Mitosis and Meiosis- Brennan H
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Somatic cells are diploid cells because their chromosomes are in ____________.
pairs
Somatic cells undergo ________ instead of meiosis.
mitosis
Gametes are sex cells and undergo ___________.
meiosis
Somatic cell division results in an increase of __________ cells for growth and repair.
body
Pairs of chromosomes are called ____________ ______________.
homologous chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes have a maternal and paternal chromosome of the same _________.
number
DNA is in the form of _________ when the cell is not dividing or preparing to divide.
chromatin
DNA is packaged by _____________.
proteins
A chromosome is essentially made of one long strand of ___________.
DNA
Before DNA replication, chromosomes have __ chromatid.
1
A _________ is the region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach which is connected to the mitotic spindle.
centromere
A cell undergoes DNA replication in _____________.
interphase
The backbone of a DNA strand is made up of _____________ bonds.
covalent
The bases in a strand of DNA are connected by _______________ bonds.
hydrogen
Adenine goes with ___________.
Thymine
Cytosine goes with _____________.
guanine
DNA replication is _______ ____________ because each new strand of DNA contains one of the older ones
semi conservative
Helicase is an enzyme that separates the two strands of DNA, breaking the _________ bonds.
hydrogen
________ ________.is an enzyme that adds RNA primers to guide DNA polymerase to have a place to start
RNA primase
In the ___________ strand, DNA polymerase can have a continuous build
leading
The _____________ strand requires multiple primers for DNA polymerase and forms okazaki fragments.
lagging
Replication occurs in the ___ to ____ direction.
5' to 3'
Okazaki fragments are fragments of DNA which are spliced together by ________________.
ligase
A cell in _______________shows a distinct nucleus and an absence of chromosomes.
interphase
A cell in ___________ has visible chromosomes, the nucleus and nuclear envelope disappear, and the mitotic spindle forms.
prophase
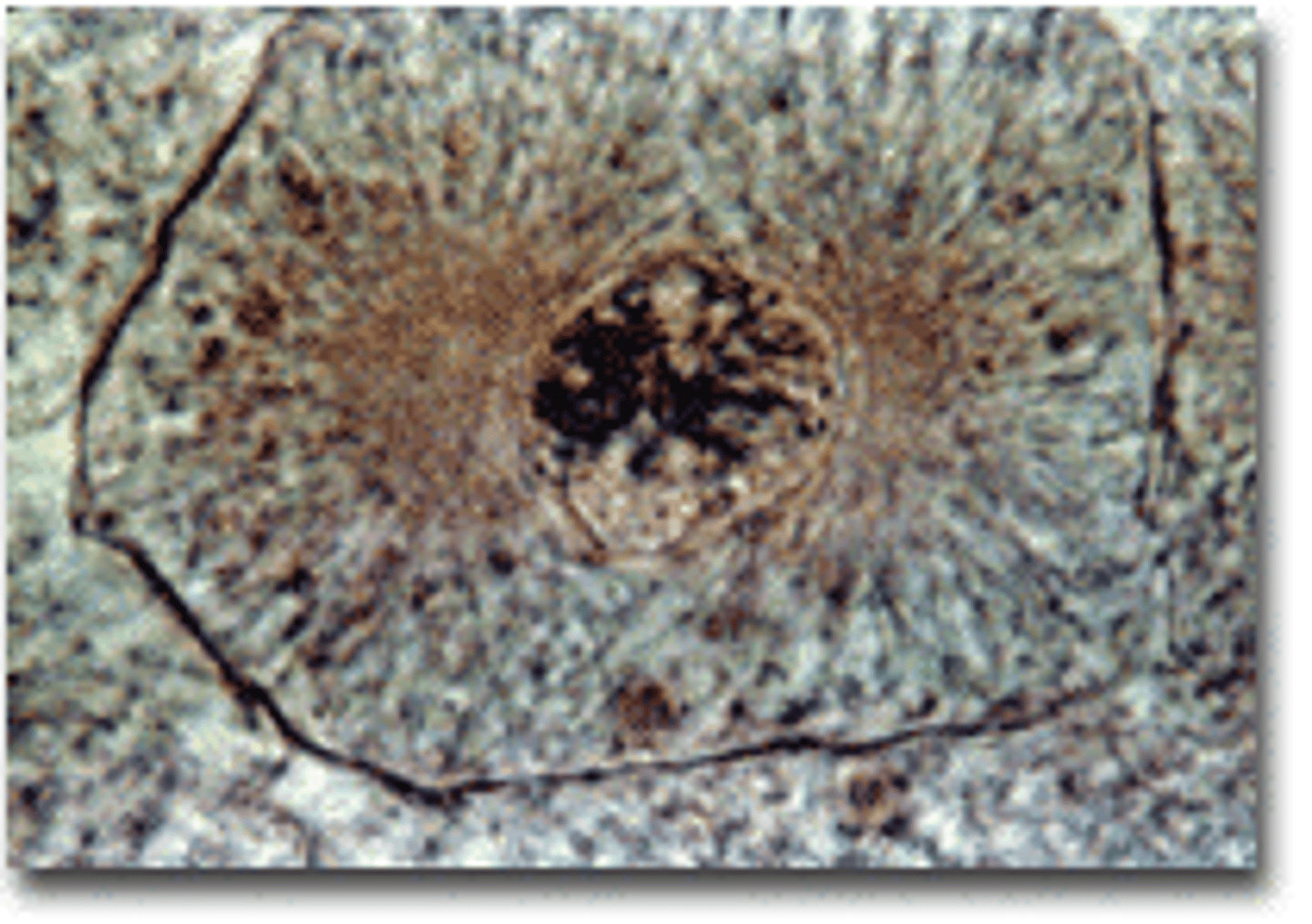
