Urinary System
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Major functions of the Kindeys
Regulation of Blood, Electrolyte balance, Acid-base balance, and blood pressure.
Excretion of Metabolic products, Foreign substances, and Excess substances.
Secretion of Erythropoietin and Renin.
Coverage of the Kidneys
Renal/Fibrous Capsule - prevents kidney infection.
Perirenal Fat - cushions kidney and attaches it to the body.
Renal Fascia - anchors the kidney.
Pararenal Fat - external to the Renal Fascia.
Renal Structure
Cortex
Medulla
Renal Column
Renal Pyramid
Minor Calyx
Major Calyx
Renal Pelvis
Uerter
Uerters
Uerters actively propel urine to the bladder.
Uerters have a trilayered wall:
Transistinal Epithelial Mucosa
Smooth Muscle Muscularis
Fibrous Connective Tissue Adventitia
Urinary Bladder
Smooth, collapsible, muscular sac and stores urine.
Lies on the pelvic floor posterior the public symphysis.
connected anteriorly to the umbilicus-median.
Collapses when empty.
The badder expands as pressure rises.
Urinary Bladder Anatomy
Has the Destursor Muscle
Has a 3 layer wall:
Transitional Epithelial Mucosa
A thick muscular layer
A Fibrous Adventitia
Urethra
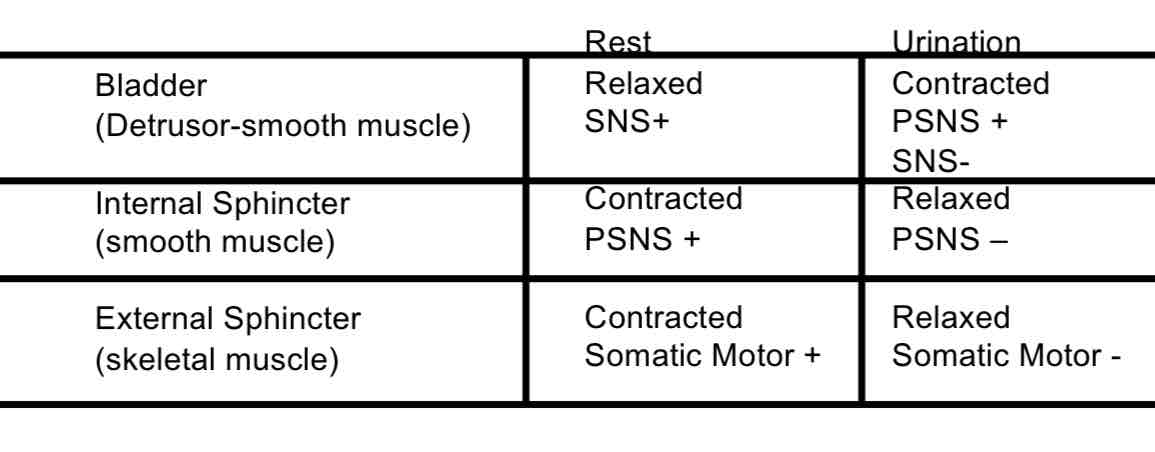
A muscular tube that drains urine from bladder, out of the body. It also has 2 sphincter to help keep it close:
Internal - INVOLUNTARY
External - VOLUNTARY
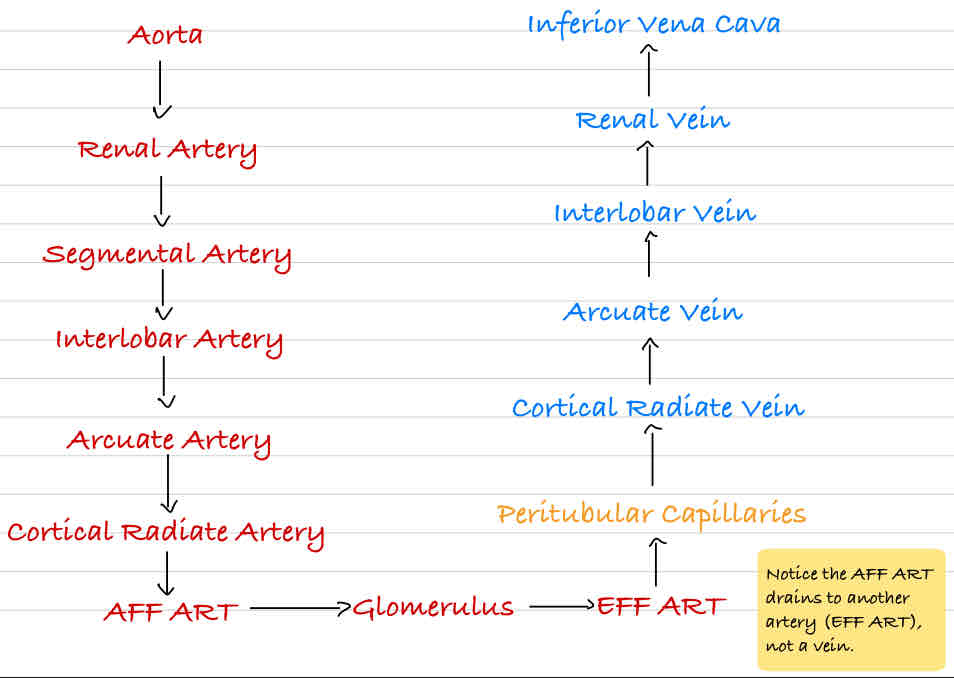
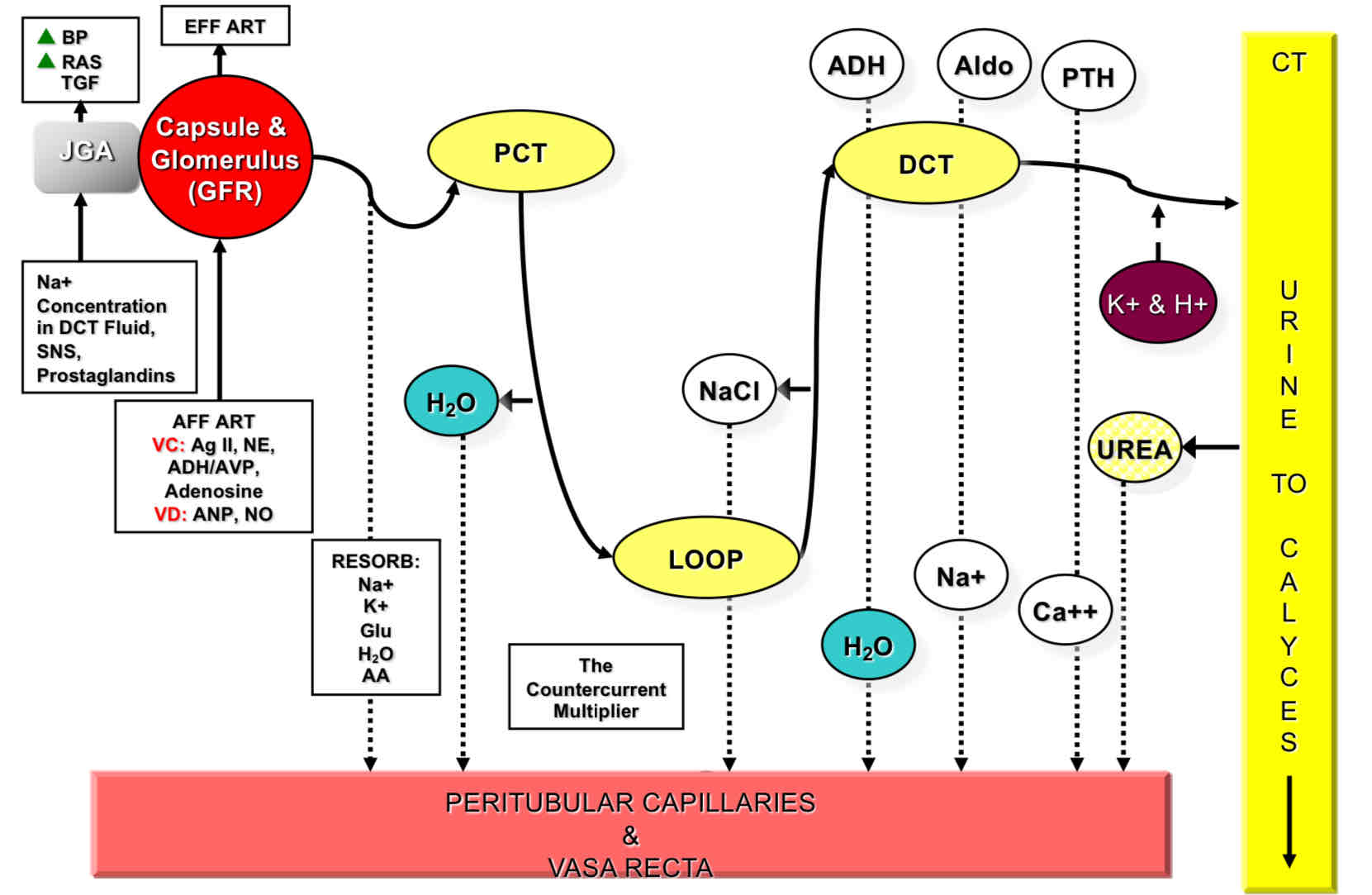
Renal Blood Flow
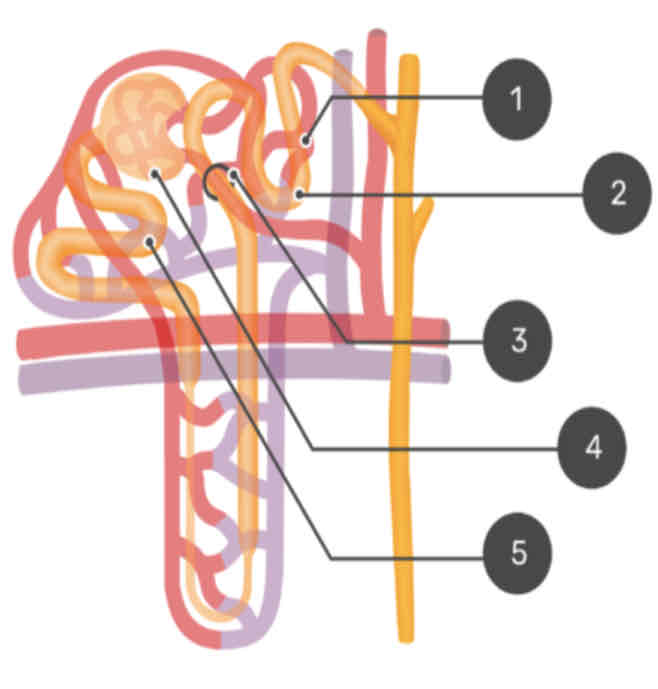
Cortex
Perutubular Capillary
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Bowman’s Capsule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
