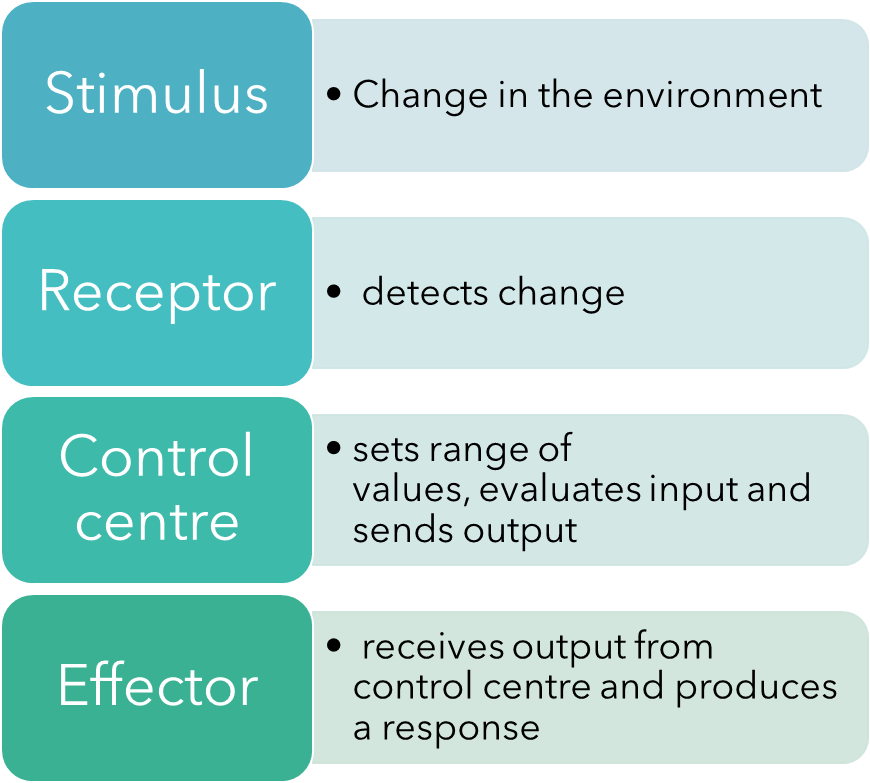
Coordination and control
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
The five senses
Sense | Stimulus | Receptor Cell | Sensory Organ |
Sight | Light | Photoreceptors or light receptors in the retina of the eye | eye |
Hearing | Sound (vibrations) | Mechanoreceptors: hair cells in inner ear | Ear |
Taste | Chemicals | Chemoreceptors or tastebuds | tongue |
Touch | Pressure Temperature Pain | Mechanoreceptors Thermoreceptors Nociceptors (pain receptors) | Skin |
Smell | Chemicals | Chemicals in olfactory cells in nasal cavity | Nose 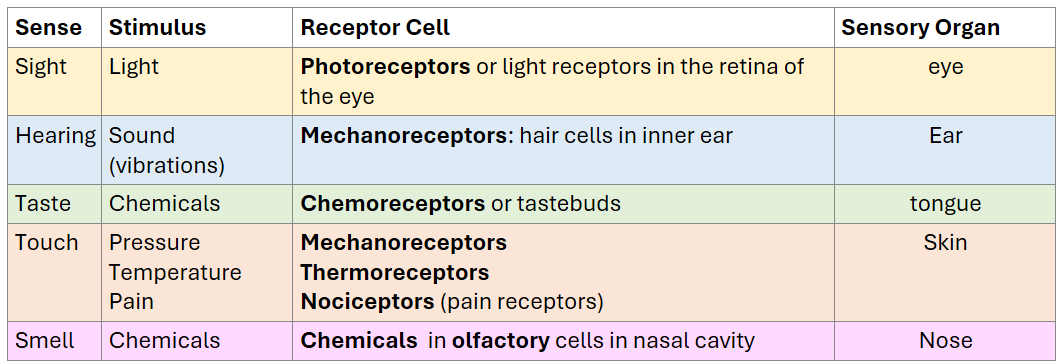 |
Eye Eyes
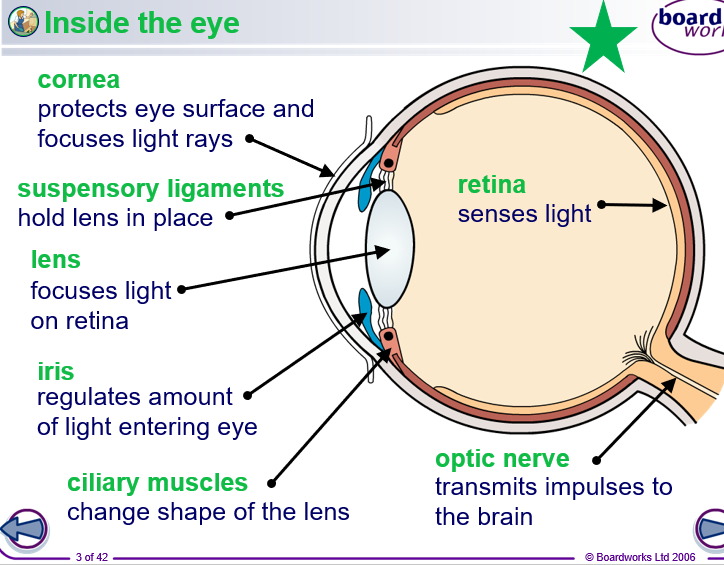
Eyes
Structure : The corneas and lesn focus light onto the retina , which contaons rods and cones
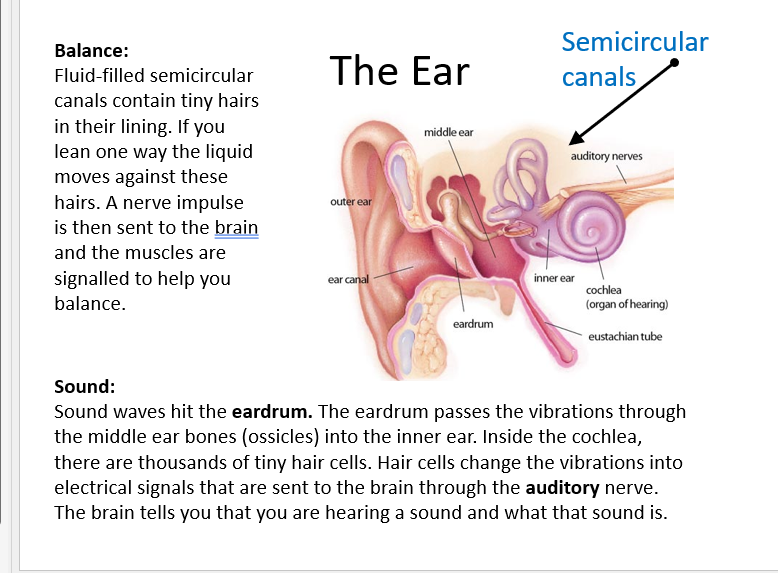
Ears
Structure : The outer ear collects sound waves , the middle ear amplifies them , and the cochlea in the inner ear converts vibrations into nerve signals . The vestibular system ( Semicucluar canals ) Detects head movement for balance
Stimulus: Detects sound waves and head postiion/movement
nose
Structure : The olfactory recetors in the nasal cavity detect airbore chemcical molecules
Stimulis: Detects chemical molecules in the air
Tongue
Structure - The taste buds on the tounge contain receptors for sweet . Salty , sour , bitter , and unami taste
Stimulus : Detects dissolved chemical in food and drinks
Skin
Structure : Contains different recpetors for pressure ( Mechnorecpetors ) , temperature ( Themoreceptors ) , Pain ( Noiccieptors )
Stimulus Detects touvh temperature changes and pain .
