Genetics - unit 4.1 - 4.3
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
List the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA
A →Adenine
C →Cytosine
T →thymine
G →guanine
Explain why DNA’s structure is called the double helix
because it has two strands of many nucleotides wrapped around each other
If the six bases on one strand of a DNA double helix are AGTCGG what are the six bases on the complementary section of the other strand?
TCAGCC
What is the main difference between a histone and a nucleosome?
Histone are the proteins that DNA wraps itself around
Nucleosomes are histones + DNA wraps
What is the difference between a nitrogenous base and a nucleotide?
Nitrogenous base is a component of the nucleotide that is found in the middle of DNA strands while the outside of the DNA is the phosphate groups
Describe the components of a DNA molecule
Made of nucleotides connected together in two strands that are wrapped around each other to form a double helix, which comprise of:
Phosphate group
Deoxyribose sugar (made of 5-carbon sugars)
Nitrogenous base (A, C, G, T)
What is the difference between nitrogenous bases that are purines and nitrogenous bases that are pyrimidines? Which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines or purines?
Purines →double-ringed structures
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines →single-ringed structures
Thymine
Cytosine
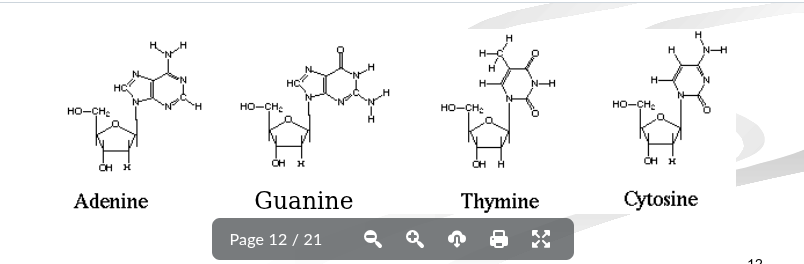
Based on the diagrams which nitrogenous bases are purines and pyrimidines
Purines:
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines:
Thymine
Cytosine
What is an organism’s genome
The complete genetic makeup of an organism (everything inside nucleus)
What is chromatin in DNA organization?
chromatin are a bunch of nucleosomes organised together to form long fibres
What are the complementary bonds of the nitrogenous bases, A, C, T, G
A →T
C → G
What are the functions of nitrogenous bases
holds information that codes for the amino acid sequences into proteins
List the following phases of the cell cycle in sequence and briefly describe what occurs in each:
M phase, S phase, G2 phase, G1 phase
G1 phase
Rapid growth for the cell
Production of proteins and organelles
Synthesis phase
Synthesis of a duplicate copy of the cell’s DNA
Key proteins associated with chromosomes (like the centromere) are produced during this phase
G2 phase
Shortest phase
Production of organelles and structures needed SPECIFICALLY for cell division
Mitosis phase
cell division occurs to produce two identical daughter cells
Why is it necessary for a cell to replicate its DNA prior to cell division?
because if it doesn’t, the daughter cells won’t be identical and just have pieces of the original DNA
What are telomeres? And in what way do telomeres protect genetic information?
Telomeres are high repetitive sequences of nucleotides in DNA strands that do not code for anything
They protect genetic material because after each cell division, a part of your genetic material gets shortened and so telomeres prevent important information from getting shortened
How many chromosomes does a human body cell contain in each of the following periods:
a) G1 phase
b) Prophase
c) just before mitosis
c) After Cytokinesis
a) 46 singular
b) 46 duplicated
c) 92 singular
d) 46 singular
Interphase is sometimes describes as a “resting phase”. Why is this description inaccurate?
Because during interphase the cell performs its daily functions and prepares for cell division
Suggest what would happen to a single-celled organism if it were to go through many rounds of mitosis but did not go through cytokinesis
A bunch of nucleuses would be in one cell with a lot of chromosomes
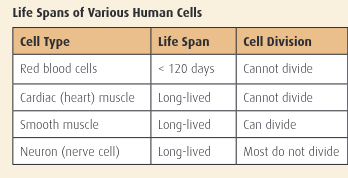
a) Which type or types of cells listed in the table would undergo mitosis? Explain.
