Unit 10 & Unit 11
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pharm Endocrine function
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Glucagon
Comes from the pancreatic alpha cells. Secreted when glucose level is low. Promotes glycogenolysis. Promotes breakdown of proteins and lipids.
Insulin
Comes from pancreatic beta cells.
Secreted when glucose levels are high.
Encourages formation of glycogen.
Gate keep of glucose entering body cells.
Prevents fat breakdown.
Blood Glucose Values?
Diabetic: 80-130
Non Diabetics: 60-110
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1:
Beta cell death
autoimmune, genetic, environment factors.
Body cannot produce insulin so glucose cannot enter the cells.
Insulin therapy is required for life.
Type 2:
Insulin receptors malfunction and cells develop “insulin resistance”
Increased blood glucose triggers more insulin secretion eventually leads to death of beta cells
Initially managed with diet, exercise and oral antihyperglycemic meds
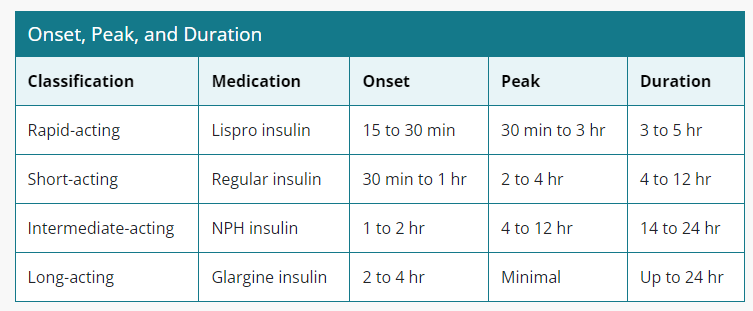
Onset, Peak, and Duration
Humulin R, Myredlin, Novolin R
Human Regular Insulin
Pancreatic hormone.
MOA: identical to insulin produced by the body. Increases cellular glucose uptake, inhibits glucagon release, stimulates storage of glucose as glycogen.
SHORT ACTING: onset 30-60 min, peak 2-4 hrs.
**CAN BE GIVEN IV!!*
Insulin Therapeutic Effects
Lower blood glucose levels in patients with T1DM
Combination therapy in patients with T2DM
Can be used in gestational diabetes
Insulin Contraindications & Side Effects
Hypoglycemia
Pregnancy
Kidney disease
Thyroid disease
S/E
hypoglycemia
irritation @ injection site
hypokalemia
weight gain
Insulin Considerations and Teaching
Rotate injection sites
Can be used in pump
Monitor blood glucose and A1C
Wear medical alert
NovoLog
Insulin aspart → RAPID ACTING
Modified to have a more rapid onset
Can be used in pumps
Onset 15-30 min
Peak 30 min-3hr
Be sure patient eats within 15 min of administration
Humulin N, Novolin N, NPH
Isophane insulin → INTERMEDIATE ACTING
Begins working within 1-2 hrs
Peaks 4-12 hrs
Provides basal coverage between meals and at night
Cloudy-draw up last and administer right away
Levemir
Insulin detemir→ LONG ACTING
Modified to have a more slow onset and longer duration of action.
Onset: 2-4 hrs
Duration: up to 24 hrs
Cannot be mixed with other insulins
Toujeo
Insulin glargine→ ULTRA LONG ACTING
Constant, long duration
No defined peak
Lasts 24-42 hrs
Once daily dosing (same time)
Cannot be mixed with other insulins
Administration Considerations
only regular human insulin can be given IV
only regular or rapid acting for SQ pumps
time meals depending on type administered
ALWAYS know blood glucose at the time of administration
Rotate and observe injection sites
Monitor for hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia Signs and Symptoms
Tachycardia
Hunger
Palpitations
Nervousness
Irritability
Weakness/dizziness
Sweating
Mental confusion
Incoherent speech
Blurred vision
Headache
Convulsions
Hypokalemia
Cold clammy skin
Hypoglycemia Treatment
Administer at least 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates
If patient cannot take oral carbs, administer glucagon IV, IM, SQ, or intranasally
Glucagon (GlucaGen)
Pancreatic hormone
MOA: increases glycogenolysis (prompts the liver to release stored glucose)
Glucagon Therapeutic Effects
Rapid increase in serum glucose levels to normal.
Used to treat hypoglycemia.
Glucagon Contraindications and Side Effects
Hyperglycemia
Clients who do not have glycogen stored in liver
CAD, sensitivity to protein compounds
S/E
Hyperglycemia
Nausea
Vomiting
BP changing (transient increase)
Tachycardia, hypo/hyperkalemia
Glucagon Considerations and Teaching
Monitor blood glucose
Wear medical alert
Keep carbohydrates or glucagon with you at all times
Limit alcohol intake.
Diabetes Type 2
Insulin Resistance
Leads to:
Metabolic syndrome
Obesity
Asymptomatic elevation of blood glucose
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemia state (HHS)
Metformin (Glucophage)
Biguanide
MOA: multiple mechanisms- suppresses hepatic production of glucose (gluconeogenesis), decreases intestinal reabsorption of glucose, increases cellular uptake of glucose.
