Cell Theory
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Cells
smallest functional units of life
3 general structures of cells
cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm
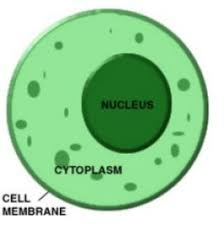
intracellular fluid
fluid in cell
2 types of extracellular fluid
Interstitial, intravascular
what are the two main types of fluid regarding cells?
intracellular, extracellular
extracellular fluid
fluid outside cell
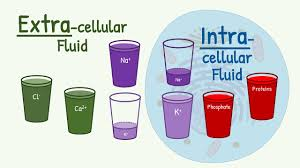
interstitial fluid
fluid between cells in tissue
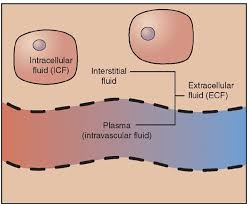
intravascular fluid
fluid in blood vessels
what structure of the cell separates intra from extracellular fluid?
plasma membrane
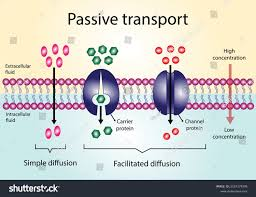
3 types of passive transport
diffusion, filtration, osmosis
what are the two types of transport across the plasma membrane?
passive, active
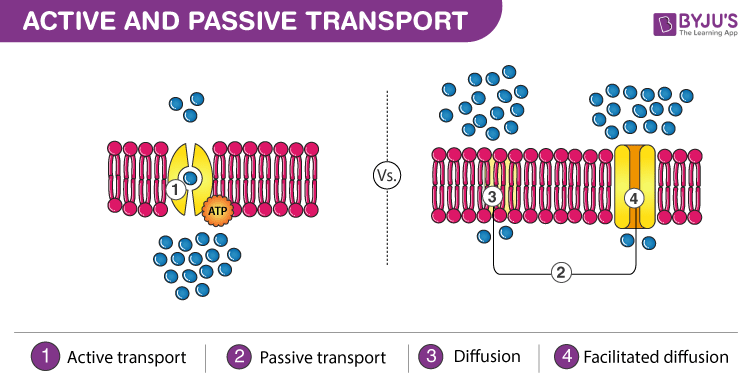
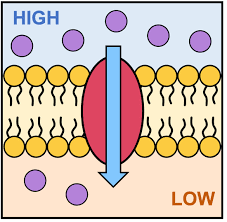
passive transport
move solutes across membrane w/o energy
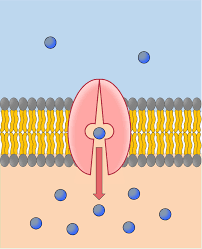
active transport
move solutes across membrane w/ energy
Passive transport moves solutes from an area of___ concentration to_____ concentration, while active transport moves them from an area of____ concentration to _____ concentration.
