ART HISTORY MONUMENTS
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms

PREHISTORIC ART: woman of willendorf, Austria, c. 24,000 BCE
Limestone figurine; goddess of fertility; represents abundance and survival.

PREHISTORIC ART: Hall of Bulls, Lascaux Caves
hunting magic and ritualistic purpose; animal movement and naturalistic representation

PREHISTORIC ART: Stonehenge, England, c. 2750-1500 BCE
a Neolithic burial and ceremonial site aligned with solar events

Ancient Near East (Mesopotamia): Waka Vase
Alabaster; ritual offering; depicts divine hierarchy and agricultural abundance.

Ancient Near East (Mesopotamia): Stele of Naram-sin, c. 2254-2218 BCE
Limestone; commemorated is the victory of Naram-Sin, king of the Akkadian empire, has a vertical hierarchal scale

Ancient Near East (Mesopotamia): Standard of Ur, c. 2600-2500 BCE
shell inlay and lapis lazuli; narrative panels; shows war and peace, social order.

Ancient Near East (Mesopotamia): Ziggurat at Ur
Mudbrick; temple platform; connects heaven and earth, reflects religious centrality

Ancient Near East (Mesopotamia): Stele of Hammurabi, c. 1792-1750 BCE
THE PUNISHMENT REFLECTS THE CRIME symbolizes justice and divine authority.
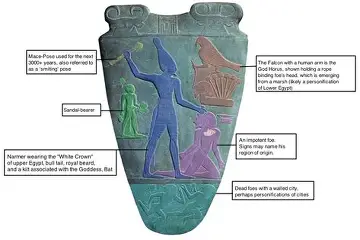
Ancient Egypt: Palette of King Narmer, c. 2950 BCE
The unification of upper and lower Egypt, divine kingship

Ancient Egypt: Khafre Enthroned, from Giza, Egypt, c. 2520-2494 BCE
Diorite; funerary statue; eternal strength and divine rule; symbolizes united egypt

Ancient Egypt: The Great Temple of Amun at Karnak, Egypt, begun 15th c. BCE
Sandstone; religious complex; reflects cosmic order and pharaonic power.

Ancient Egypt: Nebanum Hunting Birds in the Marshes, Thebes, 1350 BCE
Fresco; tomb decoration; symbolizes rebirth and leisure in afterlife.

Ancient Egypt: Akhenaten and his family
Limestone relief; domestic scene; promotes monotheism and intimacy with Aten

Early South and Southeast Asian Art: lion capitol of ashoka
Polished sandstone; imperial emblem; symbolizes dharma and Buddhist rule.

Early South and Southeast Asian Art: Great Stupa in Sanchi
Brick and stone; reliquary; represents enlightenment and cosmic axis.

Early South and Southeast Asian Art: Buddha and Attendants, from Maathura, 2nd c. CE, India
Red sandstone; devotional; conveys serenity and spiritual guidance.

Early South and Southeast Asian Art: Shiva Nataraja, 11th century, India
Bronze; ritual icon; symbolizes cosmic dance and destruction/creation cycle.

Early South and Southeast Asian Art: Buddhist Tempe at Borabudur, Java, Indoesia, c. 800 BCE
Bronze; ritual icon; symbolizes cosmic dance and destruction/creation cycle.

Early East Asia: funerary banner of lady dai, c. 168 BCE, Han Dynasty, China
Silk; burial shroud; depicts afterlife beliefs and cosmic realms.

Early East Asia: Terracotta army, Qin Dynasty, China
Clay; tomb guardians; reflects imperial power and belief in afterlife protection.

Early East Asia: Bi Disk with Dragons, China
Jade; ritual object; symbolizes heaven and spiritual purity.