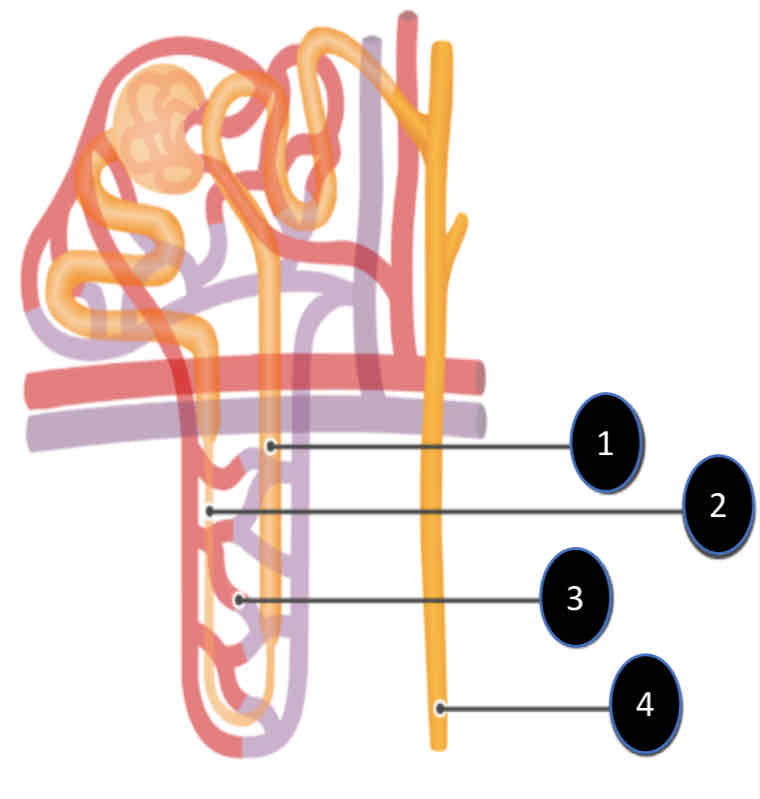
Medulla
Ascending limb
Descending limb
Vasa Recta Capillary
Collecting duct
Vasoconstriction of AFF. Art.
VC AFF. Art. → ↓Q AFF. Art. → ↓GBF → ↓GBP → ↓GFR
Vasodilation of AFF. Art.
VD AFF. Art. → ↑Q Aff. Art. → ↑GBF → ↑GBP →↑GFR
Filtration
First step in urine formation.
Bulk transportation of fluid from blood to kidney tubule. (Blood cells and proteins don’t filter)
Result of hydraulic pressure.
GFR = 180 L/day.
Reabsorption
Process of returning filtered material to blood stream.
99% of what is filtered.
May involve transport proteins.
Normally glucose is totally reabsorbed.
Secretion
Material added to lumen of kidney from blood.
Active transport of toxins and foreign substances, but also include ions.
Excretion
Loss of fluid from body in form of urine.
