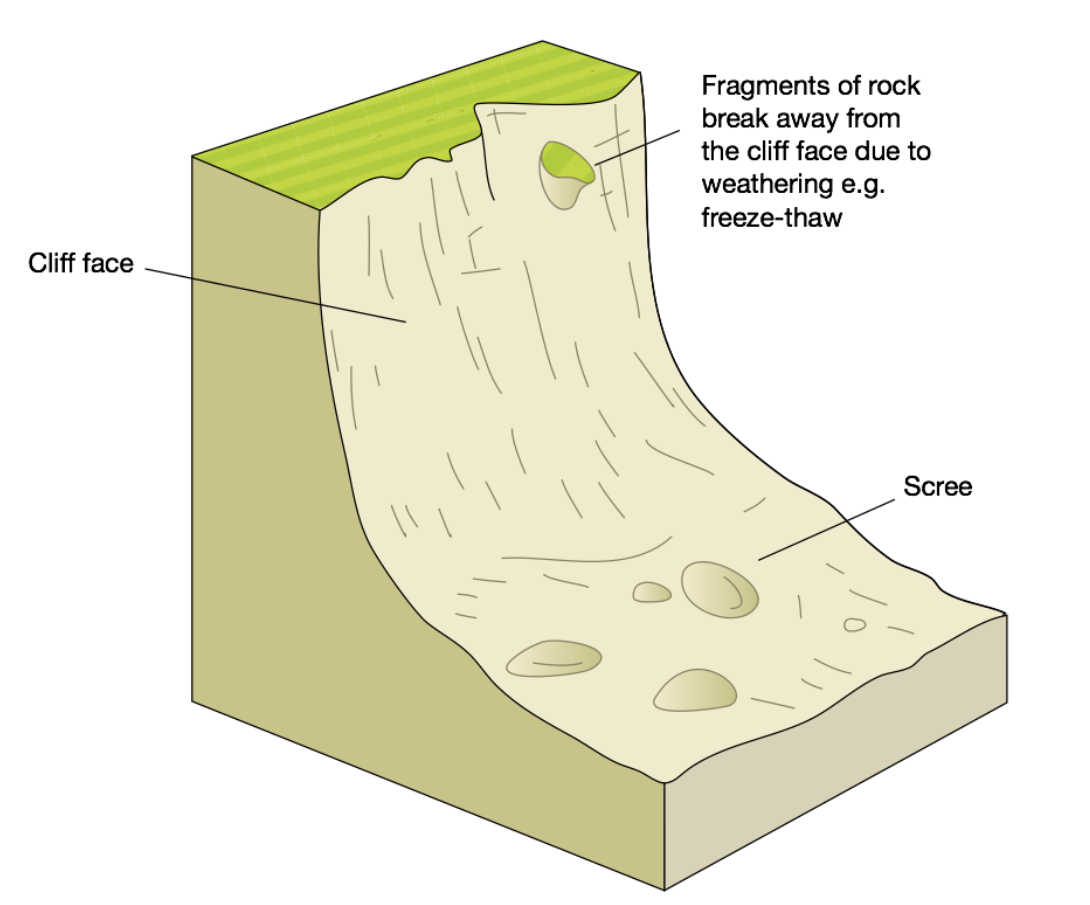
What mass movement is this?
