Food Service Exam 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
macro vs micro marketing
macro - look at the economy’s entire marketing system
micro - look at individual company
different types of economies
Free Market Economy - “capitalism”, market driving, price is a measure of value and what consumers are willing to pay
Russia - mixed economy
china - socialist market
Value exchange - something of value exchanged for something of value
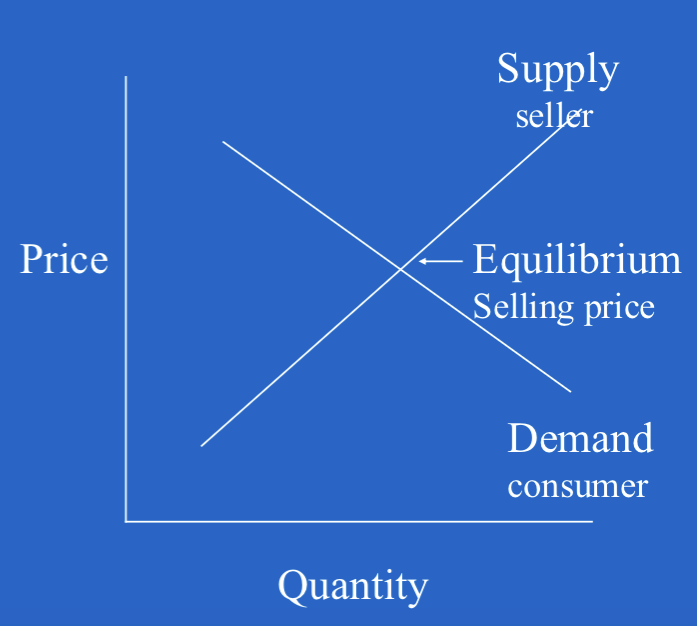
law of diminishing demand
history of marketing
late 1800s - industrial revolution
1920s - advertising and sales focus - differentiating products
1950s - marketing dept, consumer research, advise mgmt of how to design, price, distribute, and promote
marketing concepts
Management philosophy of how a company views customers and the sale of their products (goods, services, ideas)
manufacturing/production concept
available and affordable
product concept
customers prefer existing product, should focus on improvement
selling concept
need a large selling and promotion effort
marketing concept
determine needs and wants of target market
societal marketing concept
org determine needs and wants and company needs deliver to improve consumers and society’s well being
marketing strategy
plans
goals and objectives
standards
contracts
policies and procedures
programs
target mix
fairly homogenous group of customers to whom a company wishes to appeal
marketing mix
controllable variables which the company combines in order to satisfy the target group
product
price
place
promotion
approaches to plans
strategic plan, defined target market and marketing mix, identify resources needed, objectives to be received
look at duration, scope, and method of development
short range - 1 year
med range - 2-5 years
long range - 5 years
scope - what you will concentrate on
bottom up - info from employees
top down - developed by top mgmt
strategic plan
long term, overview of marketing in the organization
done after market has been defined
outlines resource allocation
objectives
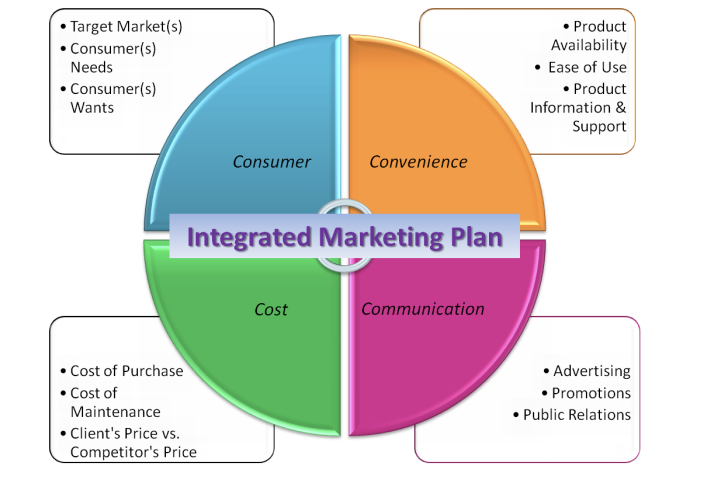
integrated marketing plan
a management concept that is designed to make all aspects of marketing communication such as advertising, sales, promotion, public relations, and direct marketing work together as a unified force, rather than permitting each to work in isolation
Press-Gainey patient satisfaction
patient satisfaction surveys
rate 1 to 5
situation analysis (SWOT)
identify marketing opportunities and potential problems
current condition and where organization is going
SWOT - strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
market segmentation
division of total market into groups of customers who have similar needs, wants, values, and buying behaviors
market research
systematic assembly and analysis of facts relevant to marketing, need good facts to make decisions
define the problem
secure internal data
finding secondary data
collecting primary data
data analysis
interpret research and make recommendations
report
stages of marketing activities
pioneering state - bringing, extensive advertising-promotion
competitive stage - try to increase place in market, know your niche
retentive stage - have customers need to keep them happy
market share
percentage of industry sales for a product
environmental factors and impact on marketing
brand
name, term, design, symbol, or feature that identifies on seller’s good or service as different from another
