Class 14 - Weathering
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
Geomorphology
________ is a sub- discipline of geography concerned with the origin of and processes by which landforms change.
2
New cards
Denudation
________ refers to all exogenic processes working to reduce elevations or relief (i.e., flatten the surface)
1. weathering
2. mass movement
3. erosion
4. transportation
5. deposition
1. weathering
2. mass movement
3. erosion
4. transportation
5. deposition
3
New cards
Limestone
________ is a sedimentary rock that forms in the ocean from shelled marine organisms (i.e., in the ocean)
4
New cards
Chemical weathering
processes that alter rock chemistry, changing it from one mineral state to another, weakening the overall structure of solid rock.
5
New cards
Physical weathering
processes that modify the physical state of rock only, no chemical change.
6
New cards
Exogenic processes
processes that destroy or modify landscapes.
7
New cards
Landforms
the product of endogenic and exogenic processes
8
New cards
Endogenic processes
build ‘initial landscapes (e.g., rock formation, mountain building)
9
New cards
Weathering
refers to processes that physically or chemically alter rock at or near the surface
10
New cards
Physical weathering
processes that __*modify the physical state of rock only*__, no chemical change
* frost action (freeze thaw)
* root wedging (tree roots)
* salt-crystal wedging
* impact from precipitation, abrasion, and rock falls
* pressure-release jointing/exfoliation
* frost action (freeze thaw)
* root wedging (tree roots)
* salt-crystal wedging
* impact from precipitation, abrasion, and rock falls
* pressure-release jointing/exfoliation
11
New cards
Chemical weathering
processes that __*alters rock chemistry, changing it from one mineral state to another*__, weakening the overall structure of solid rock
* __*Dissolution*__ of carbonate minerals by acidic precipitation (dissolution of limestone or the carbonate cement within sedimentary rock)
* __*Hydration*__ of minerals
* Hydrolysis; deconstructs weak silicate minerals to form clay
* __*Oxidation,*__ rusting of iron-bearing minerals in rock
* __*Dissolution*__ of carbonate minerals by acidic precipitation (dissolution of limestone or the carbonate cement within sedimentary rock)
* __*Hydration*__ of minerals
* Hydrolysis; deconstructs weak silicate minerals to form clay
* __*Oxidation,*__ rusting of iron-bearing minerals in rock
12
New cards
Karst topography
* associated with limestone dissolution. Limestone is a sedimentary rock that forms in the ocean from shelled marine organisms (i.e., in the ocean).
13
New cards
Erosion
refers to the translocation of weathered materials by wind, water or ice, driven by gravity and solar energy
14
New cards
Erosion Processes (include driving vs resisting forces)
when driving forces exceed the resisting forces
\
* **Driving forces -** climate, gravity, momentum, slope, tectonics
* **Resisting forces -** friction, inertia, cohesion of particles, vegetation
\
\
* **Driving forces -** climate, gravity, momentum, slope, tectonics
* **Resisting forces -** friction, inertia, cohesion of particles, vegetation
\
15
New cards