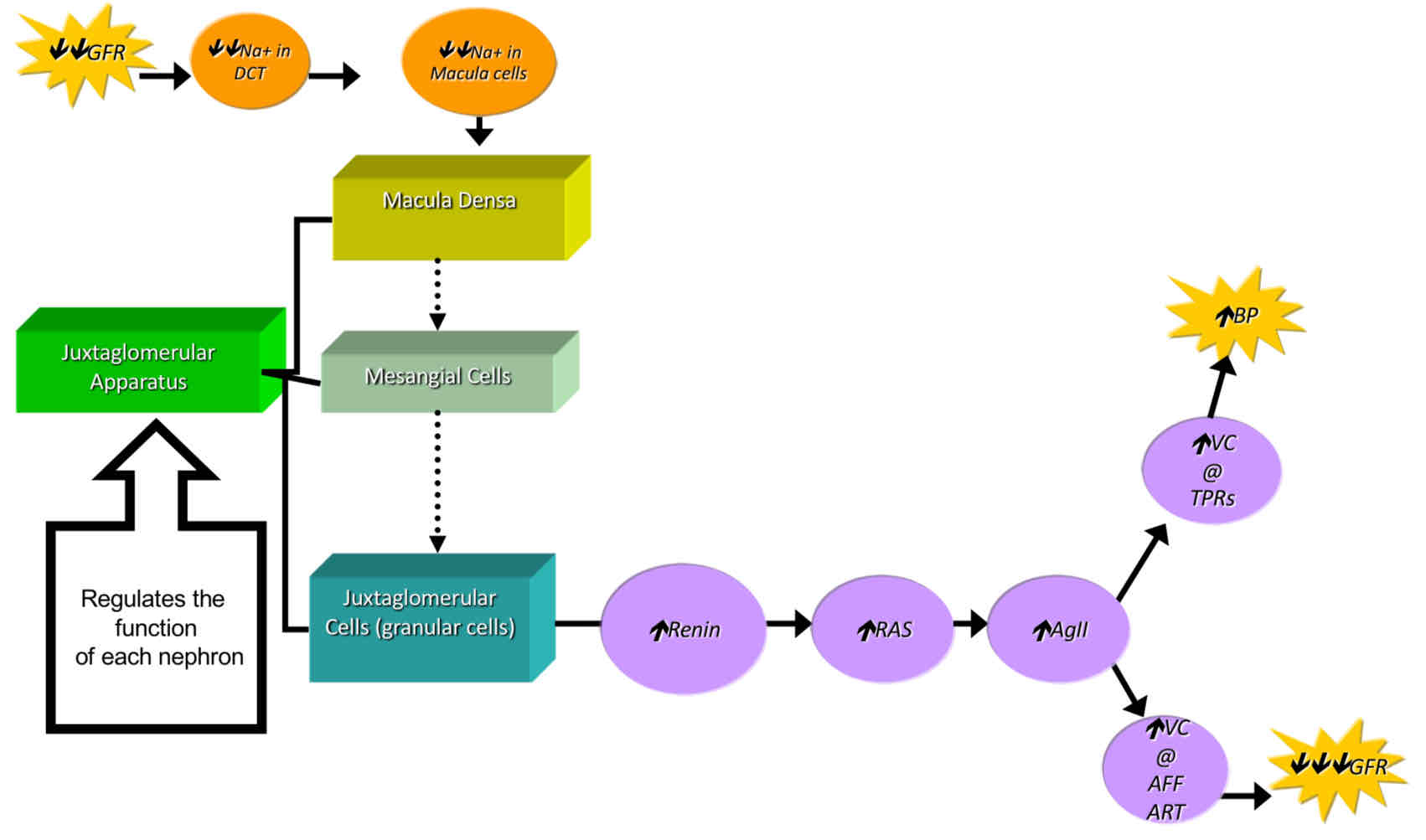
JGA Feedback (↓GFR)
↓GFR → ↓Na+ in DCT → ↑NO Release → VD of Aff. Art. → ↑GBF → ↑GBP → ↑GFR
JGA Feedback (↑GFR)
↑GFR → ↑Na+ in DCT → ↑Na+ in Macula → ↑Adenosine → VC of Aff. Art. → ↓GBF → ↓GBP → ↓GFR
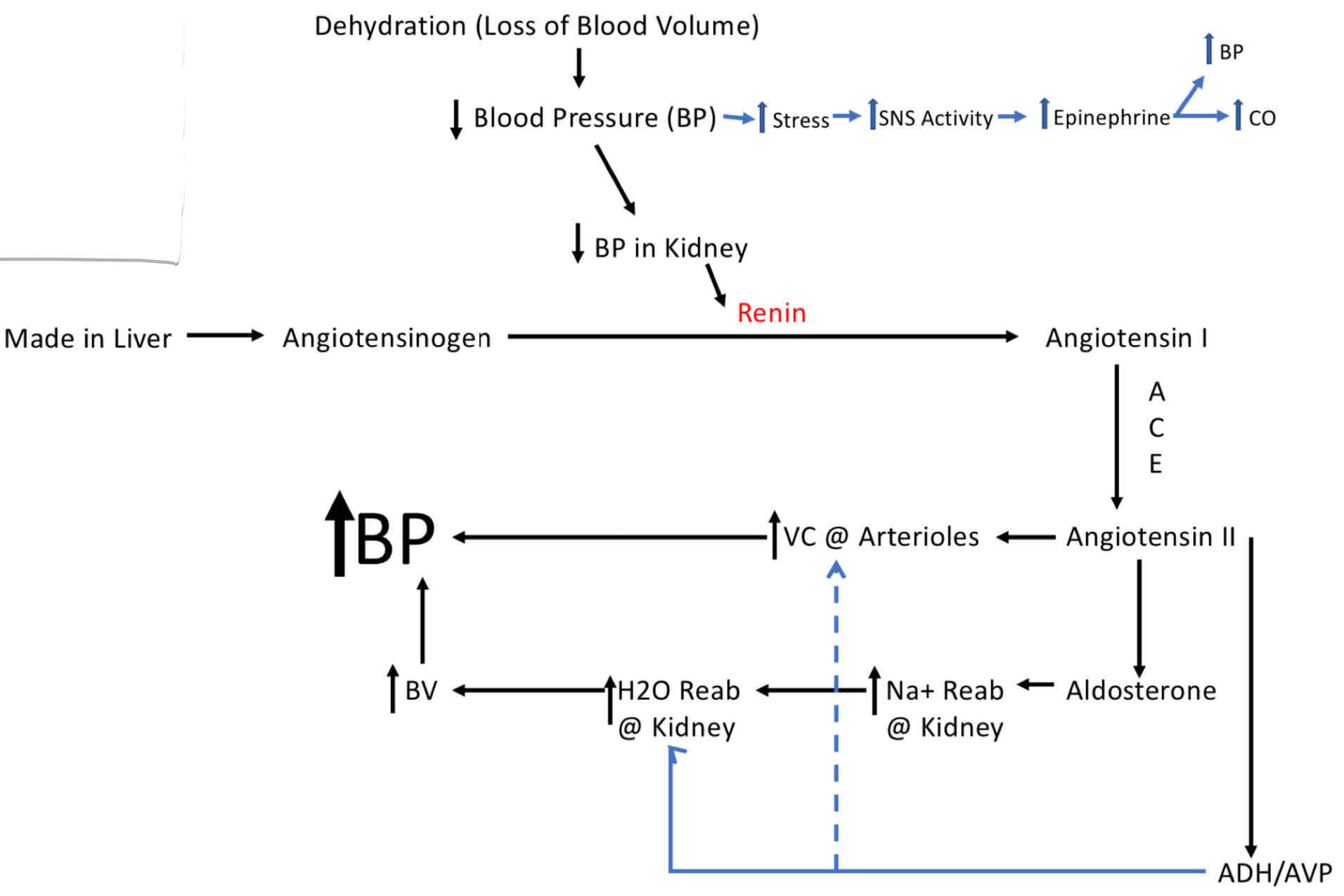