Early East Asia: pagoda at horyu-ji, 7th century CE, Nara, Japan
Wood; Buddhist temple; reflects harmony, balance, and sacred geometry.
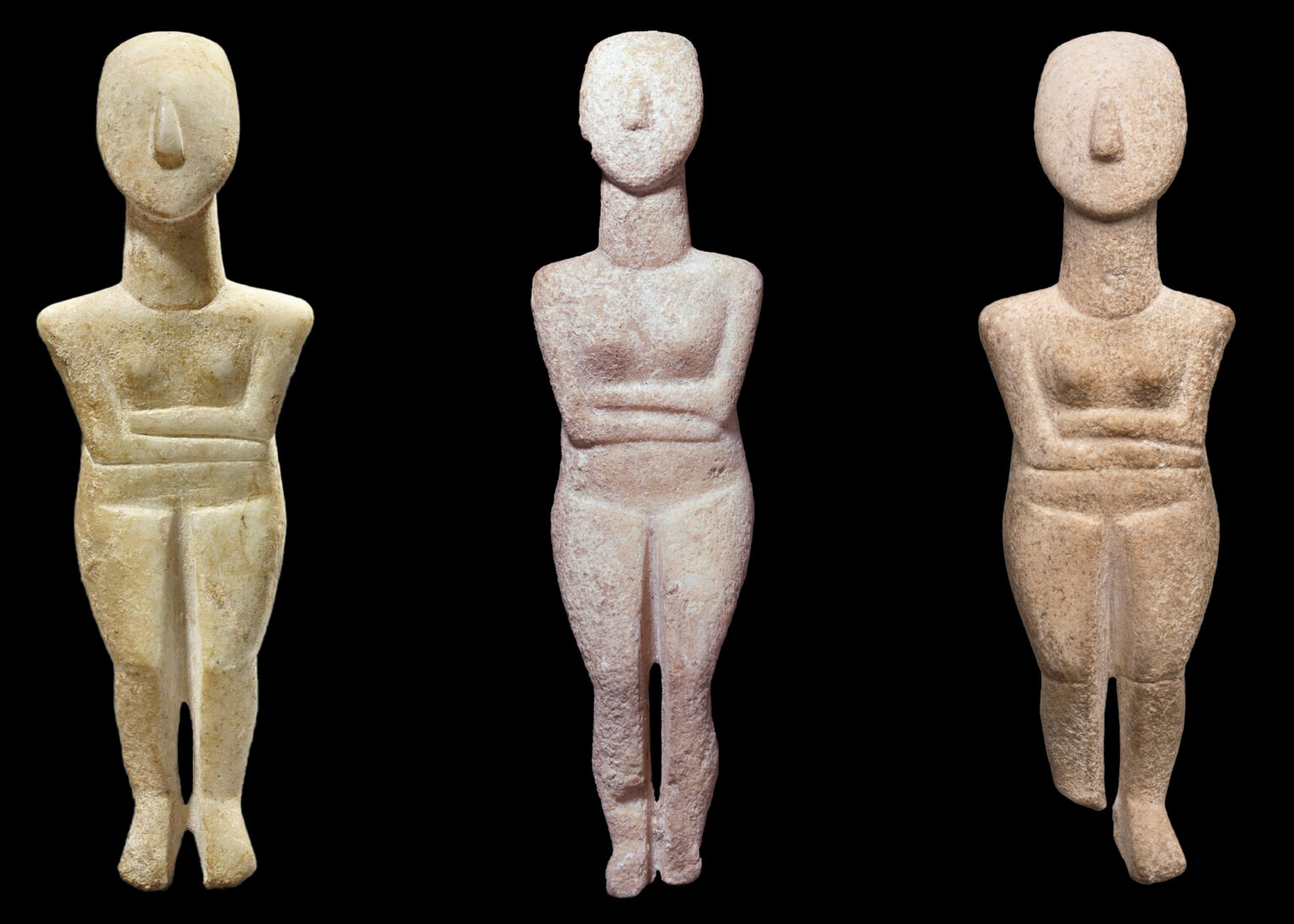

