Lecture 12 - Development of B Lymphocytes
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
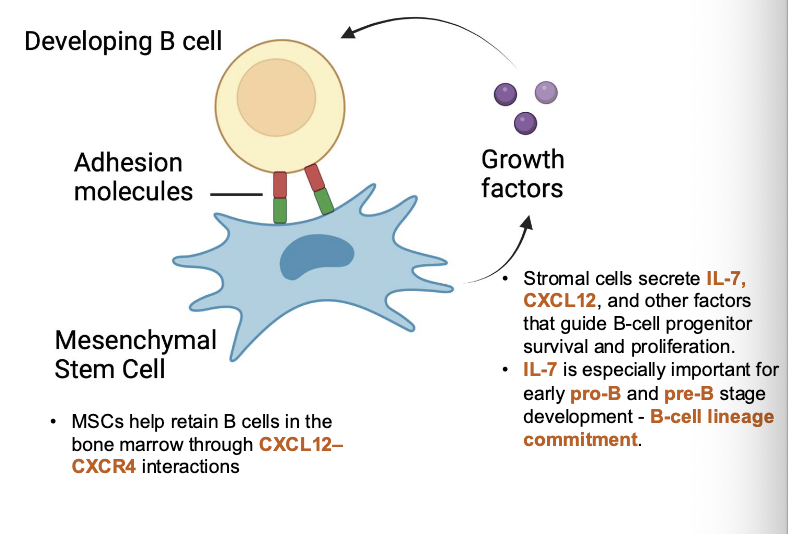
the goal of B cell development phase 1
generate a diverse BCR through V(D)J recombination
the goal of B cell development phase 2
edit or eliminate self-reactive immature B cells (central tolerance)
the goal of B cell development phase 3
activate antigen-specific B cells in secondary lymphoid tissues to differentiate into plasma and memory cells (peripheral activation)
what is involved in phase 1 of B cell development
B-cell precursor rearranges its immunoglobulin genes
what is involved in phase 2 of B cell development
immature B cell bound to self cell-surface antigen is removed from the repertoire by receptor editing or apoptosis
what is involved in phase 3 of B cell development
mature B cell bound to foreign antigen is activated
activated B cells give rise to plasma cells and memory cells
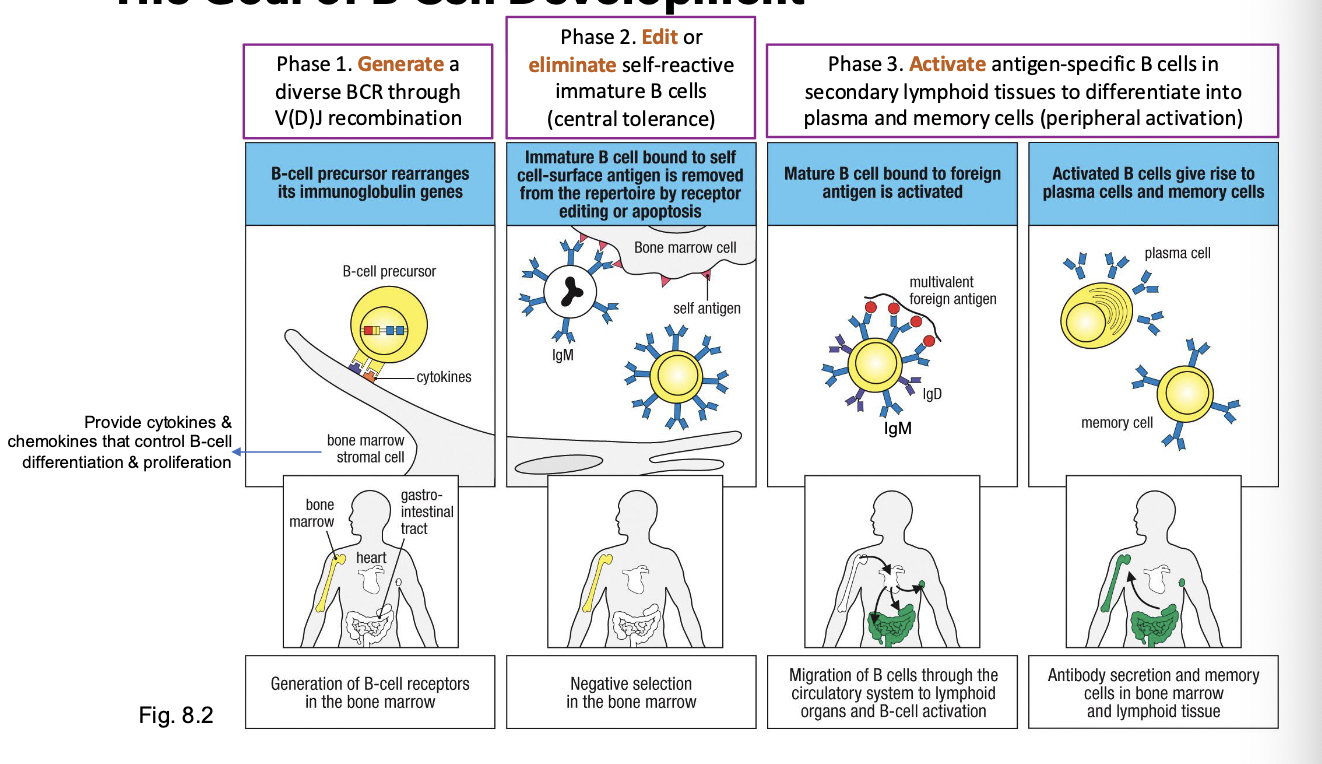
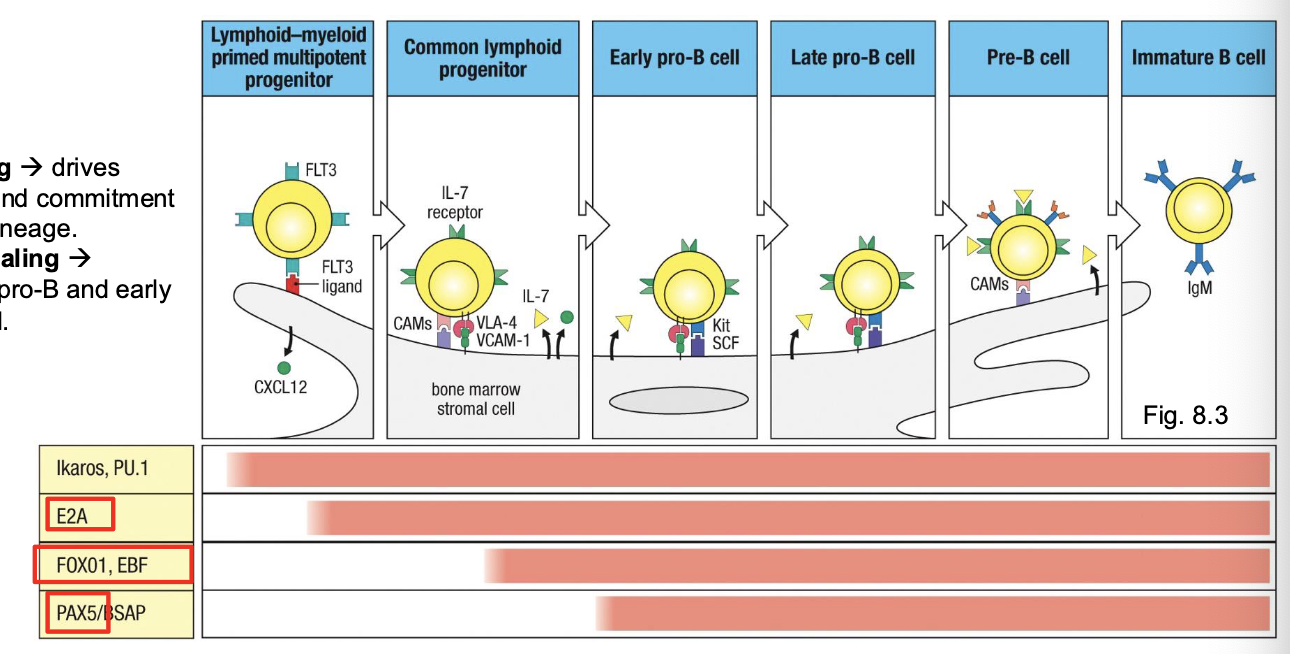
what supports early B-cell survival and differentiation
bone marrow and stromal cells
what do stromal cells secrete and what do they do
stromal cells secrete IL-7, CXCL12, and other factors that guide B-cell progenitor survival and proliferatoin
what is IL-7 especially important for
early pro-B and pre-B stage development - B cell lineage commitment
