Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Polymers
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What are alcohols?
Compounds with the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group, which is covalently bonded to the carbon atom and does not dissociate in water
What is the general formula for alcohols
Cn H2n+1 OH
Describe the melting and boiling points of alcohols
Increases down the homologous series
Molecular size increases → strength of IMF increases
More energy is needed to overcome stronger IMF between molecules
Describe the solubility of alcohols in water
Decreases down the homologous series
First few are soluble
Carbon chain length increases → hydrophobic character increases
Shorter-chain alcohols are volatile liquids at r.t.p. and pressure
What are the conditions for combustion with alcohols?
Limited oxygen (incomplete combustion)
Excess oxygen (complete combustion)
Describe the flammability of alcohols
More flammable than alkanes due to O in OH functional group
What are the conditions for oxidation of alcohols to form carboxylic acids?
Heat under reflux with an oxidizing agent e.g. acidified KMnO4 that supplies oxygen atoms
C2H5OH + 2O2 → CH3COOH + H2O
What are the conditions of hydration to form alcohols?
300ºc
60atm
H3PO4 [phosphoric (V) acid] as a catalyst
What are the conditions for the fermentation of alcohols?
37ºc
Yeast catalyst
Absence of oxygen
What is the products of the fermentation of alcohol?
Ethanol + CO2
What is the fermentation of alcohol for?
Making ethanol only
Distillation can give pure and concentrated ethanol despite it being diluted
What is the general formula for carboxylic acids
Cn H2n+1 COOH
What are carboxylic acids?
Organic compounds with the carboxyl (-COOH) functional group
*Weak acids
What are the physical properties of carboxylic acids?
All soluble in water
High boiling and melting points as compared to alcohols and hydrocarbons
What are the conditions and products for the carboxylic acid + reactive metal reaction
Metals have to be above hydrogen in the reactivity series
Carboxylate salt + H2
2CH3COOH + Ca -> (CH3COO)2 Ca [calcium ethanoate] + H2
What are the conditions and products for the carboxylic acid + carbonate reaction
No conditions
Carboxylate salt + CO2 + H2O
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa [sodium ethanoate] + CO2 + H2O
What is CaCO3 also known as?
Marble chips
What can carboxylic acids react with?
Acid / base
Carbonate
Reactive metal
What are the conditions and products for the carboxylic acid + acid / base reaction
No conditions
Carboxylate salt + H2O
What are esters?
Generally sweet-smelling compounds with small molecular sizes formed from the reaction of alcohols and carboxylic acids
What is the functional group for esters?
-COO
What is the general formula for esters?
Cn H2n+1 CO OCm H2m+1
Derived from carboxylic acid
Derived from alcohol
C2H5OH (ethanol) + HCOOH (methanol acid) →
[HCOOC2H5] Ethyl methanoate
*refer to notes for more
What are the conditions for esterification?
Concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst
What are polymers?
Large organic molecules containing thousands or millions of atoms formed when many small molecules, monomers, join through polymerization
What is addition polymerization?
Unsaturated monomers join without losing any molecules to form addition polymers
What are the conditions for addition polymerization?
High temperature and pressure
Catalyst
How does addition polymerization occur?
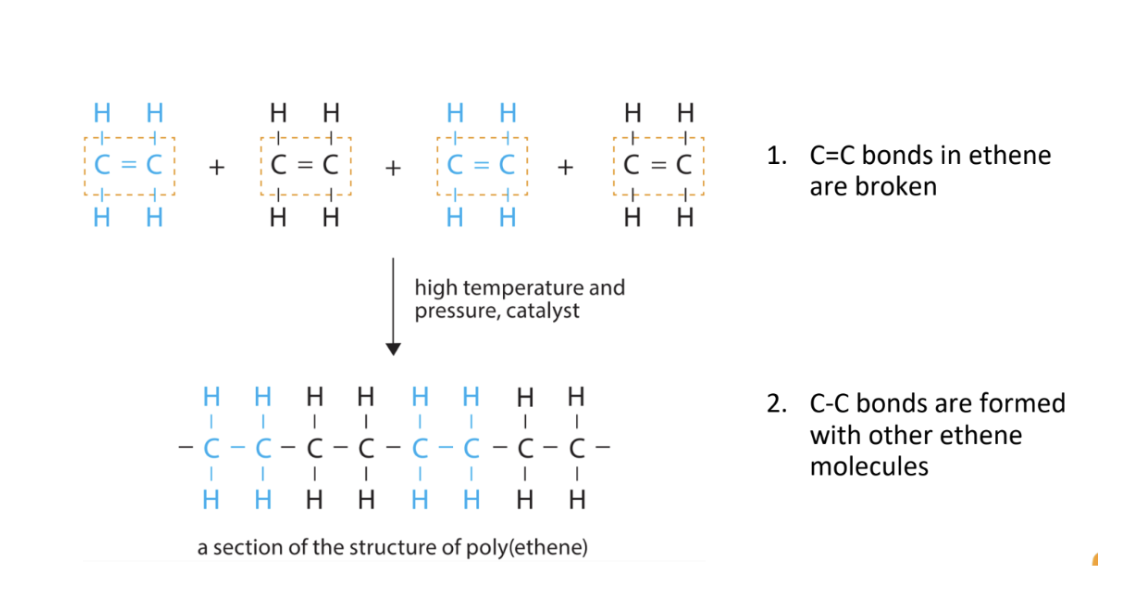
What is condensation polymerization?
Monomers combine to form condensation polymers with the removal of small molecules like water
What are the monomers of polyamides like nylon?
Dicarboxylic acid and diamine
What are the monomers of polyesters like terylene
Dicarboxylic acid and diol
What is the linkage in polyamides and polyesters respectively?
Polyamides → Amide linkage
Polyesters → Ester linkage
What are examples of addition polymers?
Polyethene
Polystyrene
Polyvinyl chloride
carboxylic acid + metal oxide →
metal salt + water