HESI Anatomy and physiology
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Histology
the study of tissues
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process where a cell duplicates its DNA and divides into two identical daughter cells.
Skin
membrane because it covers the body ; organ because it contains several kinds of tissues.
Skeletal System
supports the body, allows movement, protects organs, produces blood cells, stores minerals, and serves as muscle attachment points
Muscular System
includes skeletal muscles and tendons connecting muscles to bones, with ligaments attaching bones to each other, excluding cardiac and smooth muscles.
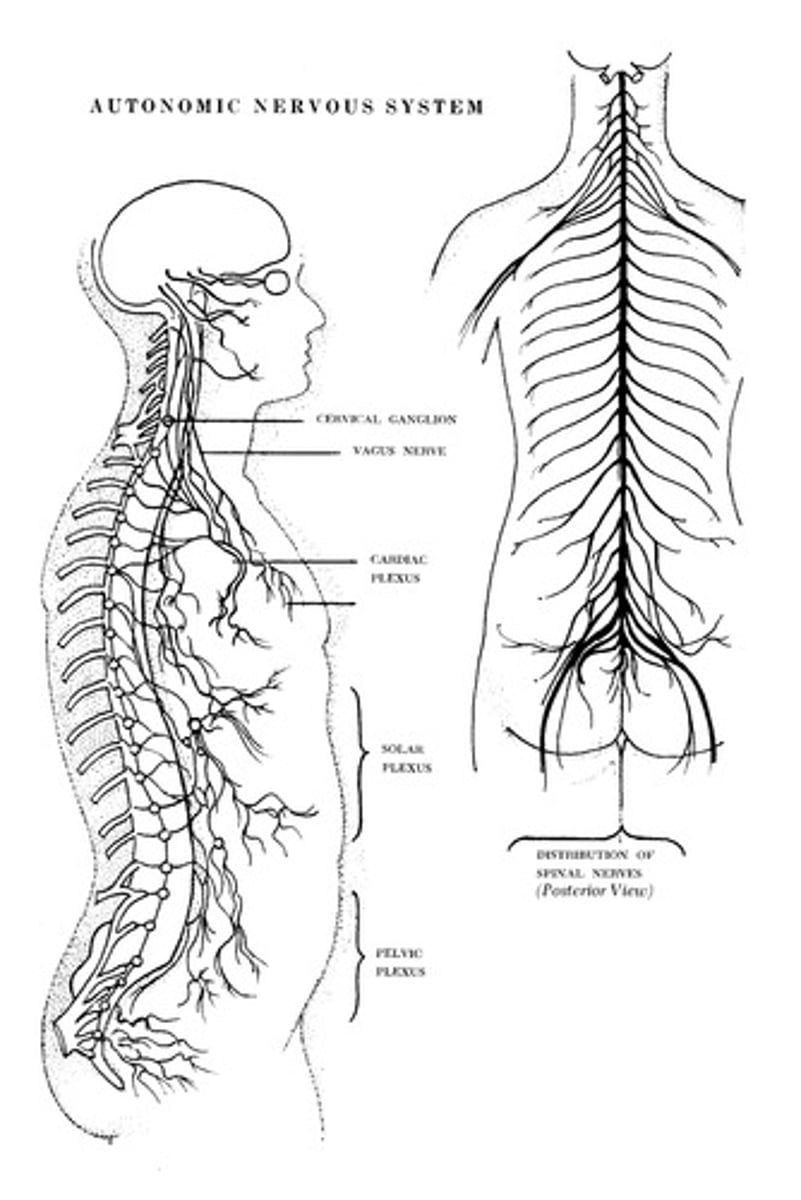
Nervous System
The nervous system detects and transmits impulses via neurons, regulating senses, heart rate, breathing, speech, and movement.
Endocrine System
A group of ductless glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream, regulating metabolism, growth, reproduction, and responses to stress.
Circulatory system
The human body system that contains the heart, blood, and all of the blood vessels. It delivers all the nutrients to the cells
Respiratory System
Organs involved in gas exchange, including the nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
Digestive System
3 main functions - break down food mechanically & chemically, absorb important molcules for the body needs, & eliminates wastes
Urinary System
Composed of kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, it removes waste (urine) and regulates fluid and electrolytes.
