Important Things to Know (Calc. AB)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Limit Properties
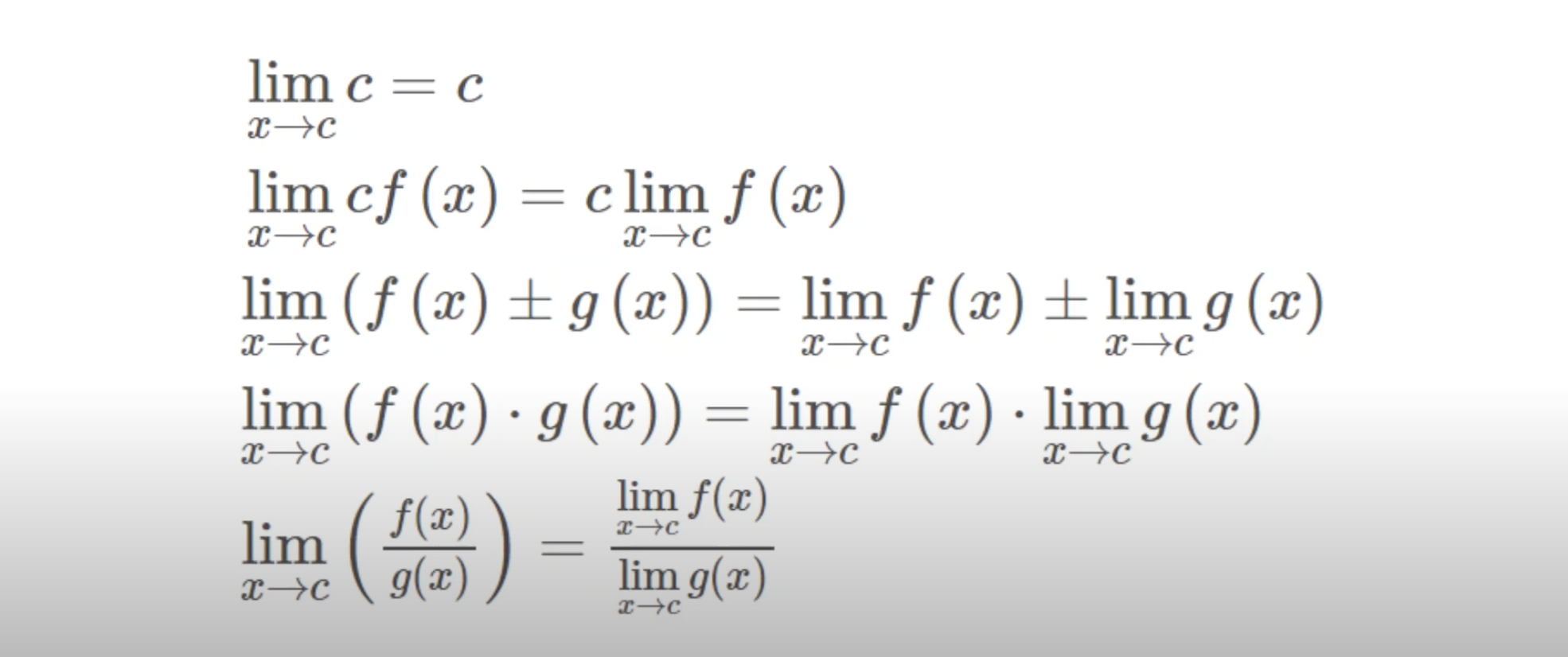
Trig. Identities + Trig. Limits
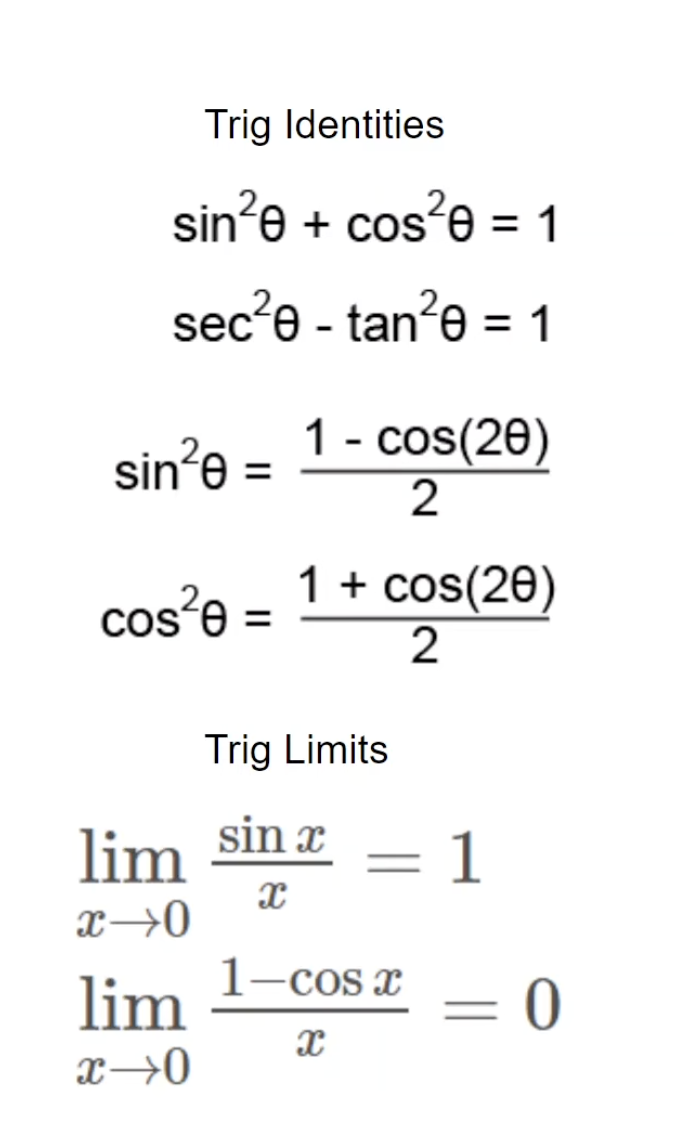
Squeeze Theorem

L’HOSPITAL’S RULE
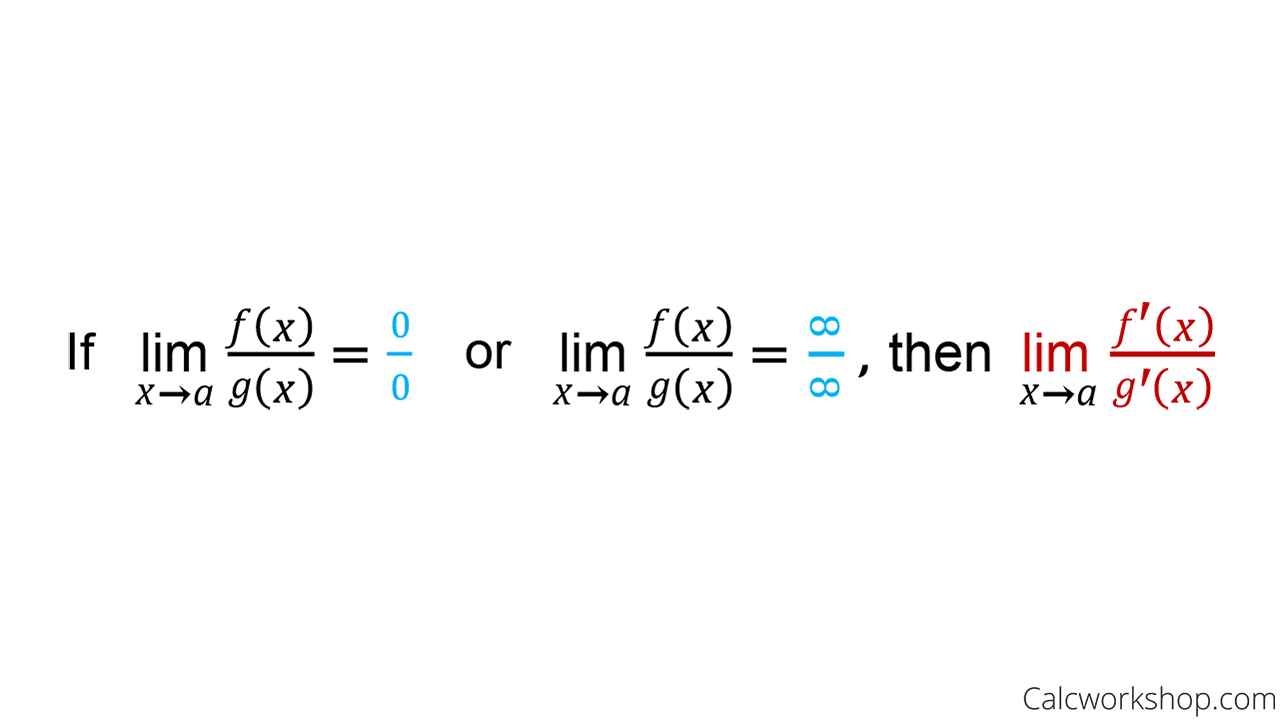
Criteria for Continuity
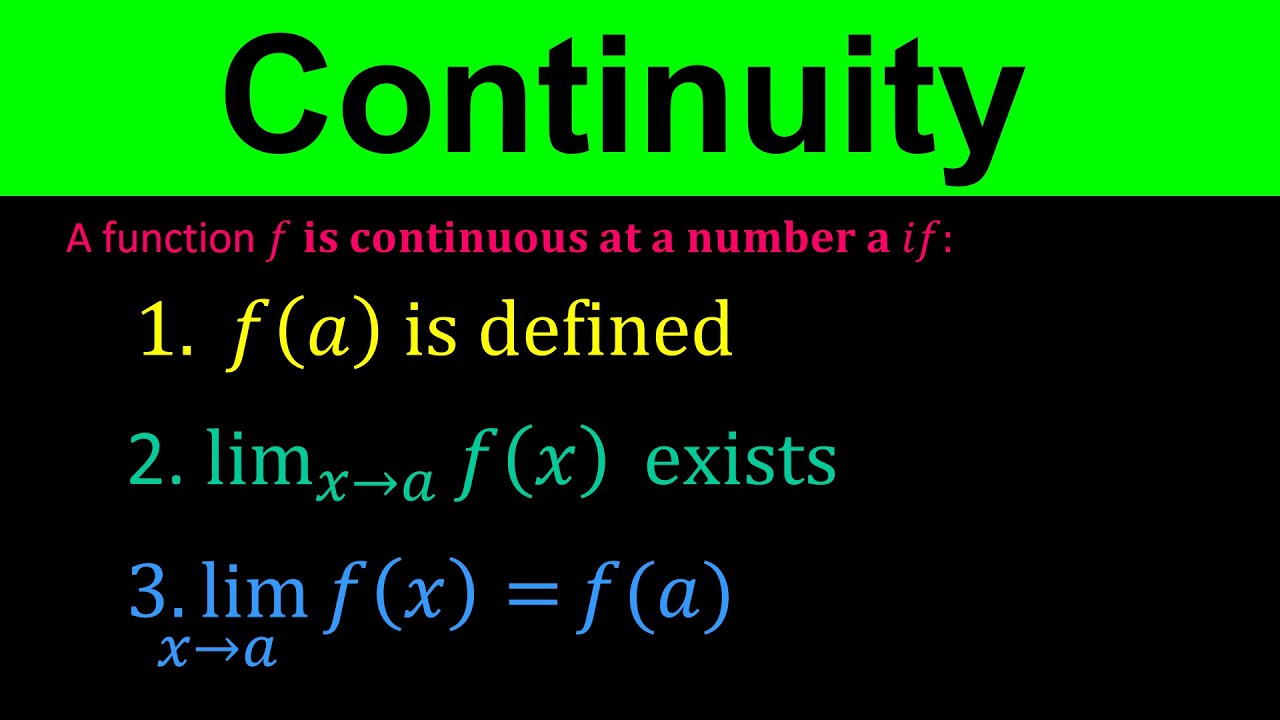
Types of Continuities
Holes occur when factors from the numerator and the denominator cancel (removable). When a factor in the denominator does not cancel, it produces a vertical asymptote (non-removable).

Horizontal Asymptote Rules + Vertical vs. Horizontal Asymptotes
Horizontal Asymptote Rules
If the degree of the den. > degree of num. = 0
If the degree of the den. = degree of num. = (leading coefficient)/(leading coefficient)
If the degree of the den. < degree of num. = no horizontal asymptote
Vertical vs. Horizontal Asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes occur where a function approaches infinity (limit), while horizontal asymptotes indicate a function's end behavior as x approaches infinity.
