Fungi (Mycology - study of fungi)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
why are there many more drugs to treat bacterial infections compared to fungal infections?
The chances of finding a target for selective drug toxicity is much less in comparison to prokaryotic bacteria
-Important differences in fungal cells, such as a cell wall of chitin & ergosterols in membranes, can be targets for antifungal medications, but similarities between human and fungal cells make it difficult to find targets for medications, and these medications often have very toxic adverse effects
Are fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Eukaryotic microorganisms as it has internal organelles and its nucleus is surrounded by membrane
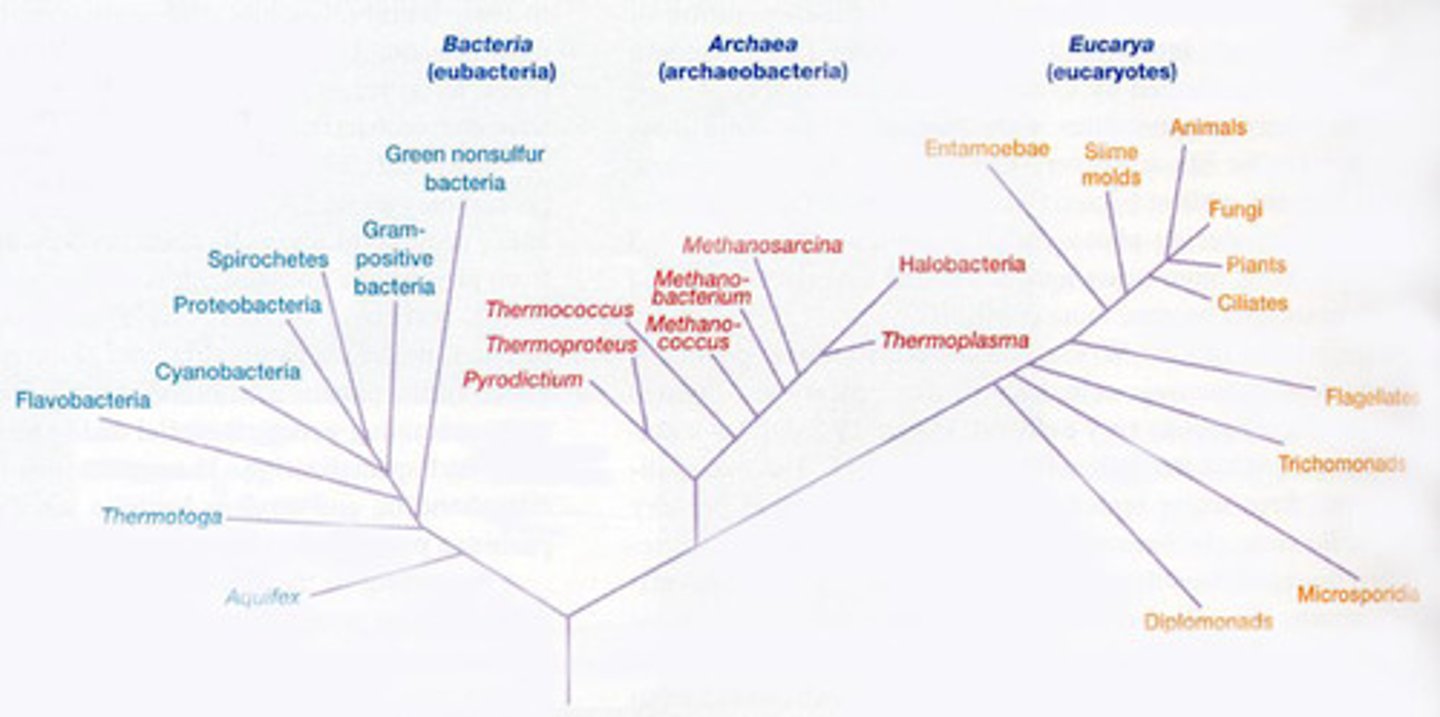
What is the Phylogeny (he evolutionary history of organisms, the study of that history, and a graphical representation of that history) of the Eumycota (name for Fungi)?