Reproductive System
Includes organs that produce reproductive cells and support embryo development in females.
Alimentary Canal
The GI tract, a muscular tube including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
Anatomic Position
Body erect with arms at sides and palms forward; serves as reference for anatomical terms.
Anterior
Front or Ventral
appendicular skeleton
126 bones that make up the shoulder girdle, arms, hands, pelvic girdle, legs, and hands.
Arterioles
Small arteries branching from major arteries, controlling blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
Axial Skeleton
The central axis of the body, consisting of the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
Bolus
Chewed food mixed with saliva, swallowed and passed to the stomach for digestion.
Cell
Collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings; basic unit of all forms of life.
Cerebellum
The 'little brain' at the back of the brainstem, responsible for balance, movement coordination, and processing sensory input
Chyme
A mixture of food and gastric juices from the stomach that passes to the small intestine.
Dermis
The skin layer beneath the epidermis, containing collagen, nerves, blood vessels, and glands.
Distal
opposite of proximal; a particular body part is farther from the trunk or farther from another specified point of reference than another part
Epidermis
The outer skin layer, composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with four cell types (melanocytes, Merkel cells, keratinocytes, and Langerhans cells), avascular but innervated, renewing every 35-45 days.
Estrogen
A hormone that stimulates uterine growth, increases blood flow to uterine vessels, and prepares breast ducts for lactation.
External Respiration
Exchange of gases in the lungs (between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the pulmonary capillaries)
Hemopoiesis
the formation of blood cells in the living body (especially in the bone marrow)
Histology
(tissues) microscopic study of structures of tissues (tissues -groups of specialized cells and cell products)
Inferior
Indicates a body part is below another or lower in an organ, moving down towards the feet.
infundibulum
A stalk that attaches the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
Internal Respiration
Exchange of gases between cells of the body and the blood
Lateral
Refers to a position relatively farther away from the midline or toward the ouside of the body
Leukocytes
White blood cells that fight diseases, categorized into agranulocytes and granulocytes, with five types: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes.
Medial
relates to an imaginary midline dividing the body into equal right and left halves
Medulla Oblongata
The lowest part of the brainstem, continuous with the spinal cord, regulating heart rate, breathing, and reflexes like swallowing and sneezing.
Meiosis
Special cell division to produce gametes (sperm and eggs) with half the normal genetic material.
Mitosis
A eukaryotic nuclear division process divided into five stages that equally allocates replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei, conserving chromosome number.
Neuroglia
Supportive cells in the CNS making up half of the brain and spinal cord volume and are 5 to 10 times more numerous than neurons including astrocytes oligodendroglia microglia and ependymal cells
osteoblasts
Bone-forming cells
Platelets
Cells essential for blood coagulation; elevated levels indicate dehydration or increased bone marrow activity, while decreased levels suggest immune issues, drug reactions, or B12/folic acid deficiencies
Posterior
Dorsal, back side of the body
Progesterone
A steroid hormone from the corpus luteum that maintains the uterine lining for implantation and is the main hormone during pregnancy
proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Sarcomeres
The smallest unit of skeletal muscle capable of contraction, serving as the basic structural and functional unit.
Superior
Above; at a higher level (in the human body, toward the head)
Synergist
Muscle that assists the prime mover in its action.
