SAM Exam 3 - Oncology
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Cancer mechanism
Out of control cellular growth
Gene mutations cause activation of oncogene or loss of tumor suppressor gene function
Oncogenes: genes in normal cells, regulate growth and differentiation
Proto-oncogenes (Gas)
Tumor suppressor genes: Induce apoptosis in damaged cells and prevent growth and replication (Breaks)
Malignant Transformation: Gene mutations cause activation of oncogene or loss of tumor suppressor
Angiogenesis: Required for tumor growth and metastasis, induced by hypoxia
Once there is blood flow, then have access to expand and invade surrounding tissues.
Carcinogens
Genetics: Renal cystadenocarcinoma and nodular dermatofibrosis (RCND) in GSD - inheritable
Viruses: Papillomaviruses, FeLV (20% PI), FIV (risk 6x)
Chemicals: tobacco, Pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, 2,4-D, glyphosphate
Tobacco: lymphoma, oral SCC - cats
chemicals: lymphoma, TCC
Physical factors: Chronic Inflam, implants, Injection site sarcomas
Enviro factors: ultraviolet radiation / sunlight, ionizing radiation
Hormones: Estrogen, Progesterone (mammary) , Androgens, Testosterone (perianal adenoma)
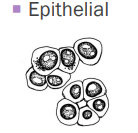
Epithelial Tumors
Benign: papilloma, adenoma
Malignant: carcinoma, adenocarcinoma
Cells in clusters/clumps/acini
Round nuclei with moderate cytoplasm
Exfoliate well
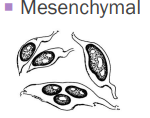
Spindle cell or Mesenchymal tumors
Benign: fibroma, lipoma
Malignant: fibrosarcoma, liposarcoma
Singular, elongate cells: may be aggregates
Cytoplasmic tails
Does not exfoliate well
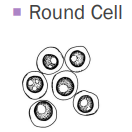
Round cell tumors
Plasma cell tumor, lymphoma, Mast cell, Transmissible venereal tumor, Histiocytoma, Melanoma ±
Discreet, small to medium-sized cells
Exfoliate well
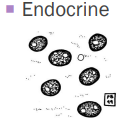
Endocrine tumors
Benign: pituitary adenoma, thyroid adenoma
Malignant: thyroid carcinoma, insulinoma (pancreas)
Free/naked nuclei in a sea of cytoplasm
Exfoliates well
Dealing with Cancer
Testing
Changes over time
Cytology: fast + cheap
FNA, impression smear, fluid
Histopathology: Gold standard, only way to obtain grade
Only on tissue biopsy
Staging
BW / UA, chest/abd rads, US, Bone marrow, LN aspiration
Metastasis: Liver, Lungs, LN, Spleen, other internal organs
Treating: Referral is never wrong
Remove: margins are VERY important, If it’s worth taking off it’s worth knowing what it is
Chemo: poison
~20% of animals experience toxicities w/ < 5% with sign toxicity
Test Collies: p-glycoprotein mutation = high toxic risk
Burn: Nasal, brain tumors
Owner expectations need to be clear!!
discuss Tx plans, cost
Tumor Growth
Gompertzian growth kinetics
Initial: high growth fraction
Clinically detectable tumor has 109 tumor cells
1,000,000,000
Tumor growth: Growth the fraction decreases and doubling time increases
Sm tumors = faster cell division
Treatments target rapidly dividing cells
Cytoreduction
Treatments target rapidly dividing cells
SX, radiation
Min gross dx = leave microscopic dx
No gross evidence of tumor < 10^9 tumor cells
SX 1st , Radiation 2nd
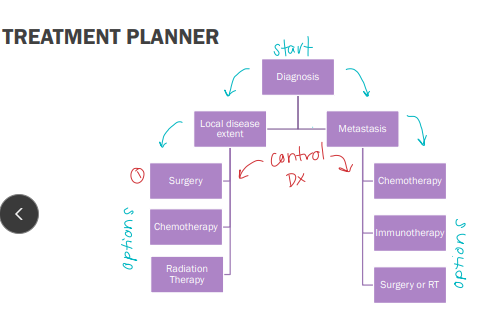
Management of different presentations of caner
Local
SX
Chemo
Radiation
Metastasis
Chemo
Immunotherepy
Sx or radiation
Surgery
Local
Excision of tumor (biopsy)
Adjuvant therapy (aid TX)
Palliation (min suffering): leg amp
Prophylaxis (prevent tumor dev) : spay/neuter
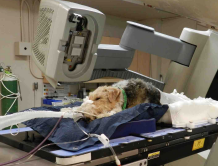
Radiation
Local
Neo-adjuvant (pre-op)
Least common- inj site sarcomas
Adjuvant (post-op)
Most common
Sole treatment
Lymphoma, not accessible, brain, nose, Palliation: bone tumors
Chemotherapy
Goal: Max survival w/ good QOL
Palliation > cure
Remission, delay metastasis, control local dx
NOT a primary tx or Sx substitute!!!