Aegean Art: cycladic figures
Marble; funerary; abstract female forms, fertility and purity.
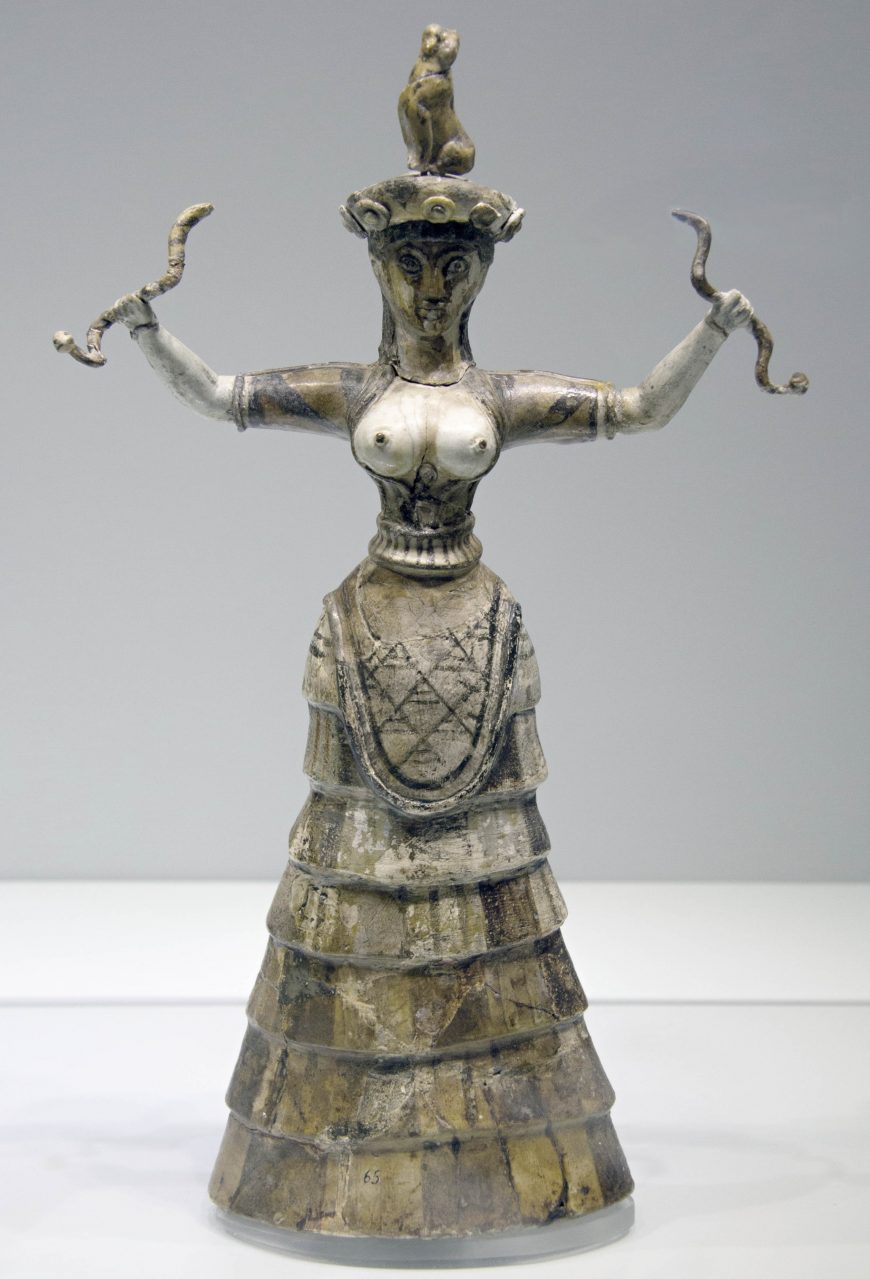

Aegean Art: snake goddess (Minoan)
Faience; household deity; symbolizes fertility and control over nature.

Aegean Art: lion’s gate at Mycenae
Stone; fortress entrance; power and divine protection.
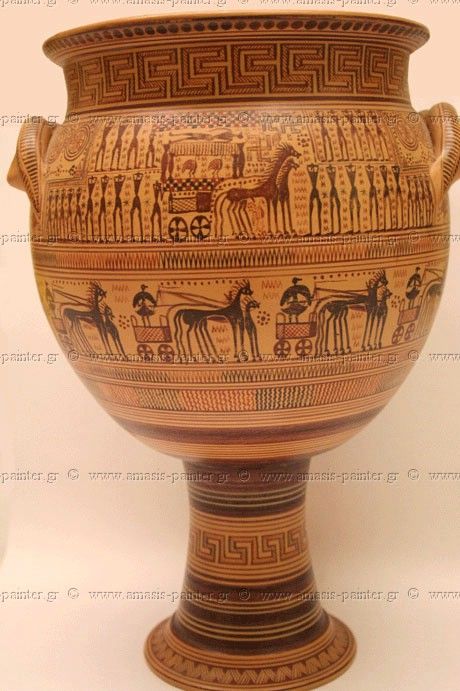