b) Red blood cells do not contain nuclei. Explain how this fact relates to red blood cells’ inability to divide
a) some nerve cells and all smooth muscle cells
b) Red blood cells don’t have nuclei to maximize their holding of oxygen and without a nucleus there is no DNA, and without DNA u can't duplicate a cell
Draw and label the following structures:
a) an individual chromosome
b) sister chromatid
List the 4 stages of mitosis and briefly describe them
Prophase
chromatin DNA condenses to form chromosomes
Nucleus breaks down
mitotic spindle starts to form
Metaphase
Mitotic spindle is fully formed
mitotic spindle moves the chromosomes to the middle of the nucleus and lines them up along the metaphase plate
Anaphase
Mitotic spindle pulls sister chromatids apart from the centromere to opposite sides of the cell
Telophase
singular chromosomes wind back to chromatin
mitotic spindle breaks down
nucleus begins reforming
Cytokinesis (not really in mitosis but in M phase)
Happens alongside telophase
Cell membrane pinches in to create a cleavage furrow and eventually splits one cell into two identical cells
What is the metaphase plate
the imaginary middle line the chromosomes line up along in metaphase
What is the function of the mitotic spindle
to move the chromosomes around the cell (align them then separate the sister chromatids)
Human nerve cells rarely undergo mitosis. On the basis of this info, why do u think complete recovery from a nervous system injury is rare.
Because when an injury happens, cells can’t duplicate themselves to repair the damage
What is the difference between cytokinesis in a plant and cytokinesis in animals/humans
Animals:
Pinches through middle easily to create a cleavage furrow and then leads to creating two identical daughter cells
Plants:
Plant cells have rigid walls, so a specialized structure called a cell plate forms in the middle and separates the two daughter cells and eventually forms the edges of the walls for each daughter cell and separates them
What is apoptosis in cells
self destruction
When a cell gets too old, it no longer goes through the cell cycle and undergoes cell death : apoptosis
Identify the processes of meiosis and order them (includes interphase)
1. Homologous chromosomes line up in the center of the cell
2. Spindle fibers pull homologous pairs to the ends of the cell
3. 4 haploid (N) daughter cells form
4. Cells undergo a round of DNA replication
5. Sister chromatids separate from each other
6. 2 haploid (N) daughter cells form
7. Spindle fibres attach to the homologous chromosome pairs
8. Individual chromatids move to each end of the cell
9. crossing-over (if any) occurs
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase II / Cytokinesis
Interphase
Anaphase II
Telophase I / Cytokinesis
Prophase I
Anaphase II
Prophase I
Compare the number and types of cells that result from meiosis vs mitosis
Meiosis
Results in 4 gametes
Mitosis
Results in 2 somatic cells
How do the genetic contents of the cells resulting from mitosis and meiosis differ?
Mitosis
Diploid
Identical
Meiosis
Haploid
Genetically different
Comparing and contrasting: Describe a similarity and a difference between meiosis I and meiosis II
Similarity:
Both result in genetically different daughter cells
Differences:
Sister chromatids are still attaches in meiosis I while not in meiosis II
Meiosis I produces 2 daughter cells while meiosis II produces 4 daughter cells
If a diploid cell containing 28 chromosomes undergoes meiosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter have
2n = 28
n = 14
Each daughter will have 14 chromosomes
How are mitosis and meiosis similar and different?
Similar:
Both produce daughter cells
Involves same steps of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
DNA copied in synthesis
Differences:
Mitosis produces 2 identical daughter cells (2 somatic cells)
Meiosis produces 4 genetically different daughter cells ( 4 gametes)
Read each statement, and then on the line write down the phase of mitosis or meiosis that the action occurs. IF the action occurs in both, write both
1. Homologous chromosome line up in the center of the cell
2. The individual chromosomes move apart
3. Spindle fibres pull homologous pairs to ends of the cell
4. 4 haploid (n) daughter cells form
5. cells undergo a round of DNA replication
6. The chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell
7. Chromosomes become visible
8. Sister chromatids separate from each other
9. 2 haploid (n) daughter cells form
10. Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes
11. Nuclear envelope re-forms
12. Spindle fibers attach to the homologous chromosomes pairs
13. Individual chromatids move to each end of the cell
14. The nucleus disappears and the nuclear envelope breaks down
15. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber
16. crossing over (if any) occurs
Metaphase I
Anaphase, anaphase II
Anaphase I
Telophase II / Cytokinesis
Interphase
Metaphase, Metaphase II
Prophase, Prophase I
Anaphase, Anaphase II
Telophase I / Cytokinesis
Anaphase, Anaphase II
Telophase, Telophase I + II
Metaphase I
Anaphase, Anaphase II
Prophase, Prophase I + II
Metaphase, Metaphase II
Prophase I

Anaphase I
Anaphase II
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Metaphase II
Telophase I / Cytokinesis
After telophase I and cytokinesis
After telophase II and cytokinesis
During which phase of the meiotic cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
a. interphase
b. prophase
c. metaphase
d. anaphase
e. telophase
a.