Indications: Systemic responsive cancer, metastatic cancer, adjuvant, radiation sensitization, palliation
Contradictions: organ disfunction, resistance
Resistance: p-glycoprotein MDR increases clearance/resistance
collies have high risk of toxicity - test before Tx
“white feet don’t treat”
MOA: rapidly dividing cells
Efficacy = dose x time
Side effects BAG: Bone marrow, Alopecia(rare), GI
How to dose Chemotherapy
Dose based on body surface area (BSA) in m2
m2 = (K x kg(2/3))/100
Metronomic Chemotherapy
Continual, low dose
Oral drugs: compounded
Target: angiogenesis
Incompletely resected soft tissue sarcoma, hemangiosarcoma
Toxicities: less severe
Monitoring response to chemotherapy
Repeat exams every other tx and compare tumor size
6-8 weeks
Complete Resp: gone, LNs <10mm short axis
Partial Resp: ≥30% reduction in size
Stable Dz: <30% reduction(pr) in size
Progressive Dz: >20% increase in size, 1 or more new lesion, change Tx
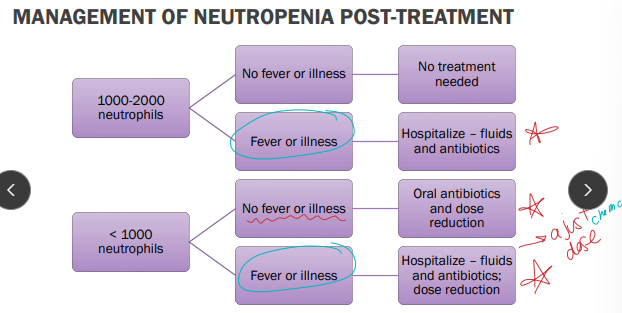
Myelosuppression with chemo
Bone marrow suppression"
Neutrophils
Normal: 3000-12,000, life span < 24hrs
Low Grade: 1 = 1500, 2 = 1000, 3 = 500-1000 (septic risk increases), 4 = < 500 cells/uL
Delay Chemo Tx: < 2000
Neutropenia alone = no CS, w/ fever is an emergency
Risk of sepsis increases as neutrophil count decreases
No neutrophils: no fever
Platelets
Normal:100,000-350,000, life span 7d
Delay Chemo Tx: < 50, 000
Anemia is rare and non-life-threatening w/ chemo
GIT problems with chemotherapy
CS: Vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia
MOA:
Direct epithelial cells damage
3-5 days to move from crypts to villi
CRTZ Stim (rare)
TX: Imodium, metronidazole, Cerenia, Zofran, Reglan
Chemotherapy drugs
Alkylating agents: carboplatin, Chlorambucil, Cyclophosphamide, lomustine, Cisplatin
Cyclophosphamide: sterile hemorrhagic cystitis
lomustine: hepatotoxicity, significant myelosuppression
Cisplatin: Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, fatal feline pulmonary edema
Give with fluids!!!