Bronze, Age, Archaic, and Classical Greek Art: dipylon terracotta krater (geometric)
Ceramic; grave marker; honors the dead, depicts funerary rituals.
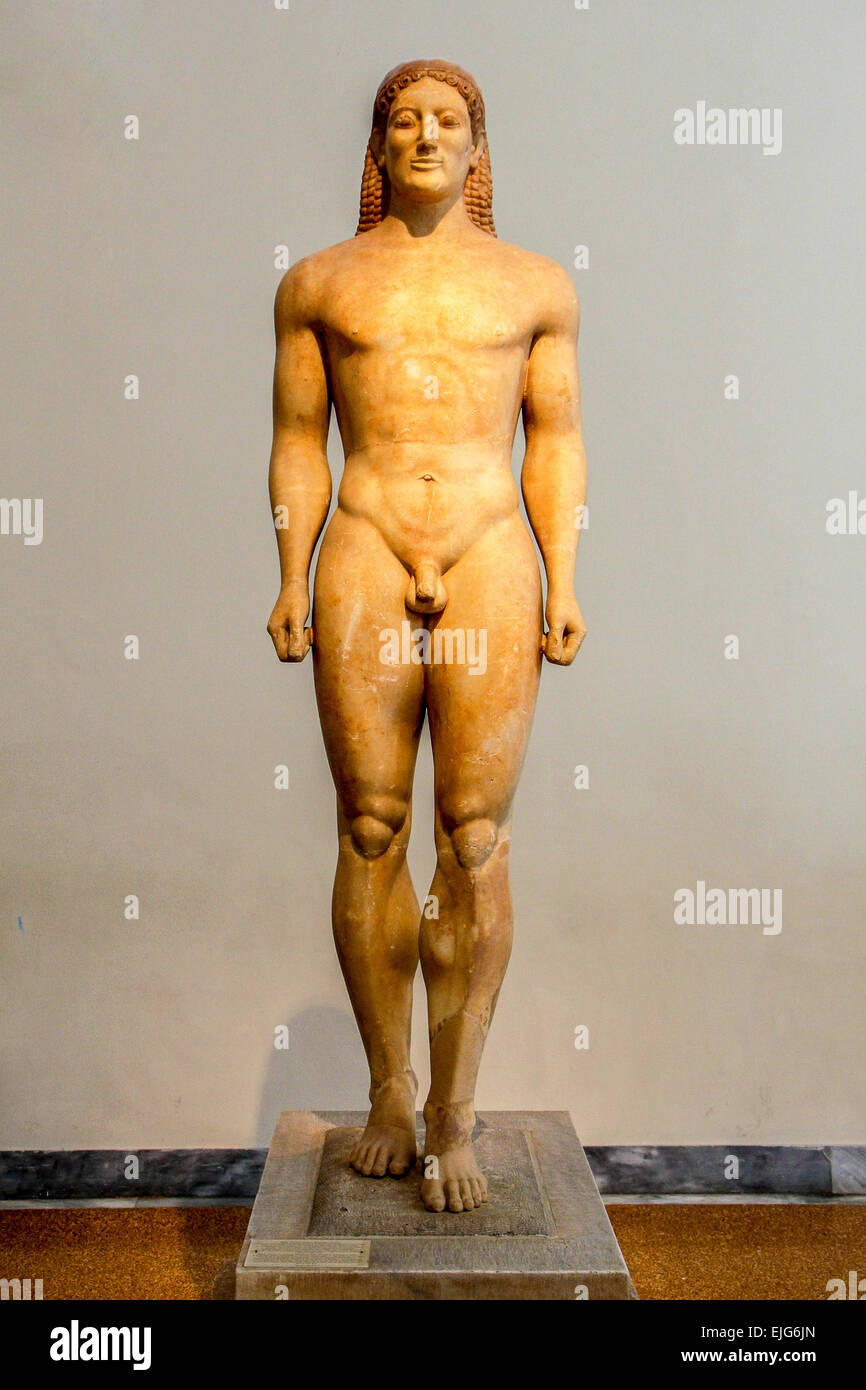

Bronze, Age, Archaic, and Classical Greek Art: anavysos kouros (archaic)
Marble; grave statue; idealized youth, heroism, and virtue.

Bronze, Age, Archaic, and Classical Greek Art: spear bearer (Daryphoros) by Polykleitos
Marble; canon of proportion; reflects harmony and physical perfection

Bronze, Age, Archaic, and Classical Greek Art: The Parthenon, Athens, 447-432 BCE
Marble; temple to Athena; symbolizes democracy, civic pride, and divine order.

Late Classical and Hellenistic Greece: Praxiteles, Aphrodite of Knidos, c. 350 BCE
Marble; first nude goddess; celebrates beauty and sensuality.

Late Classical and Hellenistic Greece: Nike of Samothrace, 180 BCE
Marble; commemorative; dynamic victory and divine intervention.

Late Classical and Hellenistic Greece: Seated Boxer, 4th-2nd, c. BCE
Bronze; realism; conveys emotion, defeat, and human vulnerability.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: reclining couple on sarcophagus from Cerveteri, c. 520 BCE
Terracotta; tomb; celebrates love and equality in afterlife.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: Augustus of Primaporta
Marble; political propaganda; divine lineage and imperial authority.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: ara pacis augustae (altar of Augustan Peace)
Marble; altar; peace under Augustus, civic religion.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: colosseum
Concrete and stone; amphitheater; imperial grandeur and public entertainment.

Imperial Roman Art: arch of titus
Marble; triumphal arch; commemorates victory and divine favor.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: column of trajan
Marble; narrative relief; glorifies military conquest and emperor’s legacy.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: pantheon
Concrete and marble; temple; symbolizes cosmic unity and Roman engineering.

Etruscan Art and the Roman Republic: equestrian statue of marcus aurelius
Bronze; equestrian; wisdom and stoic leadership.