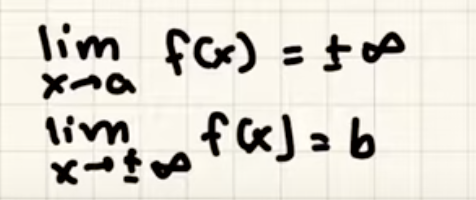
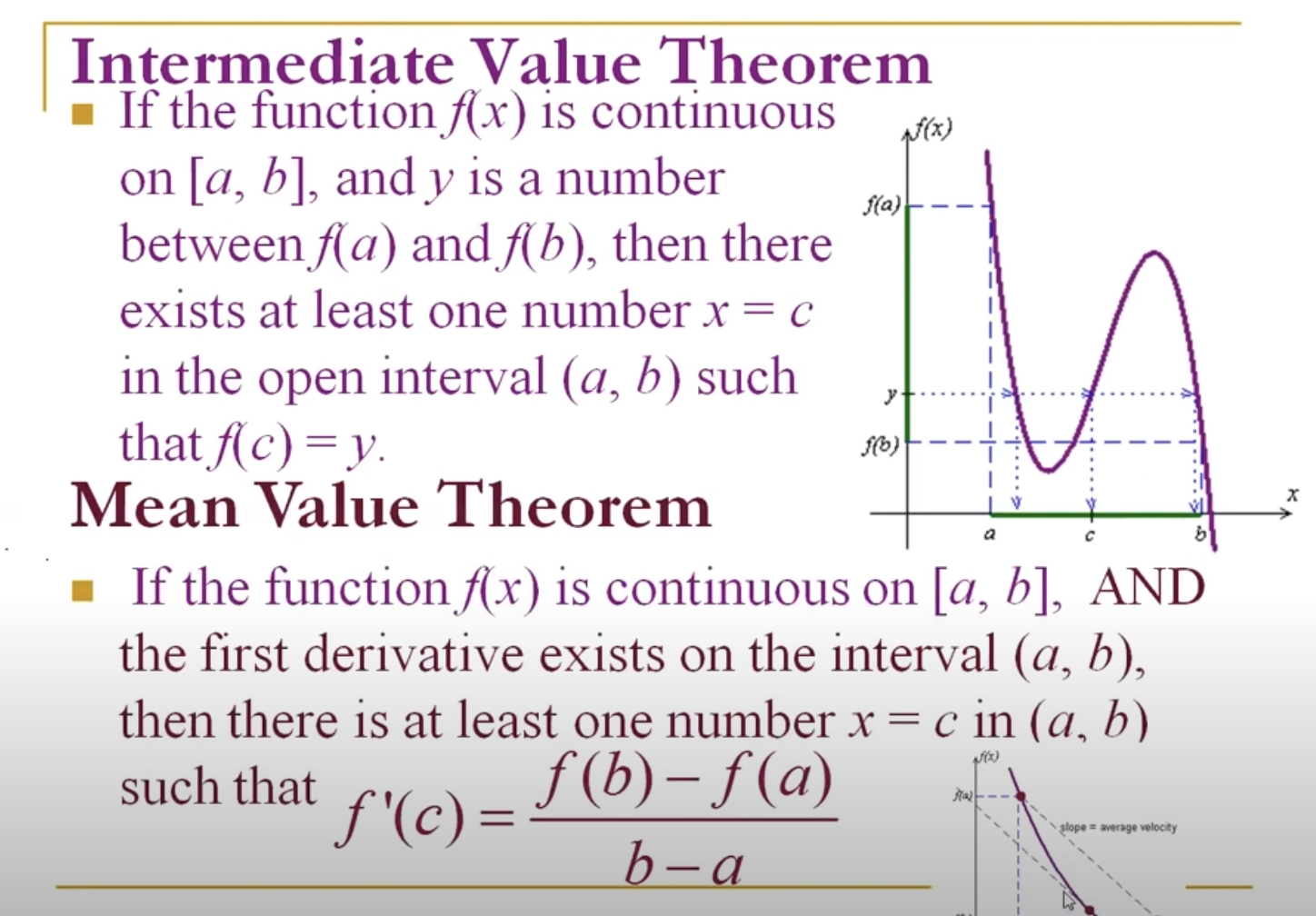
I.V.T. + M.V.T.
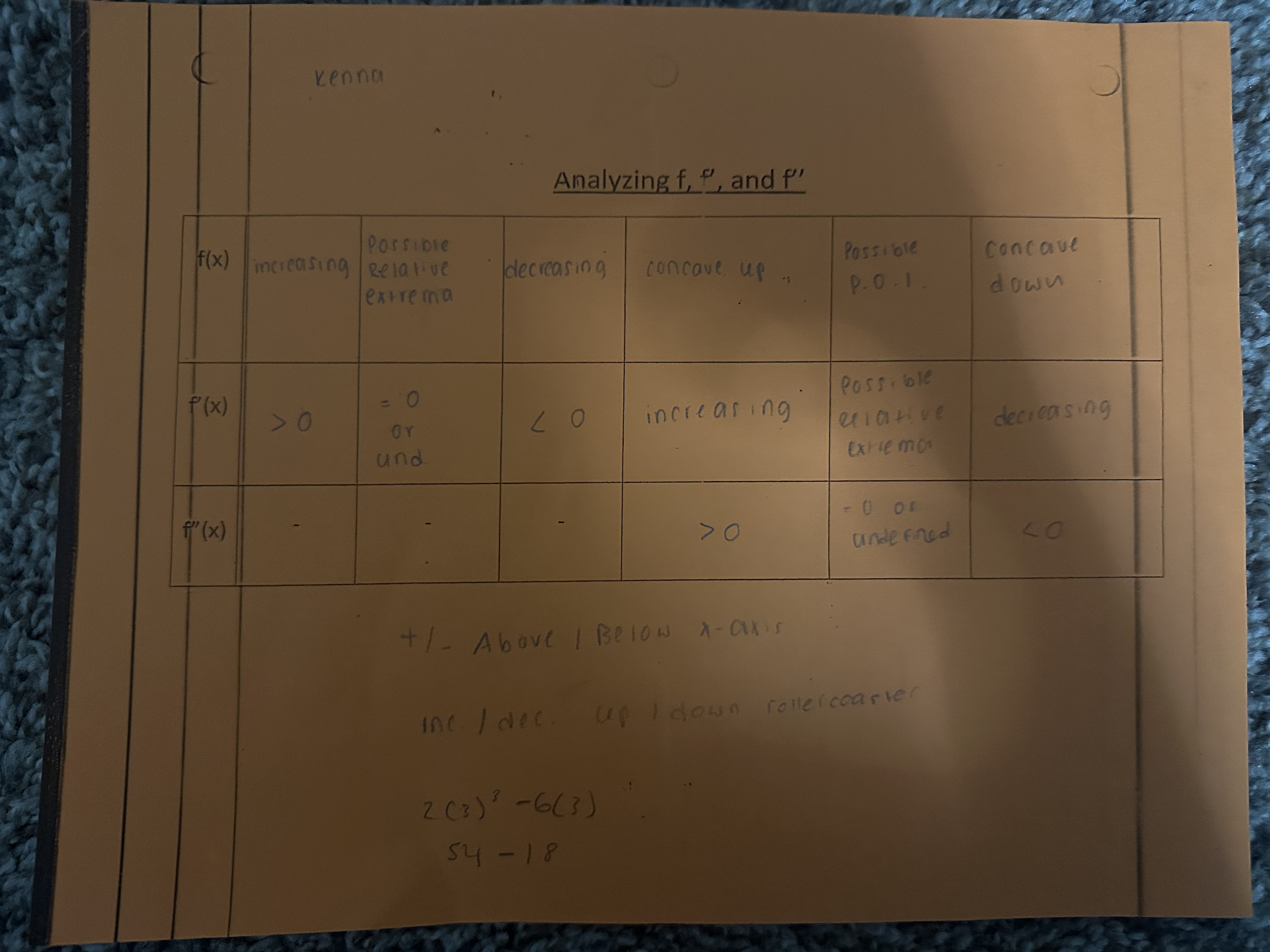
Curve Sketching
y = f(x) must be continuous at each:
critical point: dy/dx = 0 or undefined and endpoints
local minimum: dy/dx goes from - to + or d²y/d²x > 0
local maximum: dy/dx goes from + to - or d²y/d²x < 0