--------------------------
Describe passage of information through a neuron
Neuron receives a stimuls
Electical impuse traves throguh the neruom
Impulse reaches the axon terminal
Nuerotransmitters are relased into the synaoe
Neurotransmitters bind to receprots on the nextneuron
A new electical impulse is generate int eh nect neuro
mylin Sneath
A fatty layer that insulates the axon , speeding up impulse transmission
Dendrite
The part of a neuronn that receives a message and sends it to the cell body
Axon
part of a neuron that carries an electrical message away from the cell body to synapse
synapse
A small gap between two neurons that must be crossed by neurtransmitters
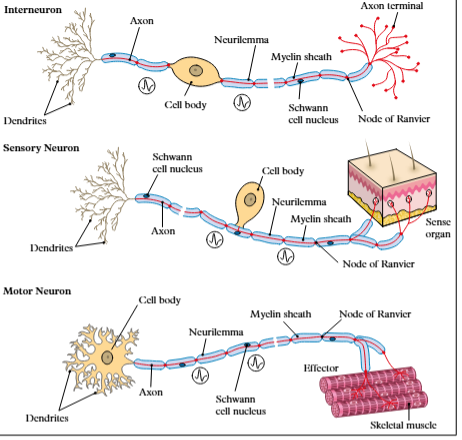
Sensory neuron
A nerve cell that carries a message from a receptor to the central nervous system
Interneurons
A nerve cell that carries a message from a receptor to the central nervous system
Motor neurons
A nerve cell thar carries a message from the central nervous system to a muscle cell .
Cell body
the Main part of a cell that contains the nucleus genetic material and processes signals
.
Neurotransmitters
n I A chemical messenger that cross the synapse between rhe axon of the neuron and the dendrite of another neuron
Passage of information through a neuron
Information travels through a neuron as an electrical impulse , moving from the dendrites to the axon terminasl . when impulse reaches the synapse , neurotransmitters are released , crossin he gap to stimulate the next cell
sensory , motor , interneurons communicate info
Sensory neurons detect stimuli and send signals to internuerons in the central nervous ssytem . Interneurons process the information and relay it to the motr=or neurons , which triggers a respnse in muscles or glands . This process enables the body from something hot ina reflex action .
Scenarios without thinking
Knee jerk reflex , when the docotr taps the knee it kicks out automatically
Blinking when something approaches your eye .
cOUGHING OF SNEEZING
Response order
Stimulus —> recpetor—> sensory neuron—> Internueron —> Brain—> Motor neuron —> Effector —> Response
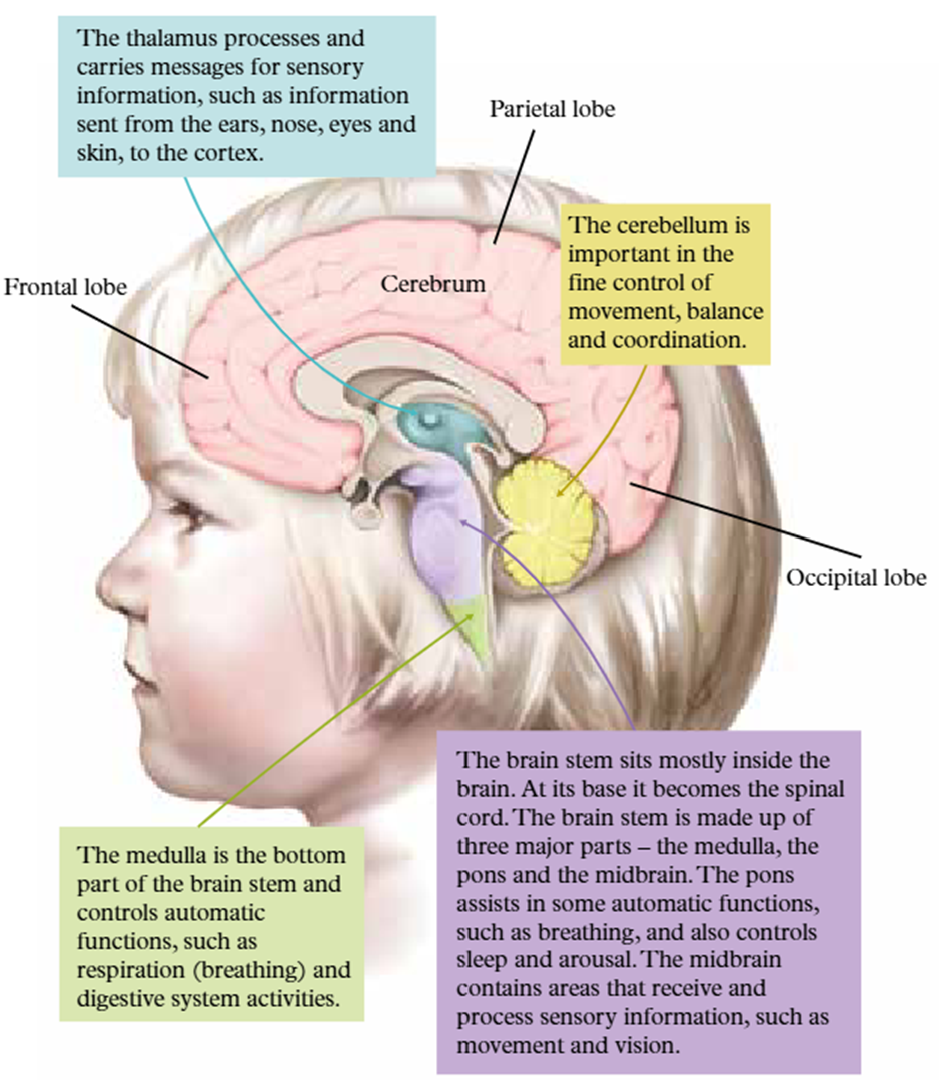
Central Nervous system (CNS
The CNS is control centre of the body . All messages from your enviroment and responses are processed
Two parts to CNS
Brain that is the processinf centre , where informatioon , is gathered by the interneuron , compares it to past experiences , and controls internal changes and movement .
