Atomic Structure
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Unstable definition
The ability for a nucleus to decay
Radioactive decay definition
The RANDOM process of radiation being released by a nucleus. A different element in formed
Nuclear radiation definition
The energy and particles released when an unstable nucleus decays
Activity definition
The rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decay
Becquerel definition
The unit of activity
Geiger-Muller tube definition
A device to measure the count rate of a radioactive source
Count rate definition
The number of radioactive decays recorded by a detector per second
Ionising power definition
How well it knocks off electrons and damages cells
Half life definition
The time it takes half of a group of radioactive nuclei to decay
Radioactive contamination definition
Unwanted presence of radioactive atoms on other materials- hazardous- decay of atoms- release radiation- lasts for long period of time, source of radiation transferred
Peer review definition
When the findings of one expert are double checked by another expert to make sure they are correct- essential on effect of radiation on humans- if initial studies get wrong- safety levels based on study cause people to die
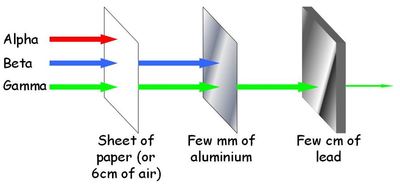
Alpha (a) : made of, charge, range in air, penetration and ionising power
helium nucleus
+2
5cm
blocked by paper and skin
high
loses two from proton number and 4 from mass number
Beta (β) : made of, charge, range in air, penetration and ionising power
fast moving electron
-1
15cm
blocked by thick aluminium
medium
loses neutron gains proton, proton number increases by 1 BUT atomic mass doesn’t change
Gamma (γ) : made of, charge, range in air, penetration and ionising power
electromagnetic wave
no charge
very long range
blocked by thick lead
low
no change
describe it as a diagram
matched up
Irradiation definition
Lasts short period of time, source emits radiation- reaches object, exposed to radiation- doesn’t become radioactive
Net decline definition
half number of nuclei, and keep doing so after X number of times
net decline = initial number - number after X half lives/ initial number
Long half life
Doesn’t remain strongly radioactive- initially very radioactive- dies down, less of long-term risk
Short half life
Remains weakly radioactive for long period e.g. americium in smoke alarms (alpha emitter), emitted into air, doesn’t reach far as alpha is weakly penetrating. If smoke reaches, amount of alpha particles drop- alarm sounds
1st model of atom
Dalton- ball, solid sphere
2nd
Plum pudding- sphere positive charge- negative electrons embedded
3rd
Rutherford- nuclear, positive nucleus in centre of atom and electrons in cloud around nucleus
Scattering experiment
alpha particles fired at sheet of gold foil
most went straight through- most atom empty space
some deflected- nucleus must be charged positively- deflecting positive charge of gold
some deflected straight back- nucleus contained most of mass
3rd and 4th
Bohr- shells around atom
Chadwick- neutron