point of inflection: concavity changes
d²y/d²x changes sign
Basic Derivatives

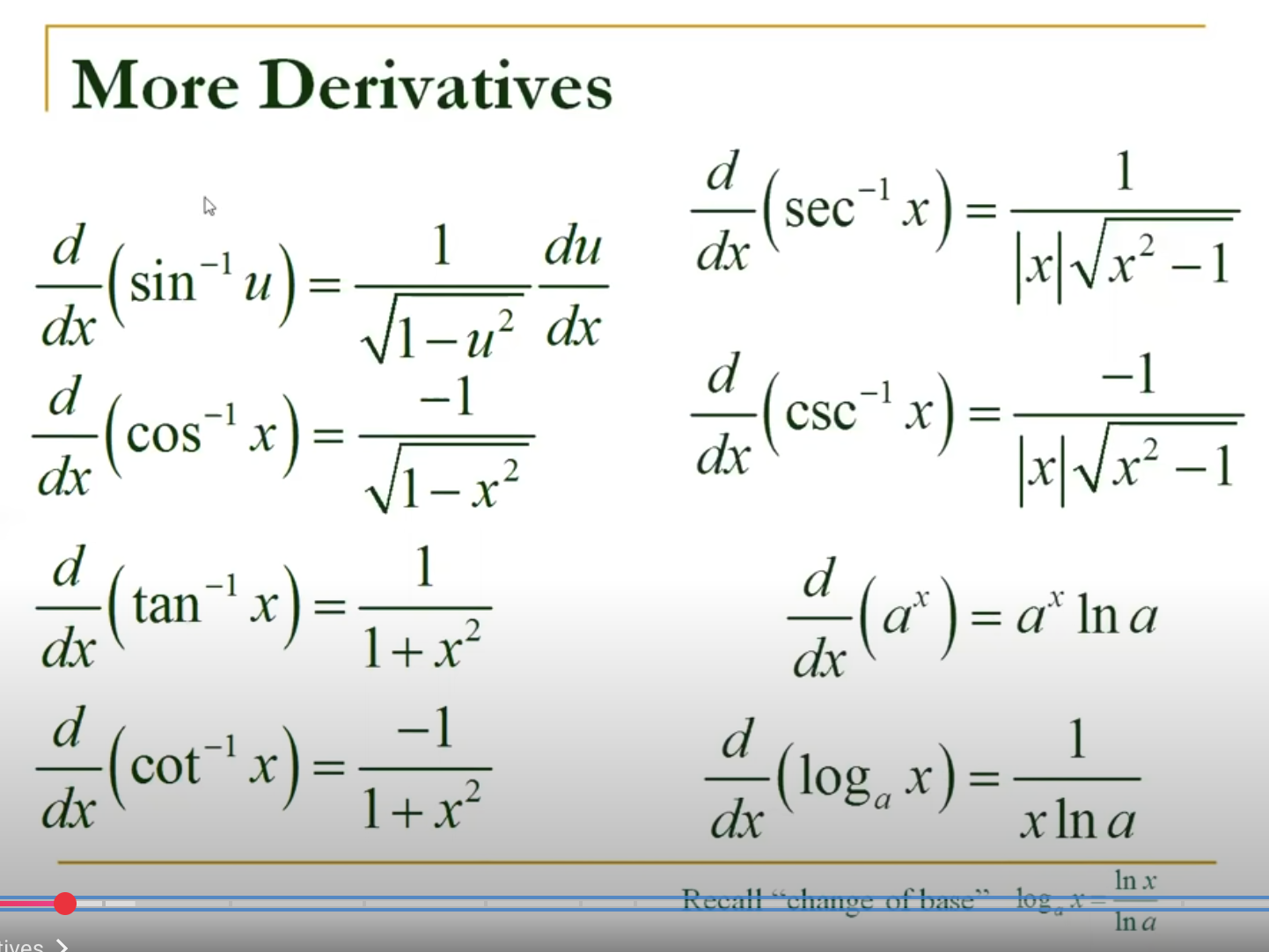
Additional Derivatives
Basic Integrals
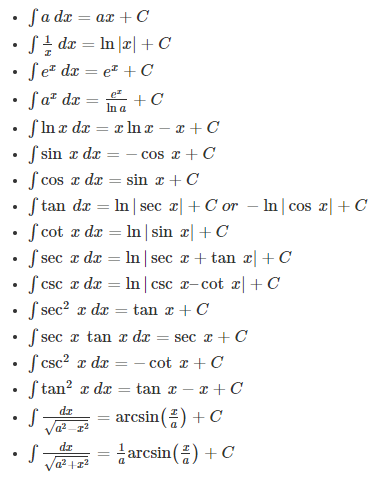
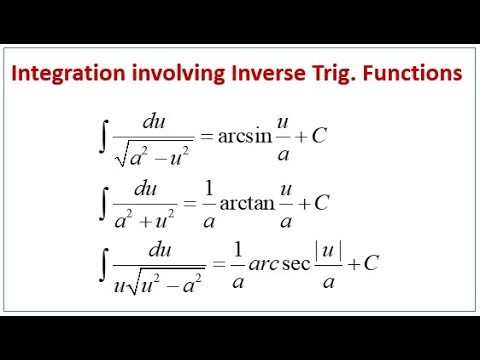
Integrating Inverse Trig. Functions
Differentiation Rules
Chain Rule: If y = f(g(x)), then y' = f'(g(x)) * g'(x).