what do mesenchymal cells do
help retain B cells in the bone marrow through CXCL12-CXCR4 interactions
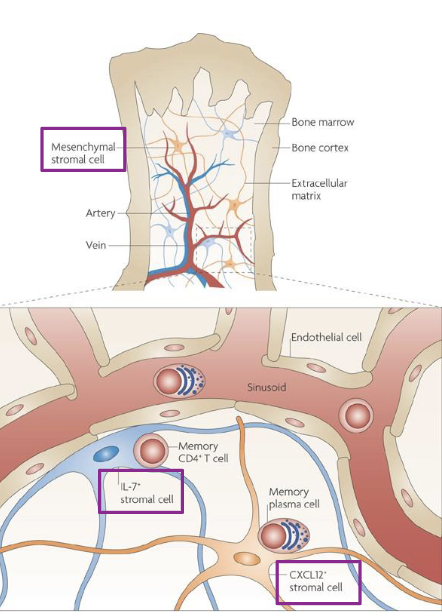
early B cell development requires signals from what
bone marrow stromal cells
in the earliest stages (up to pre-B cell), developing B cells are physically attached to stromal cells through ______
adhesion molecules (VLA-4/VCAM-1)
stromal cells provide survival and differentiation signals through _____
IL-7 and stem cell factor (SCF)
once the pre-BCR forms, what happens
B cells detach from stromal cells and progress toward independence
IL-7 signaling
drives proliferation and commitment to the B-cell lineage
Kit-SCF signaling
supports pre-pro-B and early pro-B survival
transcription factors do what
control lineage commitment, stage progression, and gene rearrangement
E2A and EBF → upregulate Rag1/2 → enable V(D)J
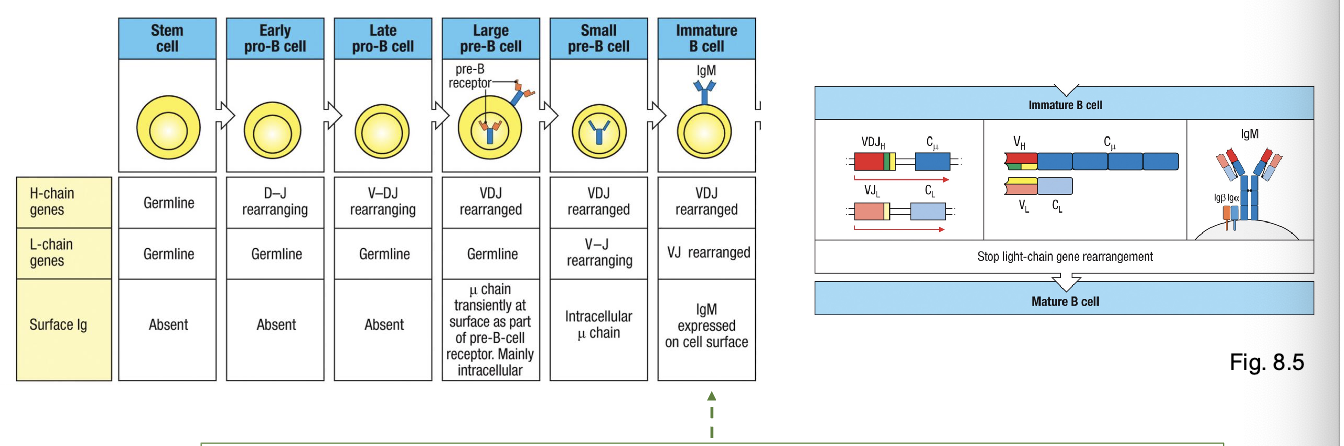
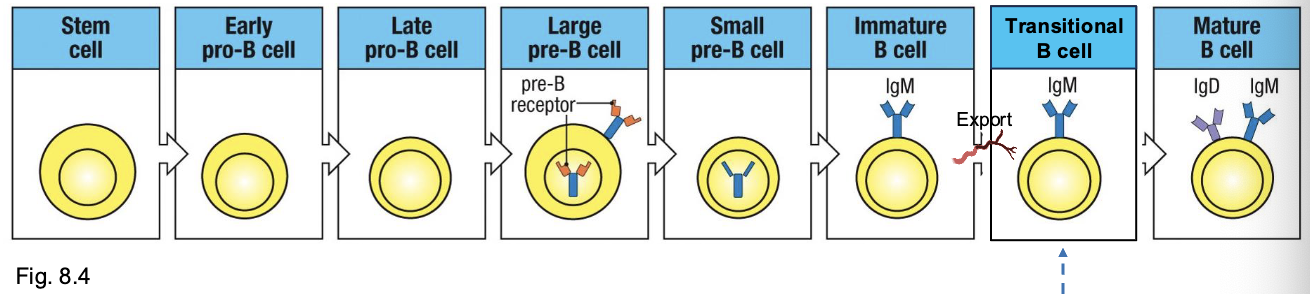
stages in B-cell development
checkpoint #1
at large pre-B cell stage
tests in H chain can pair with the surrogate L chain to form a pre-BCR
pass→ proliferate and rearrange L chain
fail → apoptosis
checkpoint #2
at immature B cell stage
negative selection 1 - central tolerance
expresses IgM on surface
Tested for self-reactivity against self-antigens
checkpoint #3
negative selection 2
peripheral tolerance
begin co-expressing IgM and IgD and they mature
