Ch.21 Anatomy of the lymphatic and immune systems OpenStax / Wescott courses Physiology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are the three main components of the lymphatic system?
The Lymph nodes (site for production of the lymphocytes)
lymphatic vessels ( carry lymph through the body)
and the lymph ( fluid that circulates into the lymphatic system that carries the lymphocytes and interstitial fluid throughout the body)
What is the role of the dendritic cell in infection by HIV?
Dendritic cells present the proteins of HIV to the B-ells present in the lymph nodes, which differentiates into plasma cells to produce anti bodies. The concentration of these HUV specific antibodies is used to detect aids in a person
Phagocyte chemotaxis is the movement of phagocytes according to the secretion of chemical messengers in the form of interleukins and other chemokines. By what means does a phagocyte destroy a bacterium that it has ingested?
Phagocytes contain lysosomes that have hydrolytic enzymes which can digest any foreign particle entering the body. The bacteria is internalized in a vesicle, which fuses with the lysosome. The bacteria is digested by these enzymes.
Immunity can be acquired in an active or passive way, and it can be natural or artificial.What is an example of natural immunity acquired passively?
Breastfeeding is an example of a natural immunity that is acquired passively by the baby.
The mothers milk also know as the colostrum milk is rich in proteins, carbs, and certain antibodies that are transferred to the feeding baby. This is known as the natural immunity as it comes from a natural source and acquired from the mother passively.
Which of the following cells is phagocytic?
plasma cell
macrophage
B cell
NK cell
A: Macrophage
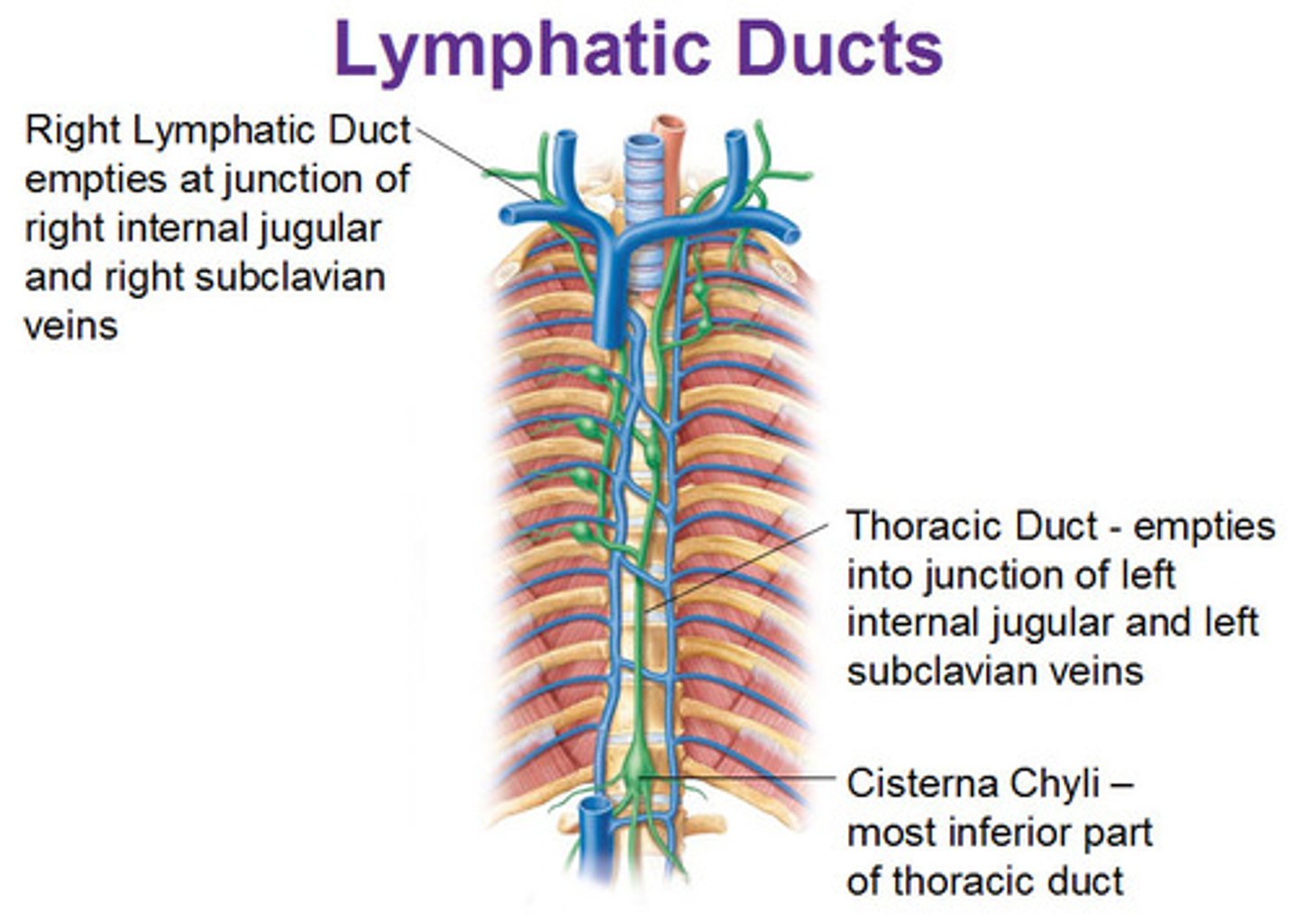
Which structure allows lymph from the lower right limb to enter the bloodstream?
thoracic duct
right lymphatic duct
right lymphatic trunk
left lymphatic trunk
A: Thoracic duct
The lymph fluid from the lower right limb enters the bloodstream through the thoracic duct. The thoracic duct is a large duct that drains the lymph from the lower limbs, left thorax, left upper limb and the left side of the head.
Which of the following cells is important in the innate immune response?
B cells
T cells
macrophages
plasma cells
A: Macrophages
Innate immunity is the immunity present in the body naturally due to genetics or physiology. it does not require antigens for its production
Macrophages are a type of phagocytic cell present in the blood stream
Which of the following cells would be most active in early, antiviral immune responses the first time one is exposed to pathogen?
macrophage
T cell
neutrophil
natural killer cell
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells are the first to respond to a cell infected by viruses. granzymes released by natural killer cells enters into the cells through pores formed by perforins, another protein released by natural killer cells and causes apoptosis (cell death)