Product Rule: If y = f(x) g(x), then y' = f'(x) g(x) + f(x) * g'(x)
Quotient Rule: If y = f(x) / g(x), then y' = [f'(x) g(x) - f(x) g'(x)] / [g(x)]² (lo de hi/hi de lo)/lolo
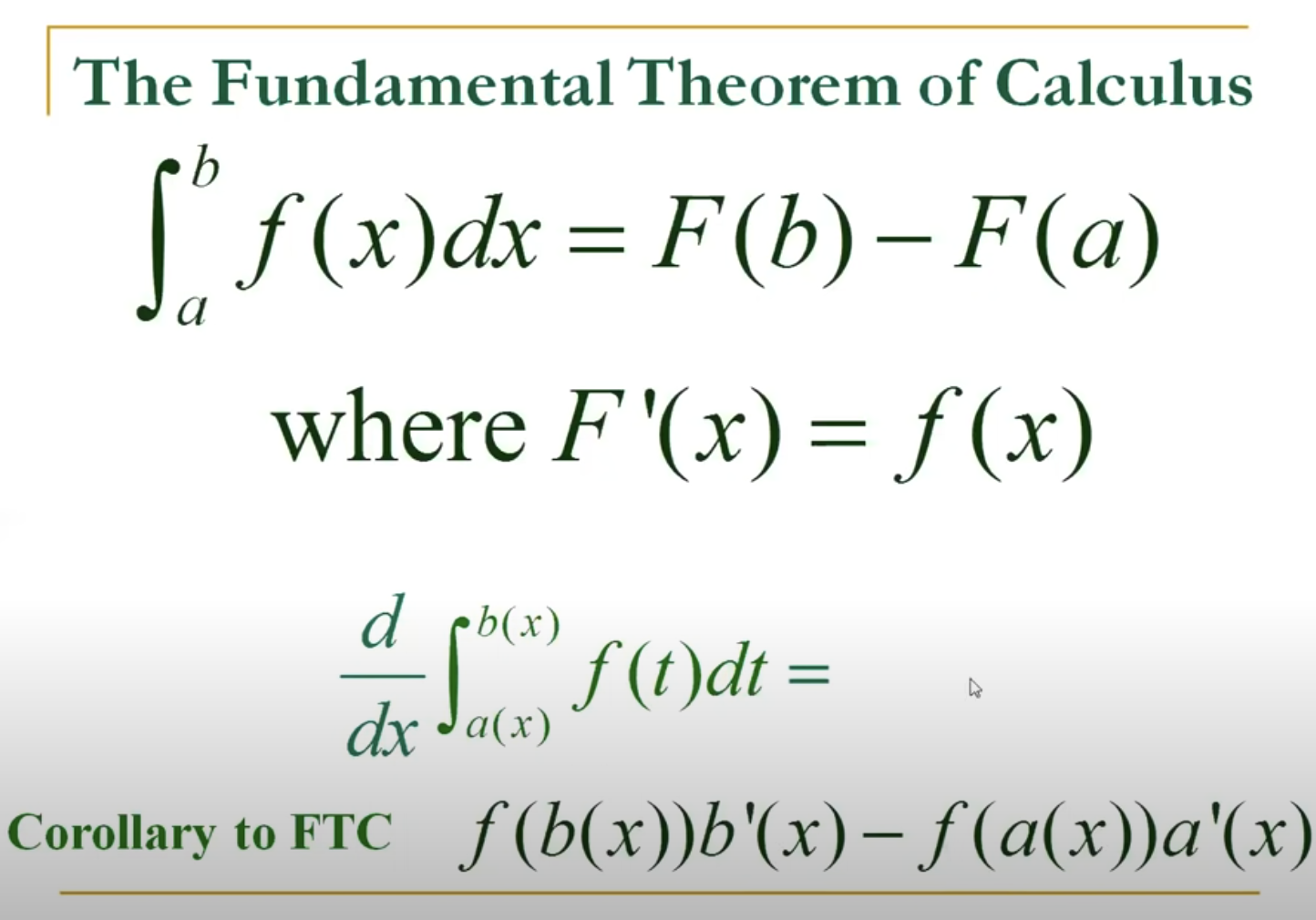
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Average Value
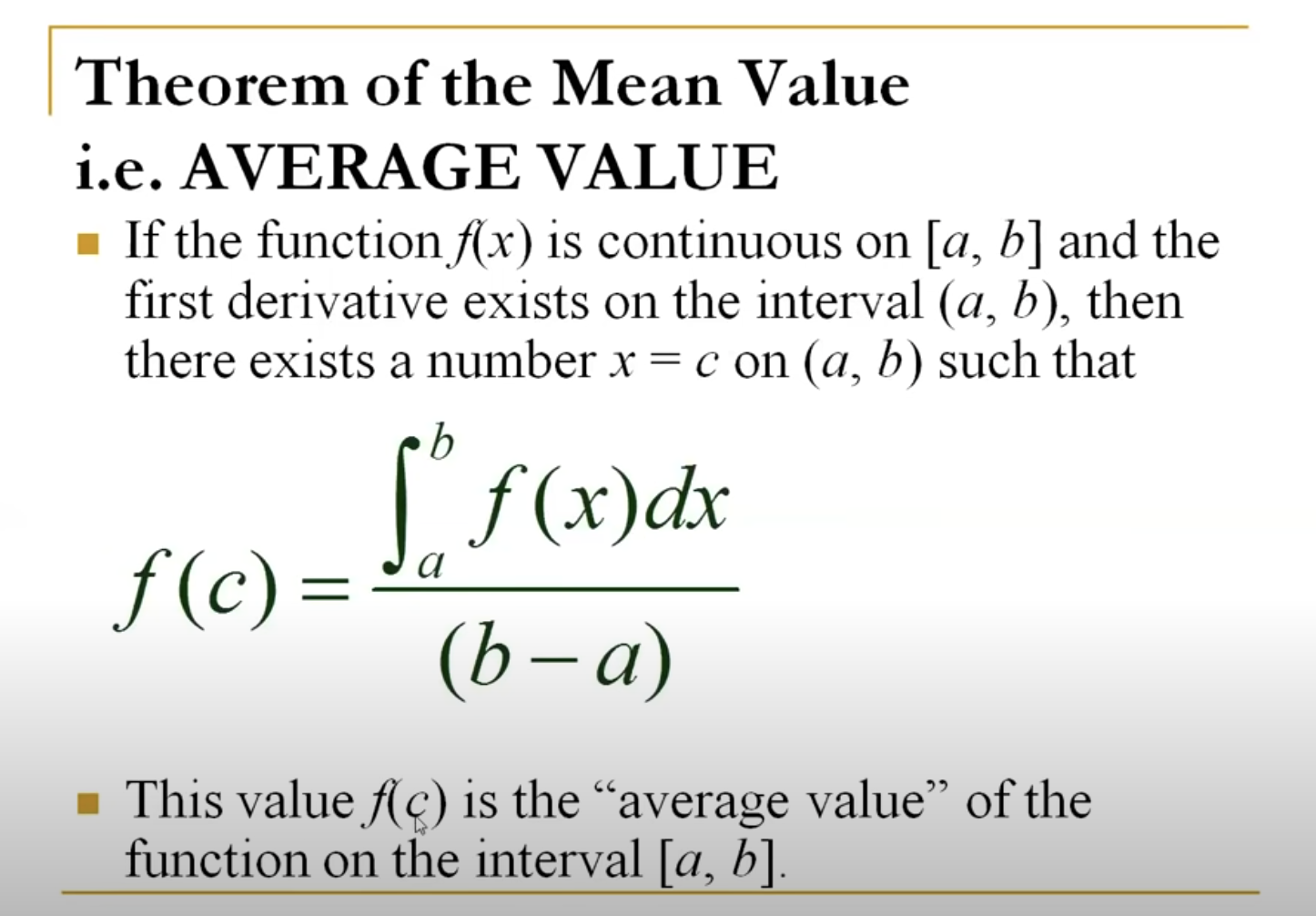
Volume Methods

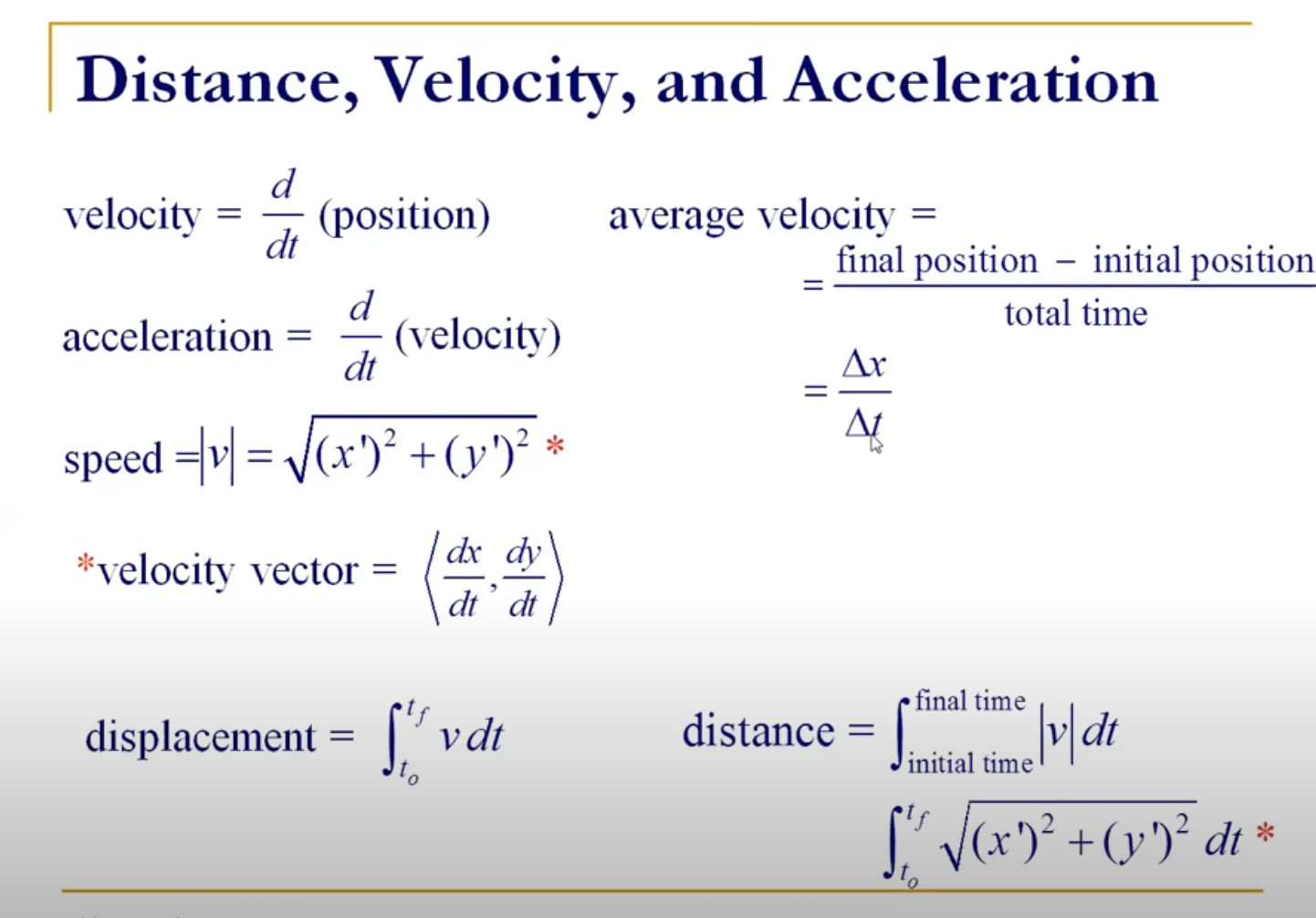