-Similar to animals and plants but more like plants
What do we mean when we describe fungi to be Saprotrophic?
-Fungi feed oof of dead, decaying matter of the environment
-They secrete enzymes to break down this matter and absorb these nutrients to provide energy
Why do we study Fungi?
-They are major decomposers in the environment
-They can go from mutualistic/commensal state to become parasitic
-Can cause diseases - in humans they feed off of keratin structures (skin hair nails) as food sources
-Also used in research (to find about more from other things e.g. cancer and the cell cycle)
-Microorganisms can be a source of drugs
How does Fungi break down oranges?
-Fungi grows on the surface on the orange and releases enzymes to break down the pectin layer of the orange
-Fungi produce penicillium which produces penicillin.
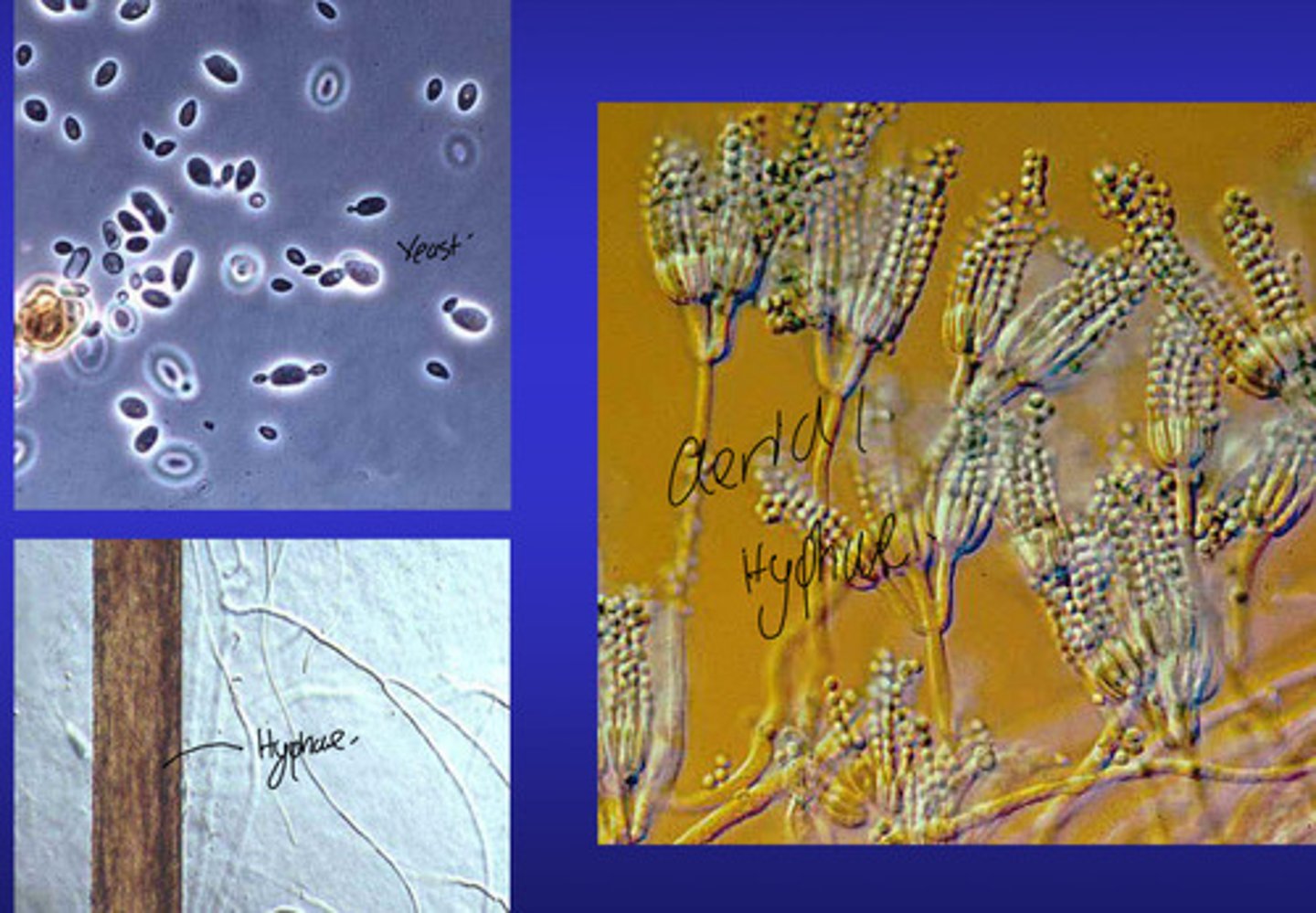
What are the 2 Basic Fungal forms (Micro?
