6.1.2 pattern of inheritance / evolution
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
what does genotype mean?
the Alleles of a organism
what does phenotype mean?
the physical characteristics of a organism
what is a allele?
different version of the same gene
what does the dominant gene mean
gene that’s always expressed ( makes the protein )
what does the recessive gene mean?
only expressed when both genotypes are recessive
how are recessive genotype shown?
aa ( lower case letters)
how are Dominant genotypes shown?
AA ( upper case letters)
what does homozygous mean
2 identical alleles
what does heterozygous mean
2 different alleles
what are the types of genotypes
monogenic
polygenic
what factors affect phenotype
environmental and genotype
what does monogenic mean
1 gene controls characteristics
what does polygenic mean
multiple genes control characteristics
what are the two phenotypic variation in plants
chlorosis
Etiolation
what are the two phenotypic variation in plants caused by
the environment
Chlorosis meaning and what causes it ?
Plants don’t produce enough chlorophyll and turn yellow
Lack of Mg in the soil
Etiolation meaning and what causes it ?
plants grow abnormally long and spindly
due to a lack of sunlight
Codominant definition
both alleles are expressed in a phenotype
Carrier definition
A Organism carrying an allele which is not expressed in the phenotype
Monogenic Punnet square
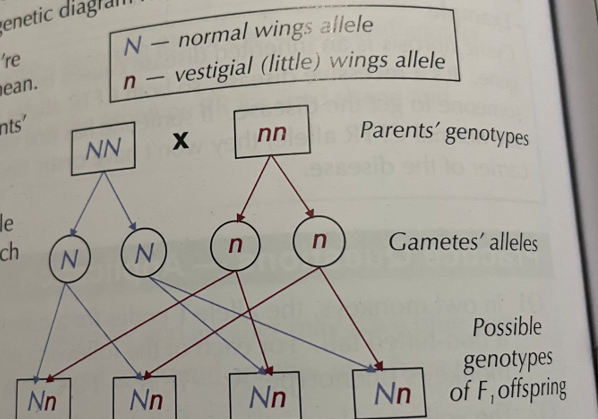
How to complete a punnet square
1) show parents genotype
2) show the gametes
3) times the letter ( FOIL)
4) produce punnet square
what is the usual ratio for Dihybrid crosses between two heterozygous parents
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
how to work out offspring genotype in punnet square
allele x allele ( RY X rY) = RrYY
how to work out gametes in punnet square
FOIL ( first outer inner last)
Dihybrid punnet square image

Explain why observed results don’t match predicted results
sex linkage occurred
what do sex chromosomes in a question mean
there’s sex linkage