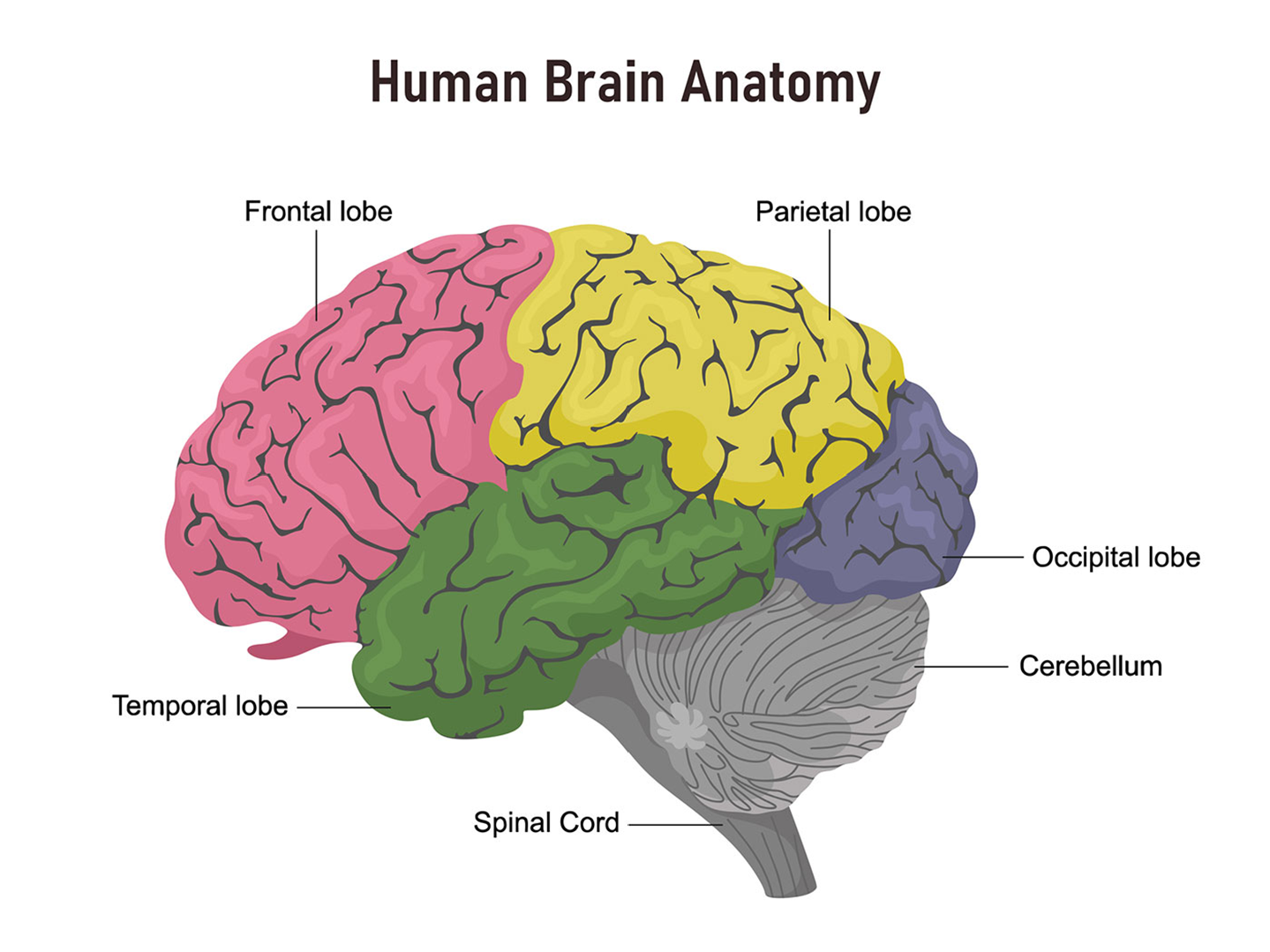
parts of the brain
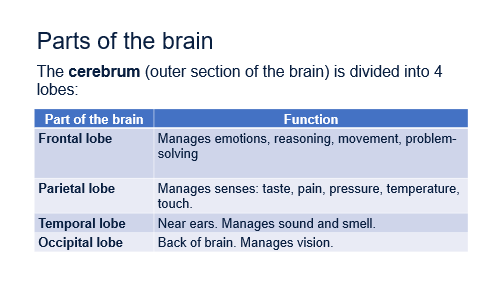
Peripheral nervous system ( PNS)
The oerioheral neurvous system connects the body to the central nervous system , transmitting information between the cns and organs , limbs , and tissue
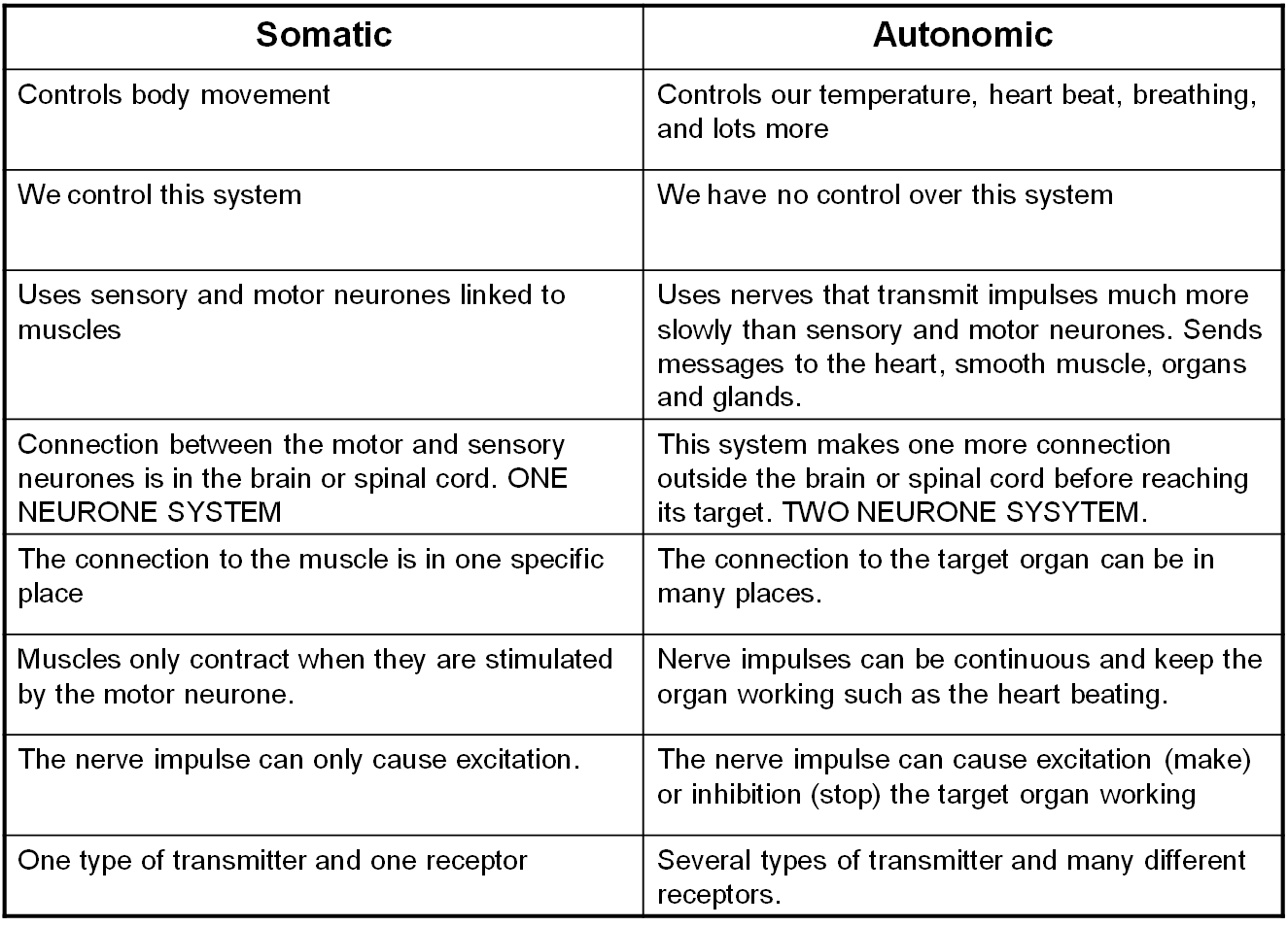
PNS split 1 - SOmatic nervous system
ontrols voluntary skeletal muscle movements , such as waving or reaching out to take an object
PNS split 2 - Autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary actions. This includes heartbeat, digestion, respiration, salivation and perspiration. It maintains a constant internal environment of the body.