high, low, low, high
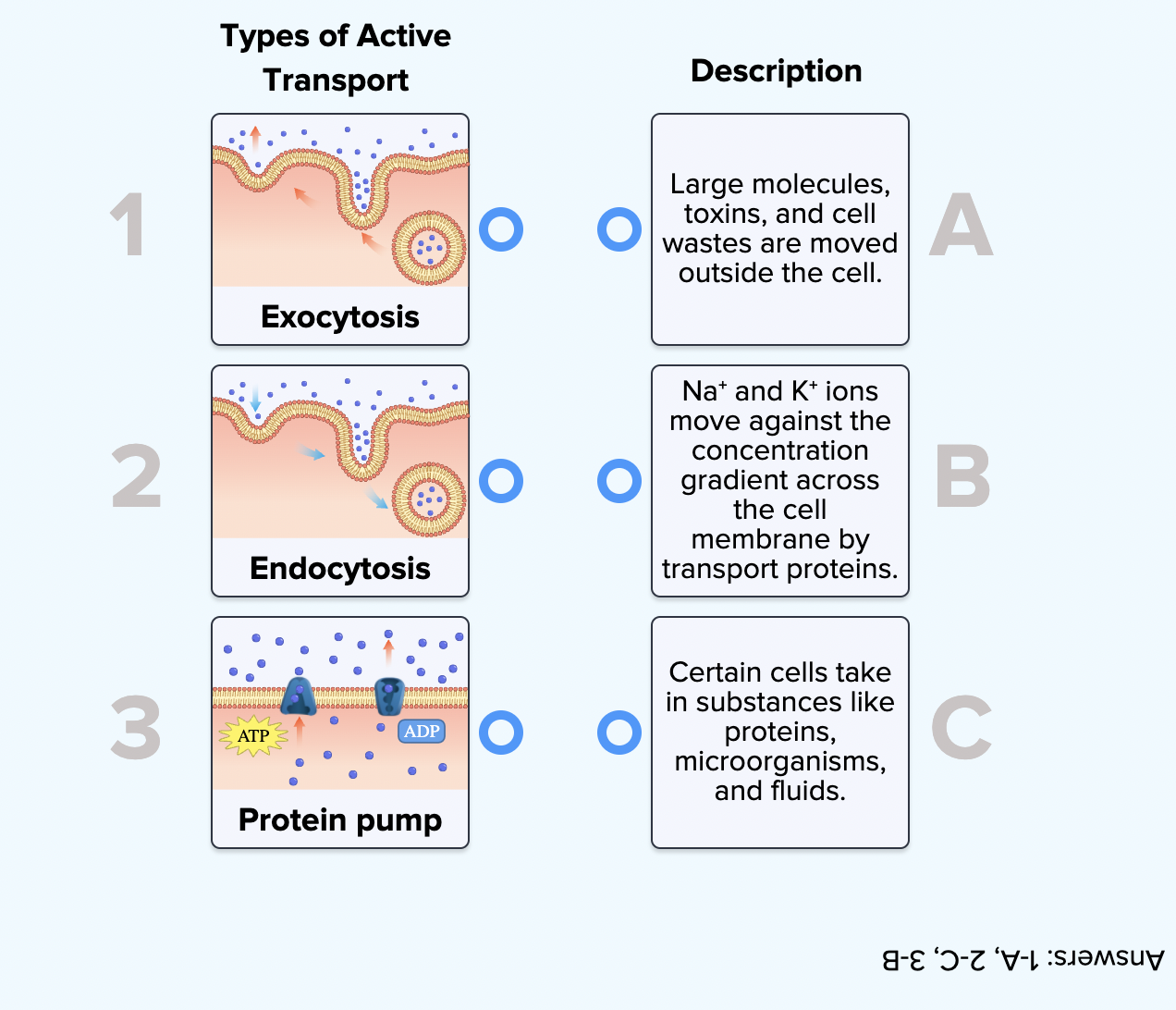
what are the three types of active transportation?
solute pumping, exocytosis, endocytosis
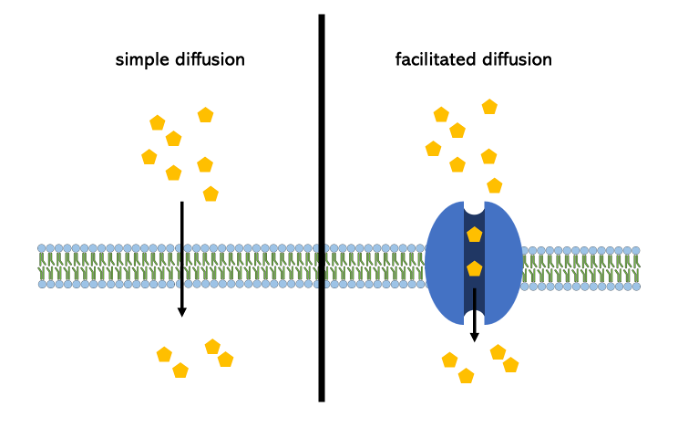
Two types of diffusion
simple, facilitated
simple diffusion
small, non-polar moving directly across membrane
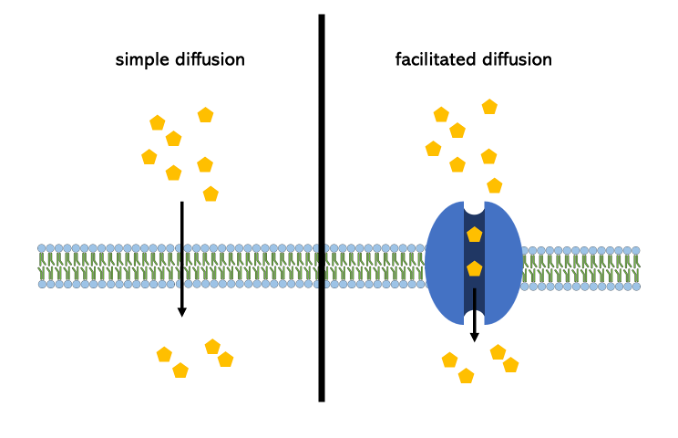
facilitated diffusion
large, polar molecules needing proteins to cross membrane
diffusion example
Gas exchange in lungs
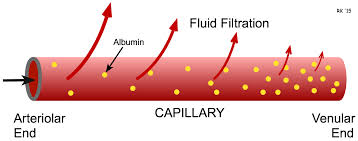
filtration example
blood pressure forcing fluid out of capillaries