Response to Severe Drop in Blood Pressure
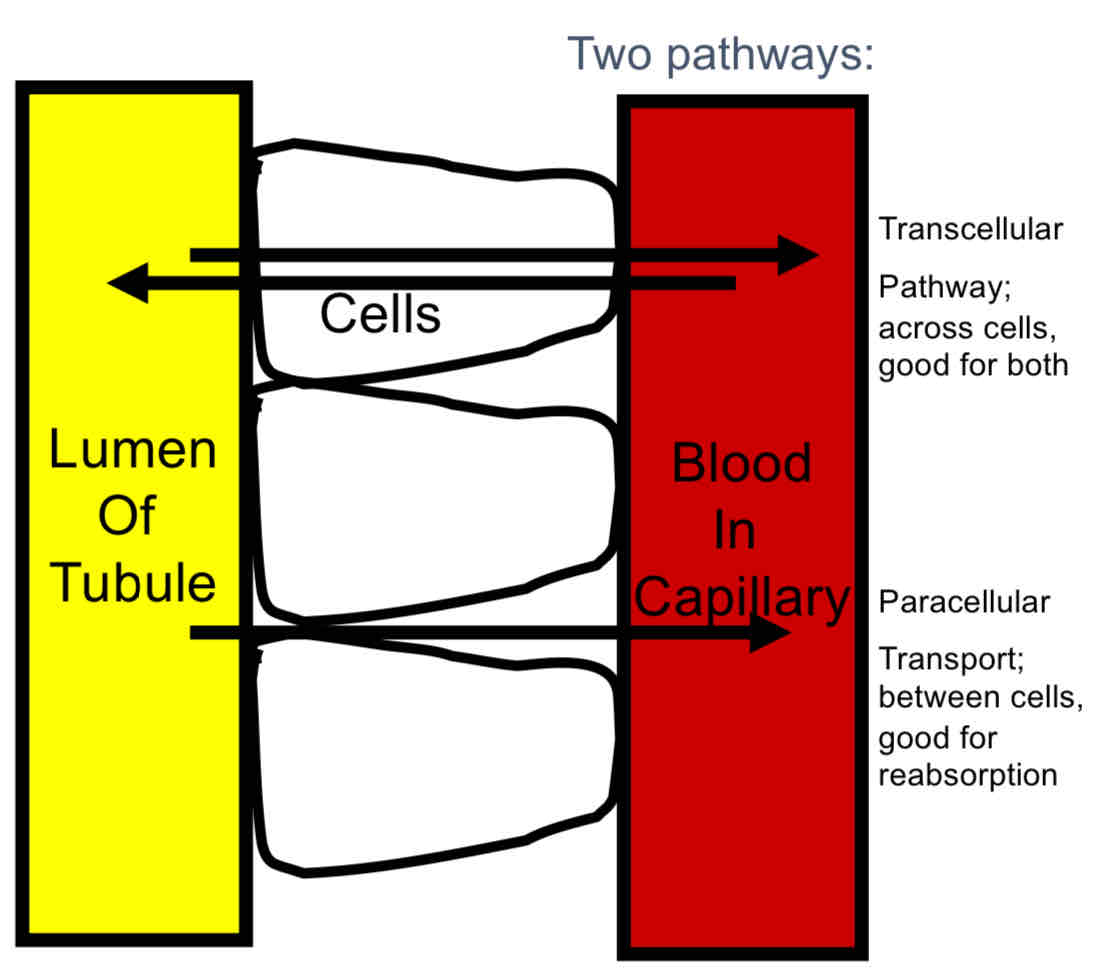
Reabsorption and Secretion
Primary Active Transport: actual “pump”, usually against the concentration gradient. REQUIRES ATP
Secondary Active Transport: moves with concentration gradient. USES ATP INDIRECTLY
Passive Transport: Diffusion.