When does crossover take place in meiosis
a. interphase
b. prophase
c. metaphase
d. anaphase
e. telophase
b.
During which phase of meiosis does the nuclear membrane reform around chromosomes?
a. interphase
b. prophase I
c. metaphase II
d. anaphase I
e. telophase II
e.
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is
a. a somatic cell of a male
b. a zygote
c. a somatic cell of a female
d. a sperm cell
e. an ovum
d.
Homologous chromosomes move towards opoosite poles of a dividing cell during…
a. mitosis
b. meiosis I
c. meiosis II
d. fertilization
e. binary fission
b.
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that…
a. homologous chromosomes synapse
b. DNA replicates before the division
c. The daughter cells are diploid
d. sister chromatids separate during anaphase
e. the chromosomes number is reduced
d.
Metaphase of meiosis I and meiosis II differ in that…
a. chromosomes line up at the equator
b. homologous line up in meiosis I and duplicated chromosomes line up in meiosis II
c. Sister chromatids line up in meiosis I and chromosomes line up in meiosis II
d. there are the same number of chromosomes
b.
Asexually reproducing organisms produce offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parents. What type of cell division are the offspring a product off?
a. mitosis
b. meiosis
c. binary fission
d. fertilization
a.
At which stage of meiosis do chromatids seperate and become daughter chromosomes?
a. metaphase I
b. anaphase I
c. metaphase II
d. anaphase II
e. telophase II
d.
The process in which haploid gametes are formed in diploid organisms is called:
a. cytokinesis
b. interphase
c. meiosis
d. mitosis
e. nuclear division
c.
Which of the following correctly ranks nucleic acid structures in order of size, from smallest to largest
a. Chromosome, nucleotide, gene, codon
b. nucleotide, codon, gene, chromosome
c. chromosome, gene, codon, nucleotide
d. codon, nucleotide, chromosome, gene
b.
A human cell containing 44 autosomes and two x chromosomes is
a. a somatic cell of a male
b. a zygote
c. a somatic cell of a female
d. a sperm cell
e. an ovum
c.
Independent assortment is one of the factors that contributes to genetic diversity. Independent assortment is associated with which stage of meiosis
a. anaphase I
b. prophase I
c. metaphase I
d. anaphase II
e. metaphase II
c.
The fertilized egg (zygote) of a human contains how many chromosomes?
a. 1
b. 22
c. 46
d. 23
e. 48
c.
Which cells of the human body are made through the process of meiosis
a. gametes
b. somatic cells
c. all cells of the body
d. X and Y chromosomes
e. autosomes
a.
A _______________ is the complete set of chromosomes of an organism, arranged, and displayed in pairs and ordered by size (select Best answer)
a. genome
b. karyotype
c. nucleus
d. heredity
e. gene
b.
Which 2 cells would be more genetically similar to each other?
a. two gametes produced by the same person
b. two somatic cells produced by the same person
c. two eggs produced by the same woman
d. two sperm produced by the same man
b.
If a diploid organisms has a genome consisting of 22 chromosomes, its gametes will have ____ chromosomes
a. 44
b. 11
c. 22
d. 88
e. 19
b.
When does DNA replication occur during meiosis
a. interphase I
b. prophase I
c. interphase II
d. prophase II
e. interphase I and II
a.
go to diagram in last pages of meiosis package and practice that
What is chiasma
the region of crossing over and connection and exchange of the homologous pairs chromosomes
What is a chromosomal mutation? What are the different types?
When there is the correct number of chromosomes but changes in the gene sequences
Inversion
Duplication
Deletion
Translocation
What is a karyotype?
display of all the condensed chromosomes arranged in pairs
a) what is chorionic villus sampling (CVS)?
b) what are the benefits of prenatal genetic testing using CVS?
c) what are some risks associated with this procedure?
a) Taking tissue from the chorionic villi tissues in the area surrounding the fetus and having it tested
b) finding out if your baby has any genetic disorders ahead of time
c) Maternal bleeding, miscarriage, premature birth
What is prader-willi syndrome? What are some characteristics of prader-willi syndrome?