3 types of osmosis conditions
isotonic, hypertonic, hypotonic
Diffusion
solutes from high to low concentration
filtration
solutes and water from high to low concentration
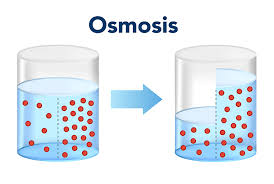
osmosis
water from high to low concentration
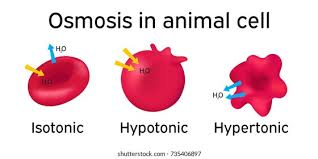
isotonic solution
equal solutes to cell, no change
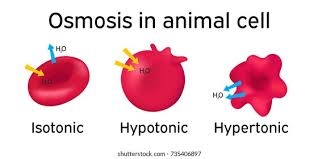
hypertonic solution
more solutes than cell, shrink
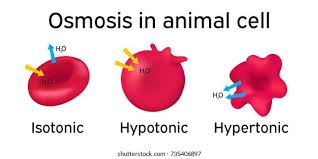
hypotonic solution
less solutes than the cell, swell
solute pumping
proteins move solutes from low to high with atp
Sodium potassium pump
3 na out, 2 k in
exocytosis
materials moves from interior to extracellular
endocytosis
material moves from extracellular to interior
exocytosis process
vesicle fuse with membrane, expelling material out
endocytosis process
membrane fold and pinch into cytoplasm as vesicle
Two types of endocytosis
phagocytosis, pinocytosis
phagocytosis
cell eating
pinocytosis
cell drinking
chromatin
simply condensed DNA in nucleus
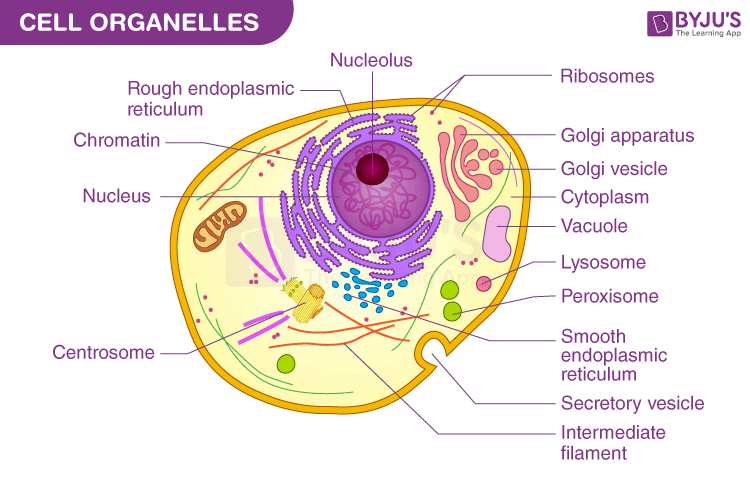
cytoplasm
everything inside cell