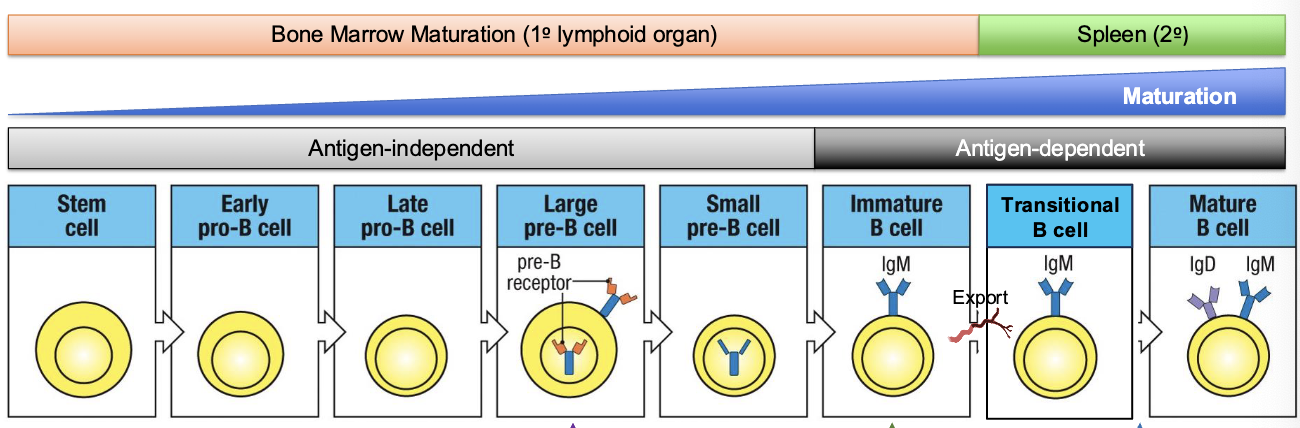
where does antigen-independent B cell development occur
a) thymus
b) spleen
c) bone marrow
d) lymph node
c) bone marrow
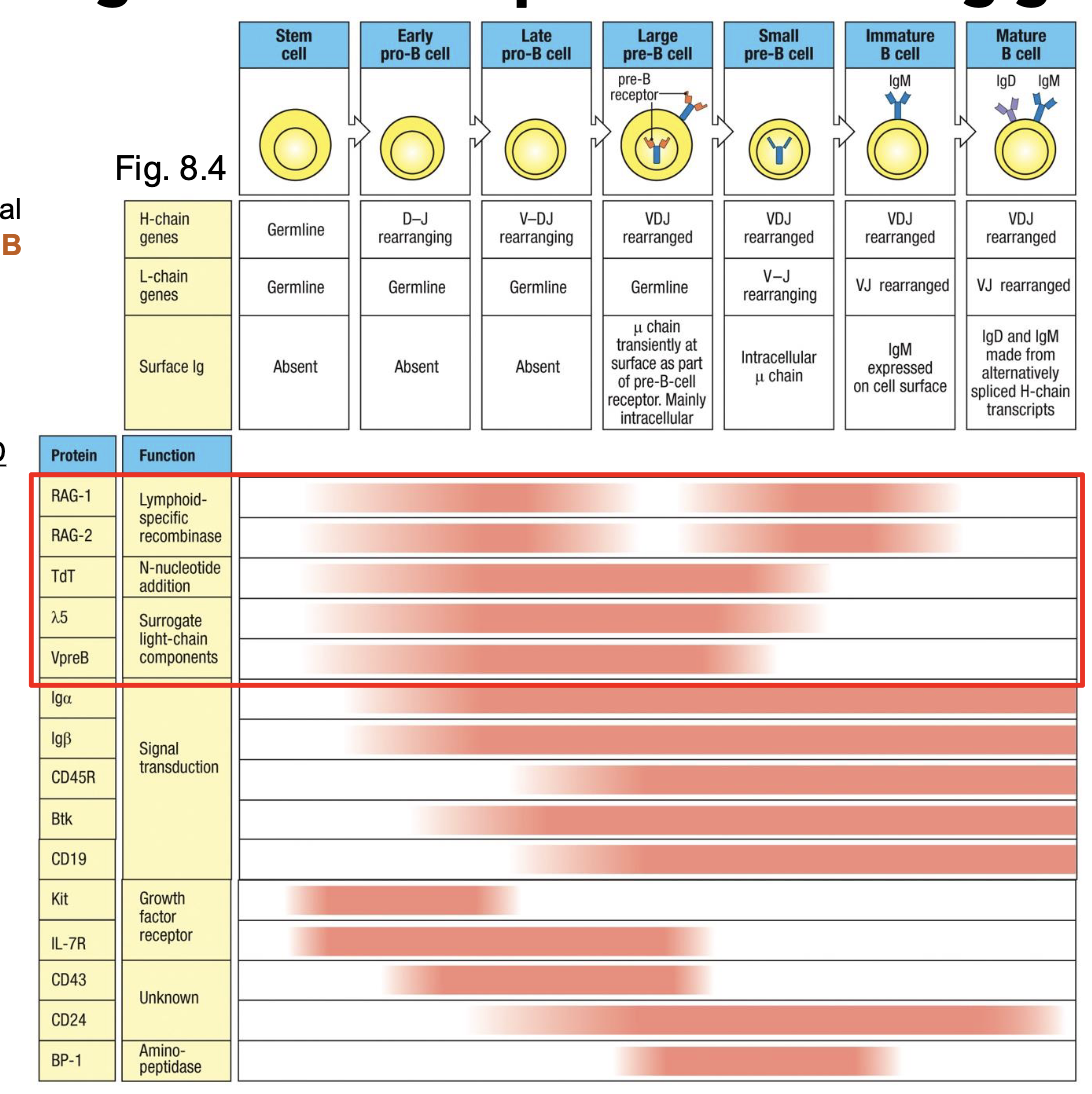
development of a B-lineage cell proceeds through several stages marked by what
rearrangement and expression of the Ig genes
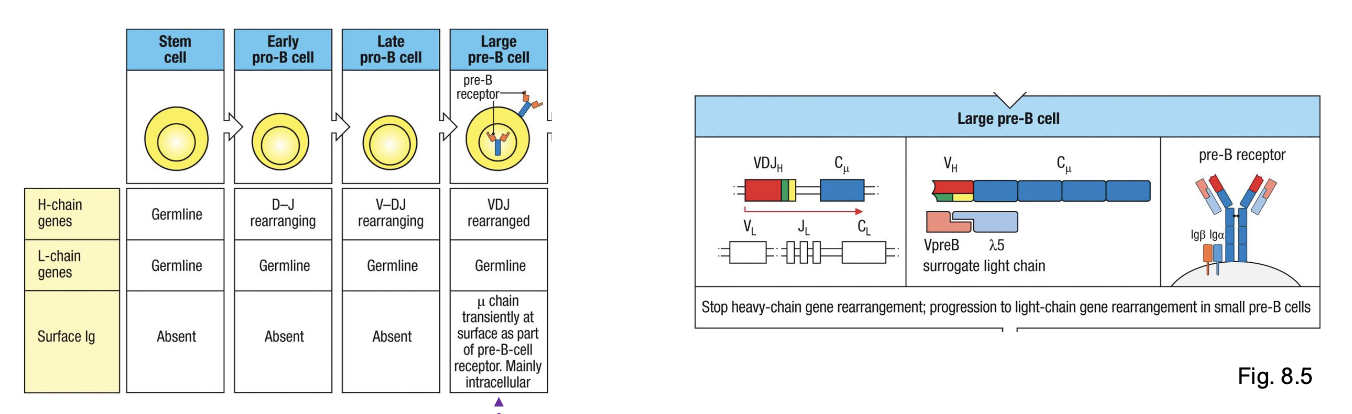
early pro-B cell
starts D→ J rearrangement on H chain
late pro-B cell:
adds V→ DJ rearrangement (completes H chain)
large pre-B cell:
expresses a functional u H chain with surrogate L chain (VpreB +λ5) → forms pre-BCR
small pre-B cell
starts rearranging L chain (V→ J)
immature B cell
expresses IgM on surface
mature B cell
co-expresses IgM + IgD through alternative splicing
checkpoint 1:
Pre-BCR test (H chain works)
checkpoint 2
L chain works, IgM on surface → test for self-reactivity
checkpoint 3
IgM + IgD expression → mature and leave bone marrow
Ig L and H chains undergo recombination at distinct phases of B cell development
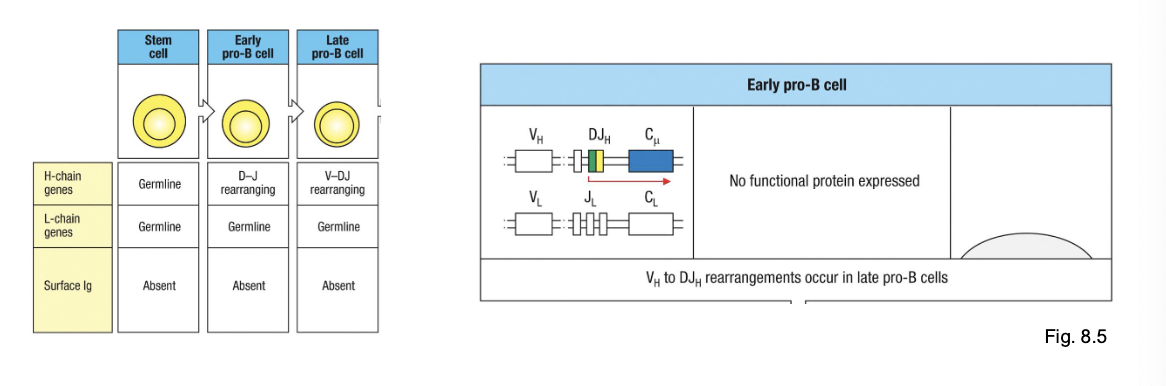
generation of a diverse BCR begins with the rearrangement of the H chain
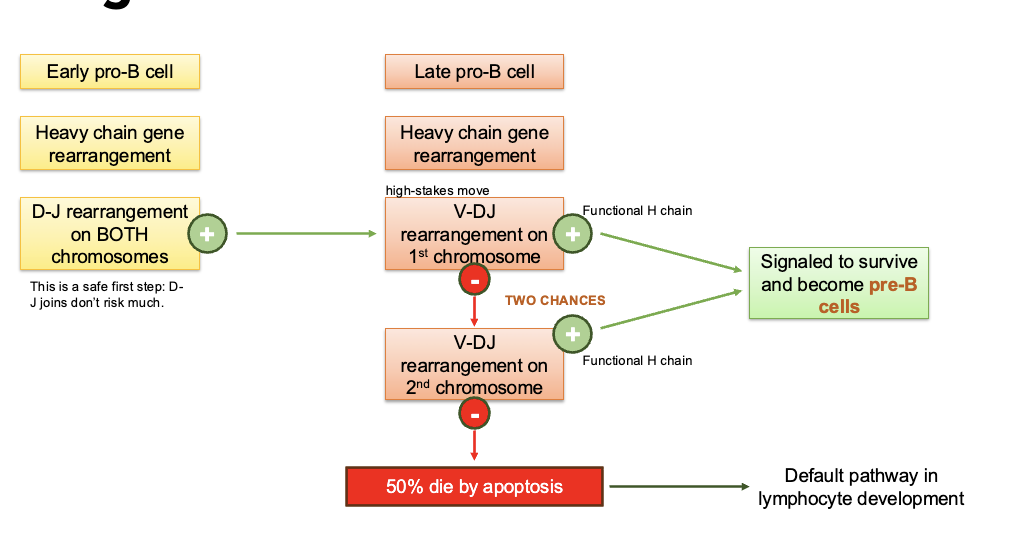
checkpoint #1
Pre-BCR testing
pairs with surrogate : chain (λ5 or VpreB) to form pre-BCR (allows for testing of H chain functionality
results in proliferation + progression to L chain rearrangement (small pre-B cell)