Prader-willi syndrome happens when there is a deletion in chromosome 15
characteristics include:
reduced muscle tone
obesity
short stature
reduced hormone production
extreme flexibility
developmental delays
learning disabilities
Give an example of a genetic condition that can result from errors in meiosis
down syndrome
patau syndrome
Edwards syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome
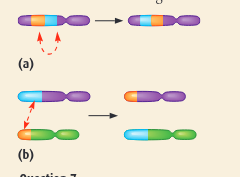
what do the following show
a) inversion
b) translocation
What is the karyotype of an individual with Klinefelter syndrome?
has XXY
Suppose an animal has a diploid number of 6 chromosomes (2n = 6). If a trisomy were to occur in one of the animals gametes, how many chromosomes would that gamete contain?
4
Suppose an individual has the karyotype XXX. Explain what might have occurred in their parent’s gamete that resultured in this karyotype
meiosis during egg cell of mom went through nondisjunction, meaning one of the chromosomes did not separate during anaphase 1 or 2
Explain why individuals might have problems from inversion
because when a chromosome does inversion and then does crossover with another chromosome, it can cause a gene to be duplicated or deleted (draw it out)
draw out non-disjunction for anaphase I and anaphase II in cells during meiosis
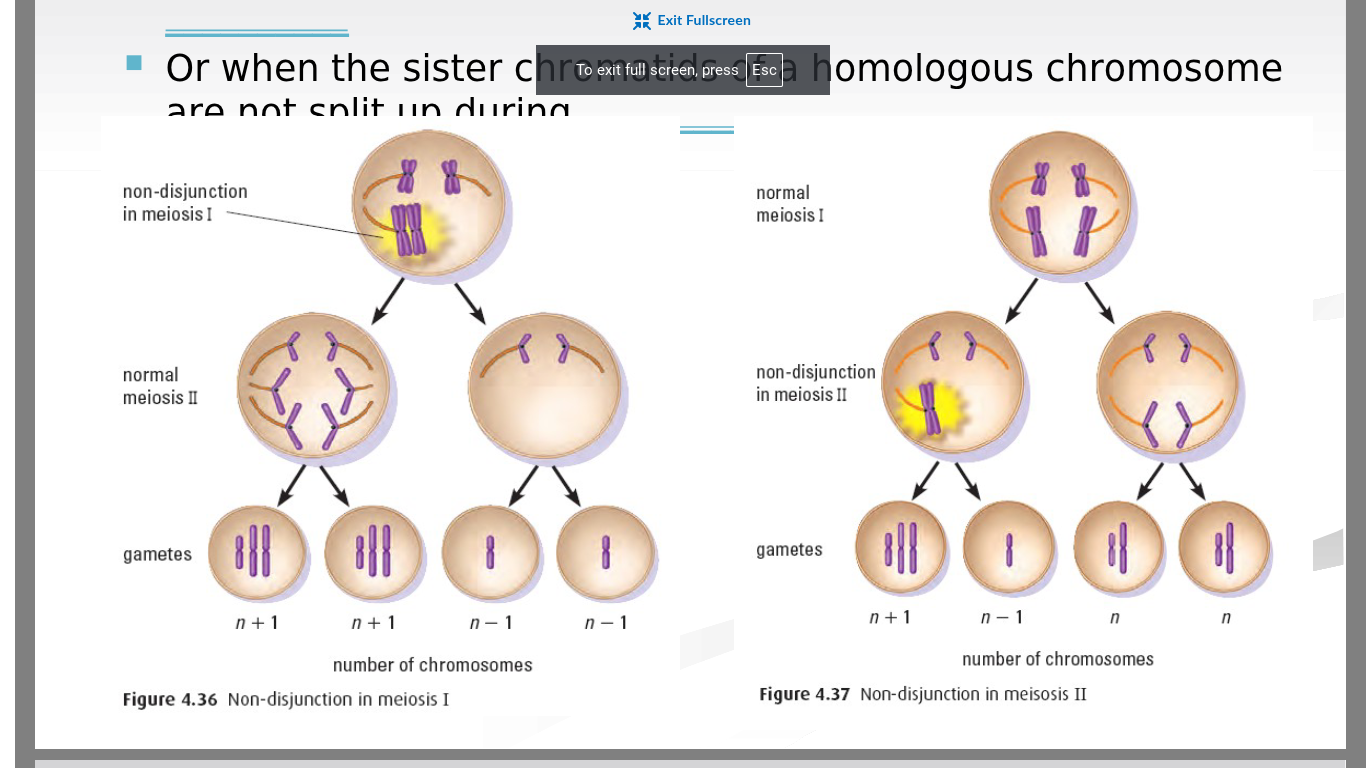
what causes down syndrome and what are the characteristics?