two main components of cytoplasm
cytosol, organelles
golgi apparatus function
packages proteins for transport
lysosome function
digests damaged organelles and pathogens
peroxisome function
detoxify harmful substances
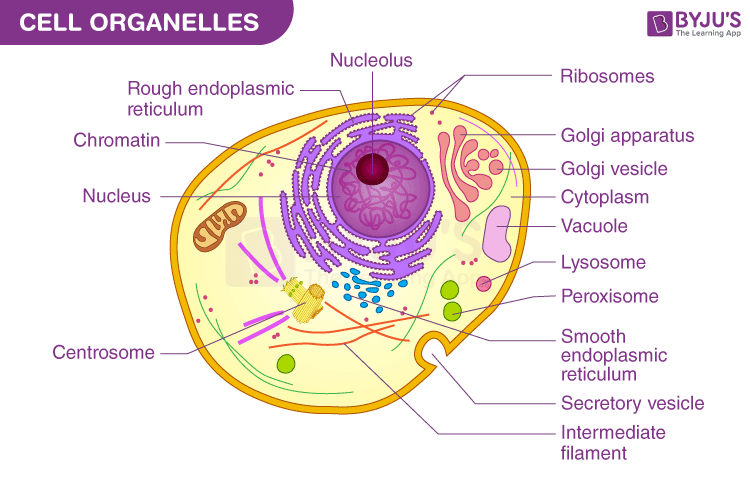
ribosomes function
protein synthesis
cytoskeleton function
support and motility
centriole function
forms mitotic spindles
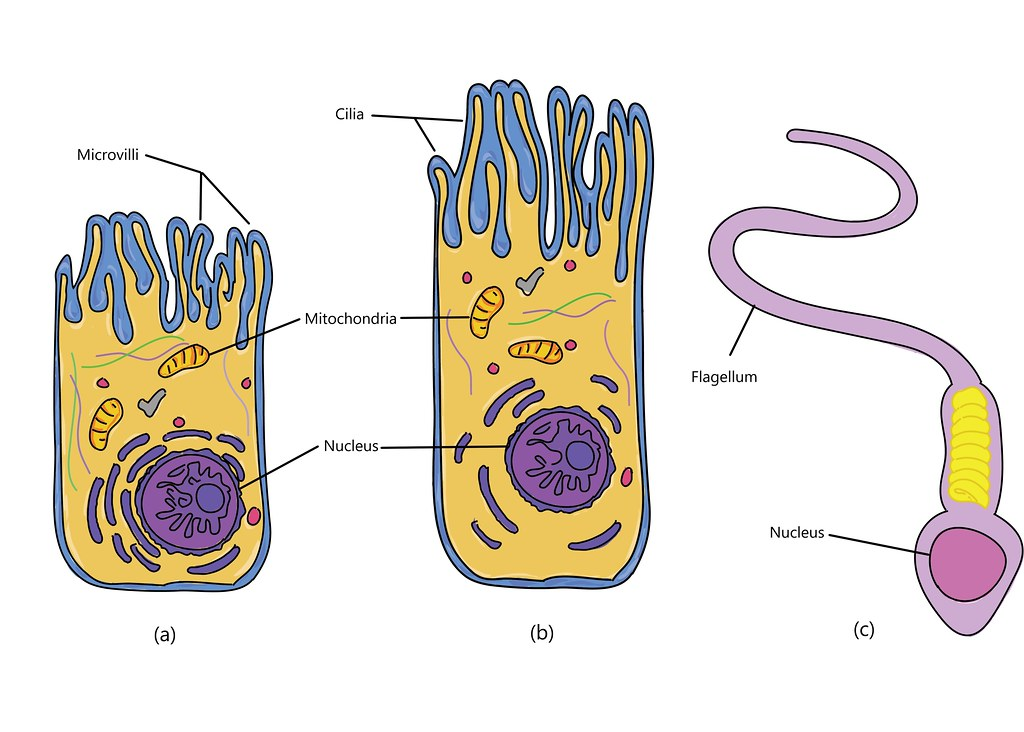
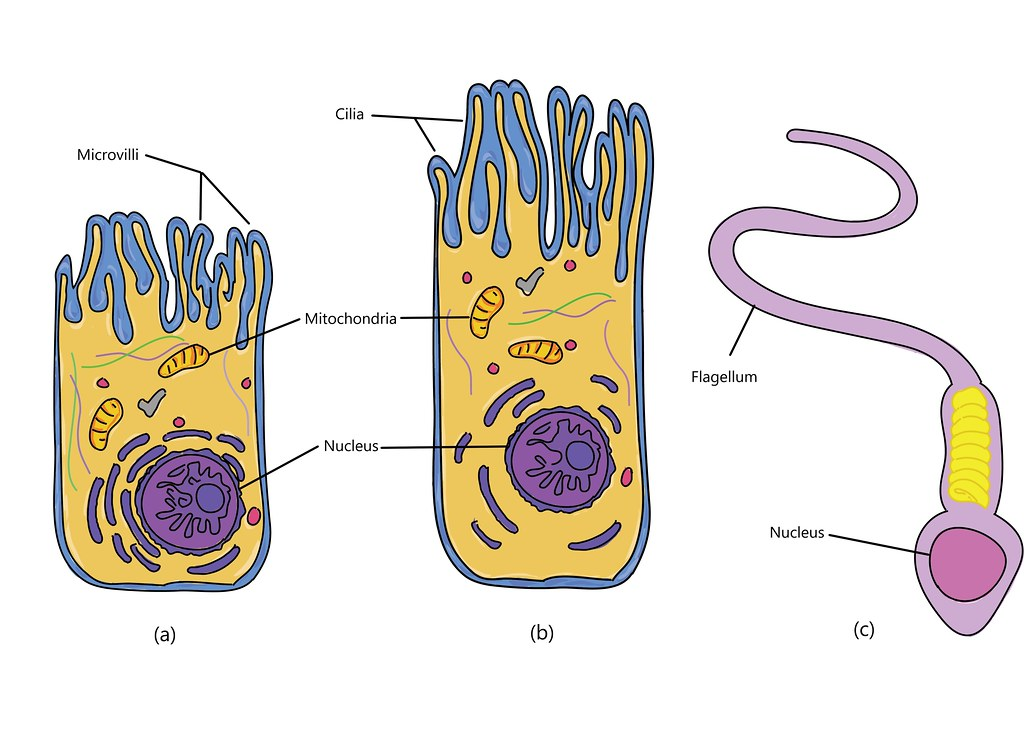
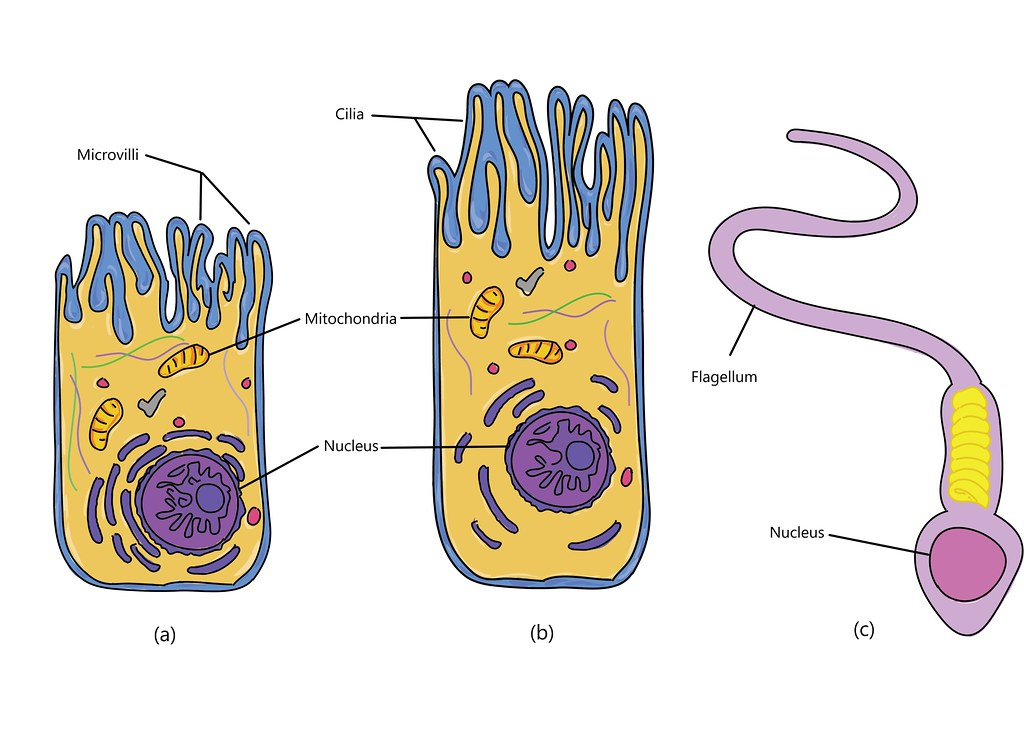
what are the three types of cellular projections?
