CCNA 3 v7 Modules 9 – 12: Optimize, Monitor, and Troubleshoot Networks Exam Answers
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the term used to indicate a variation of delay?
latency
serialization delay
speed mismatch
jitter
jitter
A network engineer performs a ping test and receives a value that shows the time it takes for a packet to travel from a source to a destination device and return. Which term describes the value?
jitter
latency
priority
bandwidth
latency
What role do network devices play in the IntServ QoS model?
Network devices ensure that resources are available before traffic is allowed to be sent by a host through the network.
Network devices provide a best-effort approach to forwarding traffic.
Network devices are configured to service multiple classes of traffic and handle traffic as it may arrive.
Network devices use QoS on a hop-by-hop basis to provide excellent scalability.
Network devices ensure that resources are available before traffic is allowed to be sent by a host through the network.
Which device would be classified as a trusted endpoint?
switch
router
firewall
IP phone
IP phone
What is the benefit of deploying Layer 3 QoS marking across an enterprise network?
Layer 3 marking can carry the QoS information end-to-end.
Layer 3 marking can carry QoS information on switches that are not IP aware.
Layer 3 marking can be carried in the 802.1Q fields.
Layer 3 marking can be used to carry non-IP traffic.
Layer 3 marking can carry the QoS information end-to-end.
What is the function of a QoS trust boundary?
A trust boundary identifies the location where traffic cannot be remarked.
A trust boundary only allows traffic to enter if it has previously been marked.
A trust boundary identifies which devices trust the marking on packets that enter a network.
A trust boundary only allows traffic from trusted endpoints to enter the network.
A trust boundary identifies which devices trust the marking on packets that enter a network.
What are two approaches to prevent packet loss due to congestion on an interface? (Choose two.)
Decrease buffer space.
Disable queuing mechanisms.
Drop lower-priority packets.
Prevent bursts of traffic.
Increase link capacity.
Drop lower-priority packets.
Increase link capacity.
What configuration scenario would offer the most protection to SNMP get and set messages?
SNMPv2 for in-band management with read-write community strings
SNMPv1 with out-of-band management in a private subnet
SNMPv3 configured with the auth security level
SNMP community strings
SNMPv3 configured with the auth security level
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router:
R1# copy running-config tftp
Address or name of remote host [ ]?When the router prompts for an address or remote host name, what IP address should the administrator enter at the prompt?
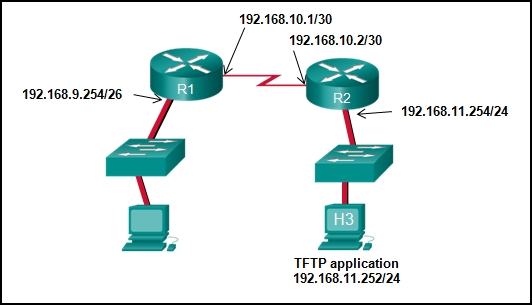
192.168.9.254
192.168.10.2
192.168.11.252
192.168.11.254
192.168.10.1
The command ntp server 10.1.1.1 is issued on a router. What impact does this command have?
determines which server to send system log files to
synchronizes the system clock with the time source with IP address 10.1.1.1
identifies the server on which to store backup configurations
ensures that all logging will have a time stamp associated with it
synchronizes the system clock with the time source with IP address 10.1.1.1
As the network administrator you have been asked to implement EtherChannel on the corporate network. What does this configuration consist of?
providing redundant links that dynamically block or forward traffic
grouping two devices to share a virtual IP address
grouping multiple physical ports to increase bandwidth between two switches
providing redundant devices to allow traffic to flow in the event of device failure
grouping multiple physical ports to increase bandwidth between two switches
What is a definition of a two-tier LAN network design?
access and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the distribution layer on a separate tier
distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier
access, distribution, and core layers collapsed into one tier, with a separate backbone layer
access and distribution layers collapsed into one tier, and the core layer on a separate tier
distribution and core layers collapsed into one tier, and the access layer on a separate tier
What are two reasons to create a network baseline? (Choose two.)
to select a routing protocol
to determine what kind of equipment to implement
to design a network according to a proper model
to identify future abnormal network behavior
to evaluate security vulnerabilities in the network
to determine if the network can deliver the required policies
to identify future abnormal network behavior
to determine if the network can deliver the required policies
A computer can access devices on the same network but cannot access devices on other networks. What is the probable cause of this problem?
The computer has an incorrect subnet mask.
The computer has an invalid default gateway address.
The cable is not connected properly to the NIC.
The computer has an invalid IP address.
In which step of gathering symptoms does the network engineer determine if the problem is at the core, distribution, or access layer of the network?
Gather information.
Narrow the scope.
Document the symptoms.
Determine ownership.
Determine the symptoms.
Narrow the scope.
A network administrator is deploying QoS with the ability to provide a special queue for voice traffic so that voice traffic is forwarded before network traffic in other queues. Which queuing method would be the best choice?
LLQ
CBWFQ
WFQ
FIFO
LLQ
What are two characteristics of voice traffic? (Choose two.)
Voice traffic latency should not exceed 150 ms.
Voice traffic is unpredictable and inconsistent.
Voice traffic requires at least 384 kbs of bandwidth.
Voice traffic consumes lots of network resources.
Dropped voice packets are not retransmitted.
Voice traffic latency should not exceed 150 ms.
Dropped voice packets are not retransmitted.
Which type of network traffic cannot be managed using congestion avoidance tools?
TCP
ICMP
IP
UDP
UDP
When QoS is implemented in a converged network, which two factors can be controlled to improve network performance for real-time traffic? (Choose two.)
delay
packet addressing
jitter
packet routing
link speed
delay
jitter
An administrator wants to replace the configuration file on a Cisco router by loading a new configuration file from a TFTP server. What two things does the administrator need to know before performing this task? (Choose two.)
name of the configuration file that is currently stored on the router
configuration register value
name of the configuration file that is stored on the TFTP server
router IP address
TFTP server IP address
name of the configuration file that is stored on the TFTP server
TFTP server IP address