brand equity
value of a brand
brand loyalty
repeated customer purchase of a specific brand
customer loyalty
frequency with which a customer consistently purchases a specific brand
social media
no longer a luxury but a necessity
pay attention to what others are talking about
find your niche
be careful - everything is public
build blog brand
SSS rule - short sweet and saturated with valuable info
promote and publicize - comments, keep readers coming back, spread the word
importance of sustainability
social - health and well being, equity
economic - resource efficiency, market stability
environment - resource conservation, biodiversity protection
ways foodservice can go green
healthy retail offerings
sustainable food
purchasing
green buildings
energy and water conservation
waste management
procurement
food
supporting products and equipment
organic
not taking off, cost
cage free/hormone free
fair trade
cocoa, coffee, bananas, tea, and sugar
must be free of forced labor or poor working conditions for laborers
crips raise through sustainable methods no GMOs
have a floor price
local
150 mile radius
food miles traveled
taste and flavor
support local farmers
convenient
community based food system
challenges with food procurement
seasonality
volume
quality
specification and packaging consistency
competitive cost
disposable products
avoid polystyrene products
avoid waxed cardboard
use products with recycled content
FDA limits use of recyclable in precuts carrying food
LEED
leadership in energy and environmental design
energy efficient equipment
program of US Environmental Protect Agency and Dept of Energy
international standard for consumer products
use ip to 50 percent less energy than conventional
energy use in food service
fryers, hot food holding, refrigerators, freezers, steam cookers, dishwashers, ice makers, griddles, ovens
water conservation and efficiency
high efficiency dishwashers, foot petal sinks, motion sensor sinks and light, high velocity pre since spray nozzles, leak inspections, only operating dishwaters when full, hand scraping food scrapes, energy efficient aerators
waste management
buy in bulk, pulpers, garbage disposals, recycling program, composting programs
types of owernship
proprietorship - owner has total decision making authority and retains all profits, least costly form of ownership, easy to initiate and discontinue, avoids double taxation. Unlimited personal liability, limited access to cash, management limited to skills and abilities of owner
partnership - increased sources of knowledge/ability/capital, easy to initiate, avoids double taxation. General partner has unlimited liability, potential for personality conflicts, partners bound by law of agency, difficult for partner to dispose of interest without dissolving the company
C corporation - limited liability of owners, easier to attract capital, ease in transferring ownership. Costly and time consuming to create, double taxation, increased legal requirements, limited control for person who starts company
S corporation - limited liability of owners, ease in transferring ownership, avoids double taxation. Can be at a higher tax rate than C corp. Limited to 75 or less stockholders
LLC/PC - limited liability of owners, can have multiple owners, avoids double taxation. Costly and time consuming to create. Transfer of ownership requires approval of all the owners.