cilia, flagella, microvilli
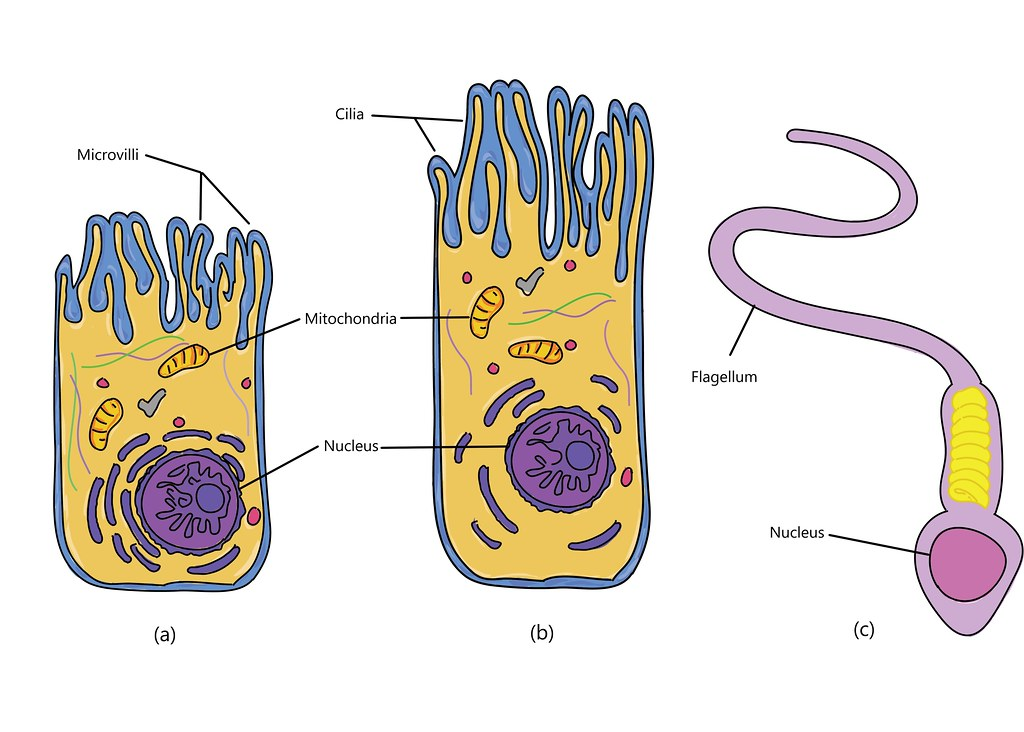
cilia function
move substances along cell surface
flagella function
propel cell
microvilli
increase surface area for absorption
cilia example
fallopian tube move egg
flagella example
sperm
microvilli example
small intestine
endoplasmic reticulum function
channel for transporting material
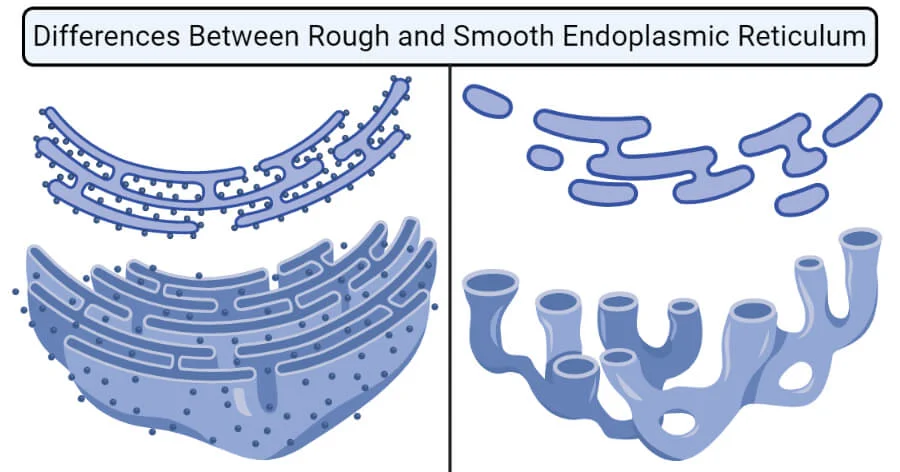
two types of endoplasmic reticulum?
rough, smooth
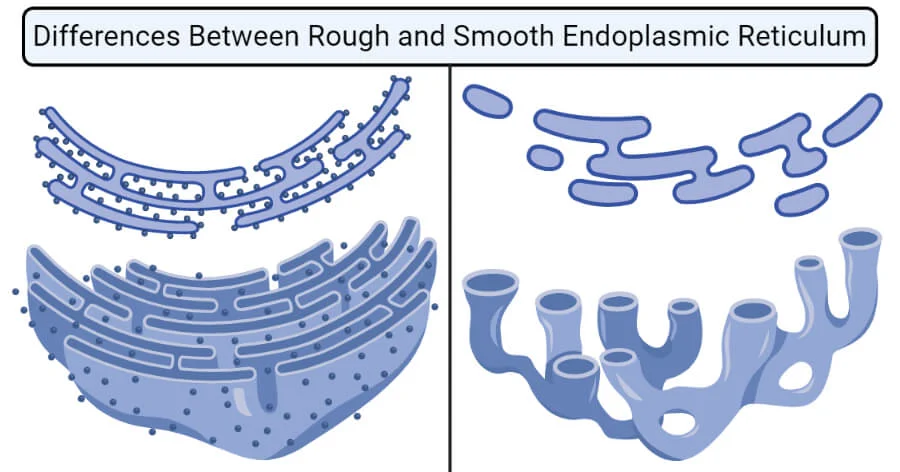
rough endoplasmic reticulum function
protein synthesis
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
lipid synthesis
what are the three components of nucleus?
DNA, nuclear envelope, nucleolus
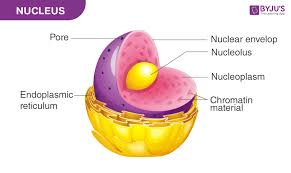
nucleolus function
produce ribosomes
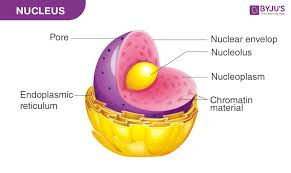
nuclear envelope
nucleus membrane
3 pathways of vesicles
secretory vesicles, membrane vesicles, lysosomes
4 parts of plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer, proteins, glycocalyx, cholesterol
2 parts of hydrophilic heads in phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail
proteins on plasma membrane function
receptors, enzymes, channels
glycocalyx
biological marker to differentiate self
cholesterol function in PM
stabilizes
Plasma membrane functions
barrier, selective permeability, cell markers/receptors, adhesion
mitochondria function
creates atp
cytoplasm two parts
cytosol, organelles
cytoskeleton parts
microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules