Language of Medicine Chapter 12
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Respiratory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What part of the brain controls respiration?
The Medulla
External respiration
Exchange of air in lungs and between capillaries
the process of oxygen (O2) moving from the air in the lungs to the blood, and carbon dioxide (CO2) moving from the blood to the air in the lungs.
Internal respiration
Exchange of gases in the cells
the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the body's cells.
Mediastinum
Middle of the chest where trachea divides into two bronchi.
The space outside and between 2 lungs
Hilium of Lung
Blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic tissue and bronchial tubes enter and exit
entrance point for nerves
enter and exit point for lots of tubes, ducts, and vessels
Lungs
Right is larger than left
Right has 3 lobes, left has 2
Bronchi
Bifurcate from trachea. Each bronchus leads to a separate lung
Alveolus
where gas change occurs
Sympathetic nerves
Regulate respiratory/lungs and bronchial dilatation
Respiratory Flow Chart
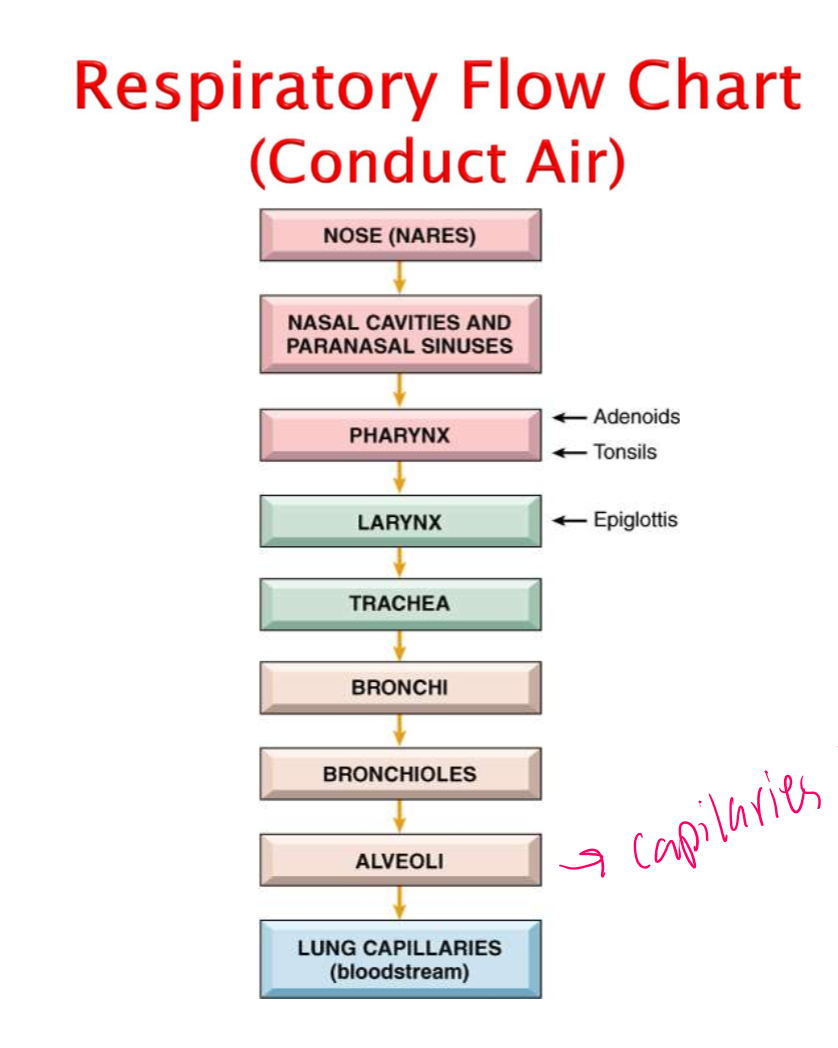
Alveoli
Is the air exchange which are coated with capillaries and pick up oxygen, are the PARENCHYMAL CELLS
Pharynx
Have adenoids and tonsils to fight infections for upper respiratory system
Pulmonary artery
takes low oxygen blood, circulates through lungs and air exchange takes place, converting it to high oxygen blood
BLUE-CARRIES OXYGEN POOR BLOOD FROM HEART TO LUNGS
Pulmonary veins
RED- CARRIES OXYGEN RICH BLOOD FROM LUNGS TO HEART
Apex of Lungs
The top
Hilium of Lungs
The middle
Base of lung
Bottom
POLL EVERYWHERE:
Tubes that bifurcate from the windpipe (trachea) are called
A. Alveoli
B. Sinuses
C. Adenoids
D. Bronchi
D. Bronchi
POLL EVERYWHERE:
Pulmonary parenchymal cells are
A. Trachea
B. Pharynx
C. Alveoli
D. Red Blood Cells
E. Cilia
C. Alveoli
POLL EVERYWHERE:
What is the structure where blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic tissue, and bronchial tubes enter and exit?