Autpnomic system two parts
The autonomic system is further split into two systems, the two divisions have opposite effects, e.g:
Sympathetic system speeds up heart rate.
Parasympathetic system slows down heart rate.
The systems work together in the body to maintain a balance.
SOmatic vs automatic
Examples of diseases and problems affecting nervous systek
ALzheimers disease - Affects memeory and thinking due to brain cell damage
Multiple sclerosis - The immune system attacks the mylein sneath , leading to muscle weaknesss and coordination problems
Stroke - occurs when blood flow to the brain is blocked , leading to brai damage .
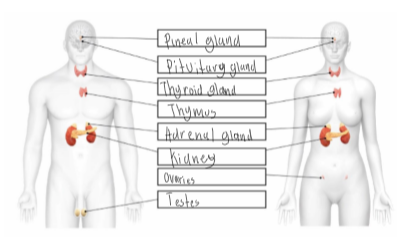
Endocrine system
Endocrine system – a collection of glands that make and secrete (release) hormones.
Hormone
– a chemical messenger that travels through blood vessels to target cells.
Target cells
a cell that has a receptor that matches a specific hormone.
Flight or fight
The bodies automatic reaction to danger , drivenby the sympathetic nervous system . It increases heart rate , breathing ,and muscle readiness , while slowing digestion , preparing the body for either fight or escape .
example hormon - adrenalin
Adrenal glands
Produce the hormone adrenaline/ epinephrine.
Normally it stimulates heart rate and enlarges blood vessels.
In danger it floods your system causing the ‘fight or flight’ response:
Increased strength and heart rate
Raises blood pressure
Glycogen converted to glucose faster
Blood diverted to the muscles (for energy).

a hormone released by the adrenal glands that prepares the body for a "fight or flight" response, triggering physiological changes like increased heart rate and blood flow to muscles, in response to stress or danger.

effects
Effects that the relese of adrenalin causes
Heart beats faster to increase the delivery rate
of fuel and oxygen to muscles and remove their waste
products quickly.
Breathing increases. Active muscles need extra oxygen so they can use more fuel to get more energy.
Muscles able to work harder .Muscles need to be more
efficient as they prepare for ‘fight or flight’ situations.
Skin goes pale. Blood is diverted from the skin to essential organs and muscles.
Skin starts to sweat. We need to dissipate heat as
our muscles become active.
Type of hormone - Peptide hormone
Made of protein and produced by the anterior pituitary , parathoid gland , placenta , throid glnd and pancrease .
Travel through bloodstream until they find and interact with specific repetor on surface of their target cell. causing the target cell to respond
Steroid hormone
Secreted by the adrenal glands and the ovaries ( women ) and testtes ( men) .
Produced from cholesterol

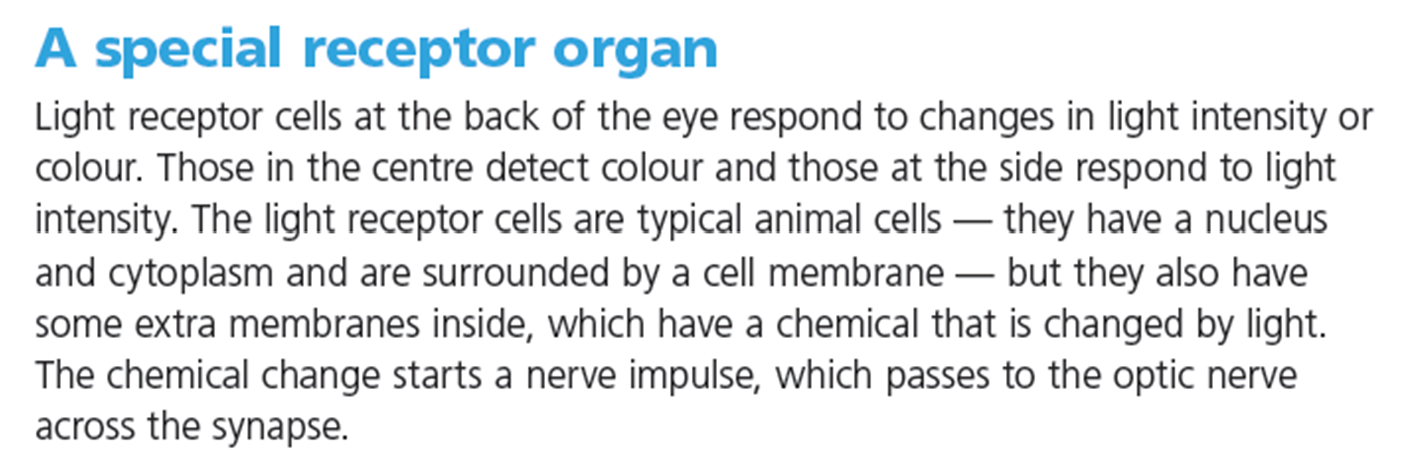
Homeostasis
The process when the body detcts and responds ti stimuli to ensure a stable internal state is maintained .