Rockfall
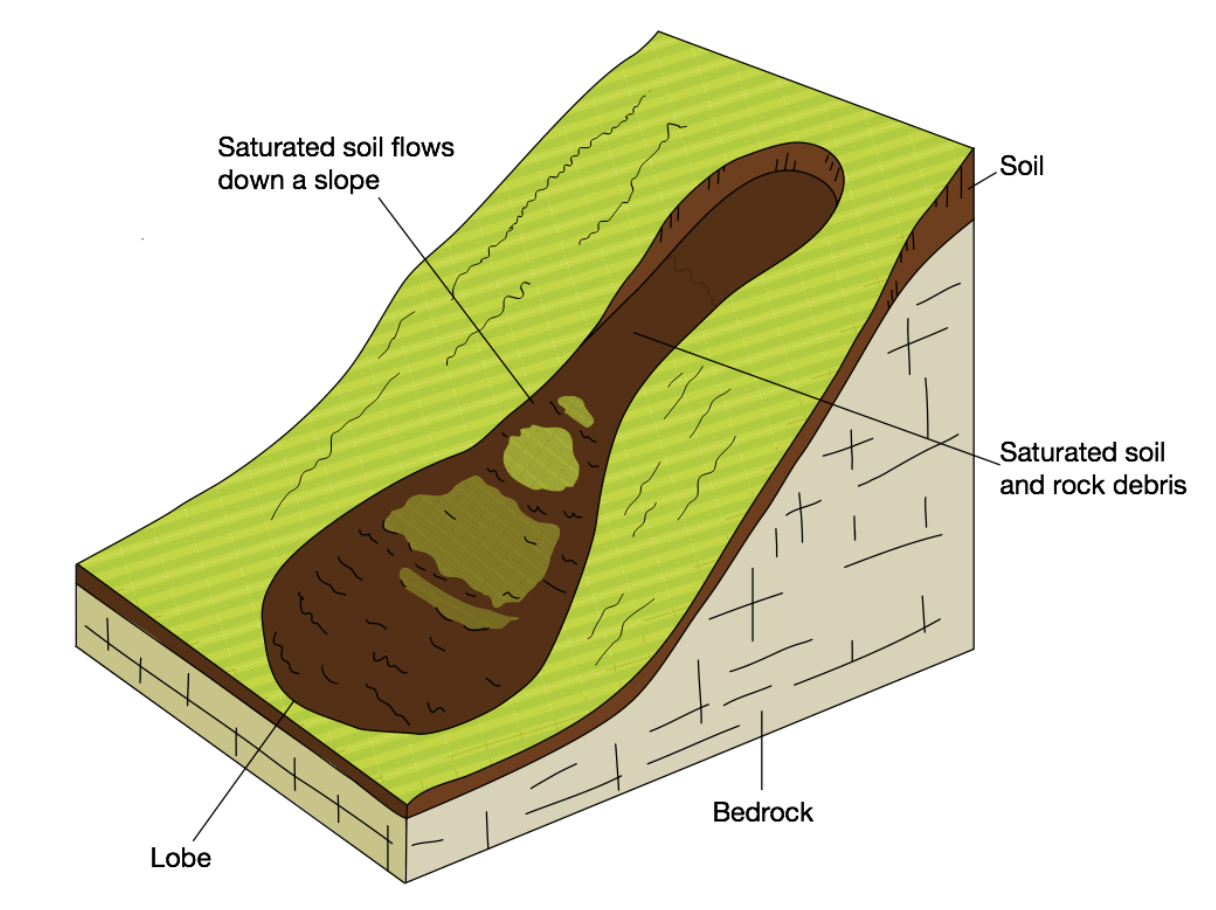
What mass movement is this?
Mudflows
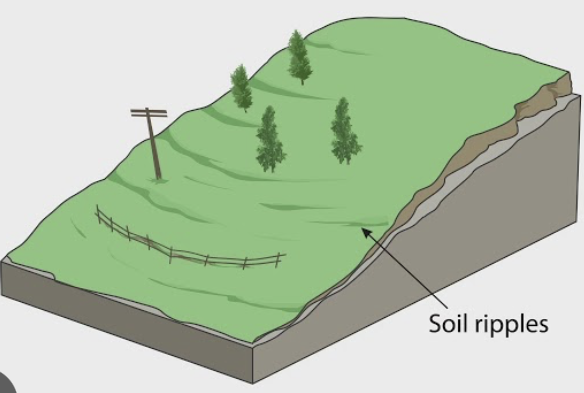
What mass movement is this?