Distance, Velocity, and Acceleration
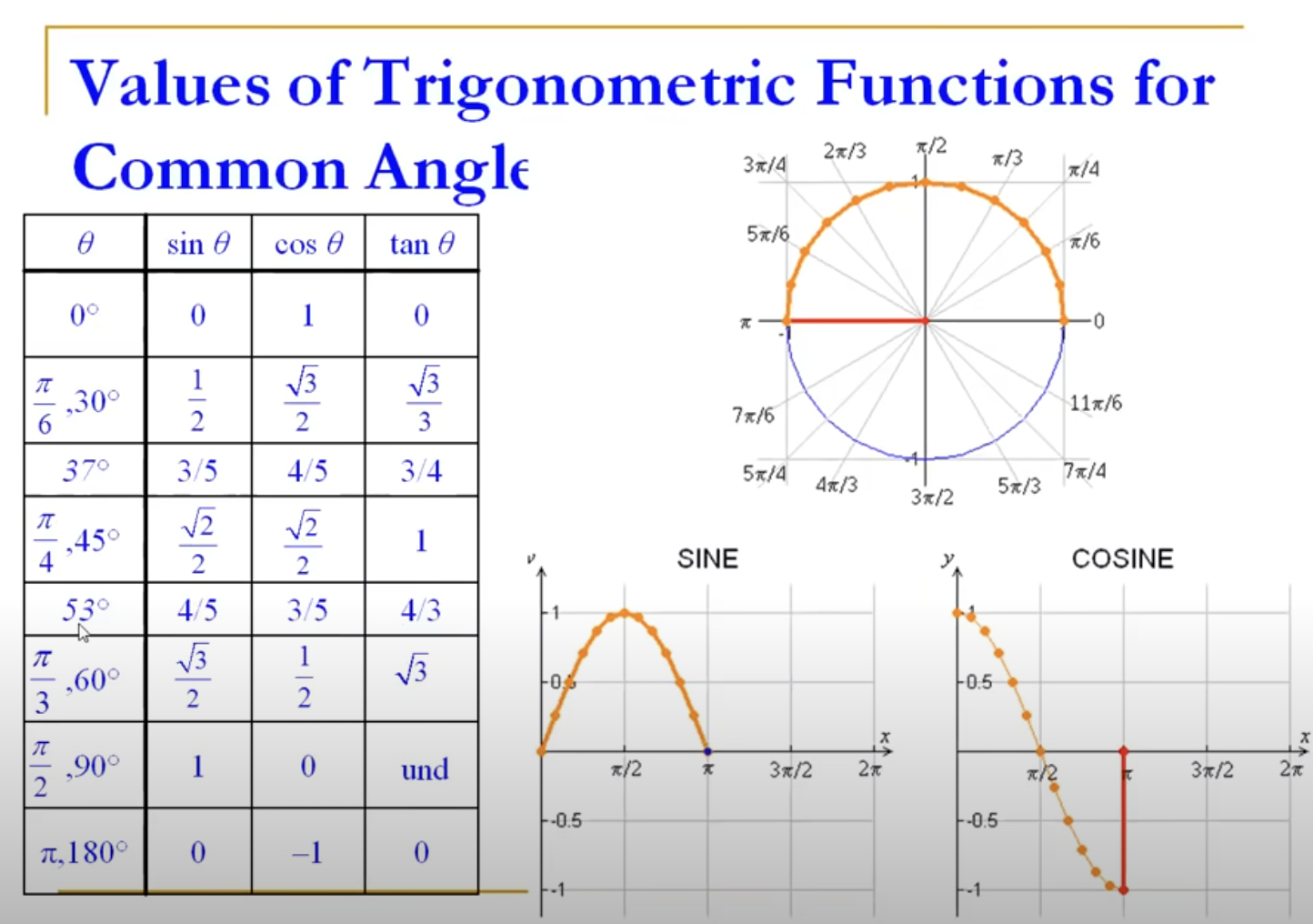
Values of Trig. Functions for Common Angles
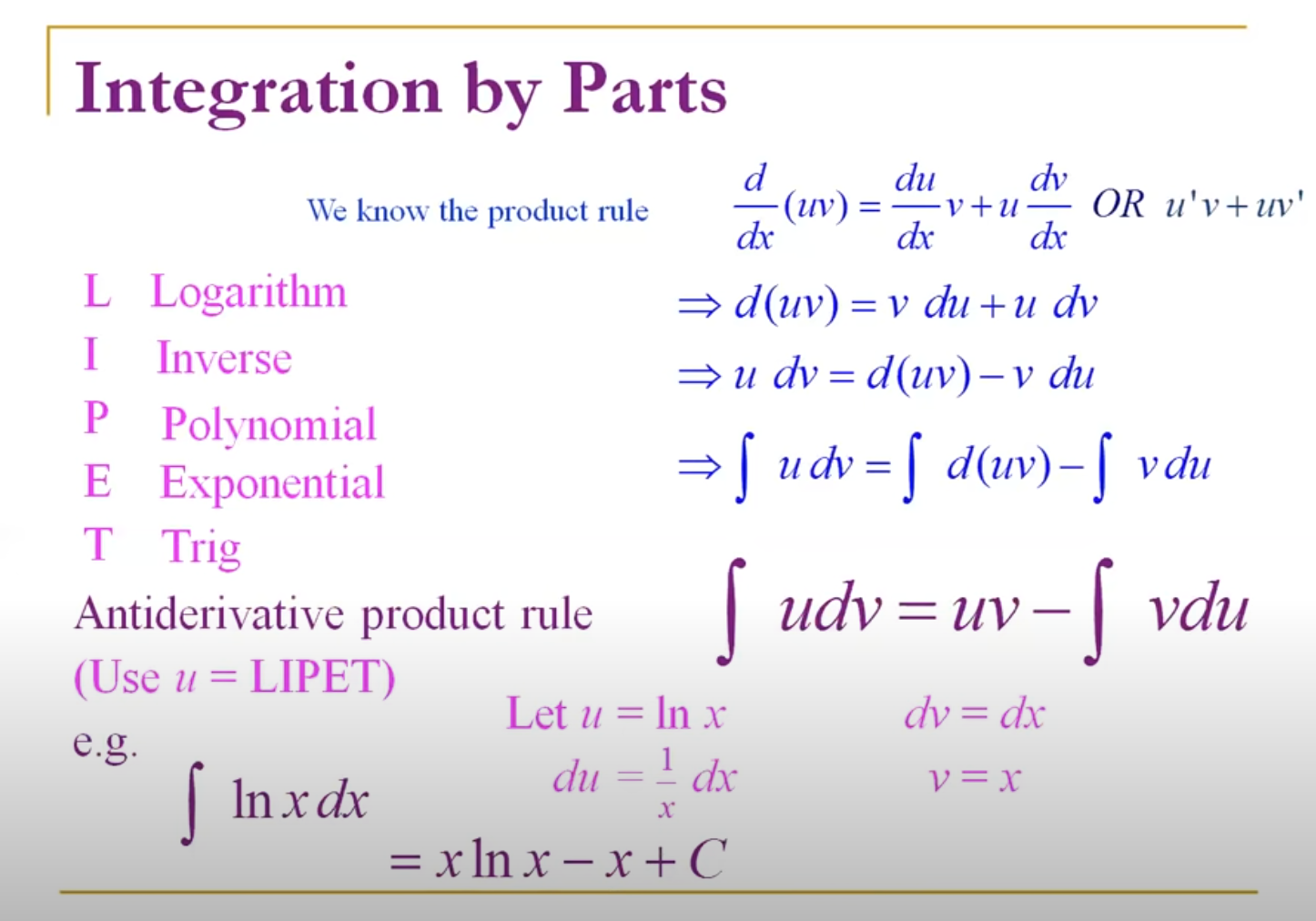
