Combined flash cards final
1/330
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
331 Terms
BIFMA
Business and Institutional Furniture Manufacturers Association
creates safety, durability, and sustainability standards for commercial furniture
EPD and HPD
Environmental Products Declaration
Health Product Declaration
EPD focuses on the environmental impact of a product
HPD focuses on human health rather than environmental impact
FloorScore
tests flooring products for indoor air quality (VOC Emission)
FSC
Forest Stewardship Council
certifies that wood products are sourced from responsibly managed forests that meet environmental, social, and economic standards
Green Label Plus
ensures carpet products have low VOC emissions to protect indoor air quality
Green Seal
verifies that products meet strict environmental and human health standards
LEED
leadership in energy and environmental design
a green building rating system used to evaluate and certify the overall sustainability of buildings and interiors
Living Building Challenge
a performance-based certification that requires buildings to operate as regenerative systems, producing their own energy and water while eliminating toxic materials
Scientific Certification Systems
verifies environmental, health, and sustainability claims through testing, audits, and life-cycle assessments
UL Greengaurd
ensures that products have low chemical emissions to protect indoor air quality
WELL Building Standard
measures and improves how buildings support human health, comfort, and well-being
What are properties/advantages of plastic?
inexpensive
durable
scratch resistant
organic forms
weather resistant
What is plastic?
a synthetic polymeric material of the petrochemical, gas, and coal industries which can be molded into any desired shape when heat and pressure are applied
Where do all plastics come from?
the petroleum industry
How do plastic get its strength?
from binders
What are examples of binders?
glass, carbon, boron, and metal fibers
How does plastic get its elasticity?
from plasticisers which gives it its mold abilities
What are examples of Plasticisers?
low-melting solids, organic liquids, camphor, and castor oil
How does plastic get is durability?
from fillers
What are fillers?
small particles that make a plastic more resistant to fire, attack by heat, light, or chemicals, and abrasion
How does plastic get its color?
from pigments
What are pigments?
control hue, shade, and tone
What are the two basic types of plastics?
Thermoplastics and thermosets
What is thermoplastic?
can be reheated and shaped multiple times (recycled)
What is thermoset?
can be heated and shaped once (can’t be recycled)
What is a decorative laminate?
a durable thermoset flat sheeting material used in home and industrial furnishings
What is a popular brand name for decorative laminate?
Formica (FOR - in place of + MICA - mineral used as electrical insulation)
What is high pressure decorative laminate (HPDL)
Made of thin layers of resin-impregnated kraft paper and coated with a veneer of melamine (top layer - transparent film, second layer - decorative layer the color/pattern, bottom layer)
Steps of of making HPDL
impregnating, drying, thermosetting, finishing
Colors and Patterns in Plastic Laminate
multi-colored images and patterns can be silk-screened onto the top layer of paper which is them formed into a laminate sheet
Applications for plastic laminate
Decorative laminate is commonly used for interior millwork to surface kitchen counters tabletops, and cabinetry because of its resistance to stains, scratches, and heat.
It is NOT recommended for areas with high humidity or intense, continuous, direct sunlight
What is the substrate of plastic laminate made of?
plywood, fiberwood, MDF, or particleboard
What remains visible on plastic laminate?
The melamine core on the edge
How do you make translucent plastic laminate with desings?
translucent high-pressure laminate with 3D design coloration using translucent paper with melamine resin
What are the quality standards of plastic laminate?
specifications (European Standard EN438)
anti-bacterial (ISO 22196:2007)
anti-fungal (ASTM G21-09)
low chemical emissions (greenguard)
What is European Standard EN438?
It is the standard that most decorative laminates manufacturers selling to the worldwide market adhere to
What is Anti-Bacterial ISO 22196:2007?
it is important for decorative laminates because these laminates are used as kitchen tops and counter tops, cabinets and table tops that may be in constant contact with food materials and younger children
What is Anti-fungal ASTM G21-09
useful for certain medical applications
Low Chemical Emissions
One of the internationally-acknowledged “Green” certificates for decorative laminates is GREENGAURD.
The GREENGAURD marks are to certify that the products have low chemical emissions.
Chemicals tested include VOCs, formaldehydes and other harmful particles.
What is a solid surface?
a thermoplastic composite sheet material developed by DuPont
What are qualities of Solid Surface Materials?
non-porous
low maintenance
impact resistant
scratch resistant
stain resistant
seamless moldable
Where are solid surfaces used?
curved surfaces, food prep areas, bathrooms, bathroom fixtures, work surfaces, millwork
What are solid surfaces made of?
acrylic polymer, alumina trihydrate, and pigment
What is acrylic polymer?
the plastic component that is a binder that holds everything together and gives it flexibility
Petroleum-based which is why it is considered plastic
What is Alumina Trihydrate (ATH)
the filler which is the bulk of the material.
it gives the solid surface hardness, fire resistance, and a matte stone-like appearance
What are some Pros for solid surfaces?
Durable, recyclable, LEED approved
What is the standard size of solid surface panels?
4’x8’ with 1/4”, 1/2”, 3/4” thickness
What is Resilient Flooring?
functional flooring for spaces where easy maintenance, low cost, and durability are required.
It’s considered medium strength as its not as hard as stone or wood but not as soft as carpet.
What are different types of resilient flooring?
Vinyl, linoleum, cork, rubber, and composites
Where is resilient flooring used?
Areas that require heavy use, easy cleaning, and long service life like commercial and health care facilities
What is Vinyl?
A resilient floor covering composed of binders, fillers, and pigments.
The binder consists of vinyl chloride resins (very toxic for workers) and/or polymers, combined with plasticizers and stabilizers.
What type of flooring is second to carpet in popularity?
Viynl
What is a pro to using viynl flooring?