Factors that need to be controlled
Some factors that need to be controlled:
•Temperature (37°C)
•Water levels
•Oxygen & carbon dioxide levels
•Blood glucose levels
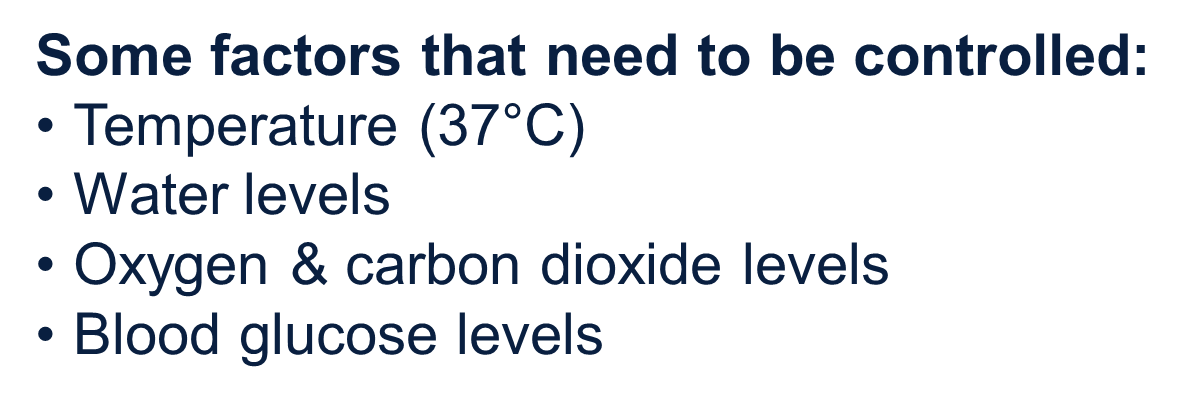
Negative feedback
Ne
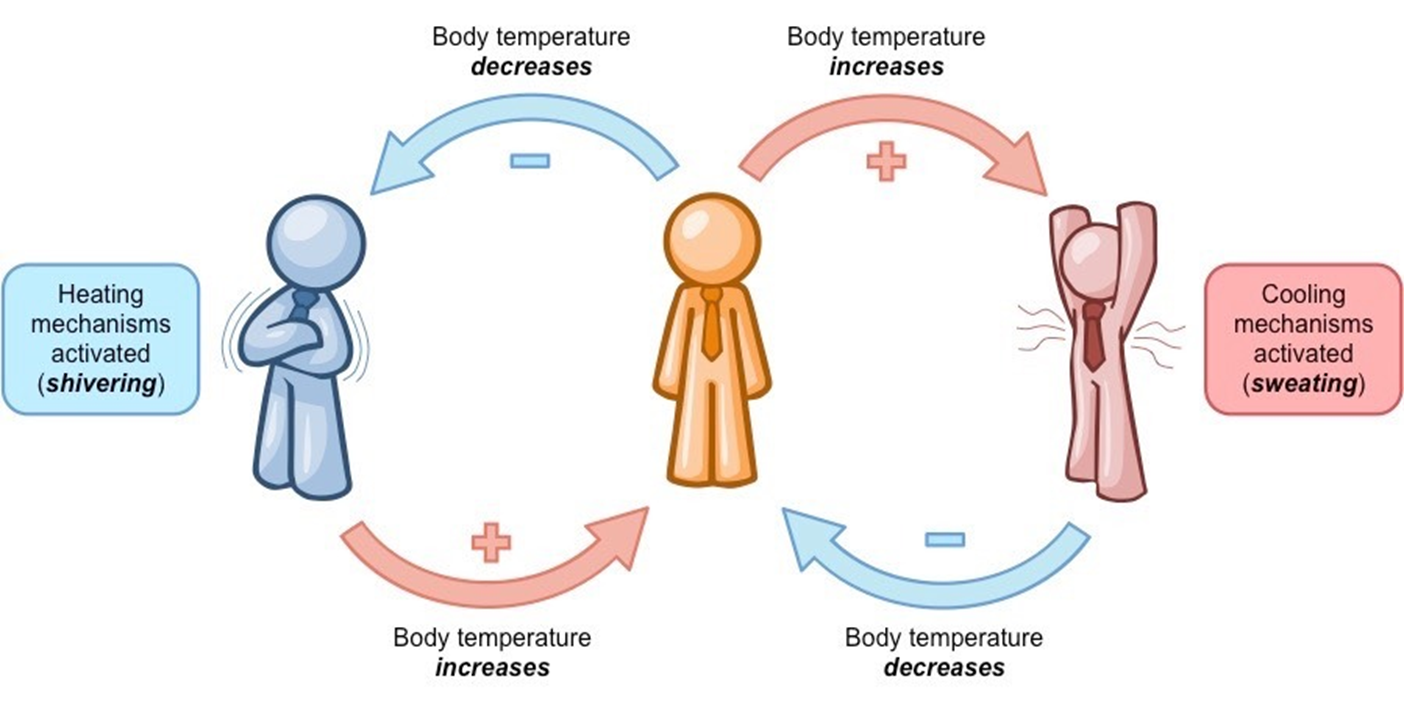
Negative feed back
ative feedback – a mechanism that works to remove the stimulus
Is the process when the body detects a change and activates mechanisms to revere change , brining the system back to its normal state . Helping the body matain balance ( Homeostasis in the body )
Homeostasis feedback
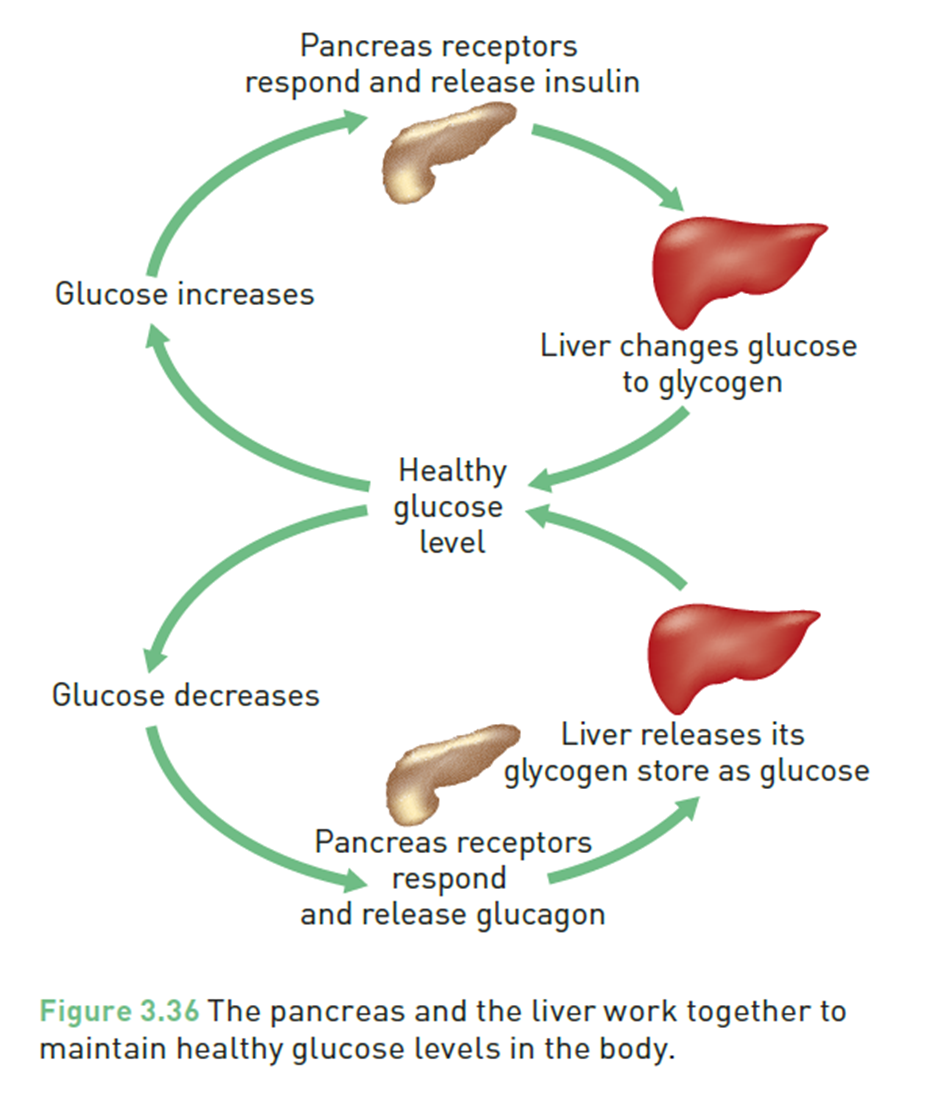