Soil Creep
Explain Salt Weathering
Saline enters pores or cracks in rocks.
Water evaporates forming salt crystals.
The crystals expand, exerting pressure.
The rock cracks and falls apart.
Explain Freeze-thaw Weathering
Water enters joints in rocks.
Temperatures drop below 0, the water freezes and expands.
It melts and over time, repeated action weakens the rock causing it to break.
Explain Chemical Weathering
Carbon Dioxide dissolves in rainwater.
The acid reacts with rocks containing calcium carbonate. (Carboniferous limestone)
Rocks are gradually dissolved.
What is the difference between concordant and discordant coastlines?
Concordant coastlines have bands of rock which run parallel to the sea, with the sea. Discordant coastlines have bands of rock which run perpendicular to the sea.
What landforms are caused by erosion?
Cliffs and wave-cut platforms, headlands and bays, caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
Concordant coasts form _____ when an area of weakness in hard rock is erode and reaches the softer rock. The softer rock is eroded faster than the hard rock in-front.
Coves
What landforms are caused by deposition?
Beaches, spits, offshore bars and tombolos, barrier islands, sand dunes, estuarine mudflats and saltmarshes.
What is this an example of? “Destructive waves remove sediment and deposit as offshore bars. This reduces the steepness of the beach and encourages waves to break further out. This reduces wave energy. This will lead to a more powerful swash and the beach will build back up.”
Negative feedback loop
Name an example of a simple spit
Spurn Head, Holderness Coast
Name an example of a compound spit
Sandy Hook, New Jersey USA
What is a barrier island?
An elongated bank of sand or shingle lying parallel to the coastline, not submerged by tides.
Name two examples of a tombolo
Chesil Beach, Weymouth
The Angel Road of Shodo Island, Japan
What is an estuarine mudflat?
Low-lying areas of the shore, submerged at high tide and exposed at low tide, often developing into salt marshes.
Name 4 examples of mudflats and saltmarshes
Severn Estuary - Mudflat
Cook Inlet, Alaska, Uk - Mudflat
Slimbridge WWT, Severn Estuary - Saltmarsh
Gulf Coast, USA - Saltmarshes
What are the 6 dune stages?
Embryo
Fore
Yellow
Grey
Slacks
Mature
The Sefton Coast is home to one of the largest coastal dune systems in Great Britain, it extends ___ along shore, inland, covers ____ ha and reaches up to __ in height.
17km, 4km, 2100, 30metres
How has the Sefton Coast been impacted by humans?
Land was converted to growing asparagus, flattening the dunes.
Uncontrolled access caused serve erosion.
25% is managed as a golf course damaging habitats.
It was planted with pine trees supporting red squirrels.
What is the difference between eustatic and isostatic sea level changes?
Eustatic changes refer to global shifts in sea level, while isostatic changes involve relative sea level changes due to land subsidence or uplift.
__________ changes occur due to change in volume of water, change in the shape of ocean basins.
Eustatic
What are the main causes of Isostatic sea level change?
Uplift or depression of the Earth’s crust from melting ice sheets.
Subsidence of land due to shrinkage after abstraction of groundwater.
Tectonic processes.
Landforms: Coastlines of Submergence - sea level change submerges the existing coastline.
Rias, Fjords, Dalmation Coasts
Landforms: Coastlines of Emergence - sea level change reveals new emerging coastline.
Raised Beaches, Marine (Wave-cut) Platforms
Canvey Island
Low-lying area north-side of Thames Estuary
1m above average sea level.
Protected by 6m sea wall
Canvey Island Risks
Isostatic rebound experienced unevenly (1mm/year NW Scotland, 1.5mm/year SE England)
Eustatic change believed to be 3mm/year
By 2100, sea level in Thames Estuary between 53.1cm and 37.3cm which could overtop current sea defences.