Voluntary Muscles
Muscles that you are able to control
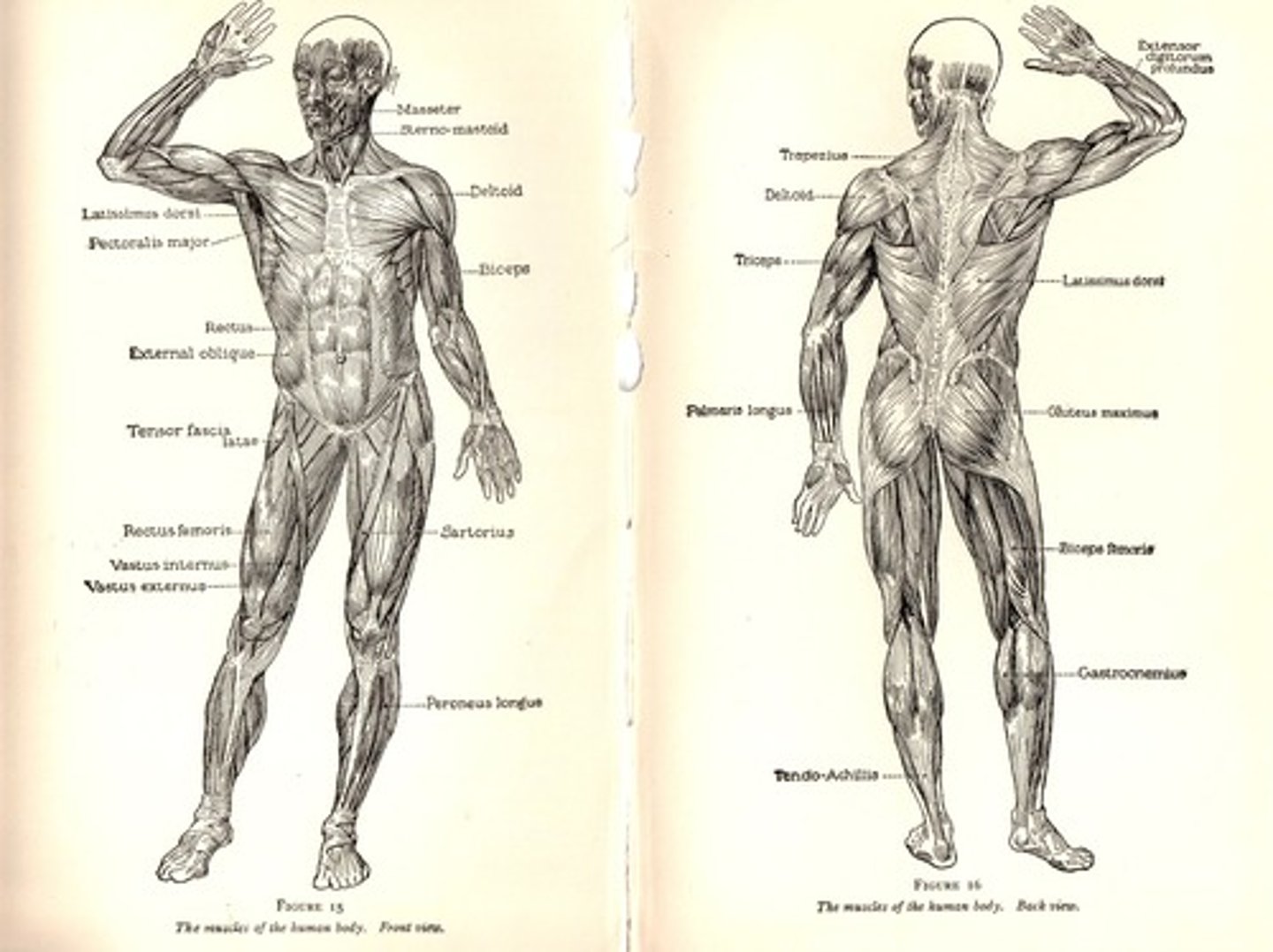
Frontal Muscle
Raises eyebrows; originates from the occipital bone and inserts into the skin of the eyebrow.
Orbicularis oculi Muscle
Closes the eye; encircles the eye, originating and inserting at the maxilla and frontal bone.
Orbicularis oris Muscle
Draws lips together; encircles lips.
Zygomaticus Muscle
Elevates mouth corners; originates from zygomatic bone and inserts at lip angle.
Masseter Muscle
Closes jaws; inserts at mandible, originates from zygomatic arch.
Temporal Muscle
Closes jaw; inserts at mandible, originates from temporal skull region.
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
Rotates and flexes head; inserts at scapula, originates from sternum and clavicle.
Trapezius Muscle
Extends head/neck; inserts at scapula; originates from skull/upper vertebrae.
Pectoralis Major Muscle
Flexes and adducts upper arm; inserts at humerus, originates from sternum, clavicle, and upper ribs.