Which of the lymphoid nodules is most likely to see food antigens first?
tonsils
Peyer's patches
bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
Tonsils
Tonsils are present in the throat and are the first lymphoid nodules to be exposed to any antigen entering inside the body by food.
.
Which of the following signs is not characteristic of inflammation?
redness
pain
cold
swelling
Cold
the inflated area becomes a little hot with the proper functioning immune cells to reduce the metabolic activity of the antigen causing inflammation.
Which of the following is not important in the antiviral innate immune response?
interferons
natural killer cells
complement
microphages
Microphage
unlike MACROPHAGES , microphages are organisms or cells that engulf the antigens in bulk instead of degrading one at a time. They are not involved in viral immune response
Enhanced phagocytosis of a cell by the binding of a specific protein is called ________.
endocytosis
opsonization
anaphylaxis
complement activation
Opsonization
Opsonization is a process by which small molecules knows as opson binds to the membrane of a pathogen and marks it for phagocytosis to the immune cells
Which of the following leads to the redness of inflammation?
increased vascular permeability
anaphylactic shock
increased blood flow
complement activation
Increased Blood Flow
Blood flow increases to the site of the infection to harbor more immune cells and carry the dead cells and debris from the site of infection to clear the site for the immune response. This leads to the redness of the area due to increased concentration of blood
T cells that secrete cytokines that help antibody responses are called ________.
Th1
Th2
regulatory T cells
thymocytes
Th2
Th2 cells are helper cells that secrete cytokines that activate the B-cells to produce antibodies.
( Th1 are a type of t-helper cell that secrete cytokines, which activates the macrophages and other T-Cells)
The taking in of antigen and digesting it for later presentation is called ________.
antigen presentation
antigen processing
endocytosis
exocytosis
Antigen Processing
antigens are recognized by T cells only after being processed followed by their attachment to the MHC (major histocompatibility complex) proteins on the cell surface. Thus antigen processing followed by antigen presentation enables antigen recognition
Why is clonal expansion so important?
to select for specific cells
to secrete cytokines
to kill target cells
to increase the numbers of specific cells
To increase the number of specific cells
the immune system is a series of responses that take place at their specific time from the start of a process of producing killers cells to the end i.e killing target cells. from this series , clonal expansion is the process of increase in the number of daughter cells from a single cell taking place to act against infection occurring in our body.