1. Yeast (unicellular) - reproduces by binary fission or by budding (when smaller daughter cells pinch, or bud, off the mother cell)
2. Mold form (Make up multicellular fungi)-
-Formed of microscopic long tubular filaments called Hyphae. -These tubes grow by apical extension and they grow across a surface - Mycelial mat (these can get really big even though they are microscopic) - where they secrete enzymes to degrade any nutrients and then reabsorbing them.
-When the nutrients finish in one area, the hyphae will then grow out to colonise new substrates but the left over mycelium will make new hyphae but those will grow upwards into the air. By the end of this aerial hyphae we get asexual spores called Canadia. These can be distributed to new areas by wind rain, splash, animals etc.
-These reproduce Asexually and/or sexually.
Note:
Some fungi can also be a combination of both yeasts and hyphae. A class of fungi called dimorphic fungi can have both a yeast form and a mold form. This is known as dimorphism, and it's a characteristic of some pathogenic fungi.
What is the largest organism on earth?
Fungi
What are the types of Asexual Spores?
sporangiospores and conidiospores
-Can cause allergic reactions
Note:
As aforementioned these can be transmitted in the air all the time (you can be breathing them in)
Fungal classification types?
-This can be done as depending on whether that type of Fungi can reproduce Sexually or asexually or both