what is the superscript in sex chromosomes
the alleles
difference between discontinuous and continuous variations
discontinuous → categorical / qualitive data
continuous → quantitative data
what is discontinuous variation controlled by
1 or few genes
how many genes cause continuous variation
many genes
graph type for discontinuous variation
Bar chart
graph type for continuous variation
Histogram
histogram image
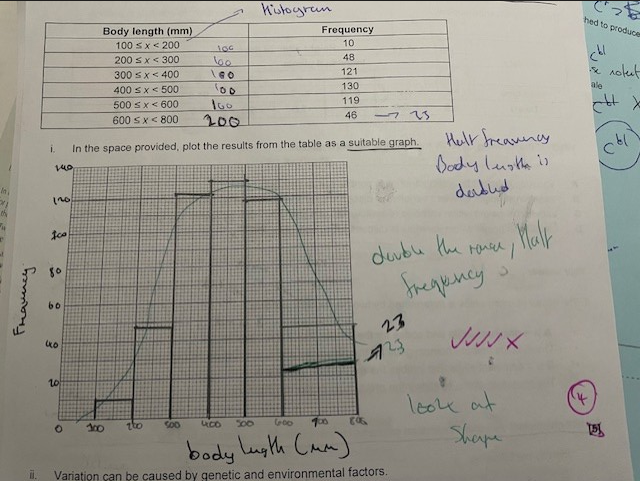
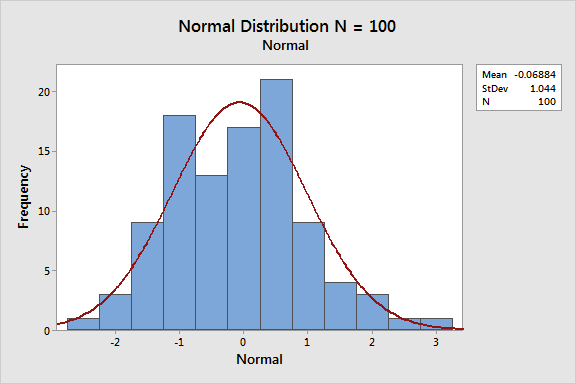
how to know if a graph/ bar chart is affected by environmental factors
Bell curve shape shows normal distribution
bell curve shape ( Image)
what are the sex chromosomes for male and female in mammals
male → XY
female → XX
description of sex chromosomes in mammals
males are heterogametic ( XY)
females are homogametic ( XX)
what does sex linked characteristic mean
alleles that code for them are located on Sex chromosomes
why are males more likely to have X- linked disorders
males have XY chromosomes
1 X chromosome → expressed when recessive
what is autosomal linkage
genes close together are linked so they stay together during independent assortment of chromosomes .
what is epistasis
allele of a gene inhibits the expression of other genes alleles.
when would you use X² test
test the difference between prediction and phenotype
X² square test equation
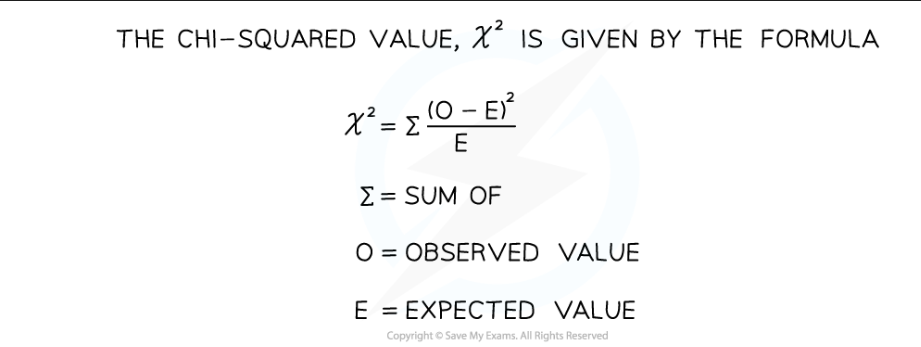
X² square test how to work out expected value
(total number of offspring / ratio total) x predicted ratio
X² square test example image
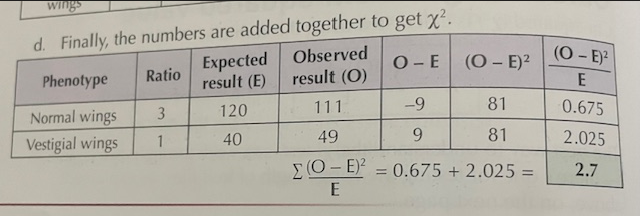
how to work out degrees of freedom in X² square
(number of phenotypes) - 1
when do you accept null hypothesis in X²
Accept null hypothesis when X² is less then critical value shows there no significance difference between expected and observed results
more then 5% probability results are due to chance
when do you reject null hypothesis in X² square
reject null hypothesis when X² value is equal / greater then critical value shows there a significant difference between expected and observed results.