The elimination of self-reactive thymocytes is called ________.
positive selection.
negative selection.
tolerance.
clonal selection.
Negative selection
self reactive T cells are eliminated via thymocyte apoptosis and are removed by thymic phagocytes.
negative selection is the process of selecting and deleting B cells and T cells that recognize MHC molecules bound to peptides of self origin.
.
Which type of T cell is most effective against viruses?
Th1
Th2
cytotoxic T cells
regulatory T cells
Cytotoxic T Cells
- are the most potential cells, they attack and kill every which is infected with any kind of pathogen. They kill cancerous cells, damaged cells, and any cell that is infected, particularly by viruses
they are t-cell receptor bearer cells that bind to antigen specific to the receptor and attacks and kills them
Removing functionality from a B cell without killing it is called ________.
clonal selection
clonal expansion
clonal deletion
clonal anergy
Clonal energy
- is the process of making the B cell ineffective without physically deleting them. It makes the clone of B cells unable to mount an immune response
Which class of antibody crosses the placenta in pregnant women?
IgM
IgA
IgE
IgG
IgG
is an antibody which removes pathogens from the blood and activates complement protein. It crosses the placenta to protect the developing fetus from diseases present in the blood and interstitial fluid to fight extra cellular pathogen
.
Which class of antibody has no known function other than as an antigen receptor?
IgM
IgA
IgE
IgD
IgD
is a class of antibody which also acts as an antigen receptor of a B cell but no other non-receptor function is known for this antibody
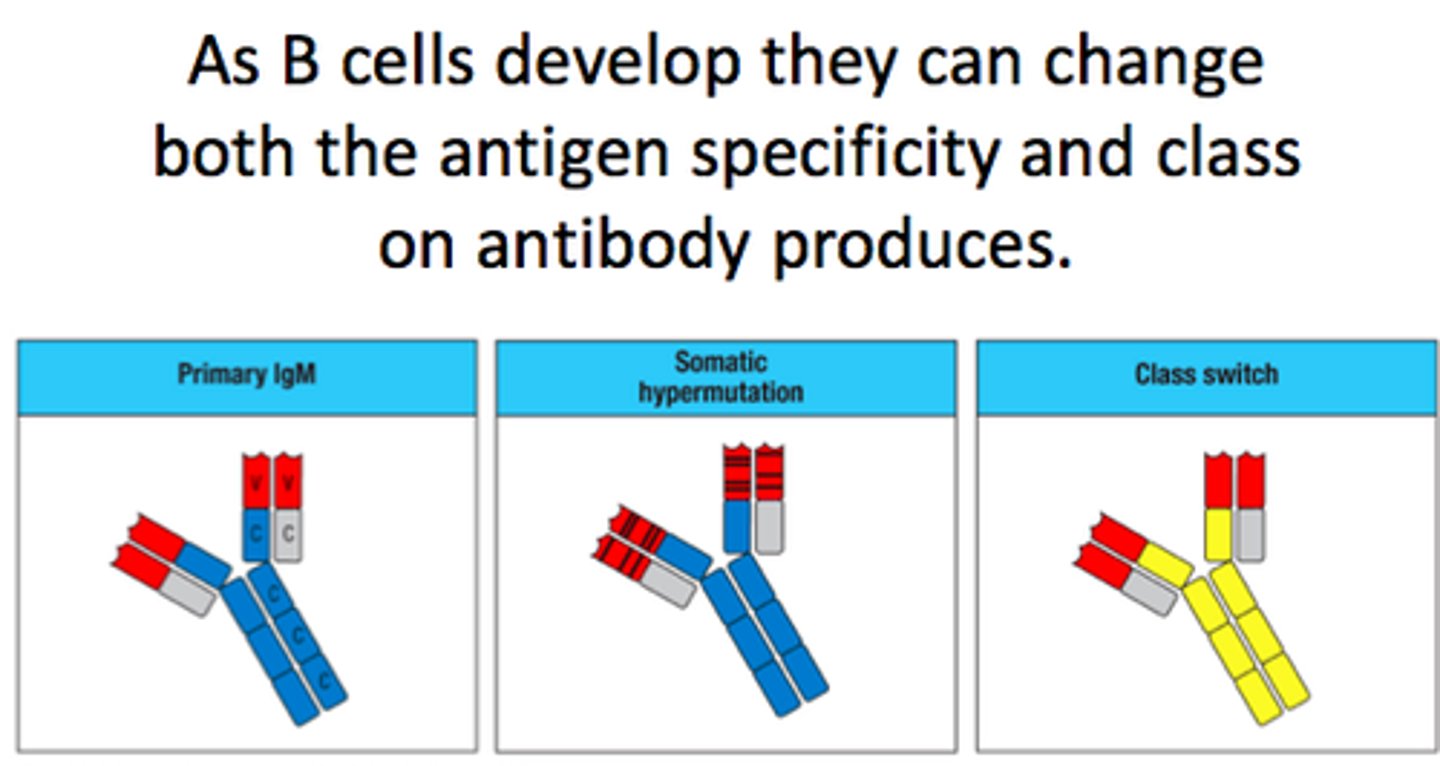
When does class switching occur?
