Chemistry - Inorganic
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is a transition metal?
An element that has an incomplete d subshell in either its atom or one of its common ions
What is the electron structure of chromium (in shorthand)?
[Ar] 4s1 3d5
What is the electron structure of copper (in shorthand)?
[Ar] 4s1 3d10
What is a ligand?
A particle with a lone pair of electrons that can bond to a transition metal by a co-ordinate bond
What is a complex?
A metal ion which has co-ordinately bonded ligands
What is the co-ordination number?
The number of co-ordinate bonds from ligands to metal ion
What are the lone pair of electrons on the ligand used for?
Forming a dative bond with the metal and filling up the d-subshell
What is the co-ordination number and angle of a linear complex?
2, 180 degrees
What is the co-ordination number and angle of a square planar complex?
4, 90 degrees
What is the co-ordination number and angle of a tetrahedral complex?
4, 109.5 degrees
What is the co-ordination number and angle of a octahedral complex?
6, 90 degrees
What metal ion occurs in a linear complex?
Silver 1+
What metal ion occurs in a square planar complex?
Platinum 2+
What ligand occurs in a tetrahedral complex?
Chloride ion
What are the 3 unidentate ligands?
OH-, H2O, NH3
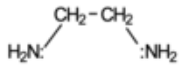
What is this bidentate ligand?
1,2 - diaminoethane (en)
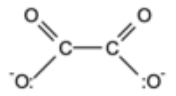
What is this bidentate ligand?
the ethanedioate ion
How many co-ordinate bonds do bidentate ligands need to make?
6
Give an example of a multidentate ligand (that is not haem)
EDTA 4-
What is Haem?
An iron complex with a multidentate ligand and one of them being bonded to globin (a protein)
How is oxygen transported around the body in terms of the bonding in haemoglobin?
Oxygen forms a co-ordinate bond to iron in haem
Why is carbon monoxide so toxic to humans?
It can easily replace oxygen and become strongly bonded to the iron in haemoglobin without being readily replaced itself.
What is a homogenous catalyst?
A catalyst in the same phase as the reactant species.
What is a heterogenous catalyst?
A catalyst in a different phase to the reactant species
What catalyst is used in the manufacture of sulphuric acid?
V2O5
What is the equation for the reaction between V2O5 and the SO2?
V2O5 + SO2 → V2O4 + SO3
How is the catalyst V2O5 regenerated after the reaction with SO2?
Reacts with ½ O2 forming V2O5
Why is the strength of adsorption being too strong a problem for catalysts?
The reactants cannot move around the surface and cannot desorb.
Why is the strength of adsorption being too weak a problemfor catalysts?
Reactants cannot be adsorbed properly
How does a catalyst become poisoned?
Impurities block active sites and prevent desorbtion. There is now less surface area that the reactants can bind to, slowing down the reaction.
What are the consequences of a poisoned catalyst?
Less yield, replacements are needed frequently, cost of reaction process increases
For the reaction between S2O8 2- and 2I- what is the catalyst?
Fe 2+
Why is this specific catalyst used for the reaction between S2O8 2- and 2I- ?
It is a positive ion so attracts the negative ions and can form variable oxidation states.
What is the activation energy for the reaction between S2O8 2- and 2I- and why is it that?
The activation energy is high because of the strong repulsion between negatively charged ions.
What is autocatalysis?
A form of homogenous catalysis where the product of a reaction becomes a catalyst, speeding up its own formation.
In the reaction between permanganate and the ethanedioate ion, what is the catalyst formed?
Mn2+
How does the rate of reaction change in an autocatalysis reaction?
As the reaction proceeds and the production of the catalyst increases, the rate of reaction increases
What are the common oxidation states for vanadium and the common ions the element exists as those oxidation states in? (oxidation states decreasing from 5+)
V+5 (VO2 +) , V4+ (VO 2+) , V3+ (octahedral monodentate complex), V2+ (octahedral monodentate complex)
What are the colours of the vanadiums and their oxidation states (decreasing from 5)
Yellow, blue, green, violet
What is the best reducing agent to form vanadium species in these oxidation states?
Zinc
When is it easier to oxidise a transition metal?
In alkaline conditions
When is it esier to reduce a transition metal?
Acidic conditions
What happens to the reactive species [Ag(NH3 )2 ]+ for the tollens reagent reaction to work?
The silver diamine ion is reduced to form 2 moles of ammonia and silver which forms the mirror
In ligand subsitution reactions, most of them are reversible, what is an example of a reaction that isnt?
Chelation
What is chelation?
Swapping a monodentate ligand for a bi/multi dentate ligand
Why is chelation important?
Enhances stability and forms stronger complexes
When stronger complexes are formed from chelation, what 4 things must you reference in the explanation?
Enthalpy change, entropy change, T x entropy change and free energy change