Chapter 2, Lesson 1: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 2, Lesson 1 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Element
The simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus; the periodic table is arranged by these and is accompanied by a symbol
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorus
The six elements that make up 98.5% of a person’s body weight alongside small amounts of trace elements
Minerals
Inorganic elements extracted from soil by plants and passed up food chain to humans; they constitute about 4% of body weight and are important for body structure and enzyme function
Electrolytes
Mineral salts needed for nerve and muscle function; they ionize and conduct electricity in water
Neils Bohr
Scientist who proposed the planetary model of the atomic structure in 1913
Nucleus
The center of the atom
Protons
A particle located in the nucleus with a positive charge and mass of 1 amu
Neutrons
A particle located in the nucleus with no charge and mass of 1 amu
Atomic mass
Calculated by adding protons and neutrons
Electrons
Particles with a single negative charge and very low mass that exist in a cloud around the nucleus; they maintain neutrality to counter the positive protons
Valence electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell and determine the chemical bonding properties of an atom
Isotopes
Varieties of an element that differ in neutrons; they are heavier due to the neutrons but have the same number of valence electrons
Atomic weight
A weighted average of the commonality of isotopic weights
Radioisotopes
Unstable isotopes that decay and give off radiation
Free radicals
Electrons that are ejected from radioisotopes which can cause cancer and destroy molecules
Physical half-life
Time required for 50% of a radioisotope to become stable
Biological half-life
Time required for 50% of a radioisotope to disappear from the body
Sievert (Sv)
Unit of radiation dosage
5 Sv
Fatal dosage of radiation
50 mSv
Standard acceptable exposure per year
Background radiation
Comes from natural sources like radon gas and cosmic rays; transfers about 2.4 mSv per year
Artifical sources of radiation
Comes from X-rays, color TVs, etc.; transfers about 0.6 mSv per year
Madame Marie Curie
First woman to recieve a Nobel Prize and discovered, created treatment for, and died of radioactivity

Ion
A charged particle with an unequal number of protons and electrons
Ionization
The transfer of electrons from one atom to another
Anion
Particle with a net negative charge due to gain of electrons
Cation
Particle with a net positive charge due to loss of electrons
Free radicals
Short-lived particles with an unusual number of electrons, they are produced by metabolic reactions, radiation, and chemicals; may destroy molecules and cause aging and cancer
Antioxidants
Chemicals that neutralize free radicals
Molecule
Particle composed of two or more atoms united by a chemical bond
Compound
Molecule composed of two or more different elements
Molecular formula
Identifies elements and how many of each are present
Structural formula
Identifies location of each atom
Isomer
Molecules with identical formulae but different arrangements of atoms
Molecular weight
Calculated by finding the sum of the atomic weights of each atom
Chemical bonds
Holds atoms together within a molecule; examples include ionic, covalent, hydrogen, and van der Walls forces
Ionic bond
Attraction of a cation to an anion by transferring an electron, but is easily broken by water
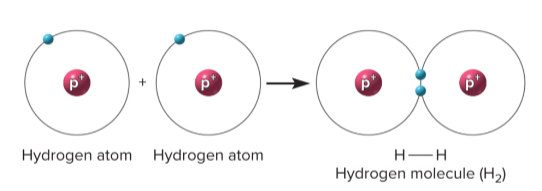
Covalent bond
A bond where atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
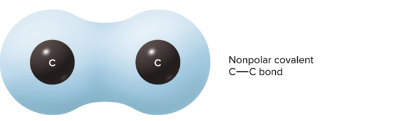
Nonpolar covalent bond
Electrons are shared equally between atoms, symmetrical
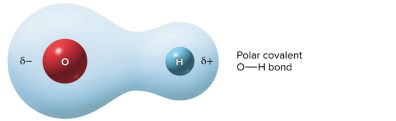
Polar covalent bond
Electrons are shared unequally, nonsymmetrical
Hydrogen bond
Weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom in one molecule and a slightly negative oxygen or nitrogen in another; affects cohesion and adhesion in water and DNA molecular structure
Van der Walls forces
Very weak and brief attractions between neutral atoms which create polar bonds