-If you can only recognise one of the stages, they are put into the fungi imperfecti class
-Zygomycota (common name : Zygomycetes)
-Asycomycota (Sac Fungi)
-Basidiomycota (Club Fungi)
-Deuteromycota (Fungi imperfecti)
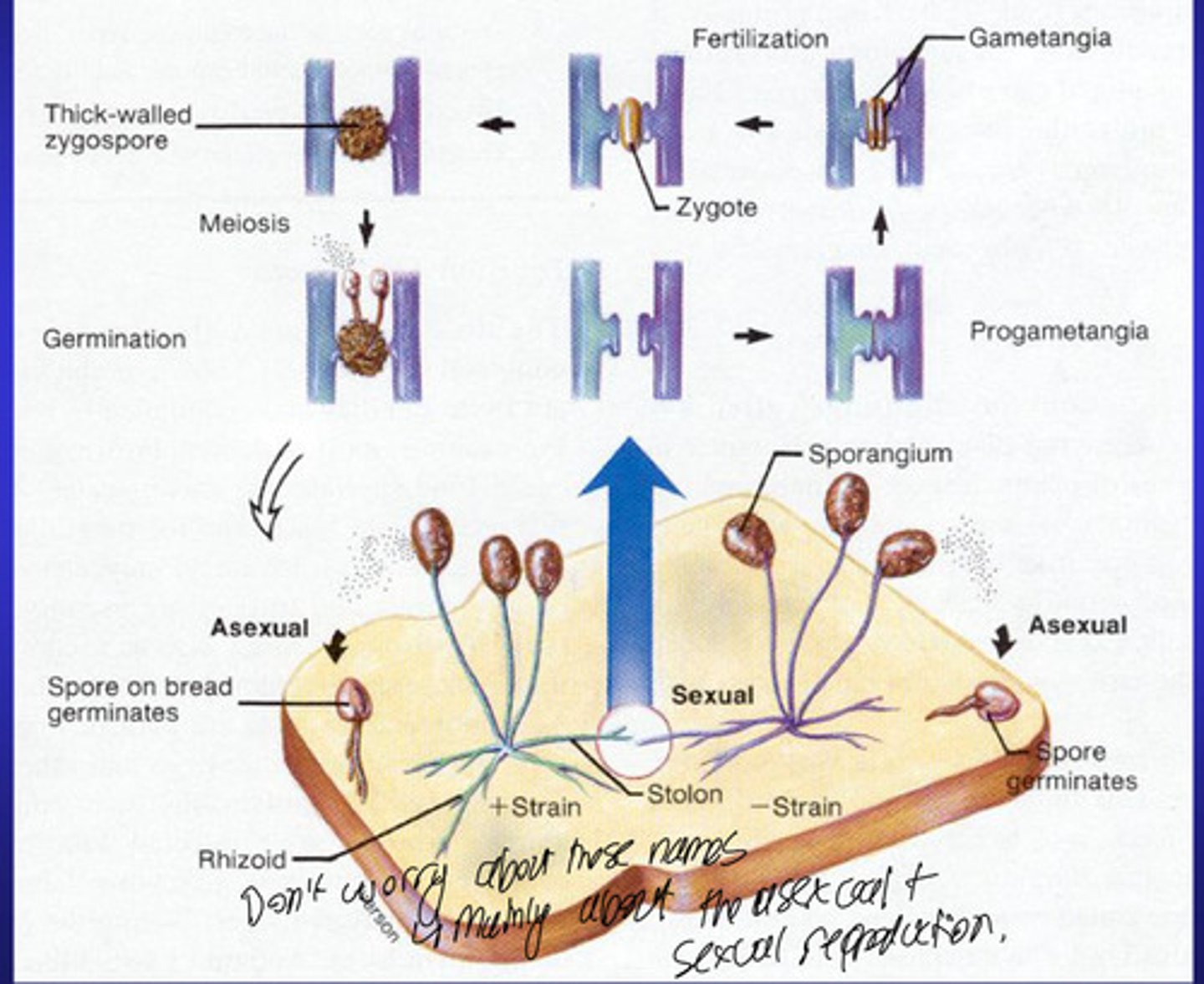
How does Asexual and Sexual reproduction in the Zygomycota (common name : Zygomycetes) class of fungi occur?
e.g. mouldy bread
-Asexual reproduction is occurring on the bread and hyphae is covering the bread until the nutrients in the bread run out
-Then it starts producing its spores - hyphae grow upwards into air producing asexual spores
-Can introduce Sexual reproduction for genetic variability via mating Hyphae (Plus +or Minus - NOT MALE AND FEMALE)
-The two hyphae will come together and fuse to fomrm a Zygote where the haploid nuclei join together to form a diploid.
-This then thickens its cell wall then we get meiosis = reduction from diploid to haploid stage and the spores are then released and the asexual cycle continues.
Describe how Zygomycetes are emerging fungal pathogens
-Seen as a comorbidity in patients with uncontrolled diabetes - they inhale spores
-Anti-inflammatory drugs can cause a co-morbidity with SARS-COV-2 infection
-SARS-COV-2 infection + Uncontrolled diabetes + immunosuppression= Ideal conditions for an opportunistic fungal infection to occur
-Big in india (Black fungus infection)
What is the significance of The Ascomycetes (A class of fungi)?