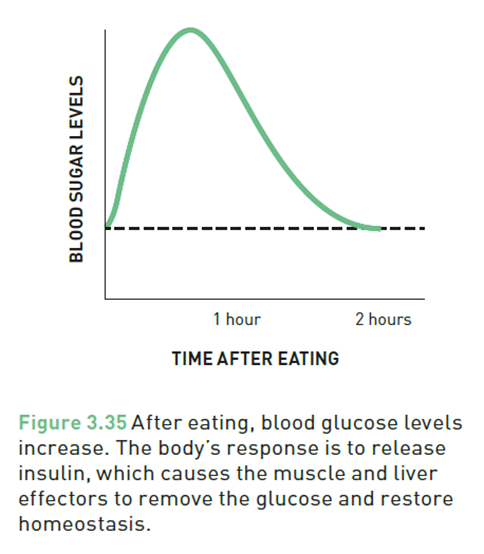
Controlling blood sugar levels
Glycogen is a polymer of glucose monomers.
This is how animals store sugar.
Glucose is soluble in blood.
Glycogen is insoluble and is in the liver.
Controling water levels
ADH travels in the blood until it gets to target effector cells in your kidney.
When it binds to the receptors on the effector cells it causes them to reabsorb extra water out of your urine.
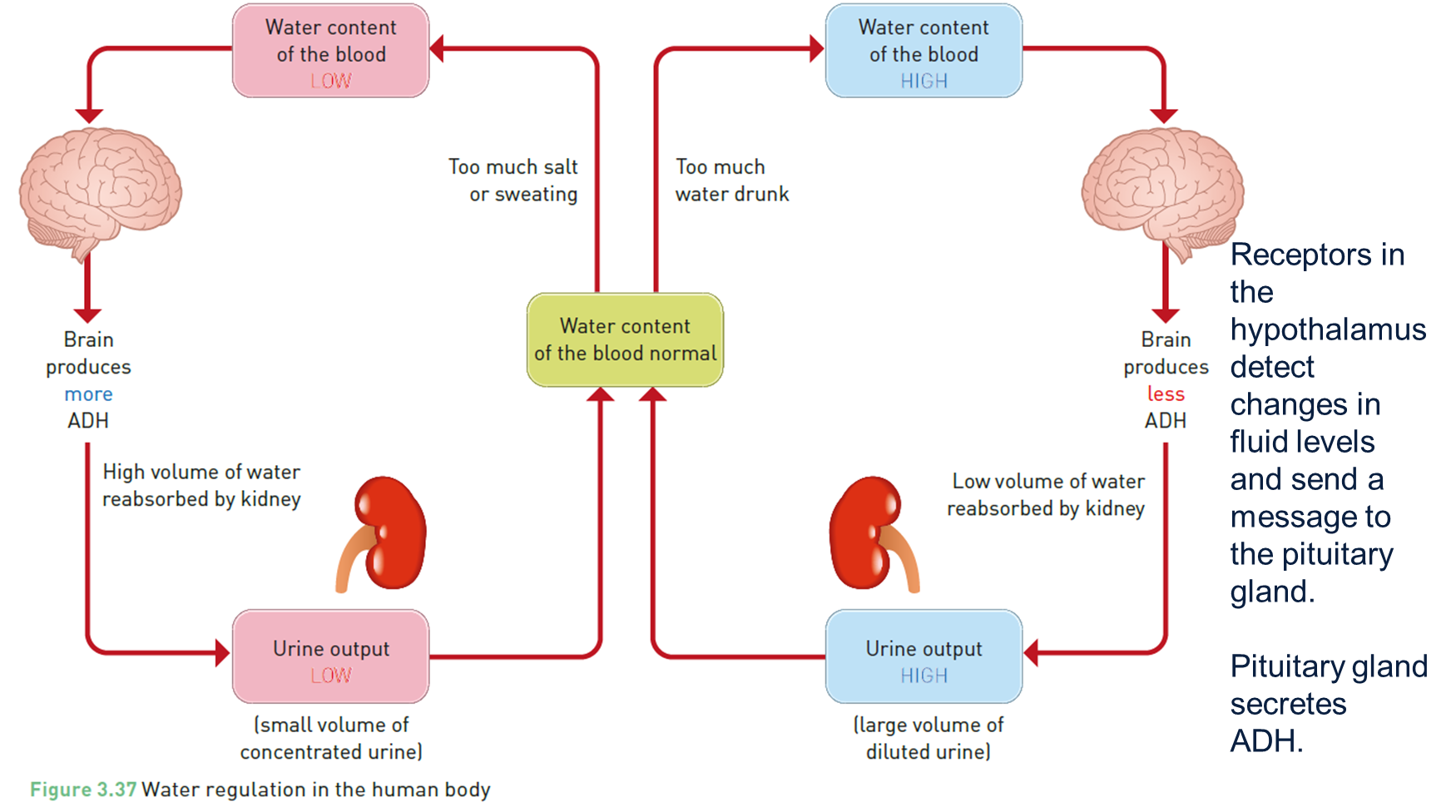
Receptors in the hypothalamus detect changes in fluid levels and send a message to the pituitary gland.