less then 5% probability results are due to chance
gene pool definition
compete range of alleles in a population
allele frequency definition
how often a allele occurs in a population
what does a small gene pool result in
low variation , low allele frequency
what is a selective pressure
something in the environment that gives a specific allele a advantage
Are selective pressures natural or artificially occuring
Both
artificial in selective breeding
what are the types of natural selection
Directional
stabilising
Disruptive
natural selection process
Random mutation in DNA creates a new allele
selective pressure creates struggle for survival
selective pressure selects specific alleles that are advantageous
individuals with allele are more likely to survive and reproduce - pass allele to offspring
over many generations → allele frequency in population increases
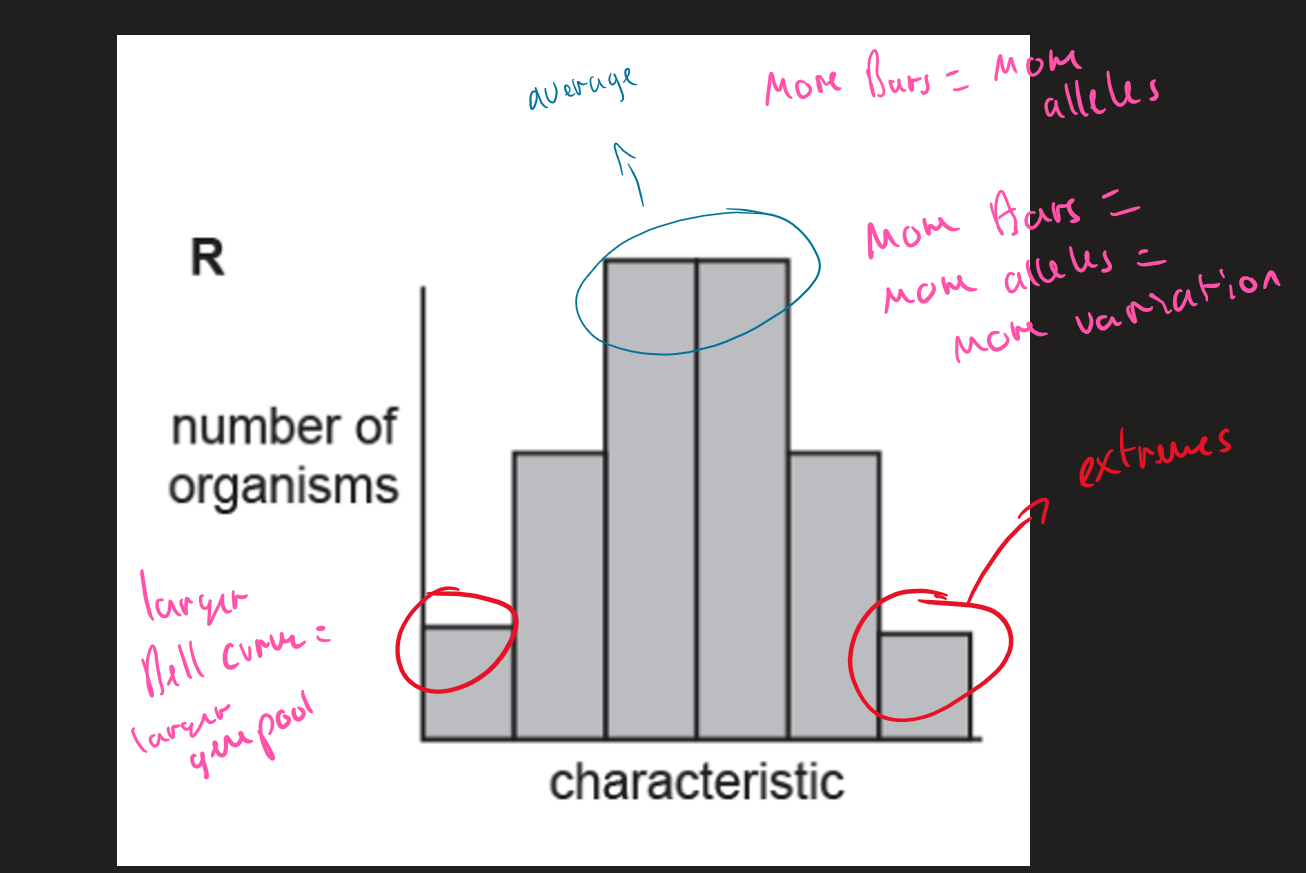
what does a larger bell curve mean on a graph
larger gene pool
Graph ( image)
what is Directional selection
individuals are favoured in one direction
what is disruptive selection
extremes are favoured
what is stabilising selection
average individual favoured
Directional selection image
temperature decreases → longer fur population increases becomes average
moves right
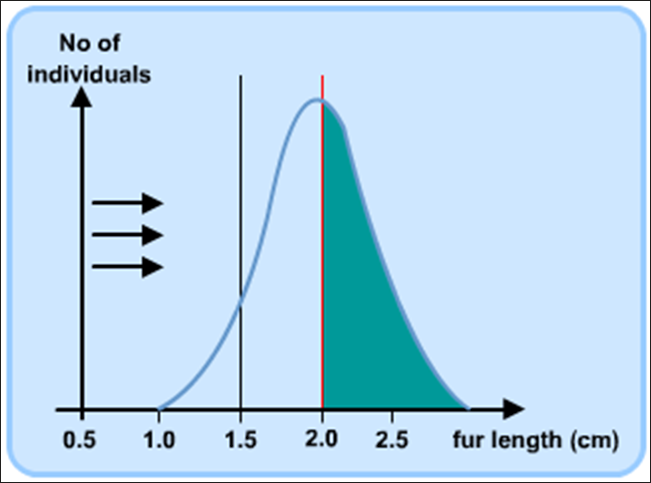
effect of stabilising selection on population ( image)
mean remains the same but fewer extremes
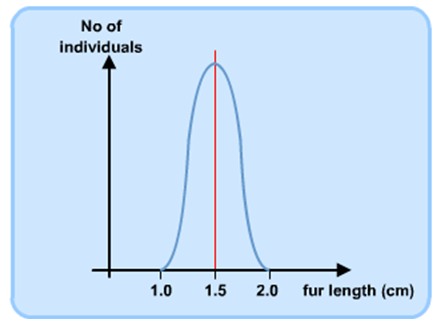
what causes speciation
disruptive selection
what is disruptive selection
natural selection that maintains high frequencies of two different sets of alleles.