-A reproductive structure (the same as a mushroom) following sexual reproduction their are a dispersion of spores
-Heavily Pathogenic
-They can produce toxic salts and when ingested you can get ergot alkaloid poisoning which are powerful hallucinogenic compounds
-Can also be used in research - Alexander Fleming, observed that penicillin was inhibiting his staphylococci on his agar plate
What are the stages of the sexual cycle of The Ascomycetes
-Fusion of 2 mating hyphae (plus and minus)
-Fusion of haploid nuclei to form diploid (formed in ascospore in this case - will be formed in some form of structure)
-The mitotic division will occur back to the haploid phase to give us a characteristic number of spores released into these reproductive structures e.g. the truffles and the morales
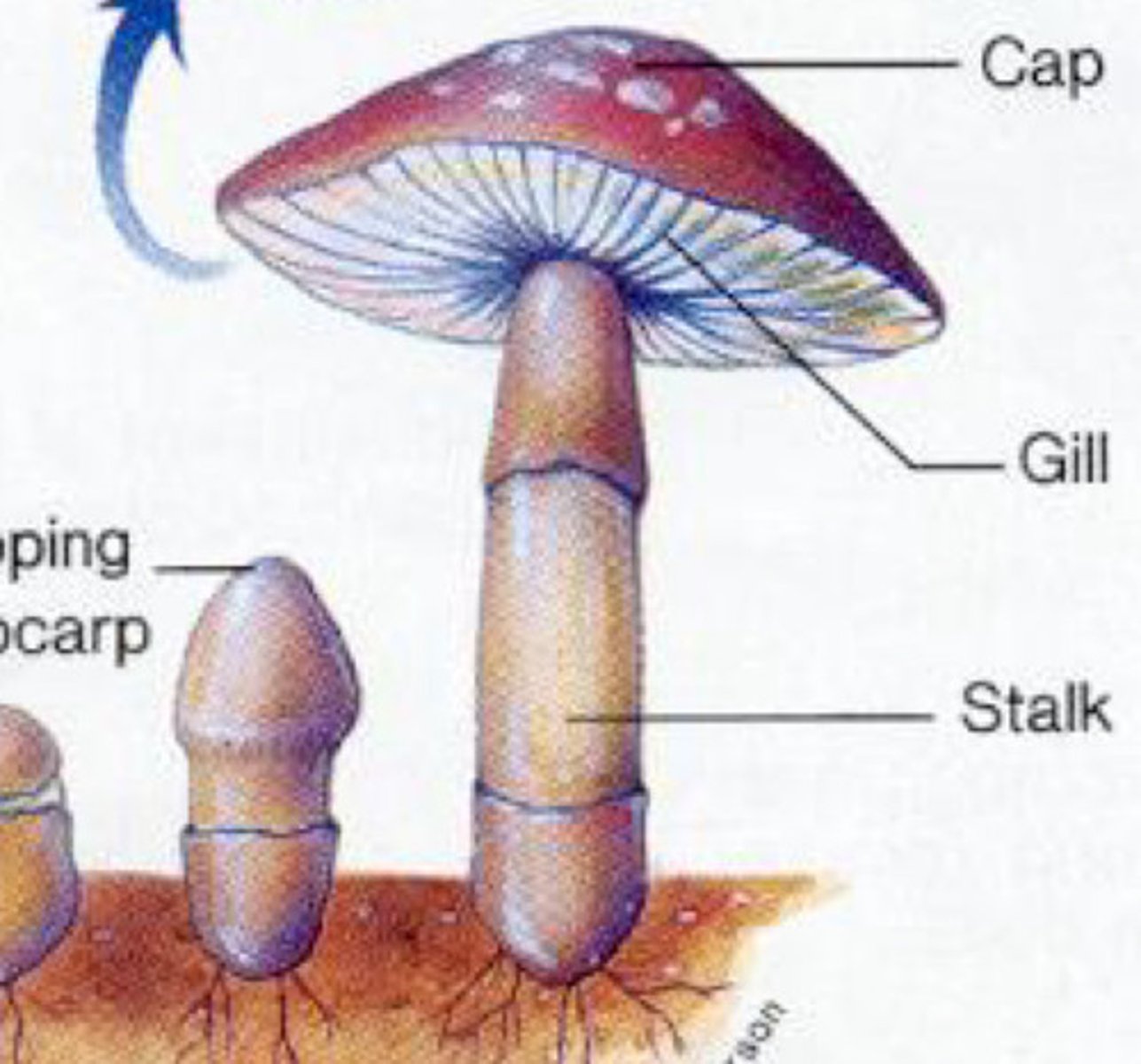
What are the stages of the sexual cycle of Basidiomycetes ?