Metformin (Glucophage) Contraindications and Side Effects
Chronic kidney disease
Use caution in heart or liver failure, hx of lactic acidosis, 2 days before or after radiographic contrast
pregnancy
S/E
Nausea
Vomiting
Metallic taste
Diarrhea
Weight loss
Risk for lactic acidosis → BBW
Metformin (Glucophage) Considerations
Rarely causes hypoglycemia
Used off-label for PCOS
Formulated as tablets, solution, and extended release
Know signs and symptoms of lactic acidosis
fatigue, somnolence, n/v, tachycardia, tachypnea, jaundice, muscle weakness, muscle pain or cramping
Glyburide (DiaBeta)
Sulfonylurea
MOA: Stimulates insulin release from beta cells and increases tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Glyburide (Diabeta) Contraindications and Side Effects
Sulfa allergy
Primary tx for T1
CKD
Hepatic disease
S/E
GI distress
Hypoglycemia
Hepatotoxicity, blood dyscrasias (rare)
Glyburide (DiaBeta) Considerations
Avoid alcohol
Take with food - hold if not eating
May use during pregnancy, but discontinue 1 months before delivery
Repaglinide (Prandin)
Meglitinide
MOA: stimulates insulin release
Contraindications for T1DM
Caution: hepatic impairment, pregnancy, lactation
S/E: hypoglycemia, GI distress, headache, URI
Take just before each meal. Rapid onset and short duration
No renal excretion, so can be used with CKD
Rosiglitazone (Avandia)
Thiazolidinedione
MOA: Increases cell sensitivity to insulin and decreases glucose synthesis by the liver
Contraindications: severe heart or live disease, pregnancy, T1DM
S/E: edema, increased serum lipid levels, URI, increased fluid retention can worsen heart failure and increase risk of MI → BBW
Not recommended with insulin or nitrates
Monitor liver function
Teach pt signs of liver/heart failure.
Semaglutide (Ozempic)
Incretin Mimetic
MOA: activates GLP-1 Receptors in the brain, pancreas, and GI tract. Works by increasing insulin secretion in response to increased blood glucose and decreasing glucagon release. Also slows gastric emptying.
Contraindications: fam hx of thyroid cancer, pregnancy/breastfeeding, T1DM
Caution: CKD, hx of pancreatitis, hx of suicide ideation
S/E: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, heartburn, burping, constipation, headache, nervousness, hypoglycemia.
Semaglutide (Ozempic) Considerations
Weekly SQ injection; dose usually increased after 4 weeks.
Rotate site
May increase risk of aspiration with surgery d/t delayed gastric emptying
May change absorption of other medications
Teach pt about potential liver failure and thyroid tumor.
Considerations with Oral Hypoglycemia Medications
Monitor blood sugar levels
Notify care provider of signs of illness or infection
Monitor I&O’s
Monitor appropriate labs: LFT’s, A1C
Monitor for adverse effects
Monitor for compliance
Emphasize non-pharmacological management of DM
Patient/Family Teaching for Oral Hypoglycemic Meds
Teach s/s and treatment for hypoglycemia
Beta-blockers may antagonize effects and mask symptoms of hypoglycemia
Avoid alcohol
Wear medical bracelet
Consult with provider if you are pregnancy or considering pregnancy
Thyroid Importance
Stimulates the basal metabolic rate of nearly all tissues.
GI function
Weight
Increases oxidation of energy (heat)
Increase in sympathetic activity
Thought processes
Hypothyroidism
Slowing of metabolic rate
Myxedema- mucous type of edema
Causes: hashimoto’s, thyroid gland dysfunction, hypothalamus disorder.
Treatment: removing or destroying the thyroid causing hypothyroidism.
Levothyroxine (Synthroid)
Synthetic thyroid hormone
MOA: identical to endogenous thyroid hormone
Levothyroxine (Synthroid) Therapeutic Effects
Regulation of thyroid hormone:
Increases O2 use, respirations, heart rate, nutrient metabolism
Promotes growth and maturation
Increases weight loss and diuresis
Improves activity tolerance
NOT TO BE USED FOR WEIGHT LOSS→ BBW
Levothyroxine (Synthroid) Contraindications and Side Effects
Acute MI
Cardiovascular disease, current adrenal insufficiency, HTN
S/E
Therapeutic dose should make patient feel normal
High doses: anxiety, insomnia, palpitations, diarrhea
Interactions:
may increase need for antidiabetic drugs
increases effects of warfarin
digoxin decreases effectiveness
Levothyroxine (Synthroid) Considerations and Teaching
Administer 1 hour before food or other meds to prevent interference with absorption
Check aspirin allergy (yellow dye)
Monitor labs: T3, T4, TSH, CBC, electrolytes, glucose, lipids
Patients with diabetes should check blood glucose frequently and watch for hypoglycemia
Keep labs appointments to monitor dosage
Weigh yourself 2-3 times/week and report changes
Report symptoms of hypo/hyperthyroidism