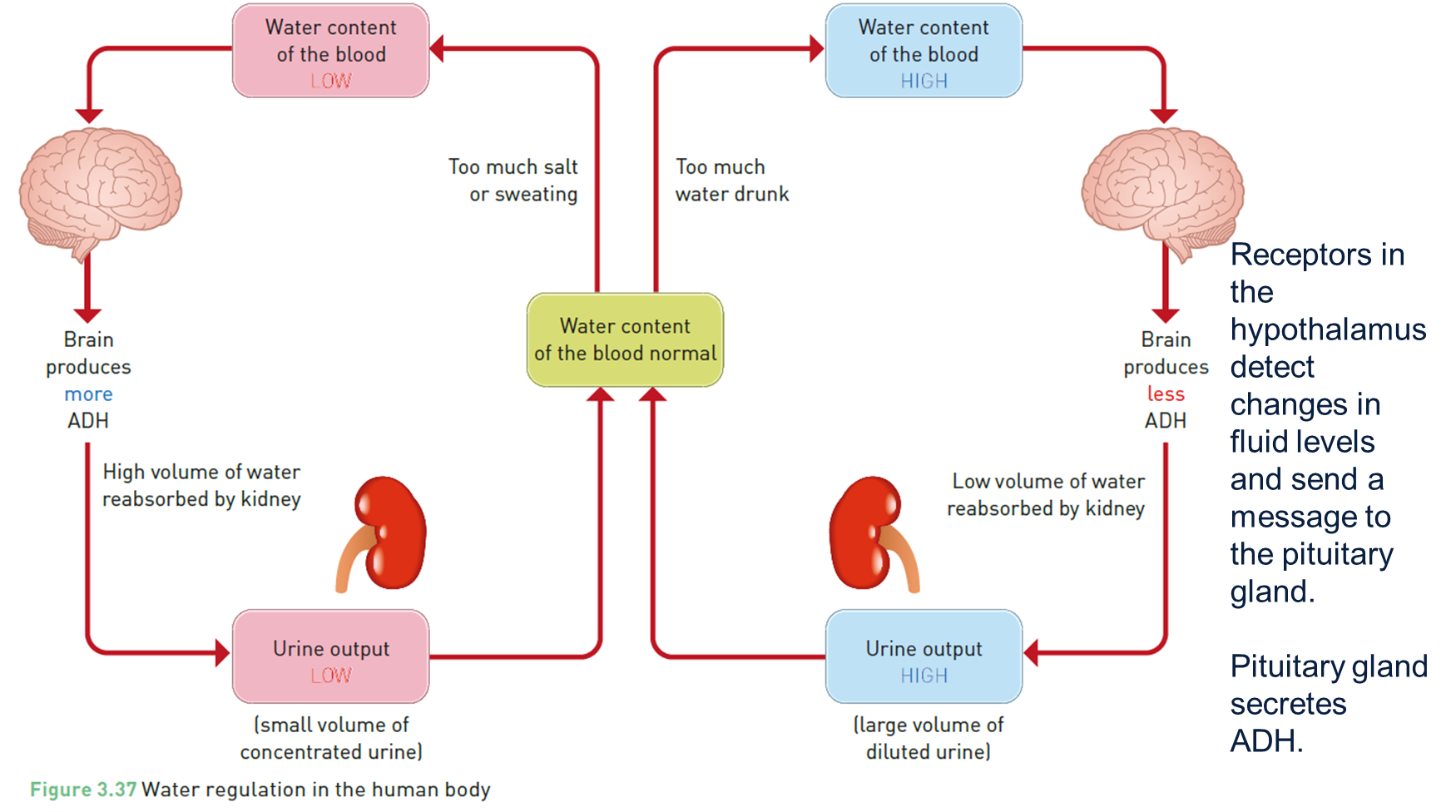
Pituitary gland secretes ADH.
Types of neurons
High blood glucose- how hormonse regulate blood sugar
When blood glucose is too high , the pancrease releasese insulin . Insulin helps cells in the muscle and liver absorb glucose , lowerining blood glucose .
Low blood glucose- how hormonse regulate blood sugar
When blood is too low , the pancrease releaseses glucagon signals the liver and muscles to release stored glucose , raising blood glucose levels back to normal .
How hormonse regulate water level
Hormonse including the antidiuretic hormonse ( ADH regulate water levels in the body ,
When dehydrated , the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to release ADH
This hotmone helps the kidneey reabsorb water , reducing urine output and concentratiing it .
When over hydrated , the hypothalamus signals the pituitary ro stop releasing adh , allowing more water to be excreted in dilute urine .
This proccess maintains wtaer balance through negative feed back
WHat is sound made up of
It is forme by vibration that travel as waves . Its key properties is frequency , amplitude and timbro
HOw is smell linked ot taste
BOth senses detect chemicals and wrk together by detecting food molc=ecules in the nose , combining wiith taste
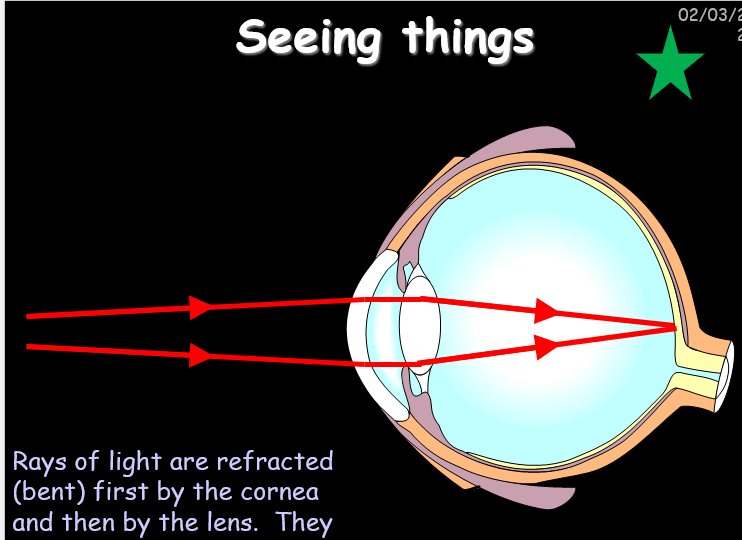
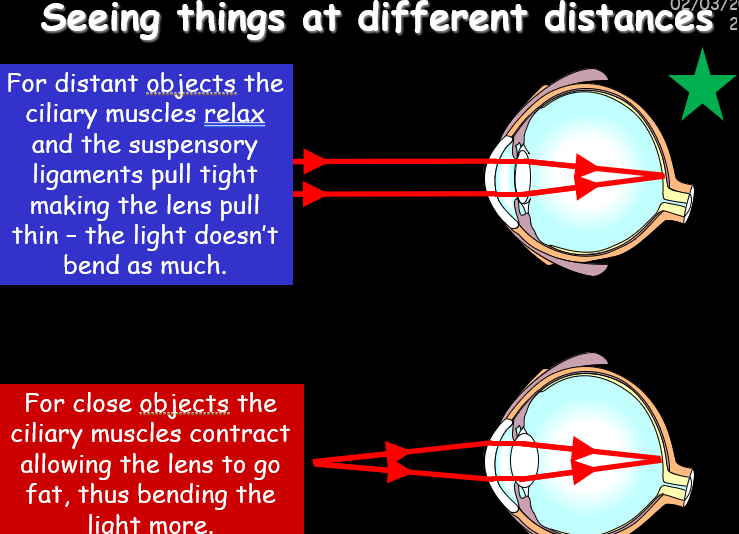
WHat allows you to see
LIght enetering the eye through the cornea and lens , which focus on the retina
How does the nose detect and interpeate smell and transfer it to the brain .