Pinocytosis: not a major player, but useful for reacquiring larger proteins.
ADH/AVP
VC which increases systemic BP, and decreases GFR.
Retention of water (ONLY WATER) is controlled by ADH.
Released in response to Hypothalami’s Stimulation (Dehydration) or increased AgII levels.
ADH increases the number of Aquaporina incorporated into the membrane of Tubule cells.
ANP
It is released by atrium in response to atrial stretching due to increased blood volume.
ANP enhances Na+ and water losses by increasing glomerular flow (Aff. Art. VD).
It also inhibits ADH secretion. Thus, it promotes sodium excretion and water excretion in urine.
Aldosterone
Sodium balance is largely controlled by Aldosterone.
Released in response to increased AgII levels.
The net effect of Aldosterone is to make the kidney reabsorbed Na+ (WATER FOLLOWS) and secrete K+ into the Tubule Fluid.
Works by stimulating the Na+ and K+ ATPhase pump on the basolateral side (Back Door).
Aldosterone also increases the Na+ permeability of the luminal side (Front Door).
AgII
Stimulation of Aldosterone release form Adrenal Cortex.
Stimulation of ADH/AVP release from the Post. Pit.
VC of many systemic arterioles, increasing BP.
VC of the Aff. Art., decreasing GFR.
Renin
It is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversation of Angiotensinogen to AgI.
Flow in the formation and releasing of urine.
Glomerulus (Blood)
Glomerulus Capsule (Filtrate)
PCT (Filtrate)
