AICE Computer Science Unit 7
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Databases & Flowcharts/Pseudocode
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Database
An organized collection of data that is electronically stored and accessible through a database management system (DBMS)
Issues with File Based Approach
Data integrity Issues - incorrect or incomplete data
Data privacy issues - All departments must access whole files or folders
Redundancy - Same data stored more than once
Data dependency - Location of files. File systems can be difficult to navigate if your do not know the storage structure
Relational Database
Data is stored in a relation, or a special type of table. Each column has a label and contains attributes. Each Row (tuple) contains information pertaining to one instance of the table
Referential Integrity
Prevents data from being entered when no reference is found in other tables
Catches errors for data that does not match referencing values
Ensures data integrity in DBMS
DBA
Database Admin uses the DBMS developer interface to create tables, define keys and attributes and search and collect data points for use by the company.
The DBA has access to the query processor, which uses a Structured Query Language (SQL) to create a Query
Query
A selection of data that has defined conditions.
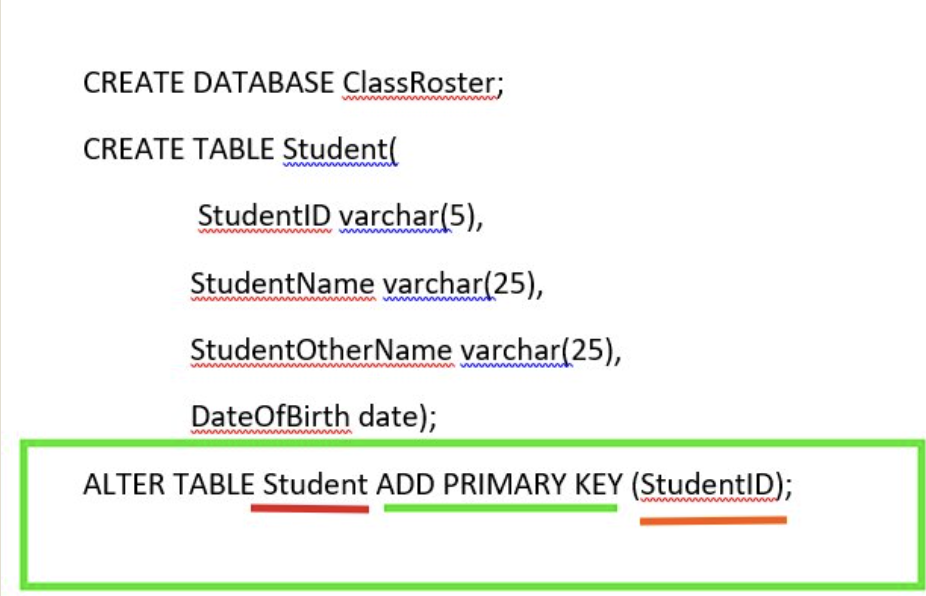
SQL DDL (Data Definition Language)
SQL DML (Data Manipulation Language) 1

SQL DML (Data Manipulation Language) 2

SQL DML (Data Manipulation Language) 3

1nf
Must have a primary key
every value for an attribute must have atomicity (one value only)
2nf
Fulfil the requirements of first normal form
Each non-key attribute must be functionally dependent on the primary key
3nf
Every attribute that is not the primary key must depend on the primary key and the primary key only.
Involves further breakdown of attributes into their own table. No repeating attributes besides PK.