Cellular Levels Organization
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Cell
The smallest, basic unit of life. A structural and fundamental unit of life.
Cell Biology
The study of cells from its basic structure and functions of every cell organelle
Robert Hooke
He discovered the cells in 1665 by observing a thin slice of cork with a compound microscope.
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
What are the 2 types of cell?
Binary Fission
The cell division of Prokaryotes
Mitosis and Meiosis
The cell division of Eukaryotes
Prokaryote
Has no nucleus; no presence of organelles and has smaller cell size, a single-celled microorganism
Eukaryote
Has presence of organelles and has bigger cell size, a multicellular microorganism
Cell Metabolism
All chemical reactions that occur within our body is called
Metabolize & release energy, Synthesize Molecules, Communication, Reproduction & Inheritance
What are the functions of a cell?
Asexual Reproduction
What kind of reproduction are Mitosis and Binary Fission?
Sexual Reproduction
What kind of reproduction is Meiosis?
Nucleus
Contains genetic material of the cell (DNA); site of RNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Has many ribosomes attached; site of protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Site of Lipid Synthesis; participates in detoxification; a storage of Calcium
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Golgi Apparatus
Modified protein structure and packages proteins in secretory vesicles
Secretory Vesicles
Contains materials produced in the cell; formed by the Golgi Apparatus; secreted by exocytosis
Lysosomes
Contains enzymes that digest material taken into the cell
Mitochondrion
Site of aerobic respiration and the major site of ATP synthesis
Centrioles
Facilitate the movement of chromosomes during cell division
Microtubule
Supports cytoplasm; assists in cell division and forms components of cilia and flagella
Cilia
Move substances over surfaces of certain cells
Microvilli
Increase surface area of certain cells for absorption and secretion; modified to form sensory receptor
Plasma Membrane
Outermost component of cells
Phospholipid Bilayer
Boundary separates the substance inside the cell (Intracellular) to the substance outside the cells (Extracellular)
Potassium In, Sodium Out
What does PISO stand for?
Glyco
Stands for Carbohydrates
Glycoproteins
Glycolipids + Glycoproteins
Glycolipids
Stability and cell to cell communication through bilayer
Glycoproteins
Cell recognition or self-recognition; Responsible for the attachment or bind to other cells
Glycocalyx
Contains your molecules absorb outside your environment; Knows precise boundaries between your plasma membrane and the extracellular of our environment
Fluid Mosaic Model
What is this model called
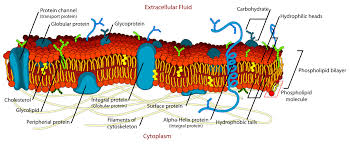
Peripheral Proteins
Found on the outer surface of your plasma membrane
Integral Proteins
Deeply integrated in your plasma membrane
Marker Molecules
Molecules that identify or recognize
Receptor Proteins
Can be a receptor to a specific chemical
Cadherins and Integrins
What are the Attachment Proteins
Cadherins
Attachment of cell to cell
Integrins
Attachment of cell to extracellular material
Transport Proteins
What do you call Channel, Carrier, ATP power pumps
Leak Channels
Channels that leaks, always open
Gated Channels
Channels that opens and closes upon the entrance of a specific ion or molecule
Uniport
Refers to the transport of one molecule across the plasma membrane
Symport
Also known as co-transport, refers to the movement of two different ions or molecules in the same direction
Antiport
Also known as your countertransport, refers to the movement of two different molecules in opposite direction
Enzymes
Increases the rate of chemical reaction
Cell Membranes
Selectively permeable; Allow some substances, but not others, to pass into or out of the cells
Na (Sodium), Ca (Calcium), Cl (Chloride)
What elements are found concentration in extracellularly
Interstitial fluid
Fluid outside cells
amino acids, sugars, fatty acids, vitamins, hormones, salts, wastes
Rich, nutritious “soup”
Selective Permeability
Plasma membrane only allows some substances to enter cell; Nutrients in, wastes out through passive or active transport
Passive Transport
a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes
Diffusion
tend to move from an area of higher concentration of a solute to an area of lower concentration of that same solute in solution
Isosmotic
Same concentration of solute and osmotic pressure
Hyperosmotic
Same high concentration of Solute and Osmotic Pressure
Hypoosmotic
Same low concentration of Solute and Osmotic Pressure
Tonicity
The ability of solution to change shape or tone of cells by changing water volume
Isotonic
Equal concentration solutes
Hypertonic
Higher conc. of solutes
Hypotonic
Lower conc. of solutes
Facilitated Transport
A mediated transport process by which transport proteins mediate or assist the movement of large, water-soluble molecules or electrically charge molecules
Active Transport
Move molecules against concentration gradient from low to high concentration; Energy (ATP) is needed
Antiport
Directly uses ATP to drive transport
Vesicular Transport
Fluid & large particles are transported across membranes in vesicles
Exocytosis
“Out of cell” - eject substances
Endocytosis
“Within the cell” - ingest substances
Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, Receptor-mediated endocytosis
What are the 3 types of Endocytosis
Phagocytosis
Cell eating, engulf large or solid material
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking, fluid with dissolved molecules
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Concentrate specific substances (ligands) that bind receptor proteins
Meiosis
Makes distinct gametes; sex cells
Mitosis
Clones body cells; somatic cells
Atrophy
This type of disorder of cell structure decreases its cell size
Hypertrophy
This type of disorder of cell structure increases in cell size
Hyperplasia
This type of disorder of cell structure increases its cell number
Metaplasia
This type of disorder of cell structure has the ability to change into another type of cell
Neoplasia
This type of disorder of cell structure changes in cell structure
Hypoxia
This type of disorder of cell structure decrease in the amount of oxygen in the blood flow to cellular structure