Antimetabolites: cytarabine, gemcitabine, rabafosaside, 5-FU
Rabacfosadine: skin or pulmonary fibrosis
5-FU: fatal feline neurotoxicity
Anti-tumor antibiotics: Doxorubicin, mitoxantrone
Doxorubicin: cumulative cardiotoxicity, feline nephrotoxicity, severe vesicant, anaphylaxis
Plant alkaloids: Vincristine, vinblastine, vinorelbine
Vincristine: neurotoxicity, vesicant
Hormones: Prednisone/prednisolone
Enzymes: L-asparaginase
NSAIDs: piroxicam, carprofen, deracoxib
Small molecule inhibitors: Toceranib

Canine lymphoma signalment
Common: 2nd only to skin tumors in dogs
Multi-centric most common in dogs
MOA: Unknown, multifactorial
Risk: middle aged / older dogs
Low: intact females, Dachshund, Pomeranian, Toy Poodle, Chihuahua
High: older, Boxer, Basset hound, St. Bernard, Scottish Terrier, Airedale, bulldogs
ID: palpable lumps w/ ± CS, ± PU/PD

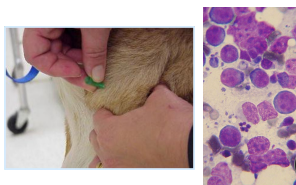
Diagnosing canine lymphoma
#1 Cytology: diagnostic
Avoid mandibular LN
cell appearance & size associated with grade
Histopathology: Morphologic type and immunophenotype (B vs. T)
Biopsy(rare): Grade, architecture, immunophenotype
PCR (PARR): Blood, LN aspirate, BM
colony evaluation (B vs. T)
Not ideal as a screening test for healthy animal
#2 Flow cytometry: live cells in solution
ID and quantify cell surface markers, size and immunotype
CD34+ : acute leukemia
Homo = neoplasia
Hetero = reactive disease
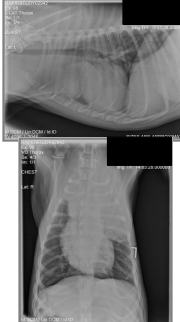
Staging diagnostics for canine lymphoma
CBC: Anemia, Thrombocytopenia
Bld Chem: Hypercalcemia (#1), Hypoalbuminemia
UA: UTI, Kidney function
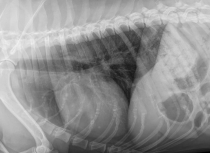
Rads: 2 view Thoracic mediastinal mass, Pleural effusion, heart dx, Abdominal: Organomegaly, Lymphadenomegaly
US: Diffuse change of involved organs (“Swiss cheese”), LN sizes, ± Echo: doxorubicin
BM sample: Even if CBC normal, determine if stage V dx, blood cell reserves
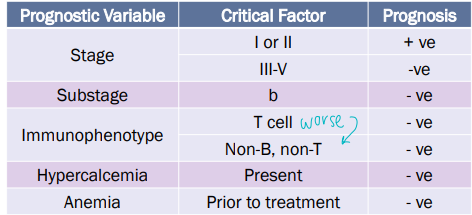
Stages of lymphoma
Stage I: One LN
Stage II: regional lymphadenopathy, multi LN
one side of diaphragm
Stage III: generalized lymphadenopathy, multi LN
both sides of diaphragm
Stage IV: Liver or spleen involvement
Stage V: non-lymphoid tissue involvement
BM, Blood, Renal, Eyes, Skin, CNS, GIT
Substage
a = asymptomatic
b = symptomatic
Treating canine lymphoma
90% systemic Dz at diagnosis
Radiation: CNS, Mediastinum
Most patients don’t get: only for local Dz
SX: Splenic tumors, GI involvement
Chemo: #1!!!
Multi agent: CHOP(gold standard), 90% remission rate - MST 8-12m
cyclophosphamide (@ w 2), doxorubicin (@ w 4), vincristine (@ w 1, 3), prednisone (@ w 1, 2, 3, 4)
Repeat 5-week cycle four times
Single agent: Doxorubicin (#1) B-cell, 85% remission, shorter and cheaper - MST: 6-8m
Lomustine: T-cell
Steroids: Prednisone
50% response rate
DO NOT give without diagnosis or if owner wishes to pursue chemo!