Integration by Parts
Derivative of Inverse Functions

First Derivative, Candidate, Concavity, and Second Derivative Tests

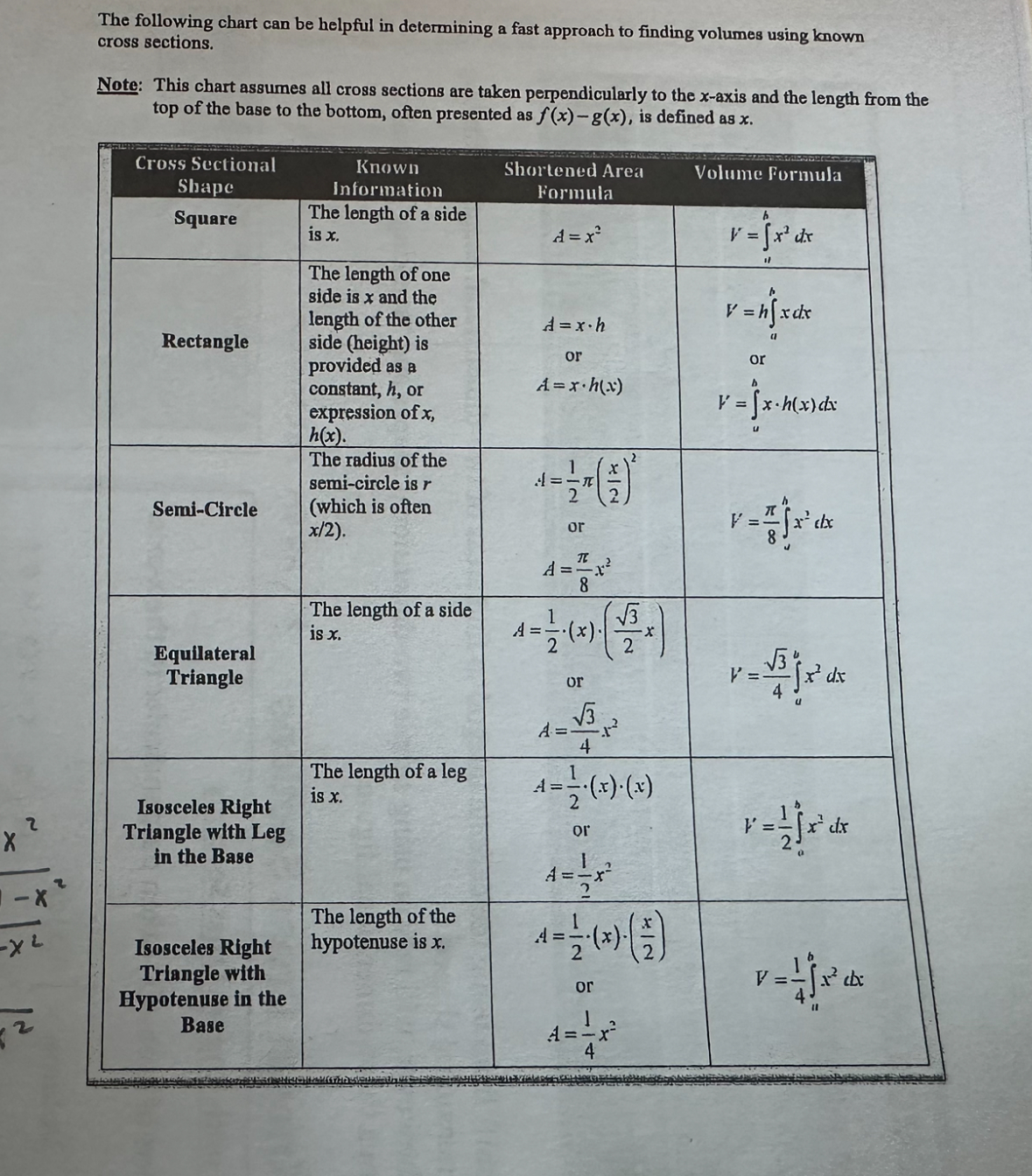
Cross Sections