DL (Filtrate)
Loop (Filtrate)
AL (Filtrate)
DCT (Filtrate)
Collecting Duct (Filtrate/Urine)
Minor Calyx (Urine)
Major Calyx (Urine)
Renal Pelvis (Urine)
Ureter (Urine)
Urinary Bladder (Urine)
Internal Sphincter (Sm. Muscle)
Urethra (Urine)
(External Sphincter (Sk. Muscle)
Neurological Reflex
Tubule cell that moves Na+ and K+ ions
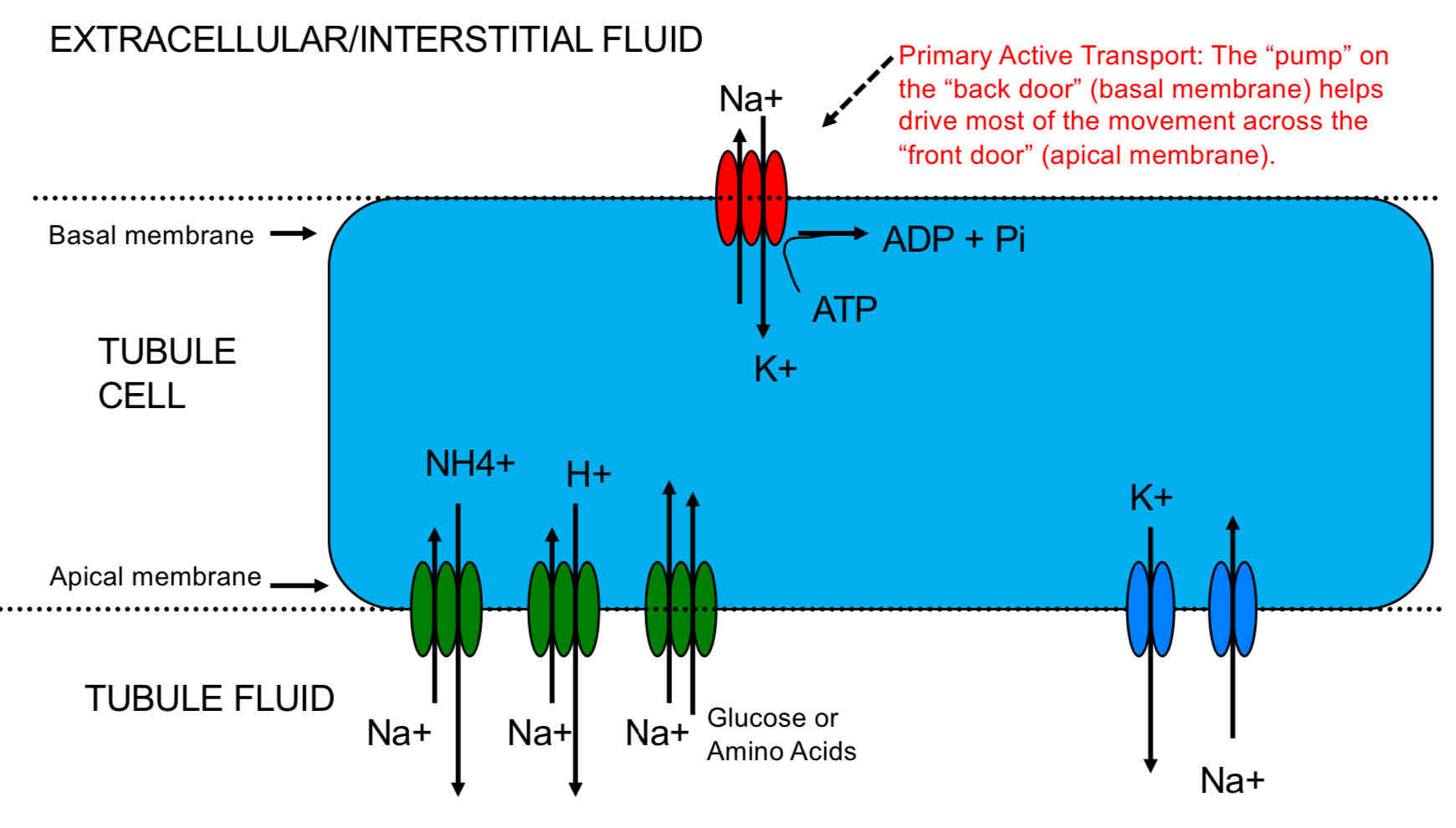
Tubule cell that moves H+ ions
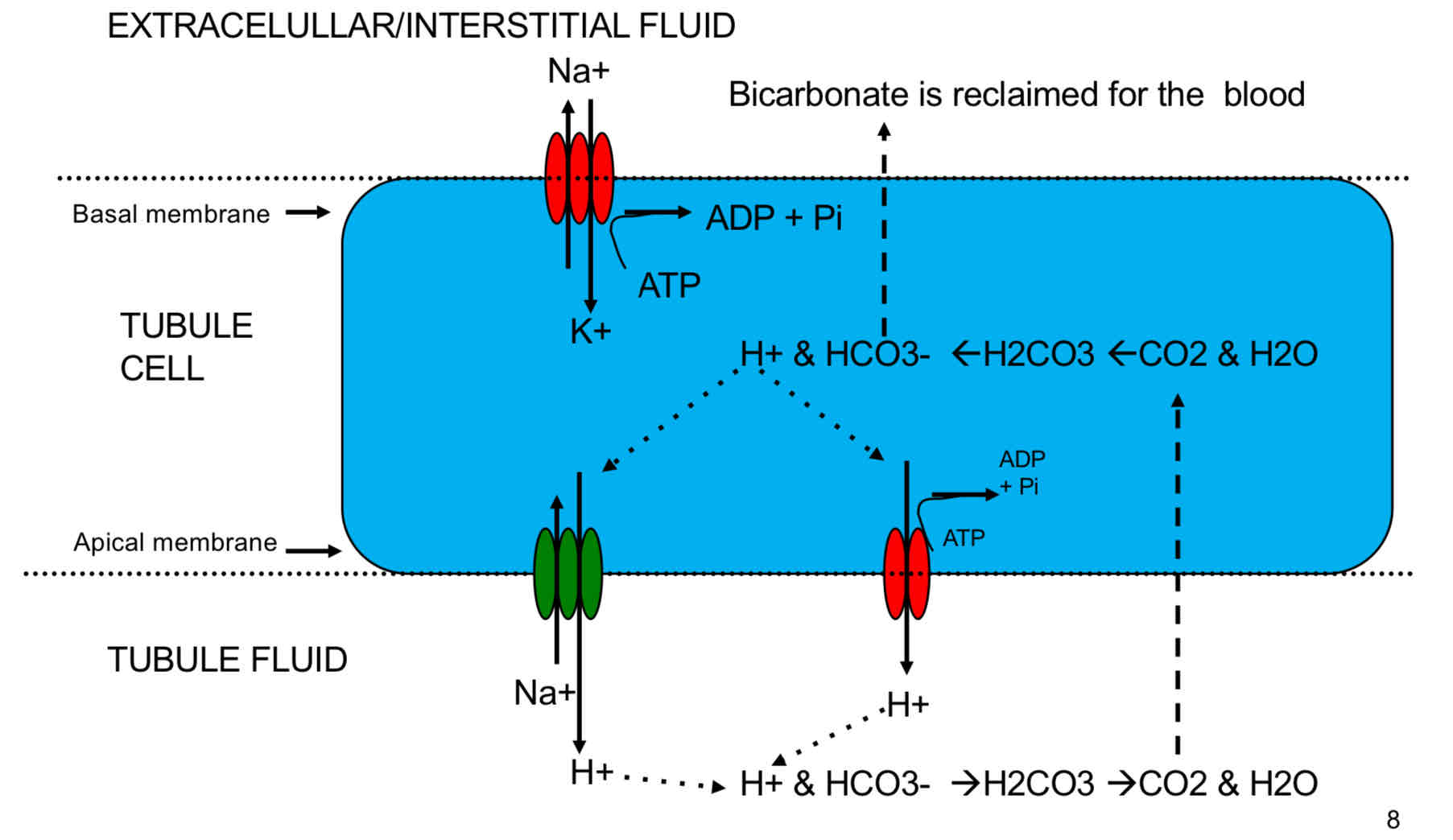
Tubule cell that creates HCO3- (Bicarbonate)
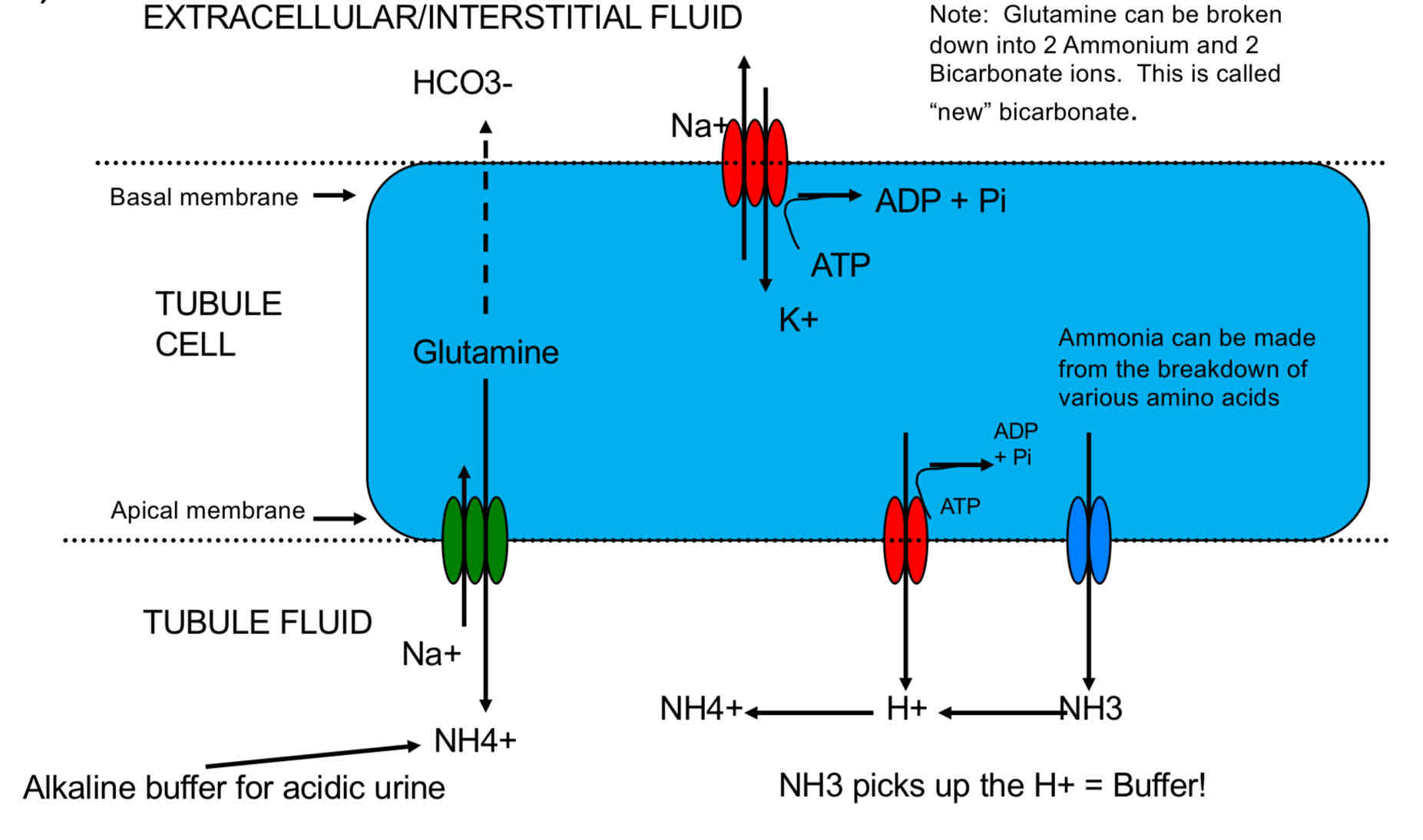
Nephron
Functions of the SNS in the Kindey
Reduce the GFR through VC Aff. Art.
Increase the Na+ reabsorption in the proximal tubules.
Increase the release of renin.
Maintaining BP during Dehydration