No tx: Dead within 6-8 weeks
pred is cheap, atleast try that
Feline lymphoma cases
Breed: Manx, Burmese, Siamese
Predisposition: FeLV, tobacco exposure increases risk
FeLV +: Young cats(3-5y) w/ Mediastinal lymphoma or Peripheral nodal lymphoma
FeLV - : Older cats(11-13y), Nasal, alimentary
CS: lethargy, weight loss, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, LN enlargement, Icterus, Cough, Muffled heart and lungs, Nasal discharge, Facial deformity
ID: Cytology, biopsy(often required), FeLV/FIV testing, xrays/US
staging based on location
Histo: LG cell vs. SM cell
Imaging

GIT feline lymphoma
MOA: Most common GI tract tumor in cats
Sm intestine > Lg intestine
PE: Poor body condition, abdominal discomfort, thickened intestinal loops, palpable abdominal mass, icterus, dyspnea/tachypnea
ID: FNA, biopsy
TX: Chemo, Vit B12, Anti-emetics, anti-diarrheals, appetite stimulants
Sm cell chemo: Chlorambucil & pred
good prognosis, 3m resolution
Lg cell chemo: CHOP, Doxorubicin & pred, Lomustine, Pred
guarded to poor prognosis

Nasal feline lymphoma
PE: nasal discharge, stertorous breathing, facial deformity
ID: Coagulation profile, CT, Rhinoscopy for biopsy for histopathology
TX: radiation, CHOP chemo(not the best)
good prognosis

Medistinal feline lymphoma
Risk: young cat (2-4y) w/ FeLV
PE: Muffled heart and lung sounds, decreased compressibility of cranial chest, Horner syndrome
ID: thoratic rads, US guided FNA for cytology, Pleural fluid evaluation
Lg lymphocytes
DDX: mediastinal mass, thymoma
Sm lymphocytes or chylous-like effusion
TX: Chemo (CHOP, Doxorubicin & pred), Radiation (High-risk anesthesia patient) repeat thoracocentesis
Prognosis: FeLV+ = poor, FeLV- : 90% response rate
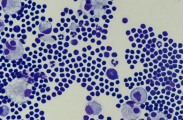
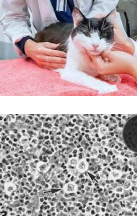
Peripheral nodal feline lymphoma
ID: single/regional LN enlargement, Cytology, Biopsy
Single LN = Hodgkin’s-like lymphoma
TX:
Chemo: CHOP, Doxorubicin & pred, Pred
Hodgkin’s-like lymphoma: Sx resection, radiation
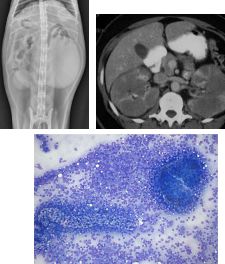
Renal feline lymphoma
CS: Acute renal failure, renomegaly, Abdominal discomfort, Kidney pain
ID: rads, US guided FNA
TX: CHOP, cytarabine (crosses BBB), Lomustine
Not doxorubicin = nephrotoxicity
Poor prognosis
Lymphoproliferative Leukemia cases
Lymphocytes
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): sm cell
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): lg cell
MOA: FeLV, acute = young, old = chronic
CS: Non-specific, ADR
CLL: slowly progressive, no CS, High WBC and lymphocyte counts: most common
no organomegaly or lymphadenomegaly
can dev into ALL
ALL: Weight loss, anorexia, PU/PD, ADR, Hemorrhages, lymphadenomegaly, organomegaly, Blast cells in circulation
ID: #1 Send blood to path, #2 Flow cytometry
TX: <60,000 lymphocytes
CLL: none yet(Check BW), Initial: CHOP, chlorambucil, maintenance: pred
ALL: multi agent, poor prognosis
hard to tx
Skin tumors
Dogs: Most common tumors
Lipoma, mast cell (MCT), Histiocytoma, perianal adenoma (B)
Cats: 2nd most common, likely malignant
Basal cell (M), mast cell, SCC (M), FSA
MOA: Most are primary
Skin is rarely a site of metastasis
ID: map location + needle stick: FNA