A. Base
B.Lobe
C. Apex
D. Hilum
D. Hilum
Diaphragm
Outlines total space in thoracic cavity
Contracts and relaxes, creates negative pressure to allow air to come in
Glottis
Has vocal folds to make sounds
ADBUCTED-OPEN
ADDUCTED-CLOSED
POLL EVERYWHERE:
The opened vocal cords are ____; and the closed are called _____
A. Adducted; Abducted
B. Abducted; Adducted
C. Abducted; Abducted
D. Adducted; Adducted
B. Abducted; Adducted
Epistaxis
Nose bleeding
Diphtheria
Deadly tonsil disease that stops all vital organs
Asthma
combo of genetic and environmental factors by reversible airflow obstruction and bronchospasm
Thickened vessels/duct which makes poor air exchange
Bronchiectasis
Permanent, enlargement of parts of the airway of the lung such as bronchi
Symptom of conditions like pneumonia, tuberculous, cystic fibrosis, etc
makes elasticity lose, and scar tissue makes it rigit and not expanded well
mucus becomes sticky and keeps germ in airway, which causes infection
Cystic Fibrosis
Has bad protein that secretes sticky and thick mucus which enables pulmonary infection
Emphysema
Hyperinflation of air sacs due to loss of elasticity and destruction of alveoli
Narrowing of the small airways and breakdown of lung tissue
KILLS ALVEOLI, HARDER FOR AIR EXCHANGE AND BREATHING
caused by smoking and is irreversible
EXAMPLE OF COPD
Chronic Bronchitis
Inflammation and excess mucus
Bronchial wall size is not enough space for air exchange
same symptoms as emphysema, difficulty breathing and poor air flow
smoking, inhaling cooking smoke, etc and worsens to lung cancer
EXAMPLE OF COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Type of obstructive lung disease characterized by long term breathing problems and poor airflow
Shortness of breath and cough
examples: emphysema and chronic bronchitis
PET Scan
identifies cancerous lung nodules, a radioactive glucose solution is injected into patient through IV
Parietal Pleura
Attached to chest wall
Visceral Pleura
Attached to Lungs
POLL EVERYWHERE:
The pleura that is in direct contact with the lungs is _____
A. Pleural Cavity
B. Parietal Pleura
C. Pleural fluid
D. Visceral Pleura
E. Mediastinum
D. Visceral Pleura
POLL EVERYWHERE:
The pleura that is in direct contact with the chest wall is _____
A. Pleural Cavity
B. Parietal Pleura
C. Pleural fluid
D. Visceral Pleura
E. Mediastinum
B. Parietal Pleura
Pleural Cavity
Space that retains small volume of fluid (creates negative pressure, lungs cannot attach to wall if pressure is broken
Atelectasis
Collapse or closure of the lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange, where alveoli are deflated
Obstruction, pulmonary effusion and pneumothorax
Obstruction
Can be heavy mucus, lego, etc that prevents airflow in lung and collpses (atelectasis)
Pneumothorax
Air outside lung and in the plural cavity- trapped outside lung and in between chest wall
Pulmonary Effusion
Fluid in the plural cavity
Can be caused by pulmonary edema or by pus (pyothorax)
Pneumoconiosis
Means Black Lungs
Occupational lung disease such as working in mines, breathing in dust, etc
POLL EVERYWHERE:
The term describing collapsed lung is _____________
A. Pneumoconiosis
B. Bronchiectasis
C. Emphysema
D. Atelectasis
E. Mesothelioma
D. Atelectasis
POLL EVERYWHERE:
Air or gas in the pleural cavity shall be named __________
A. Pneumoconiosis
B. Bronchiectasis
C. Pneumothorax
D. Emphysema
E. Pleural Effusion
C. Pneumothorax
POLL EVERYWHERE:
Fluid or liquid in the pleural cavity shall be named __________
A. Pneumoconiosis
B. Bronchiectasis
C. Pneumothorax
D. Emphysema
E. Pleural Effusion
E. Pleural Effusion
POLL EVERYWHERE:
Black lung should be named:
A. Pneumoconiosis
B. Bronchiectasis
C. Pneumothorax
D. Emphysema
E. Pleural Effusion
A. Pneumoconiosis
POLL EVERYWHERE:
The term describing a collapsed lung is _______
A. Pneumoconiosis
B. Bronchiectasis
C.Emphysema
D.Atelectasis
E. Mesothelioma
D.Atelectasis