Introduction to Veterinary Parasitology
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANS 389C
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
The discipline of parasitology includes only parasitism caused by…
protozoa, helminths, and arthropods
list some normative characteristics of parasitism
- parasites are of separate species than their hosts
- activity of parasites pose a direct harm to host and provides no benefit
- live considerable portion of life inside or on the surface of another organism
- clinical disease is dependent on population of parasitism on the host; signs may range from subclinical to severe
- parasites are invertebrates
symbiosis
the process of two different species (symbionts) living in close association with each other
list some symbiotic relationships
- mutualism
- commensalism
- parasitism
mutualism
both organisms benefit from each other
commensalism
one organism benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited
parasitism
one organism (parasite) benefits at the expense of the other organism (host)
parasite
an organism which lives inside or on surface of another organism (host) of a different species and derives its nutrition, habitat and biological resources from the host at the expense of host’s wellbeing causing direct harm to the host
host
an organism that provides nutrition, habitat, or other biological resources to a parasite or commensal organism
endoparasite
a parasite which lives inside of its host; an internal parasite
what type of parasite causes infections?
endoparasite
ectoparasite
a parasite which lives on the surface or outside of its host (an external parasite)
what type of parasite causes infestations?
ectoparasites
obligate parasite
always requires a host to live; enter life cycle on a host
facultative parasite
organism can either act as a parasite or can live independent of a host; can live either a parasitic or non-parasitic life
definitive host
the host which harbors the adult parasite or where sexually reproductive processes of the parasite take place; harbors the adult stage
what is another name for a definitive host?
primary host
intermediate host
a host that harbors the intermediate (larval) stages of the parasite; harbors the immature stage
what are examples of an intermediate host?
mosquito and heartworm larvae
paratenic host
host the carries or transports the parasite without it undergoing development; parasite does not require this host for development
what is another name for a paratenic host?
transport host
reservoir host
host that harbors the parasite in nature and acts as a long-term source of infection for other species; spreads the parasite into the environment
what are examples of a reservoir host?
opossums and Sarcocystis neurona
dead-end host
host that is not normally part of the parasite’s life cycle but becomes infected; does not spread the parasite into the environment
what are examples of dead-end hosts?
horse and Sarcocystis neurona
direct life cycle
a life cycle in which a parasite completes its entire life cycle within a single host species; does NOT require a switch to an intermediate host in order to continue developing; additional hosts are not required
what’s an examples of a parasite with a direct life cycle?
Toxocara canis (Canine Roundworm) in the dog
indirect life cycle
a life cycle in which additional hosts are essential for development; requires an intermediate host
what is an example of a parasite with an indirect life cycle?
Dirofilaria immitis (Heartworm in dogs) in mosquitoes
prepatent period
the period of time between parasitic infection to production of parasitic offspring; can be days to months
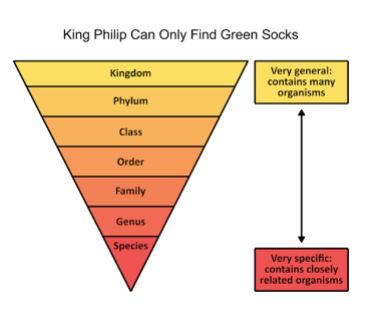
what is the hierarchy of taxonomic categories built off of?
built of subjective inductions based on similarity and dissimilarity among various groups of organisms