enthalpy changes, measurement, bond enthalpies
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
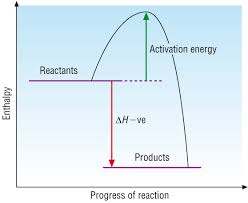
More (heat) energy released forming bonds than energy absorbed breaking bonds
ΔH-ve
Products have less energy than reactants, and therefore are more thermodynamically stable
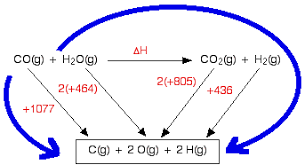
CO2 and H2O being combustion products
arrows point down at them
must add balancing numbers
-even if you need to find out Enthalpy change of formation, if you are given combustion data you have to draw a combustion cycle
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their STANDARD STATES under standard conditions
Enthalpy change of neutralisation
Formation of one mol of water from neutralisation under standard conditions
(same for all neutralisation reactions H+ + OH- → H2O)
Equation for heat energy (q) = mass (m) × specific heat capacity (c) × temperature change (ΔT)
E is in Joules
m is in grams (of water)
-heat loss to surroundings (calculated value is lower)
-incomplete combustion of fuel (lower)
-non-standard conditions
Average bond enthalpy
-Enthalyp change when one mole of covalent bonds in GASEOUS molecules is broken
-always endothermic
-calculated by energy required to break bonds - energy released when new bonds form
-in Hess cycle, arrows point DOWN to atoms
Enthalpy change of reaction
The enthalpy change when the reactants convert to products with the number of moles shown in the equation under standard conditions
-total enthalpy change accompanying a chemical change is independent of the route by which a reaction takes place
-Allows enthalpy changes to be determined indirectly
-if a reaction can take place by 2 routes & starting/finishing conditions are the same, the total enthalpy changes are the same
-an agreed set of conditions which allow fair comparisons between different sets of experimental data
-298K (25C) for temperature
-100kPa for pressure
-sometimes 1 moldm^-3
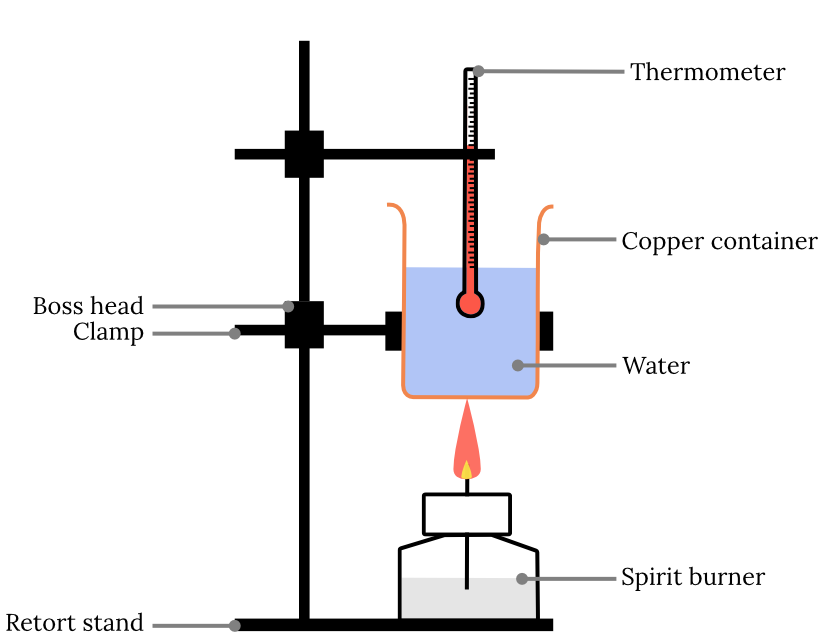
a method used to determine amount of heat energy given off by a chemical reaction
energy release is supposed to heat up a measured amount of water
1cm^3 = 1g
-the spirit burner/fuel's change in mass is weighed
-insulation needed (e.g. polystyrene cup)
-GASEOUS atoms must be at the bottom
-method is a systematic error
-measurement is a random error, usually smaller
absolute error/measured value x 100
if you take 2 readings it's absolute error x2
-e.g. temp. change from, 22 to 42 so measured value is 20
why is enthalpy change of vapourisation of bromine endothermic
energy required to break induced dipole forces