primary response
secondary response
tolerance
memory response
Primary response
Class switching occurs when the primary response proceeds change of one class of antibody to another class of antibody is known as class switching. the specificity and the antigen binding sites to the pathogens remains the same
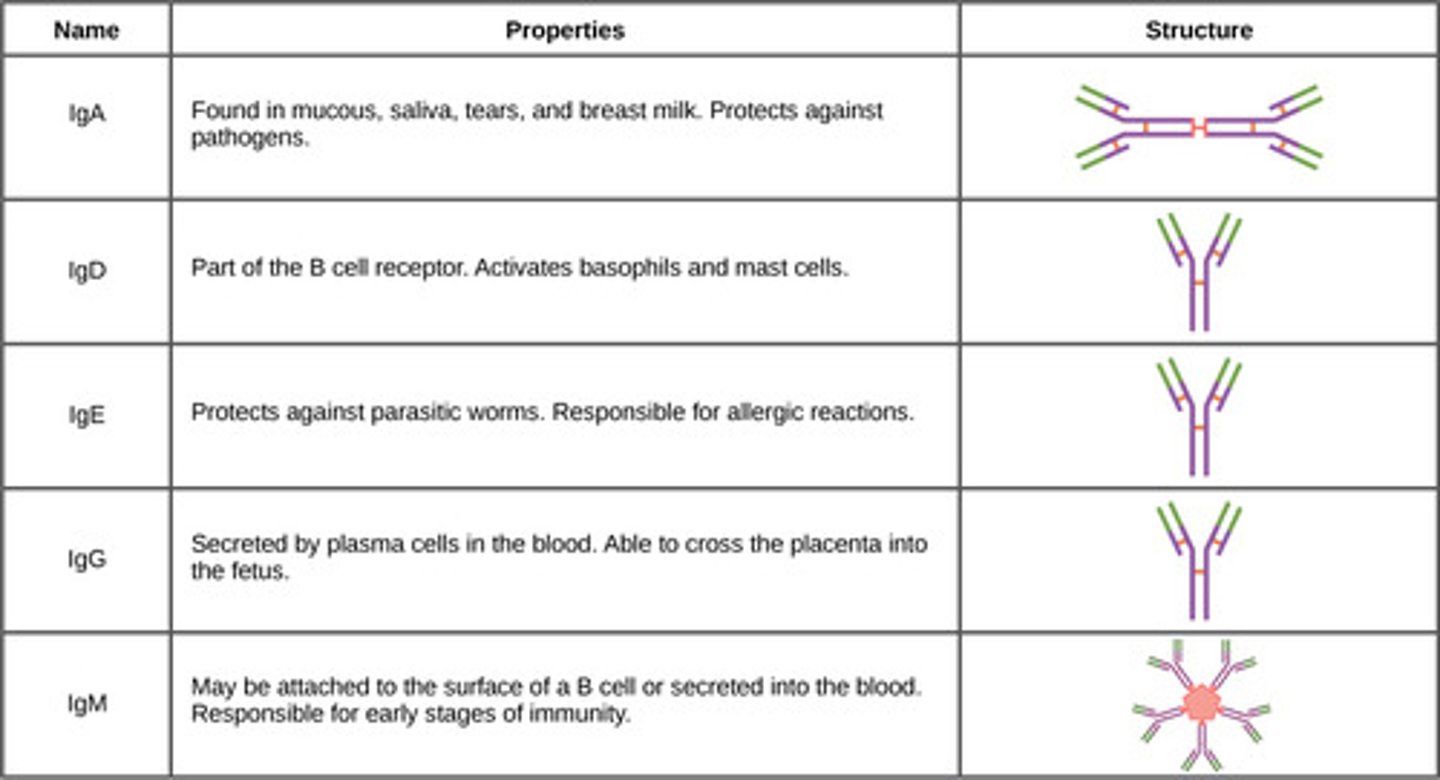
Which class of antibody is found in mucus?
IgM
IgA
IgE
IgD
IgA
is a class of antibody which exists in two forms. One is a four chain monomer , which is present in the blood and other is an eight chain structure or dimer, in the exocrine gland secretions of the mucous membranes including, mucus, tears, and saliva.
Which enzymes in macrophages are important for clearing intracellular bacteria?
metabolic
mitochondrial
nuclear
lysosomal
Lysosomal
Lysosomal enzymes present in the macrophages are important for clearing intracellular bacteria. They are derived from the golgi apparatus which destroy intracellular bacteria
What type of chronic lung disease is caused by a Mycobacterium?
asthma
emphysema
tuberculosis
leprosy
Tuberculosis
Which type of immune response is most directly effective against bacteria?
natural killer cells
complement
cytotoxic T cells
helper T cells
Complement
complement is a system of plasma proteins which is activated directly or indirectly by a pathogen bound anti body that leads reactions that occur on the surface of pathogens and generates active components with many effective functions
What is the reason that you have to be immunized with a new influenza vaccine each year?
the vaccine is only protective for a year
mutation
macrophage oxidative metabolism
memory response
Mutation
Due to the mutation viruses' surface molecules continuously enough each year that the flue vaccine for one year may not protect against flu the next year
Which type of immune response works in concert with cytotoxic T cells against virally infected cells?
natural killer cells
complement
antibodies
memory
Natural killer cells
- can recognize virally infected without MHC class I cells in concert with cytotoxic t cells
Which type of hypersensitivity involves soluble antigen-antibody complexes?
type I
type II
type III
type IV
Type III
- hypersensitivity reactions occur with disease where soluble antigens and antibodies accumulate in the blood can activate complement proteins and cause inflammation
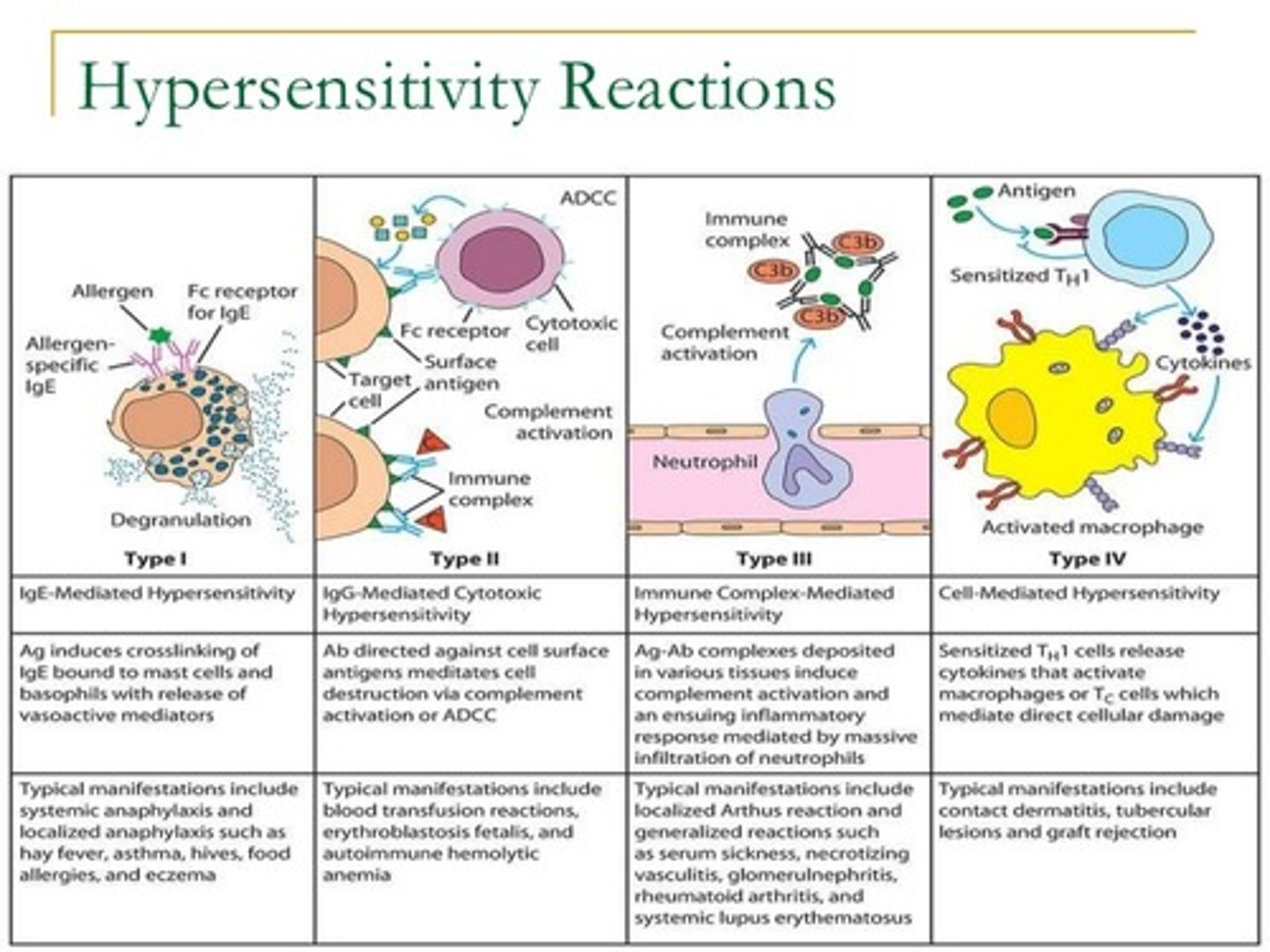
What causes the delay in delayed hypersensitivity?
inflammation
cytokine release
recruitment of immune cells
histamine release
Recruitment of immune cells
The time took which is 24-72 hours for the recruitment of phagocytes such as macrophage for secondary response is the reason for the delay in delayed hypersensitivity
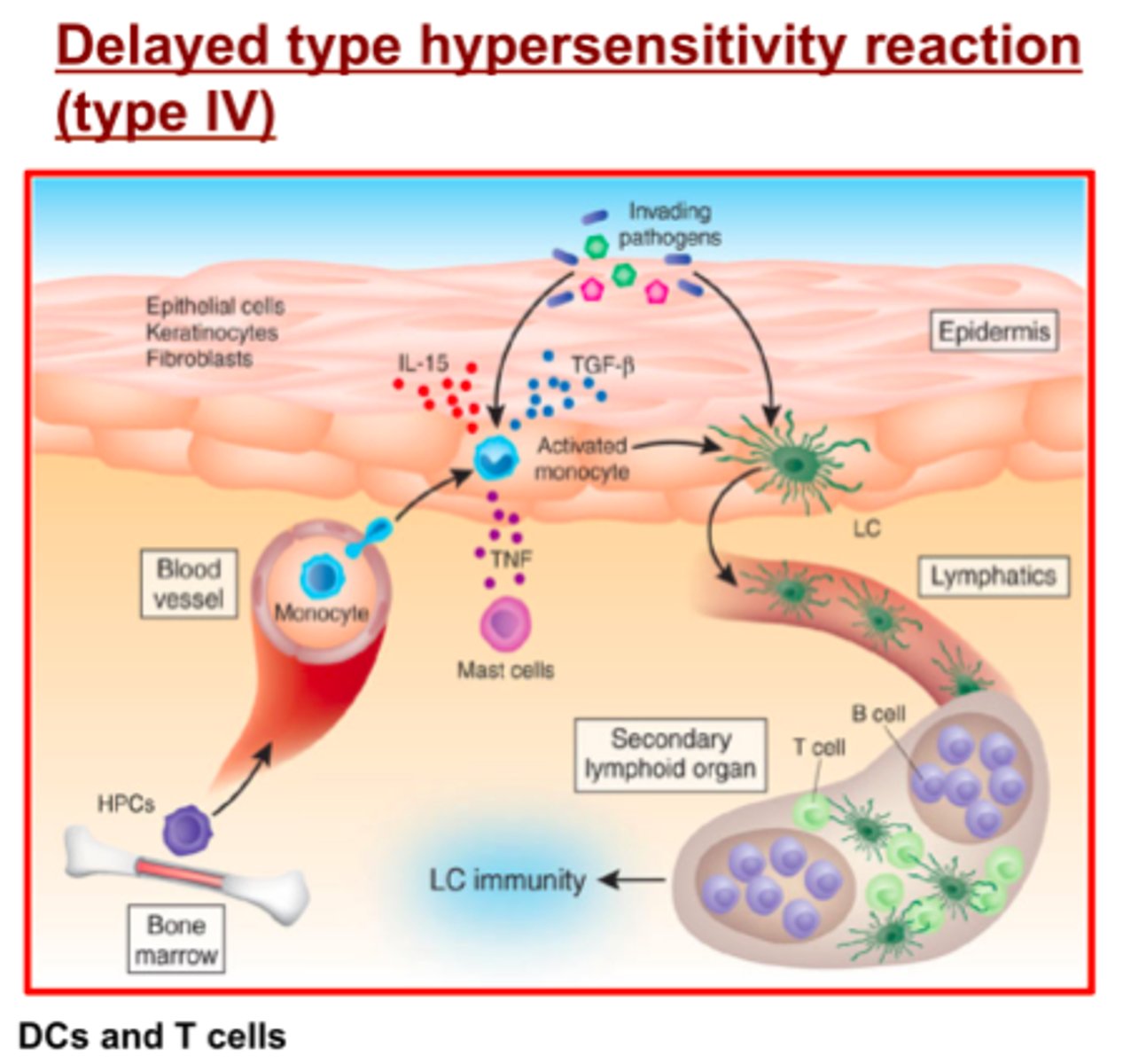
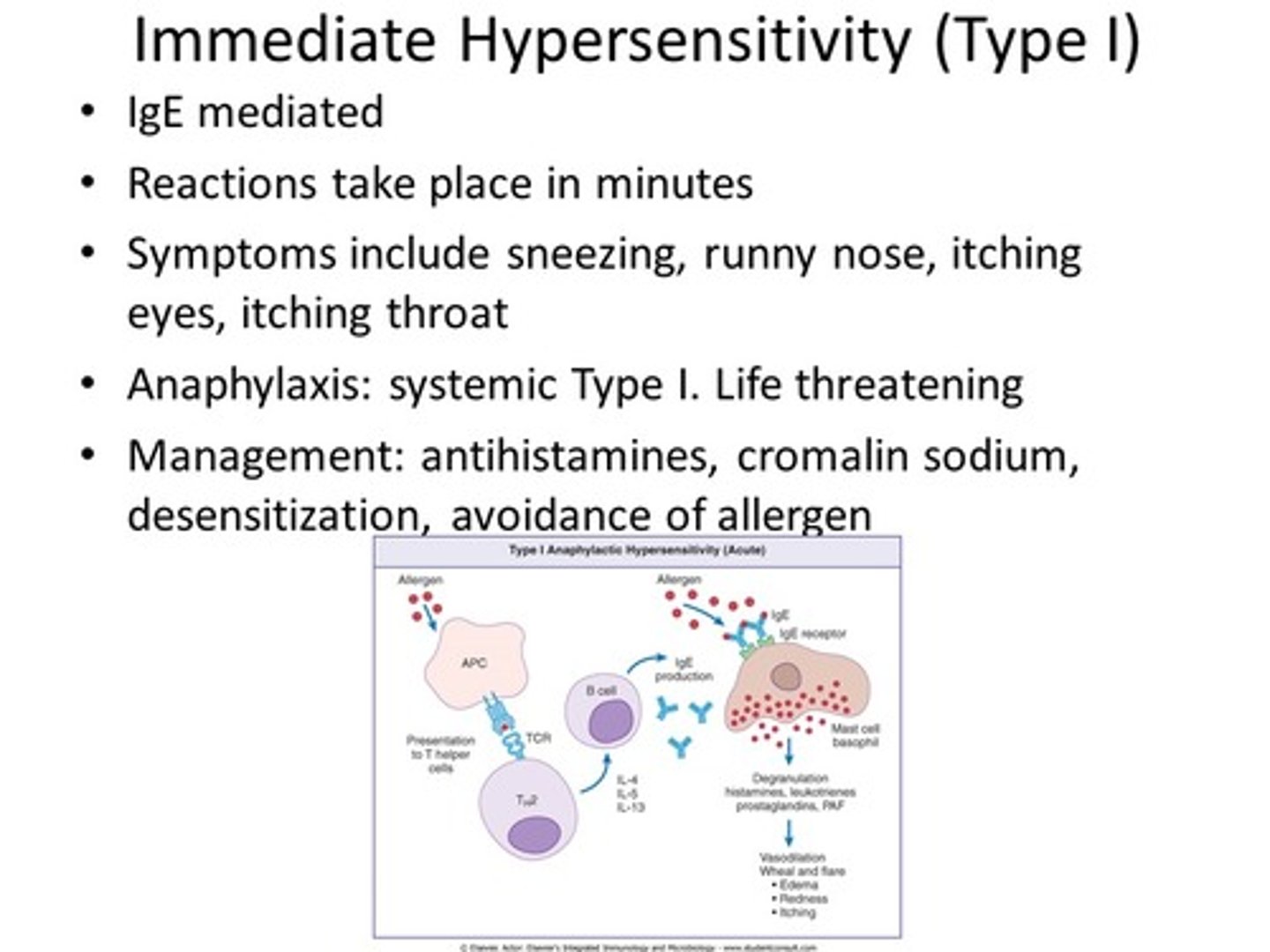
Which of the following is a critical feature of immediate hypersensitivity?
inflammation
cytotoxic T cells
recruitment of immune cells
histamine release
Histamine release
immediate hypersensitivity response is the binding of allergen specific IgE to the mast cell surface
The mast cells release histamine which is an inflammatory mediator
Which of the following is an autoimmune disease of the heart?
rheumatoid arthritis
lupus
rheumatic fever
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Rheumatic fever
an infection of streptococcus bacteria causes strep throat. As a result of this infection rheumatic fever is caused which is an autoimmune disease involving the heart.
What drug is used to counteract the effects of anaphylactic shock?
epinephrine
antihistamines
antibiotics
aspirin
Epinephrine
raises blood pressue and relaxes bronchial smooth muscle. it is used to counteract the effects of anaphylactic shock
Which of the following terms means "many genes"?
polymorphism
polygeny
polypeptide
multiple alleles
Polygeny
- refers to many genes. It means living organisms originated from many kinds of cells and not from a single cell.
Why do we have natural antibodies?
We don't know why.
immunity to environmental bacteria
immunity to transplants
from clonal selection
Immunity to environmental bacteria
natural antibodies are immunoglobulin protein which provides immunity against environmental bacterial
Which type of cancer is associated with HIV disease?
Kaposi's sarcoma
melanoma
lymphoma
renal cell carcinoma
Kaposi's sarcoma
- its a cancer caused by the human herpes virus. it is never seen in individuals having a strong immune system
How does cyclosporine A work?
suppresses antibodies
suppresses T cells
suppresses macrophages
suppresses neutrophils
Suppresses T cells
Cyclosporine A is an immunosuppressive drug which suppresses the cytotoxic T cells and makes transplant more successful
What disease is associated with bone marrow transplants?
diabetes mellitus type I
melanoma
headache
graft-versus-host disease
graft versus host disease
- is associated with bone marrow transplant. A rash and damage to the liver and mucose are the symptoms of this disease
Thrombin activates platelets. T/F?
True
One molecule of factor 10a leads to the formation of 1,000 molecules of thrombin. T/F?
True