Tests VDJ recombination of only 1 H chain per chromosome (allelic exclusion)
preBCR signaling is antigen-independent
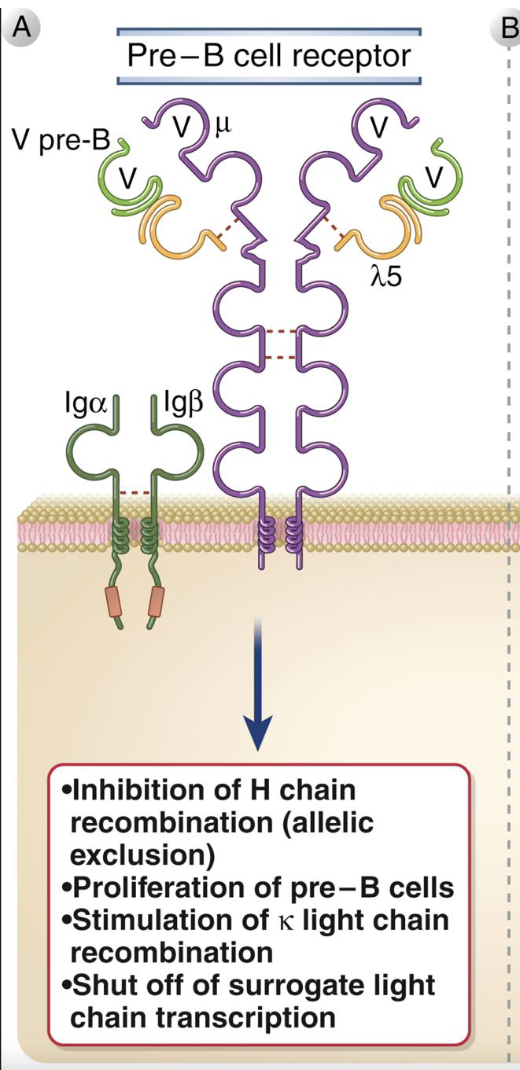
Pre-B cell receptor
composed of μ H chain + surrogate L chain (λ5 + VpreB), with Iga/IgB for signaling
signals without antigen - ligand-independent activation
outcomes of signaling:
i. stops heavy-chain rearrangement (allelic exclusion)
ii. induces proliferation of pre-B cells
iii. triggers light chain (k then λ) gene rearrangements
iv. turns off surrogate-chain transcription
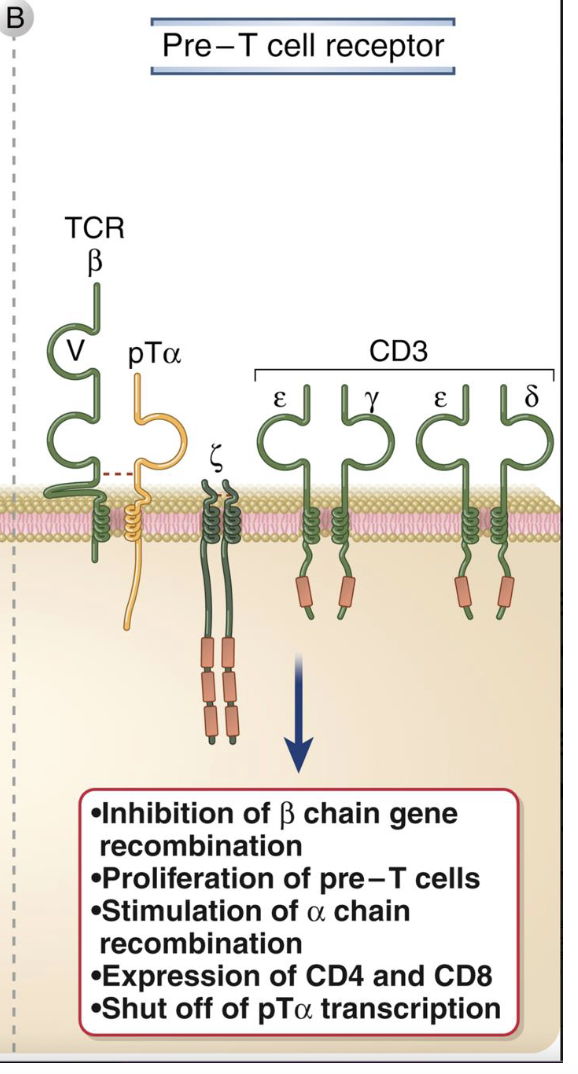
Pre-TCR
composed of B chain + pTa (surrogate a chain) and CD3 complex for signaling
also ligand-independent - tests whether B chain works
outcomes:
i. stops further B rearrangement (allelic exclusion)
ii. induces proliferation of pre-T cells
iii. stimulates a-chain rearrangement
iv. turns on CD4 and and CD8 expression (→ DP stage)
v. shuts off pTa transcription after checkpoint
which of the following correctly pairs a developmental stage with its key event?
a) early pro-B cell - expression of IgM
b) late pro-B cell - heavy chain VDJ arrangement
c) large pre-B cell - light chain rearrangement
d) immature B cell - pre-BCR expression
b) late pro-B cell - heavy chain VDJ rearrangment
at the large pre-B cell stage, what does the μ heavy chain pair with to form the pre-B cell receptor?