what are the ways evolution can occur ?
Natural selection
Genetic drift
genetic bottleneck
what is evolution by Genetic drift ?
particular alleles which are passed down a in population due to chance.
no selection
Genetic drift effect ?
increases allele frequency
Differences Genetic drift and natural selection
genetic drift → no allele selection / due to chance
Genetic bottleneck effect of the gene pool
reduces gene pool
what is Genetic bottleneck?
a event occurs that removes majority of population → small gene pool in survival paper
Genetic bottleneck ( Image)
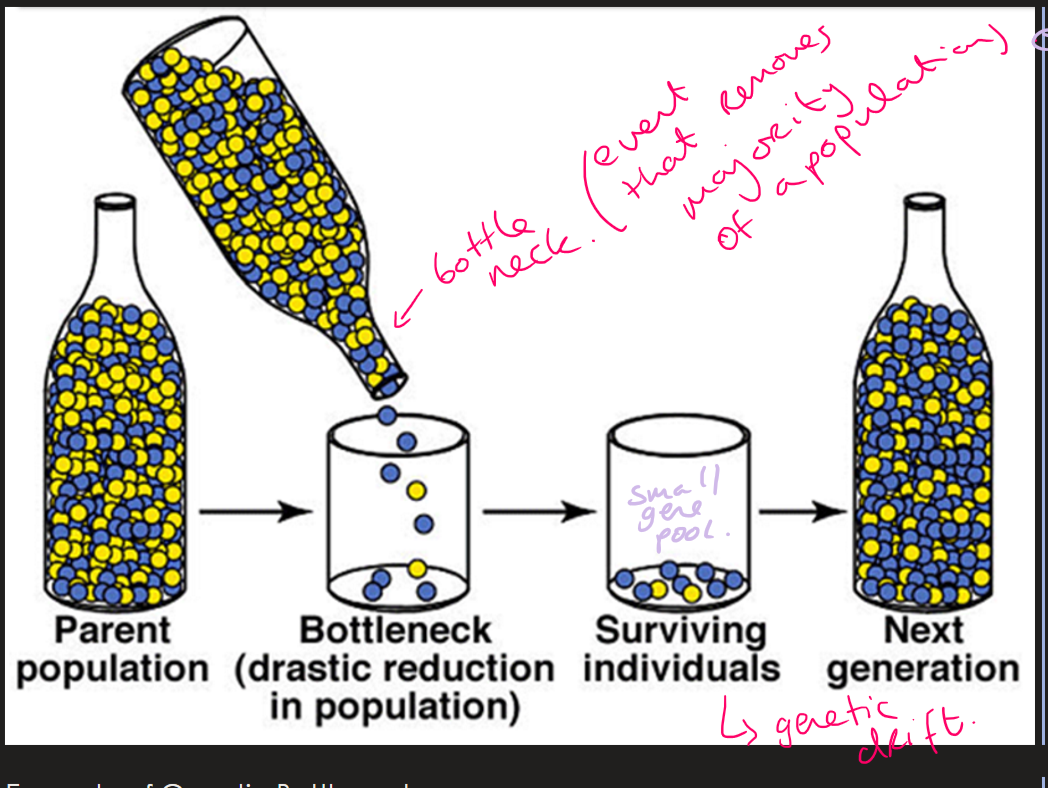
what is the founder effect
post bottleneck founding a new population
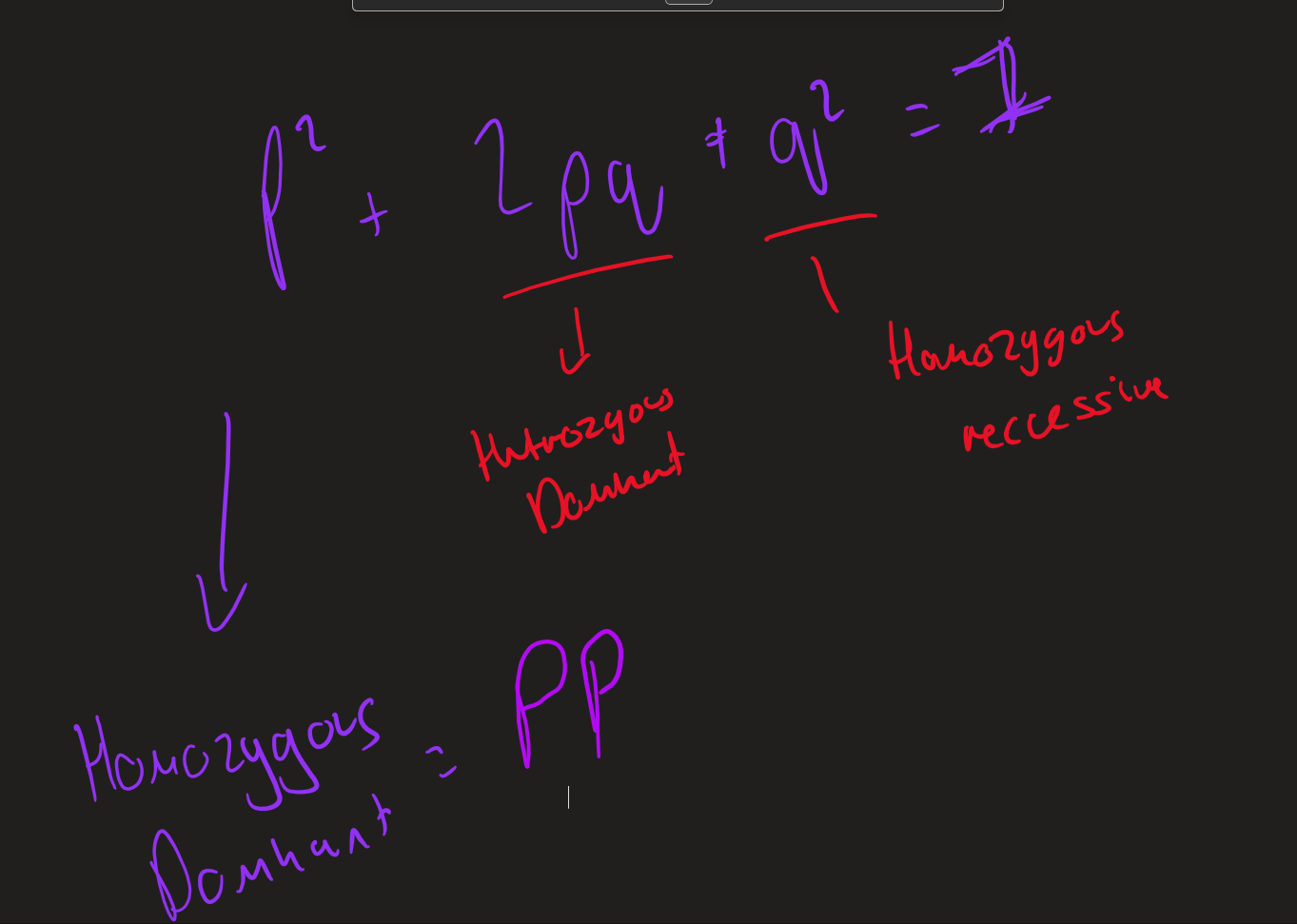
hardy Weinberg equations

when is Hardy Weinberg equation used ?