trisomy 21
characteristic facial features
below average height and poor muscle tone
mild to moderate intellectual disability
what causes patau syndrome and what are some characteristics
trisomy 13
severe intellectual disability
heart defects
poorly developed eyes
cleft lip
extra fingers/toes
weak muscle tone
brain or spinal cord abnormalities
what causes Edwards syndrome and what are some syndromes
trisomy 18
severe intellectual disability
low birth weight
small and abnormally shaped head
small jaw and mouth
clenched fists
what causes klinefelter syndrome and what are some characteristics
xxy
small testes do not produce enough testosterone
can fix with injection testoerone
when puberty hits they get boobs
infertile
reduced facial and body hair
What causes translocation down syndrome
translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21
what causes cri du chat syndrome and what are some characteristics
deletion of portion of chromosome 5
abnormal larynx and epiglottis that produces a distinct sounding cry
poor muscle tone
small head with distinct facial features
moderate intellectual disability
what causes prader-willi syndrome and what are some symptoms
deletion of chromosome 15
developmental delays
learning disability
obesity
short
decreased muscle tone
reduced hormone production
very flexible
what causes fragile x syndrome and what are some characteristics
usually there’s 55 CGG sequences in one of the genes but here there’s 200 CGG
range of learning disorders
behavioural challenges
speech and language problems
distinctive facial features
large ears
long fae
prominent jaw
What are the 4 different genetic testing Post birth
karyotype analysis
carrier testing
presymptomatic testing
diagnostic genetic testing
what is carrier testing
when u screen fror specific gene sequences
can determine if an individual carries a copy of a mutation that his or her children could inherit
what is presymptomatic testing
done if u have family history of a genetic condition
u get tested for a condition that could later develop in life
what is diagnostic genetic testing
used to confirm diagnosis when symptoms are showing of a genetic condition
what are the two pre-natal genetic screenings
amniocentesis
chorionic villus sampling
what is amniocentesis
when a needle gets sticked in a mom’s uterus and extracts the fluid that surrounds the fetus and the fluid has cells from the baby that can be tested to see if they have genetic disorder
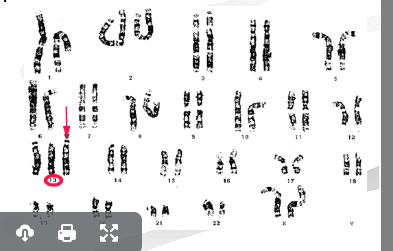
what genetic disorder is this
patau syndrome
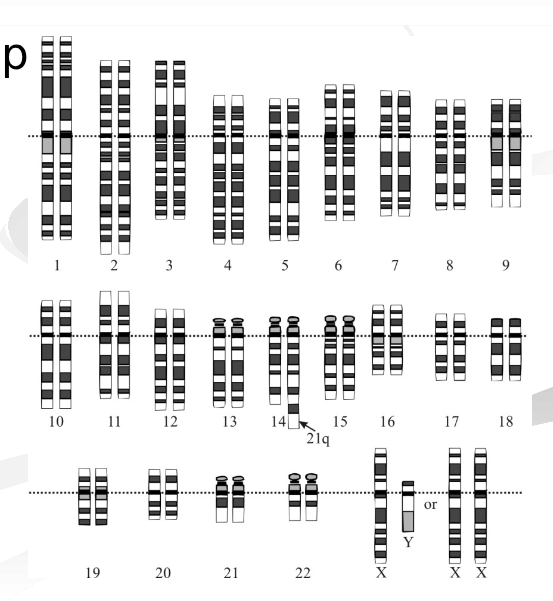
what genetic disorder is this
translocation down syndrom
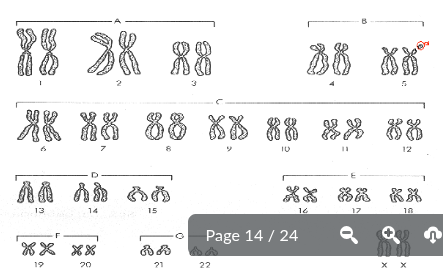
what genetic disorder is this
cri du chat
some of 15 dleeted