a) λ light chain
b) k light chain
c) surrogate light chain (VpreB + λ5)
d) Iga/IgB complex only
c) surrogate light chain (VpreB + λ5)
gene rearrangement in small pre-B cell
once H chain passes its checkpoint, the cell now moves on to rearrange L chain - first k, then λ. It gets FOUR chances before apoptosis
how many chances does the L chain have to rearrange before apoptosis
FOUR
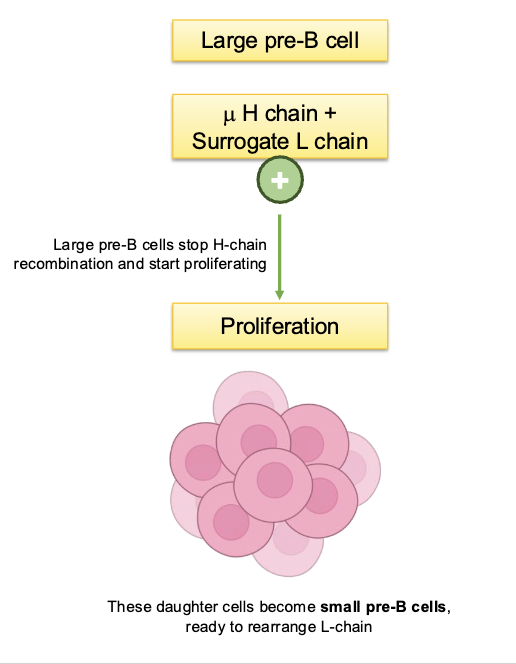
large pre-B cells stop H chain recombination and start proliferating, what do these daughter cells become
small pre-B cells, ready to rearrange L-chain
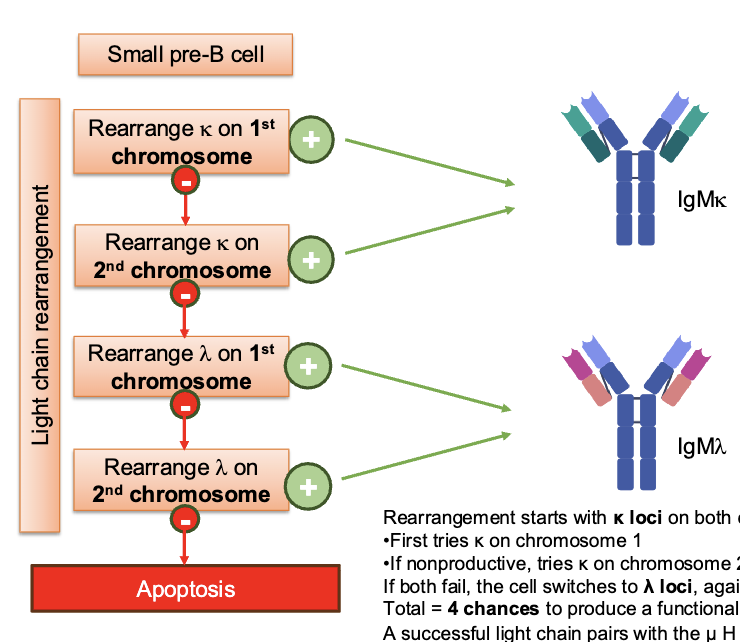
steps of L chain rearrangement
rearrangement starts with k loci on both chromosomes:
first tries k on chromosome 1
if nonproductive, tries k on chromosome 2
if both fail the cell switches to the λ loci, again with two attempts
Total = 4 chances to produce a functional light chain
a successful light chain pairs with the μ H chain to form IgM
IgMk or IgMλ depending on which gene succeeded
what establishes central tolerance
negative selection of immature B cells in bone marrow establishes central tolerance
checkpoint #2
Negative selection 1
tests whether VDJ recombination of L chain pairs with established H chain to produce a BCR that BCR does not recognize self-antigens expressed in the BM
L chain exhibits allelic AND isotypic exclusion
