Colour in Transition Metal Ions
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
When are transition metal ions coloured?
Transition metal ions are only coloured when they form complexes.
In a transition metal ion, the d-orbitals have the _____ energy level.
Same.
What happens to the d-orbitals when a transition metal ion forms a complex?
The d-orbitals split into two sets- 3 lower energy and 2 higher energy orbitals.
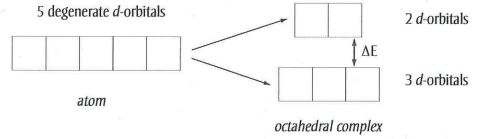
How can an electron in a 3d orbital move from a lower energy set to a higher energy set?
An electron can move from a lower energy level to a higher energy level if it gains sufficient energy.
What happens when visible light is passed through a solution of a complex ion?
Some of the light energy is absorbed which promotes an electron from a lower 3d orbital to a higher 3d orbital.
The energy needed to promote an electron from a lower 3d orbital to a higher 3d orbital corresponds to what?
A frequency of light which is absorbed.
Remember: the frequency of light absorbed corresponds to the energy gap between the orbitals.
The colour of the complex ion seen is made up of what?
The light frequencies which are NOT absorbed, i.e. those that are reflected.
Different ligands can cause…?
Different splitting of the d-orbitals.
As a result, the energy gap between the orbitals is different so different frequencies are absorbed. This gives different colours.
Why do copper (I) and scandium (III) complexes appear colourless?
Copper(I) complexes have an electronic configuration with a full d sub-shell, while Sc3+ ions have an empty d sub-shell, meaning that electrons cannot move from lower to higher orbitals.
Therefore, copper(I) and scandium(III) complexes appear colourless.