Canvey Island Responses
Safe Havens
Building mobile homes
Escape or community refuge plans
Marshlands need to be remodelled.
What are the 4 main approaches to coastal management?
Advance the Line
Hold the line
Retreat the line/ Managed realignment
Do nothing
What are the two main types of coastal engineering approaches?
Hard engineering (artificial structures) and soft engineering (working with nature to manage coastlines).
Describe a positive feedback loop due to sea defences
Groynes are built trapping sediment
This reduces width of the beach downdraft of the groyne
Waves have more energy due to less friction
More erosion of the cliffs
LSD takes sediment downdrift but nothing is replacing the lost sediment
Waves continue to erode the cliff downdrift of the groyne
Describe a negative feedback loop due to sea defences
Too much wave energy due to the beach being low
Groynes are built
Beach builds back up
This reduces wave energy due to friction
More deposition as wave energy decreases
The groynes are full and sediment can move with LSD
Wave energy builds up repeating the cycle
Name 4 hard engineering strategies and their cost and cons
Sea Walls - expensive, creates strong backwash eroding the underneath
Gabions - cheap but ugly
Rock Armour - cheap, can shift in storms
Groynes - cheap, £5000 each and can last up to 40 years with good maintenance, positive feedback loop
Name 4 soft engineering strategies
Beach nourishment
Sand Dune Regeneration
Beach reprofilling
Managed retreat
Integrated ______ ____ Management considers all elements of the coastal system and aims to protect the coast in a relatively natural state whilst allowing people to use it.
Coastal Zone
What is the Holderness Coast known for?
It is known for having one of the highest rates of coastal erosion in the UK. In Great Cowden it has been over 10m/year.
How long is the Holderness Coastline?
61km, stretching from Flamborough Head to Spurn Head
Most of the Holderness Coast is made of _____ (boulder ____) and the coast is exposed to _________ waves from the North Sea during storms,
Till, clay, destructive.
How is Holderness impacted by sea level change?
Holderness is predicted to sink by 9cm by 2050 and sea level is predicted to rise bay 2-3cm, causing over 200 homes and many roads to fall into the sea by 2100
A total of ___ of the coastline is currently protected by hard engineering.
11.4km
Management at Skipsea includes:
hard engineering measures such as gabions and revetments to protect against coastal erosion.
Challenges for Possible Schemes at Holderness
Recommend to hold the line at some settlements and do-nothing at others. This is unpopular with land and property owners.
Managed Realignment is more sustainable especially for caravan parks but there are issues with compensation and relocation isn’t always possible.
Sea defences protecting Easington Gas Terminal stretch only 1km meaning the village of Easington is not protected and at risk of increased erosion.
The _______ are a coastal zone extending over _______ in the Bay of ____ characterised by mangroves, forests and swamps.
Sundarbarns, 10000km², Bengal
What rivers deposit sediment into the Sundarbans
Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna
Wha are natural challenges in the Sundarbans?
Coastal-flooding, cyclones, high soil salinity, instability of islands, and tigers.
What are human induced challenges in the Sundarbans?
Over-exploitation of resources, conversion of wetlands to agriculture, destructive fishing, and lack of awareness of coastal issues.
The mangroves are important for what reasons?
Protection - floods, shoreline erosion, cyclones, waves
Provision - animal breeding, fishing, coastal livelihoods
Maintenance - biodiversity, soil formation
Value - tourism
Mitigation to risks in Sundarbans
3500km of embankments were built but are being eroded
Replanting of mangroves however illegal forest clearance is difficult to prevent
Cyclone shelters were built by NGOs
Adaptation in Sundarbans
Salt-resistant rice varieties are grown allowing residents to cope with flooding and sea level rise, but reduced biodiversity.
Projects to increase tourism provides jobs and incomes, however can caused environmental damage if not properly managed.
Grassroots NGOs run education programmes to encourage farmers to return to more traditional ecologically-friendly methods.