cash vs accrual accounting
cash - record transaction at the time the cash actually goes in or out
accrual - record transactions when revenue is earned
major expenses and usual percent for restaurants
labor
food
operating costs
60-65% of cost
cash handling
separation of duties
who has access to dahs
security/background checks
reconciliation - unannounced audits, cash drawers, surveillance cameras
fixed vs variable vs semi variable costs
fixed - do not vary with volume or service rendered, non controllable
variable costs - vary directly/proportionately w/ volume of business
semi variable - vary in same direction but less proportionately w/ changes to vol
direct vs indirect costs
direct - items of cost which are specifically traceable to an item
indirect - elements of cost that are associated with an item but not directly traceable to an item (utilities, supervisors salary et)
sunk vs differential costs
sunk - already incurred and cannot be recouped
differential - about of increase or decrease in cost when you compare alternative choices
assets
things that a company owns which have value
equities
ownership or claims against the assets, groups of individuals who have rights associated with the assets
liabilities
claims against the company, interest of the creditors
capital
interest of the owners in the company
what is a balance sheet
statement which shows the financial condition of a business at a given point in time
assets, liabilities, owners equity
fixed assets
purchased for long term use and are not likely to be converted quickly into cash
current vs long term liability
current - debts which are to be paid within he next operating period
long term - long term debt
what is an income statement
statement which shows the results of operating a business over a period of time
revenue, expenses
straight line depreciation formula
original cost - less salvage value/useful life
why might a business use accelerated depreciation
original cost x double declining balance %
reduce its taxable income in early years of an asset’s life
purchases method to calculate food cost
total purchases / # of meal served
inventory method of calculating food cost
beginning inventory + food purchases for that month - closing inventory / food sales for month
calculate pre-costing an item
EP cost / number of portions
conventional method for calculating selling price
raw food cost and mark up factor
100/mark up % = mark-up factors
SP = raw food cost X raw food cost
prime cost method for calculating selling price
food cost % + labor cost % = prime cost
100%/prime cost % = mark-up factor
actual cost method for calculating selling price
food cost + labor cost + variable costs + fixed cost + profit
what method for calculating selling price is used most and why
demand-oriented pricing
whatever market will bear
often time based pricing (lunch, early bird specials)
competitive pricing
compare to competition
not a calculation
odd-cents pricing
ends in odd number
just below zero
pricing by the ounce
salads, sandwich, bars
two tier food service
offering upscale items at a different price
A la carte
Table d’hote
fixed priced menus
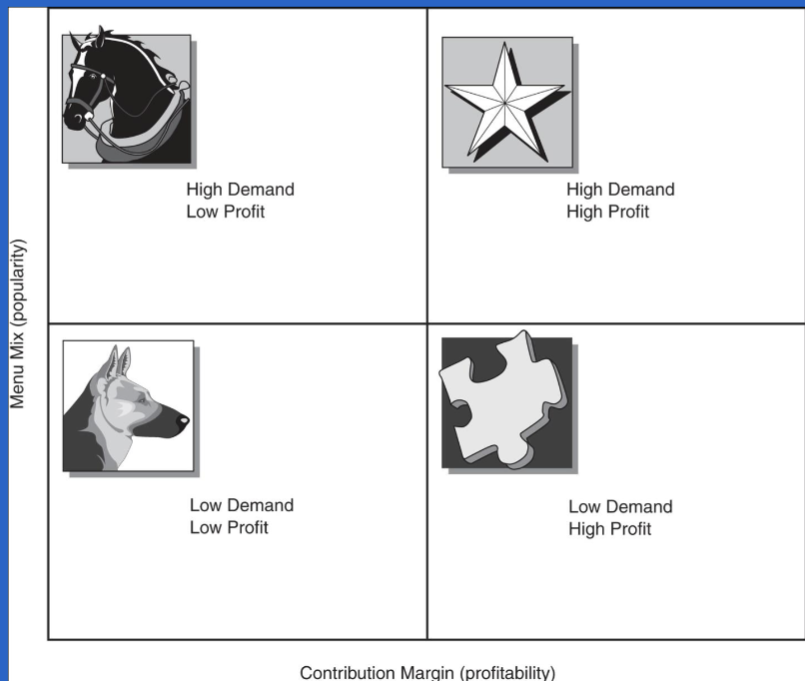
menu engineering
computerized menu analysis
focus on looking at which menu items make money