THe oflactory receptors in the nose detect odor molecules to the oflactory bulbs . These signals travel via the olfacotry nerve to the cortex in the brain,
Neurons and nerves
neurons (nerve cells) pass along the electrical impulses in the nervous system.
Lots of neurons grouped together = nerve
Electrical impulses are messages that are carried to the brain.
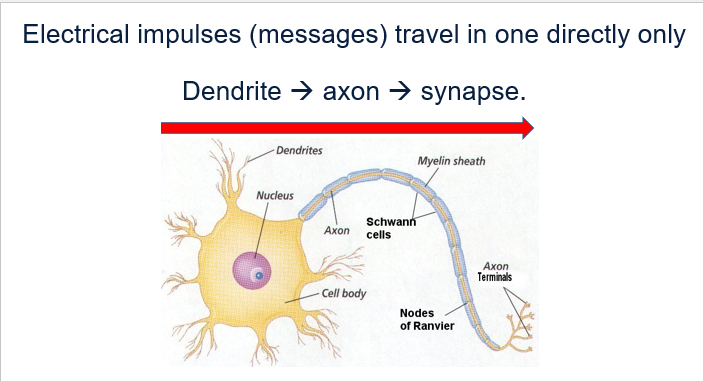
Structure of neuron - p1
.
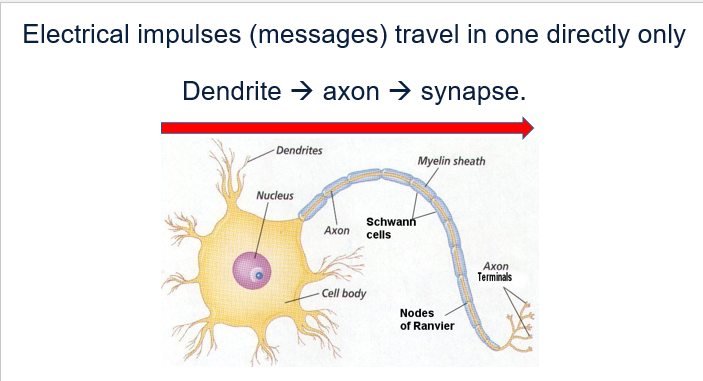
Cell body
Contains the nucleus.
Supplies energy and nutrients for the entire neuron.
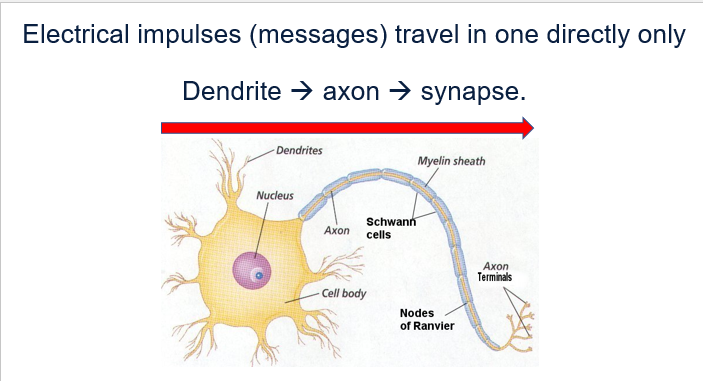
axon
Long structure.
The nerve impulse travels from the dendrites to the synaptic terminal.
The axon is electrically insulated by a sheath called myelin.
Describe where you will find neurons that deteect
Smell- Processed in the oflcatory bulb , located in temporal lobe
Taste
Processed in the gustatory cortex,which includes the insula and frontal operculum .
SOund
Processed in the primary auditory cortext in temporal lobe
Touch
Detected by receptors in the skin and by the somatory cortex in the parietial lobe .
Light
Peripheral sensory neurn
COmpare the similarities and differences between sensory and motor neurons
Both types of neurons have long axons for signal transmission
WHat are neurons
They are nerve cells that transmit signals in the nervous system
The difference between a neuron and a nerve cell
Nerves are bundles of neurons while a neuron functions to send and receive electrical signals
diagrm stimulus
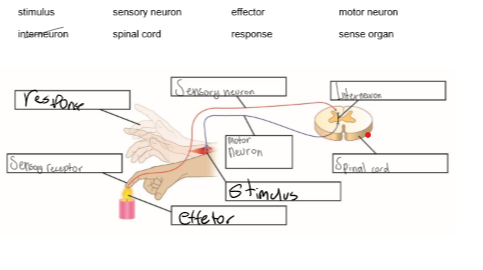
four stimulus the body responds to
heat , light , pressure and sound
WHy is the brain not involved in reflex actions
The brain is not involved because the response needs to be fast and the signals travel through the spinal cors to quickly send a message for muscle to react
Three flight or fight response
fight , light , freeze

Organs
WHen does negative feedback occur
Occurs when a systems output decreases .
How is the body like a thermostate
monitoring and regulating core body temperature, initiating responses like shivering or sweating to maintain a stable internal temperature of around 37°C (98.6°F).
Two actions the body uses in negative feedbck when body is too cold
shivering and vasoconstion
Two effectors in negative feedback mechanisms the body experiences too hot things
The sweat glands release into skin , aiding it to cool down. The blood vessels allow blood to flow into the skin , meaking heat loss
aEFfect off positive and negative feed back / body heat-positive
Worsen the condition that can posibly lead to heatstroke
Negative feed
The body sends sweating and validation to cool .
too much glucose

flow chart of pancrease and liver working together
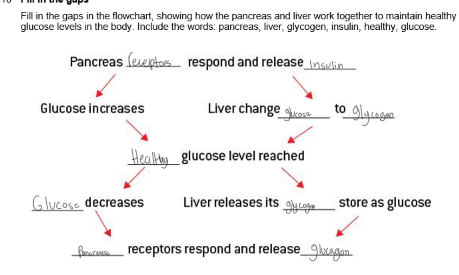
WHen does negative feedback occur
Occurs when a systems output decreases .
Why is the body liike a thermo state
Becauces when temperature recpetors on your skin and in hypothalamus of your brain detect cooling down , a message gets sent to a variety of effectors around your body .
Two actions the body uses in negative feedback when cold
Shivering and vasconsticion
What are the two effectors in the negative feedbacl mechanismm that the body experiences when it is too hot
Sweat glands release into the skin , aiding it to cool down
THe blood vessles alllow blood to flow into the skin making heat loss
What do glucose molecules travelling in the blood do ? It provides eergy towards the cell through the process of cellular respiration
Why is too much glucose in the blood unhealthy
It causes water loss from cells through osmois.