It is very resilient and hides scratches and scuffs
What are the layers of vinyl floorng?
vinyl compound (core material)
print layer
plastic wear layer
What are examples of materials that vinyl can imitate?
terrazzo, wood grain (lower quality has repeated grain pattern), and woven
What is luxury vinyl tile?
A type of flexible,viynl floor tile and/or plank that has a printed design protected by a durable urethane wear layer.
They are generally more expensive than more common VCT
It’s considered luxury because it has more protective layers, printing quality is better, and backing quality better so it makes it more durable.
What are the different methods of VCT?
adhesive and peel and stick
What is linoleum?
it is composed of oxidized linseed oil, mixed with cork or wood flour, mineral filler and pigments and bonded to a jute or suitable backing.
What are pros to linoleum?
It’s Green
renewable, recyclable, sustainable, durable, hygienic, sanitary, bio-degradable, and flame-resistant
How is linoleum manufactured?
in tiles and sheets of similar dimensions to VCT
What is cork?
a rapidly renewable material that comes from bark that is harvested from oak trees
it is considered rapidly renewable because it is harvested every 9 years, is not cut down, and may live as long as 300 years
Cork flooring has what type of characteristics?
both resilient and solid flooring
What are key points about cork flooring?
it has to be finished and maintained over time
expands and contracts
has good insulation for sound and thermal
it is a green product
What are pros about cork flooring?
it is a natural ‘green’ product
non-rigid so excellent cushioning
insulator of both heat and sound
natural fire and insect repellent
What are cons about cork flooring?
expands with high humidity
fades under direct sunlight
susceptible to scratching so recommended to use for furniture pads
What is rubber flooring?
natural and synthetic rubber is an exceptionally durable flooring surface composed of natural organic elastomer harvested from tropical rubber trees.
can be expensive
comes from the sap of trees
renewable material
What is natural rubber?
rubber trees are ‘tapped’ every 2 days for their latex which is produced for up to 25 years on cultivated plantations
What is synthetic rubber?
It’s called latex that can also be synthetically by polymerization of petroleum extracts.
Neoprene was the first synthetic rubber.
What is the safety performance of rubber flooring?
it is slip resistant (raised textures and natural grip properties)
flame resistant
electrostatically dissipative
manufactured in tiles or roles
It is NOT recommended for kitchens or areas where oil and grease will degrade material
What is the durability of rubber flooring?
it is highly resilient and resistant to indentation, stain resistant, chemical resistant, waterproof, antibacterial, and long lasting
Where is rubber flooring commonly used?
play spaces for children and adults, laboratories, areas with high traffic
What are ESD considerations for rubber flooring?
Floor coverings can be made from a mixture of pre-consumer and postconsumer waste (recycled tires) in the manufacture of recycled rubber tiles
Synthetic rubber flooring will not likely meet environmental or sustainability criteria
Natural rubber flooring contains latex which is not completely hypoallergenic - many people are sensitive to latex products
What are subfloors for resilient flooring?
Flooring tiles and sheet products can be installed over a variety of surfaces: concrete, wood, terrazzo, and even existing vinyl tile
Subfloor must be smooth, clean, level, dry, and free of residual substances
What is screed?
used to level existing concrete or wood floors before installing tile, sheet or rolled surfaces, and carpet
What is a floating floor?
a flooring application that is used when the finished floor needs to be separated from the subfloor to allow for movement
What is a transition in flooring?
resilient flooring products are typically thinner than adjacent materials so consideration must be given to how transitions and edges will be handled (metal transition strips)
Which vinyl flooring type would you recommend for an application that is prone to moisture?
Sheets/rolls
Where would you NOT recommend using natural rubber as flooring?
kitchens and healthcare environments (okay for circulation and play spaces)
True or False: because plastic laminate sheets are thermoset they cannot be formed into curved surfaces.
False, they can be initially formed into curved surfaces but never again
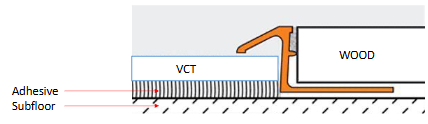
What is this a sectional detail of?
a transition strip that separates vinyl tile from wood
What is tile made from?
clay, stone, concrete, glass, metal, composite
What are specification criteria for tile?
material, formation, surface quality, size, installation
What are the two main types of tile?
ceramic and porcelain
What are ceramic tiles made from?
China clay AKA kaolin and iron
How does clay get its color or orange or brown?
iron
What is the sequence for fabricating ceramic tiles?
batching, forming, drying, glazing, firing
What are the two different ways of forming cermaic?
plastic process of molding/extrusion or dust/dry pressed process
What is wet glaze?
it is applied to dried bisques through spray or screen print methods
What is dry glazing?
involves using powders, crushed frits (glass materials) that melt when fired
How do they add color to ceramic tiles?
pigments are added to wet clay mixture
color is uniformly mixed throughout
What are the two general categories of glazes?
gloss and matte
What are bright glazes?
they have a highly polished surface and reflect an image clearly
What is a satin glaze?
it is produced between the two extremes of reflective and non-reflective surfaces (eggshell, satiny, semi-lustrous sheen)
What is a matte glaze?
a glaze with no sheen
What are the different opacities in glazed surfaces?
clear
transparent
semi-transparent
semi-opaque
opaque
What are the different surface textures in glazed surfaces?
plain
textured
polychrome
mottled
stippled
What is porcelain?
a ceramic tile made of white clay
What is the European definition of porcelain?
they refer to any white or light-colored tile as porcelain, no matter the quality
What are the three different ceramic industries in the US?
ceramic tile
dishware/pottery
sanitary ware
What is the American definition of porcelain?
any high quality tile, regardless of the tile’s color