antigen-dependent: antigens on stromal cells and soluble molecules in B<
central tolerance
binding to self molecules in bone marrow can lead to what
receptor editing or to death of immature B cells
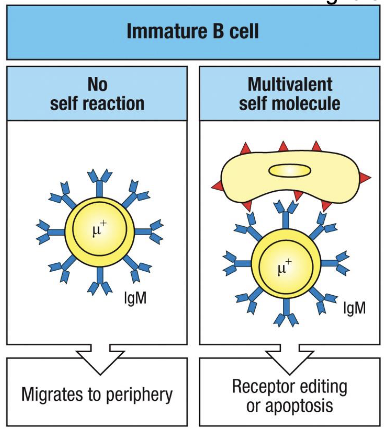
right panel shows what
if IgM binds strongly to multivalent self-antigens, the cell is flagged as autoreactive.
the B cell then gets a chance to ‘fix’ itself via receptor editing:
reactivates RAG1/2 to rearrange a new L chain
if successful→ new BCR replaces the old self-reactive one
if editing fails → the cell undergoes apoptosis
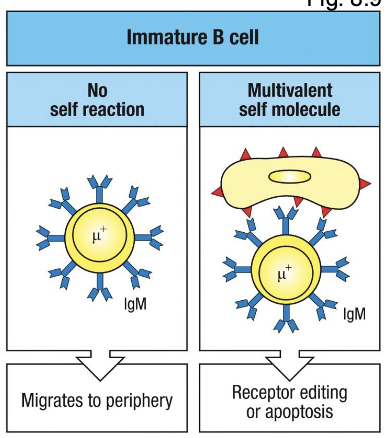
left panel shows
immature B cell expresses surface IgM after successful L chain rearrangement
if its receptor does not bind any self molecules in the bone marrow → its allowed to leave and migrate to the periphery as a transitional B cell
receptor editing
additional Ig L chain rearrangements give immature B cells in BM additional chances to replace autoreactive BCR with a non-reactive BCR
what happens when an immature B cell’s BCR binds a self molecule strongly
the cell receives a signal through the BCR that it is self-reactive
this signal re-induces RAG1/2 expression, re-opening the light-chain locus
the cell can:
delete or replace the existing k or λ light chain VJ segment with a new rearrangement further downstream in the locus
if k is exhausted (all downstream J’s used), it can still open the λ locus