Factors influencing weathering processes
* Rock type
* Rock chemistry
* Rock composition
* Rock structure
* Climate
* Sub-surface water
* Slope orientation
* Vegetation
\
\
\- Parent Material: the consolidated bedrock/ unconsolidated rock from which weathered materials originate
\
\- Regolith: the product of weathering. Includes fractured rock, fine sediments, and soil. Susceptible to erosion and transport (because it is not mechanically bound to the parent material)
* Rock chemistry
* Rock composition
* Rock structure
* Climate
* Sub-surface water
* Slope orientation
* Vegetation
\
\
\- Parent Material: the consolidated bedrock/ unconsolidated rock from which weathered materials originate
\
\- Regolith: the product of weathering. Includes fractured rock, fine sediments, and soil. Susceptible to erosion and transport (because it is not mechanically bound to the parent material)
16
New cards
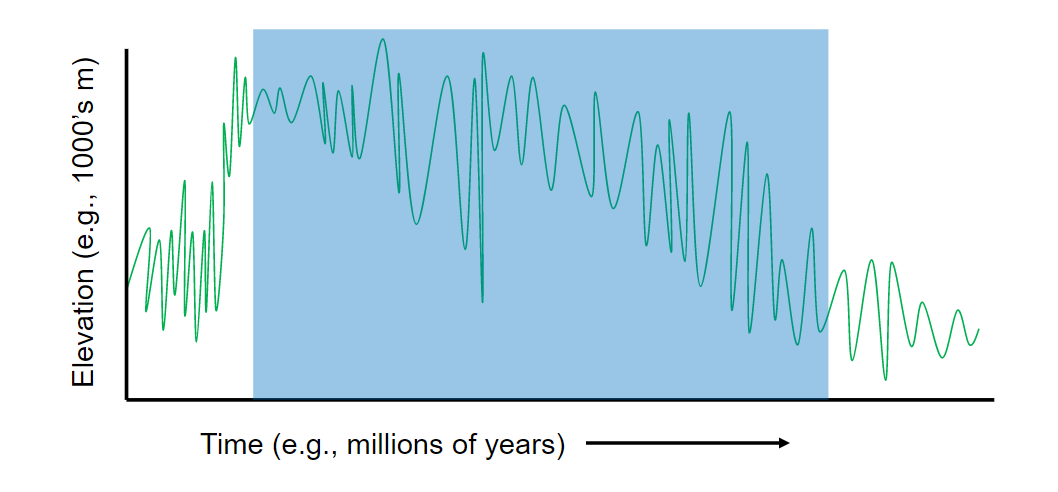
Dynamic Equilibrium Framework
* Phase 1 - little change in elevation, endogenic and exogenic factors are roughly balanced
* Phase 2 - rapid elevation increase where endogenic > exogenic briefly. roughly equal thereafter.
* Phase 3 - Highly variable but lower elevations, exogenic > endogenic factors
* Phase 4 - Stabilizing mean elevation, overall balance between endogenic and exogenic factors
* Phase 2 - rapid elevation increase where endogenic > exogenic briefly. roughly equal thereafter.
* Phase 3 - Highly variable but lower elevations, exogenic > endogenic factors
* Phase 4 - Stabilizing mean elevation, overall balance between endogenic and exogenic factors
17
New cards
Mass Movement
* Type of erosion where massive quantities of earth materials flow downslope under the force of gravity, and in some cases aided by other factors that reduce resisting forces such as cohesion and friction.
* Classes of mass movement, sorted by rate of movement and wetness
* Classes of mass movement, sorted by rate of movement and wetness
18
New cards
6 types of mass movements
* Soil Creep: ***Slow, Dry*** Mass movement
* important in cold regions
* Rock Fall: ***Dry, Fast*** Mass movement
* topples are a type of rock fall, fractured rock that is forward leaning
* Rotational slump/slide: ***mostly dry and not too fast/slow***
* Mass has slumped down and sticks out
* Translational slide: ***Slow and middle of slow/fast***
* Mudflow: ***wet and fast***
* higher water content, reduces friction between sediments and regolith (includes boulders and small clay particles)
* Human-induced ***scarification***: ***leads to slides***
* moves more earth today than all natural processes combined
* important in cold regions
* Rock Fall: ***Dry, Fast*** Mass movement
* topples are a type of rock fall, fractured rock that is forward leaning
* Rotational slump/slide: ***mostly dry and not too fast/slow***
* Mass has slumped down and sticks out
* Translational slide: ***Slow and middle of slow/fast***
* Mudflow: ***wet and fast***
* higher water content, reduces friction between sediments and regolith (includes boulders and small clay particles)
* Human-induced ***scarification***: ***leads to slides***
* moves more earth today than all natural processes combined