TX: Sx (#1), Chemo(for some), RT for re-excision or incomplete RT
No sx for Histiocytoma (Button Tumor): benign
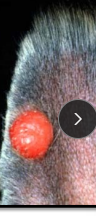
Histiocytoma (Button Tumor)
MOA: Benign tumor of Langerhans cells
CS: Raised, hairless, white/pink/red nodules in young dogs, solitary
ID: cytology
TX: Spontaneously regress in 2-4m, exception to sx rule
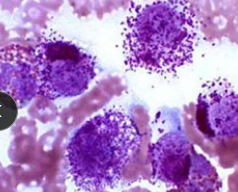
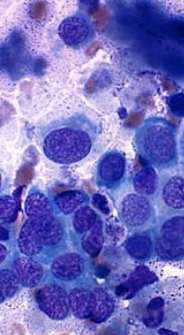
Canine mast cell tumor
MOA: mid aged dogs, waxing and waning history
Boxer, Lab, Boston, Pug, Beagle, Weimaraner
Kinases Kit dysfunction
Sm molecule inhibitors
CS: mass, vomiting, anorexia, weight loss, organomegaly, GI ulcers, Darier’s sign (Erythema and wheal formation), edema, bruising, bleeding, purities
ID: cytology for diagnosis, histo for grade
Round cells, Purple granules, Eosinophils: often present as well
Staging: Local draining LN, rads, US, BM aspirate
Graded using patnik or kiupel system
Good prognosis: MI < 5
Poor prognosis: MI > 5, c-kit mutation
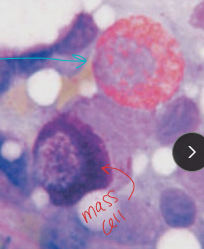
Patnaik grading system
Grade I: Benign: Low grade on Kiupel scale
Well differentiated cells, no mitotic figures, multiple large granules
Grade II: Sometimes benign/malignant: Low grade on Kiupel scale
Moderately differentiated cells, few mitotic figures, some edema
Grade III: Malignant: High grade on Kiupel scale
Poorly differentiated cells, many mitotic figures, few granules SQ invasion Edema, hemorrhage, necrosis
Treating canine mast cell tumors
H1 blockers: Diphenhydramine (Benedryl®)
Mediate allergic reactions
H2 blockers: Famotidine, cimetidine, pepsid
GIT ulcers
Surgery (#1):
Margins 2 cm and 1 fascial plane deep: ink margins
Dont debulk
Stelfonta: local intratoumor tx
Non-metastatic tumors ≤ 10cm3
destroyed by 7days
Protein kinase C activator
Concomitant medications req
Radiation: local, sx is not an option
Chemo: systemic
Vinblastine and pred most effective
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors: toceranib, palladia
Inhibit Kit, VEGFR, PDGFR
Direct anti-tumor & anti-angiogenic activity
High grade, high MI, nonresectable or recurrent, before and after sx
Cons: GI toxic, neutropenia, PLE, cramps, hepatotoxicity
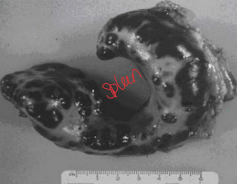
Feline mast cells
MOA: Older cats w/ Sm masses
Kinases Kit dysfunction
Sm molecule inhibitors
reactive dx
Spleen, liver, intestines, stomach
CS: weight loss, anorexia, ascites, multiple skin MCT
ID: cytology, histopathology, Circulating mast cells(blood)
TX: Sx (#1), Rare: chemo (need more than pred), remove spleen
Soft tissue sarcoma (STS)
AKA: Spindle Cell Tumor
MOA: mid/older
Arise from mesenchymal tissue: skin, SQ
Pseudoencapsulated, locally invasive, exfoliate poorly
CS: Slow growing, PNST of brachial or lumbosacral plexus (PAIN)
ID: FNA, biopsy
often ID wrong
Staging: 3-view thoracic rads: mets to lungs
TX: Sx, radiation (post sx), chemo (Doxorubicin)
can regrow, dont scoop
Prognosis: good,
poor: mets, recurrence

Feline injection site sarcoma
MOA: vaccines(adjuvanted), inflam, suture, p53 mutation, genes
4w to 10y post injection to develop
ID: FNA, Contrast CT/MRI
Granulomas appear very aggressive
TX: SX + radiation + chemo (Doxorubicin)
aggressive: 5cm margins + 2 planes deep!!