what can rescue some self-reactive B cells by changing their antigen specificity
replacement of L chains by receptor editing
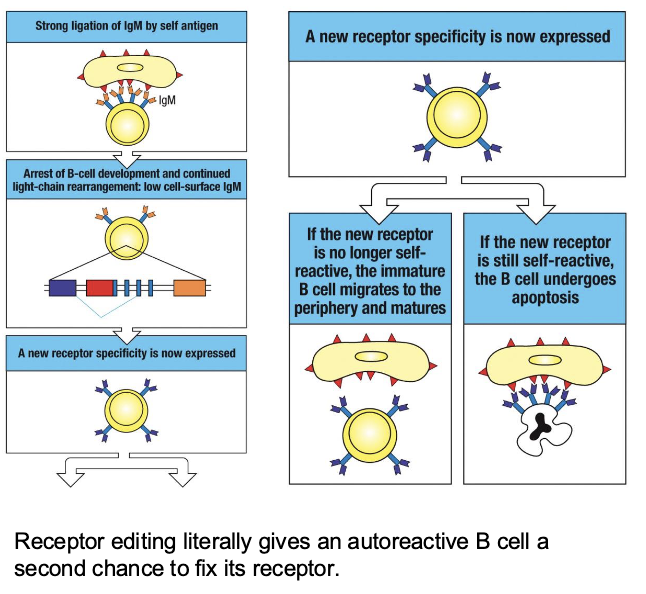
steps of receptor editing
detection of self-reactivity
reactivation of RAG1/2 and New L-Chain rearrangement
test the new BCR
detection of self-reactivity
the immature B cell expresses surface IgM
when it binds strongly to a multivalent self-antigen, this causes strong cross-linking of BCRs
that signal halts development → “wait, this BCR is self-reactive → fix it”
step 2: reactivation of RAG1/2 and New L-chain rearrangement
RAG genes are reactivated
the cell starts new V-J recombinations in the light-chain loci (usually k first, then λ if needed)
this process changes the antigen binding specificity of the BCR
step 3. Test the new BCR
if the new receptor no longer recognizes self, the cell survives and migrates to the periphery
if it still binds self strongly, it undergoes apoptosis
receptor editing does what
gives an autoreactive B cell a second chance to fix its receptor
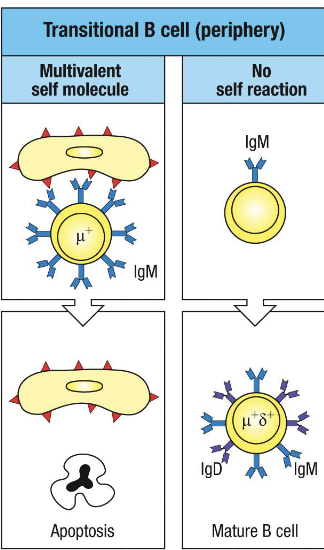
what establishes peripheral tolerance
negative selection of transitional B cells in spleen establishes peripheral tolerance
what happen to immature B cells that survive central tolerance in the bone marrow (no strong self reactivity)
they arent fully safe yet.