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
Extends/adducts upper arm; inserts at humerus; originates from vertebrae and ilium.
Deltoid Muscle
Abducts upper arm; inserts at humerus; originates from clavicle and scapula.
Biceps Brachii Muscle
Flexes elbow; inserts at radius; originates from scapula.
Triceps Brachii Muscle
Extends elbow; inserts at ulna; originates from scapula and humerus.
External Oblique Muscle
Compresses abdomen; inserts at midline; originates from lower thoracic cage.
Internal Oblique Muscle
Compresses abdomen; inserts at abdomen midline; originates from pelvis.
Transversus Abdominis Muscle
Compresses abdomen; inserts at midline; originates from ribs, vertebrae, and pelvis.
Rectus Abdominis Muscle
Flexes trunk; inserts at lower rib cage; originates from pubis.
Iliopsoas Muscle
Flexes thigh/trunk; inserts at femur; originates from ilium and vertebrae.
Sartorius Muscle
Flexes thigh, rotates lower leg; inserts at tibia, originates from ilium.
Gluteus Maximus Muscle
Extends thigh; inserts at femur; originates from ilium, sacrum, and coccyx.
Adductor Longus Muscle
Adducts thigh; inserts at femur; originates from pubis.
Gracilis Muscle
Adducts thigh; inserts at tibia, originates from pubis.
Pectineus Muscle
Adducts thigh; inserts at femur; originates from pubis.
Semimembranosus Muscle
Flexes knee; inserts at tibia; originates from ischium.
Semitendinosus Muscle
Flexes knee; inserts at tibia, originates from ischium.
Biceps Femoris Muscle
Flexes knee; inserts at fibula; originates from ischium and femur.
Rectus Femoris Muscle
Extends knee; inserts at tibia; originates from ilium.
Vastus Muscles (Lateralis, Intermedius, Medialis)
Extend knee; insert at tibia, originate from femur.
Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Dorsiflexes ankle; originates from tibia, inserts at metatarsals.
Gastrocnemius Muscle
Plantar flexes ankle; originates from femur, inserts at calcaneus.
Soleus Muscle
Plantar flexes ankle; inserts at calcaneus; originates from tibia and fibula.
Peroneus Longus and Brevis Muscles
Plantar flex ankle; originate from tibia/fibula, insert at tarsals/metatarsals.
Flexion
A motion where body parts decrease the angle between them by folding or bending.
Median Plane/Sagittal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into right and left halves; a cut along this plane is a sagittal section.
Coronal/Frontal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into front and back sections; a cut along this plane is a frontal section.
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into upper and lower portions; a cut here is a cross section.
Superior
Above
Dorsal Cavity
Includes cranial and spinal cavities
Ventral Cavity
Contains the orbits, nasal, oral, thoracic, and abdominopelvic cavities.
Four fundamental tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nerve tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
A layer of closely adhering cells that cover surfaces, line cavities, and form glands; includes simple and stratified types.
Connective Tissue
Most abundant tissue in the body, connects, binds, protects, and supports organs; found throughout the body.
Muscle Tissue
Specialized for movement; includes smooth, skeletal, and cardiac types, classified by structure (striated or smooth) and function (voluntary or involuntary).
Nerve Tissue
Tissue made of neurons and neuroglia that controls and coordinates body activities.
Epithelial Cells
Cells that cover body surfaces and line organs.
Types of muscle
3 types: skeletal, cardiac, smooth; each served by one nerve, an artery, and one or more veins
parts of a cell
Cell membrane, cell wall, centriole, chloroplasts, chromatin, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, flagella, golgi complex/apparatus, lysosome, mitochondria, nucleolus, nucleus, ribosomes, vacuole
Organelle
A specialized cell structure performing a specific function.
Nucleus
Cell structure containing nucleic acids and DNA, directing cellular activities.
Ribosomes
Structures made of protein and RNA that synthesize proteins from amino acids.
layers of the epidermis
(deepest to most outermost)Stratum Basale, Startum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum (absent in thin skin), and stratum corneum.
Eccrine glands
Sweat glands that cool the body through evaporation, mainly on palms, soles, and forehead.