Predict ratio of Dominant / Recessive allele in population
assumption made when using Hardy Weinberg equation used
no mutations → no new allele
no selection → no allele favoured
random mating
how to improve Hardy Weinberg equation
use a larger sample size → accurate
allele equation Hardy Weinberg
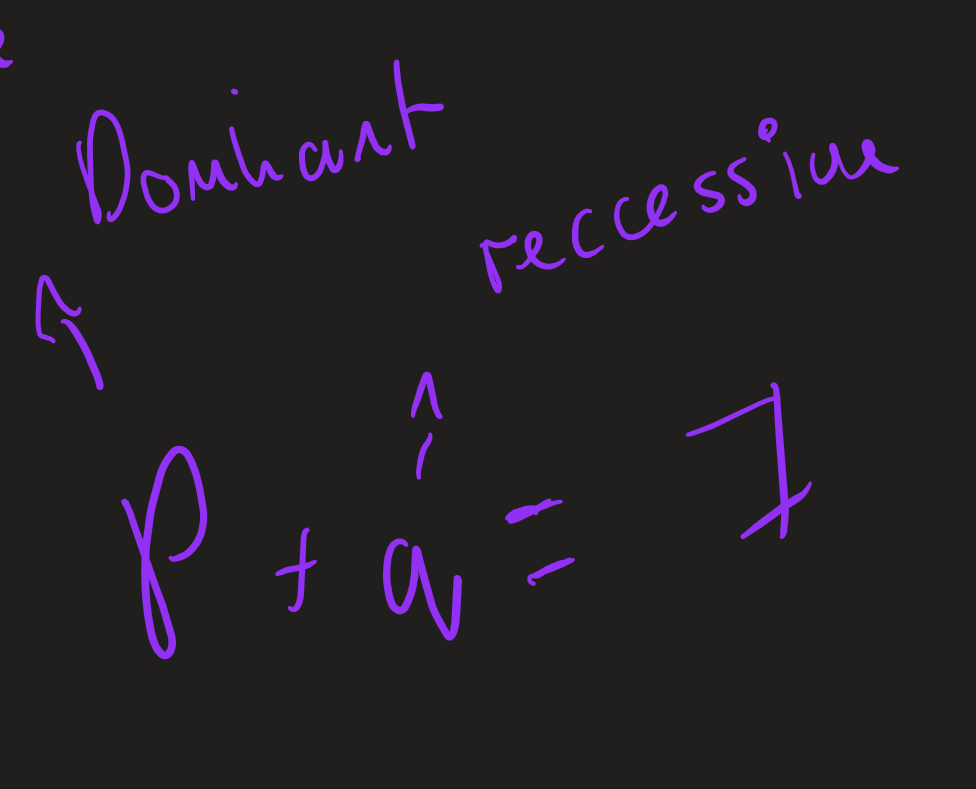
when can Hardy Weinberg equation used
Heterozygous cross
phenotype and genotype Hardy Weinberg