once they leave the marrow, they enter the spleen as transitional B cells; this is where they face peripheral tolerance
checkpoint 3
negative selection round 2
tests whether BCR with central tolerance fails to recognize any new self-antigens expressed in the periphery (i.e. outside the BM)
antigen-dependent: expression by splenocytes and soluble molecules in splees/circulating in the blood
peripheral tolerance
transitional B cells express what at first
IgM high and IgD low at first
what happens to transitional B cells
they encounter self-antigens that are only expressed outside the bone marrow: e.g. tissue restricted or soluble self-proteins
if their BCR binds these self-antigens with high affinity, they’re either:
get deleted by apoptosis, or
rendered anergic (functionally silenced)
This ensures that any B cells that slipped past central tolerance but still recognize self don’t activate in the periphery
in what ways does peripheral tolerance differ from central tolerance
BCRs that recognize self-molecules cannot undergo receptor editing
can no longer rearrange Ig L chain loci
only possible outcomes are apoptosis or anergy
what is the fate of immature B cells in the bone marrow that strongly bind multivalent self-antigen?
a) proliferation and class switching
b) receptor editing or apoptosis
c) anergy
d) migration to spleen for positive selection
b) receptor editing or apoptosis
where do transitional B cells complete their maturation
in B-cell follicles in the spleen
marginal zone B cells
arise from weakly self-reactive B cells expressing high levels of CD21
localize to marginal zones of splenic white pulp
function as first-responders to blood-borne antigens or pathogens (rapid, T-cell-independent response)
BAFF (B-cell activating factor)
produced by follicular DCs (FDCs)
binds BAFF-R on T1Bs to deliver essential survival and maturation signals
T1B: High IgM, no IgD; express BAFF-R
T2B: IgM + IgD + BAFF-R + CD21 (complement receptor)
what happens to transitional T1 B cells that fail to enter follicles
do not receive BAFF-mediated survival signals
die within 2-3 days of leaving the BM
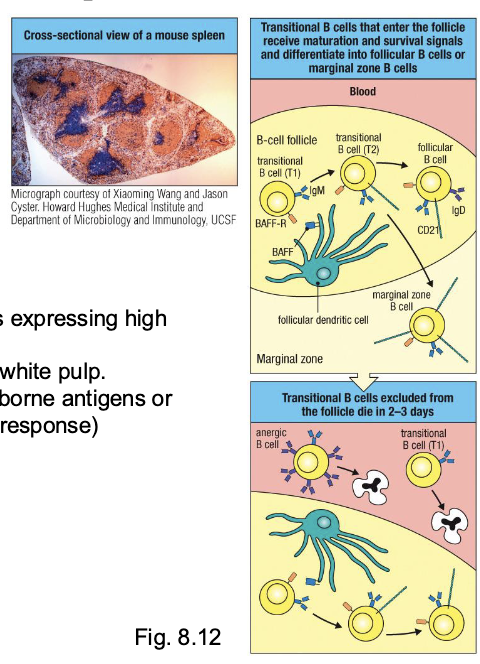
what is the role of BAFF in B cell maturation?
a) induces heavy chain recombination
b) provides survival signals to transitional B cells entering follicles
c) mediates receptor editing in immature B cells
d) promotes class switching to IgG
b) provides survival signals to transitional B cells entering follicles
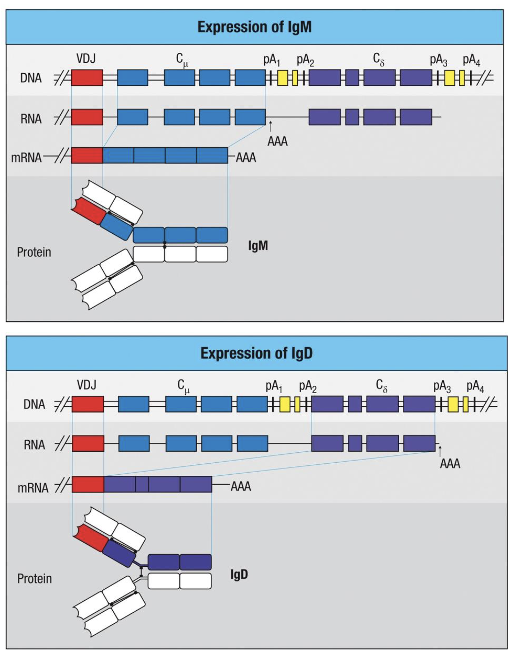
alternative splicing of primary transcript to generate what
IgM + IgD
immature B cell -
Mature B cell -
immature B cell - IgM
mature B cell - IgM + IgD
both IgM and IgD are encoded by what
the same rearranged H-chain gene (VDJ region)
what is the difference between IgM and IgD
the differenc between them ia generated after transcription, by alternative splicing of the primary RNA transcrip
what do immature B cells express on their surface
only IgM
as B cells mature in the spleen, what allows co-expression of IgM and IgD
alternative splicing allows co-expression of IgM and IgD - both have identical antigen specificity but different constant regions