3-2-1 rule: 3m post – >2cm – 1m and still increasing
Prevention: Go as distal as possible on limb
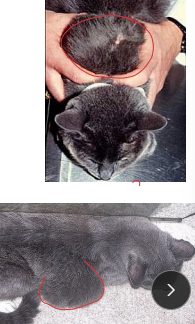

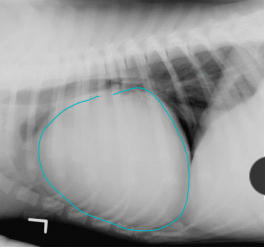
Henangiosarcoma (HSA)
MOA: middle/older dogs
Visceral (LG): GSD, goldens, labs
Spleen or right atrial, skin, liver
Cutaneous(SM): Italian Greyhound, Whippet
CS: non-specific, abdominal swelling, acute weakness, white gums, difficulty breathing, sudden death, shock, signs may wax and wane, muffled heart sounds, tachycardia w/poor pulses, Pulsus paradoxus
ID: anemia w/ schistocytes, thrombocytopenia, DIC, rads, Serosanguinous effusion, echo if metastasis/big heart/or golden, biopsy for definitive (not tru-cut)
± abdominocentesis
TX: Sx: splenectomy, chemo if visceral (doxorubicin, metronomic)
poor prognosis
can dev ventricular arrhythmias after sx
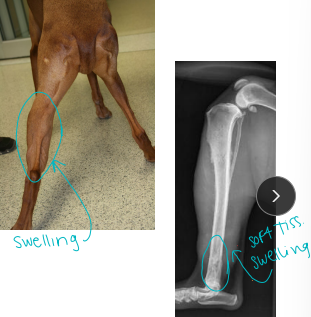
Canine osteosarcoma (OSA)
MOA: metaphysis(end), mesenchymal: osteoid present
Bi-modal age distribution: < 2y and > 5y
Lg dogs: 75% in appendicular
often away from the elbow, towards the knee
Sm dogs: 25% axal
Metastasis to lungs (diaphysis) - rarely show CS until end stage
CS: lameness, pain, dysphagia, exophthalmos, facial deformity, nasal discharge, paresis/paralysis, tenesmus
ID: #1 rads: (Codman’s triangle, don’t cross the joint), aspirate(rule out), biopsy
DDX: fungal
TX: amputation (palliative), pain meds, allograft, implants, Chemo (Doxorubicin or Carboplatin + doxorubicin), radiation (Tele or brachy): pain control, Bisphosphanates
Good prognosis: mandibular, perosteal
Poor prognosis: maxilla, ribs, scapula, spine, prox humerus, telangiectic, high ALP
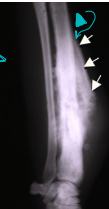
Chondrosarcoma
Second most common tumor
MOA: flat bones, slow matastocyst
Nasal most common: RT
TX: Sx, radiation (nasal)
Poor prognosis: nose
Good prognosis: ribs
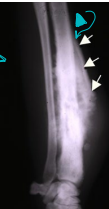
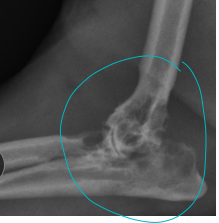
Synovial cell sarcoma
MOA: Joint lining can cross joints
Rare tumors
TX: Sx + chemo
Prognosis is good
Feline osteosarcoma
VERY rare
MOA: old, less aggressive tumor
TX: amputation alone (curative)
chemo(not recommended post amp)
No cisplatin: Fatal pulmonary edema
Bone metastisis
diaphysis
Urogenital malignancies
Oral Tumors
4th most common in dogs
Size is not predictive of metastasis!!
Types
benign: epuides (oral, single tumors)
Malignant: SCC, FSA, melanoma, sarcoma
MOA: spaniel, GSD, pointer, Weimaraner, Boxer
CS: Drooling, Halitosis, Facial swelling/mass, Weight loss, Cats w/ unkempt hair coat
ID: sedation req, radiographs, CT, fna, biopsy, Aspirate LN in all patients
Tx: SX for dogs w/ bony margins, radiation (alone for SCC, melanoma, AA), Chemo (melanoma is resistant)
Good prognosis: if rostral, Acanthomatous epulis, SCC, dogs
Poor prognosis: caudal to canines, FSA, melanoma
radiation has poor ocular prognosis
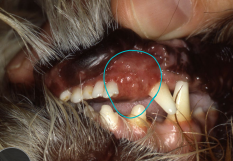
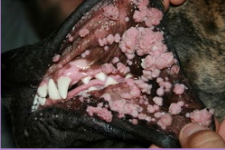
Epulides
Acanthomatous ameloblastoma
MOA: Fibromatous, ossifying, giant cell, acanthomatous
Arise from periodontal lig
benign
CS: gingival proliferation
TX: Wide SX excision (tooth + bone), radiation
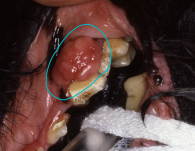
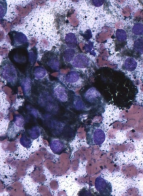
Canine Melinoma
Site, size, and stage dependent!!