-Fusion of 2 mating hyphae (plus and minus)
-Fusion of haploid nuclei to form diploid
-Then we get the mushroom like structure (Cap, stalk and Gills)
-Inside the gills we get the reduction to give us our haploid number
-Spores are on the gills so can be transferred in the air and dispersed via rain, wind etc.
What are the properties of Basidiomycetes?
-The pizza mushroom is safe to eat
-A destroying angel mushroom is a type of Basidiomycetes that produces a potent hepatotoxin = terminal liver failure
-The magic mushroom has hallucinogenic properties
Relate fungi properties to their medical importance
▪ The fungal cell wall consists predominantly of chitin (a polysaccharide - made up of N-acetyl glucosamine a monomer of peptidoglycan ) = Fungi are insensitive to antibiotics that inhibit the biosynthesis of peptidoglycans = no point in giving patient with fungal infection a B-lactam
▪ Fungal cell membranes contain ergosterol - this allows them for selective action of amphotericin and the polyenes against fungi not against human cells
▪ Dimorphism - Some fungi changing from yeast form to mould form - if external environment factors change e.g. redox potentials, temperature, CO2 potential, nutrients
▪ Infections caused by fungi can be cutaneous, subcutaneous, systemic or opportunistic
What is cutaneous mycoses ?
Caused by fungi that infect keratinised structures (skin hair nails and deep tissues)
e.g. ringworm or jock itch at the groin
What is subcutaneous mycoses ?
-Fungi from the environment are introduce into the subcutaneous tissue through trauma (initiates the immune response in the skin - phagocytic cells will go to the site of infection, but cytotoxic cells will form a hypersensitivity reaction)
-=Abscess formation which can appear chronic with pus discharging through sinuses (Fungi's attempt to escape being surround by immune cells) which may contain coloured granules
-Needs surgery - no treatment
e.g. Mycetoma
What is systemic mycoses ?
-From inhalation of spores of dimorphic fungi that have their saprotrophic mould form in the environment and their yeast forms in e.g. the lungs which can invade cells
-most people infected are asymptomatic
-In immunosuppressed people can cause destructive lesions that can be fatal
-Circulating yeast - immune response = inflammation on skin surface
e.g. Histoplasmosis
What is opportunistic fungi?
-Induce disease in individuals with an impaired deficiency in their immune systems
-Lung infection is often asymptomatic but dissemination (spreading) of yeast to the central nervous system can = Fatal meningitis (infection of the meninges, the membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord)
e.g. Candida albicans - cause of thrush (Vulvovaginal Candidiasis)
What is Vulvovaginal Candidiasis?
a yeast infection, is a fungal infection that causes inflammation of the vulva and vagina
symptoms:
Itching, burning, soreness, abnormal vaginal discharge, and external dysuria. The discharge can be thick, white, and clumpy, or it can be watery. Symptoms are often most noticeable right before a menstrual period
Cause: Usually caused by Candida albicans
What are some causes and risk factors of yeast infections?
-Antibiotics
-Oral contraceptives
-Diabetes
-Conditions/medications that weaken the immune system
-Chemotherapy
-Steroid treatment
-Pregnancy