MOA: most common oral tumor in dogs
malignant and aggressive
TX: Oncept vax + local control (stage II+III)
chest rads pre 1st, 4th, and booster shots
transdermal give 4x biweekly and booster @ 6m
improved survival
Poor prognosis and chemo resistant
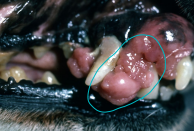
Squamous cell carcinoma
MOA: most common oral tumor in cats
malignant
Cats: VERY AGRESSIVE
flea collars, environmental tobacco smoke
Dogs: locally invasive, slow metastasis
TX: complete SX resection
Good prognosis in dogs
VERY poor prognosis in cats
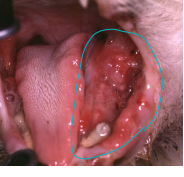
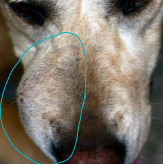
Fibrosarcoma
MOA: Histo low grade, bio high grade
LG breed, young
Goldens and Labs
locally invasive
Prognosis: Poor
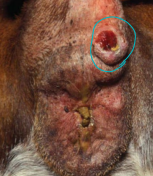
Perianal adenoma
MOA: Perianal or circumanal glands, AKA: hepatoid gland
Dev is hormone dependent
Older intact males, adrenal tumor, hyperadrenocorticism
Benign
CS: slow growing mass, straining
TX: castration
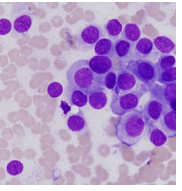
Apocrine gland of the anal sac adenocarcinoma
AGASACA: Ventral location
MOA: Old female
malignant and aggressive: sublumbar LN
CS: Paraneoplastic hypercalcemia (from PTH), straining, PU/PD
TX: Sx + chemo + Rad
good prognosis
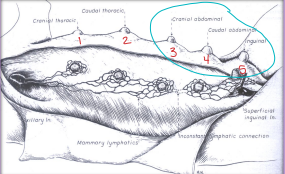
Canine Mammary tumors
MOA: older females
hormone dependent
4th to 5th glands
50% benign, 50% malignant
Types:
Malignant: carcinoma, Sacoma, Carcinosarcoma
inflam carcinoma is VERY aggressive, affect ALL glands, causes edema, firm, pain
Benign: Adenoma, Fibroadenoma, Benign mixed tumor, Duct papilloma
ID: clotting time, cytology/biopsy, CBC, Chem
TX: simplest SX/procedure, radiation(not really), spay
(once healed), chemo(maybe)For benign after surgery = no recurrence or metastasis
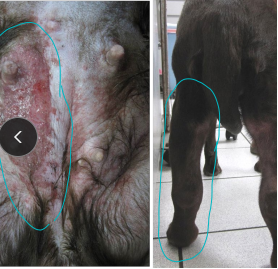
Feline Mammary Tumors
3rd most common tumor
spaying decreases risk significantly
MOA: hormone dependent
ACA most common
malignant > benign
CS: pleural effusion, ulcers
ID: clotting time, cytology, CBC, Chem
TX: Chain mastectomy, chemo add on (Doxorubicin)
poor prognosis
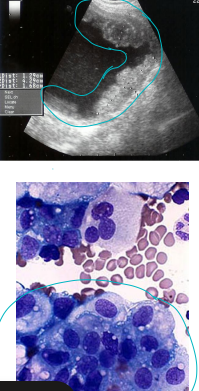
Bladder tumors
MOA: rare, TCC most common: trigone
Topical pesticides, Obesity, Female, Cyclophosphamide
Scottish Terriers, Sheltie, Beagle
CS: hematuria, pollakiuria, dysuria, lameness
ID: NO CYSTO, rads, cytology, biopsy, traumatic catheterization, BRAF assay(best test)
TX: COX inhibitor + chemo
platinum agents (DO NOT combine cisplatin and piroxicam!)
No Sx: location
feed veggies
Thyroid tumors
Dogs
carcinoma > adenoma
nonfunctional
Cats
adenoma > carcinoma
functional
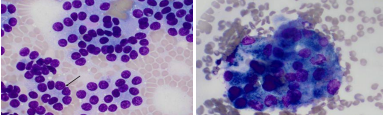
thyroid carcinomas
MOA: older dogs (10-15y)
Follicular and bilateral most common
Goldens, beagles, boxers, Siberian huskies
CS: Presence of a ventral cervical mass, voice change, horners
Mets to lungs most common
ID: Thyroid panel(no change), FNA + cytology, chest rads, US, CT, histopath
Naked nuclei in sea of cytoplasm
AVOID needle core or incisional biopsy
TX: Sx, RT(incomplete sx or non-resectable), iffy rxn to chemo
Always submit for histopathology!