A cell in _____________ will have chromosomes lined up single file in the center of the cell.
metaphase
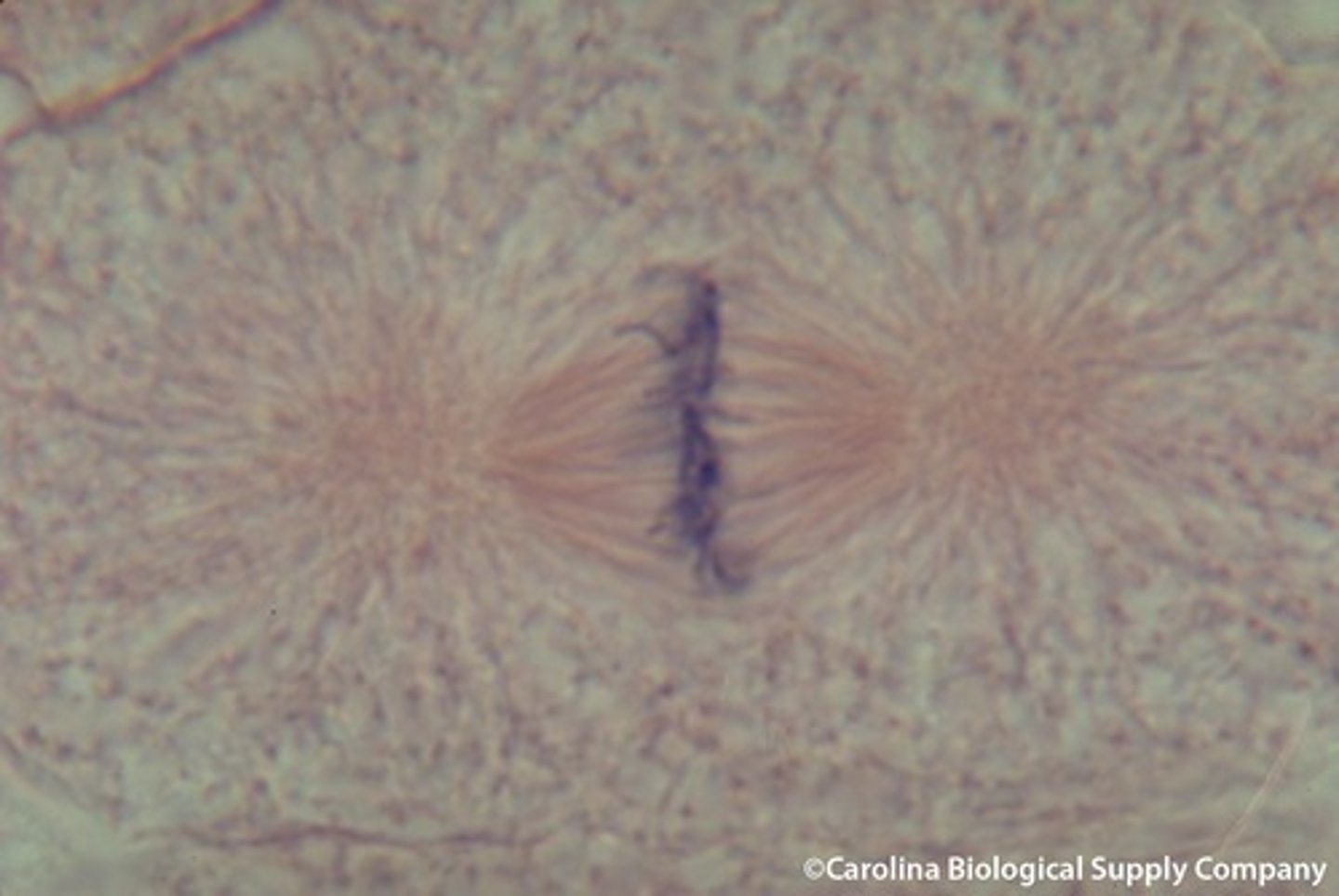
A cell in ___________ is characterized by the splitting of centromeres and the movement of the two sister chromatids to the opposite sides of the cell.
anaphase
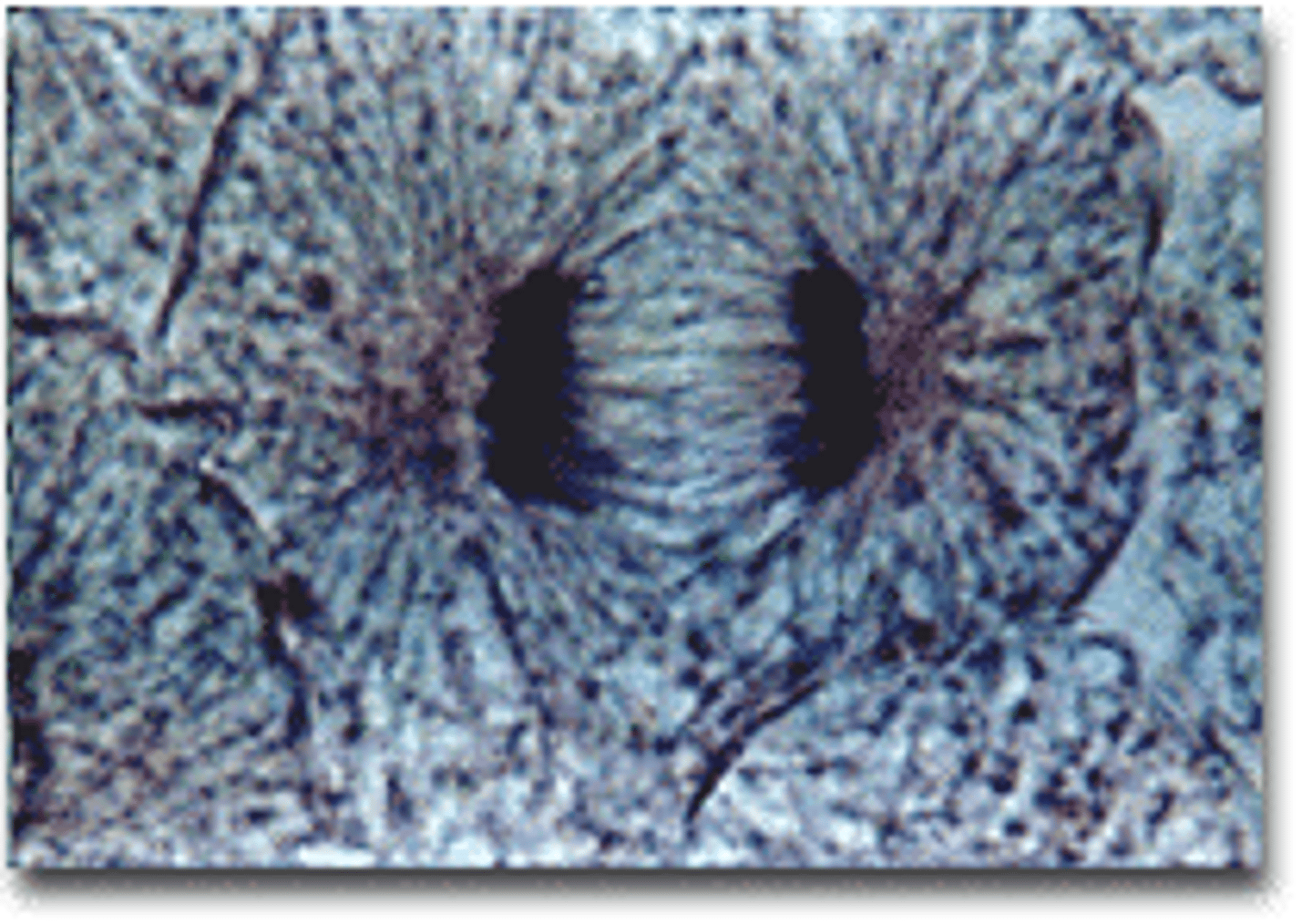
________ is the division of a parent cell's cytoplasm and organelles.
cytokinesis
A cell in ____________ will begin to form a new nucleus and have a larger cleavage furrow.
telophase
Instead of a cleavage furrow, a plant cell will develop a _______ ________ during telophase
cell plate
In sexual reproduction, the offspring will have __________.
variation
Gametes are __________, meaning their chromosomes are not in pairs.
haploid
A _________ is the result of fertilization when a haploid sperm and haploid egg come together. They WILL have chromosomes in pairs.
zygote
The location of a gene on a chromosomes is the ____________. They are at the same spot in homologus chromosomes.
locus
Reproductive cell division produces _____________.
gametes
In prophase 1 , homologous chromosomes undergo __________ and paired chromosomes undergo _________ _________.
synapsis, crossing over.
_________, pairs of 4 chromosomes form during prophase 1.
tetrads
During ____________ __ tetrads line up and chromosomes undergo independent assortment.
metaphase 1
During metaphase 1, Each pair of chromosomes can line up independent to the other pairs. This is called ________ __________.In humans, there are more than 8 million possibilities
independent assortment
At the end of Meiosis 1, cells are ____________.
haploid
______ chromosomes are present in one human gamete with 46 chromatids
23
_____________ is the time between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
Interkinesis
Meiosis 2 follows Meiosis 1 without __________ _________________
DNA replication
Prophase 2 is normal except for ____________.
synapsis
After Telophase 2, ____ cells are made.
4
After Telophase 2, 23 ____________ are present with ONE chromatid
chromosomes
After meiosis, chromosome number is _____________.
halved
Meisosis introduces genetic ___________.
variability
A ____________ is the failure of chromosomes or chromatids to separate
nondisjunction
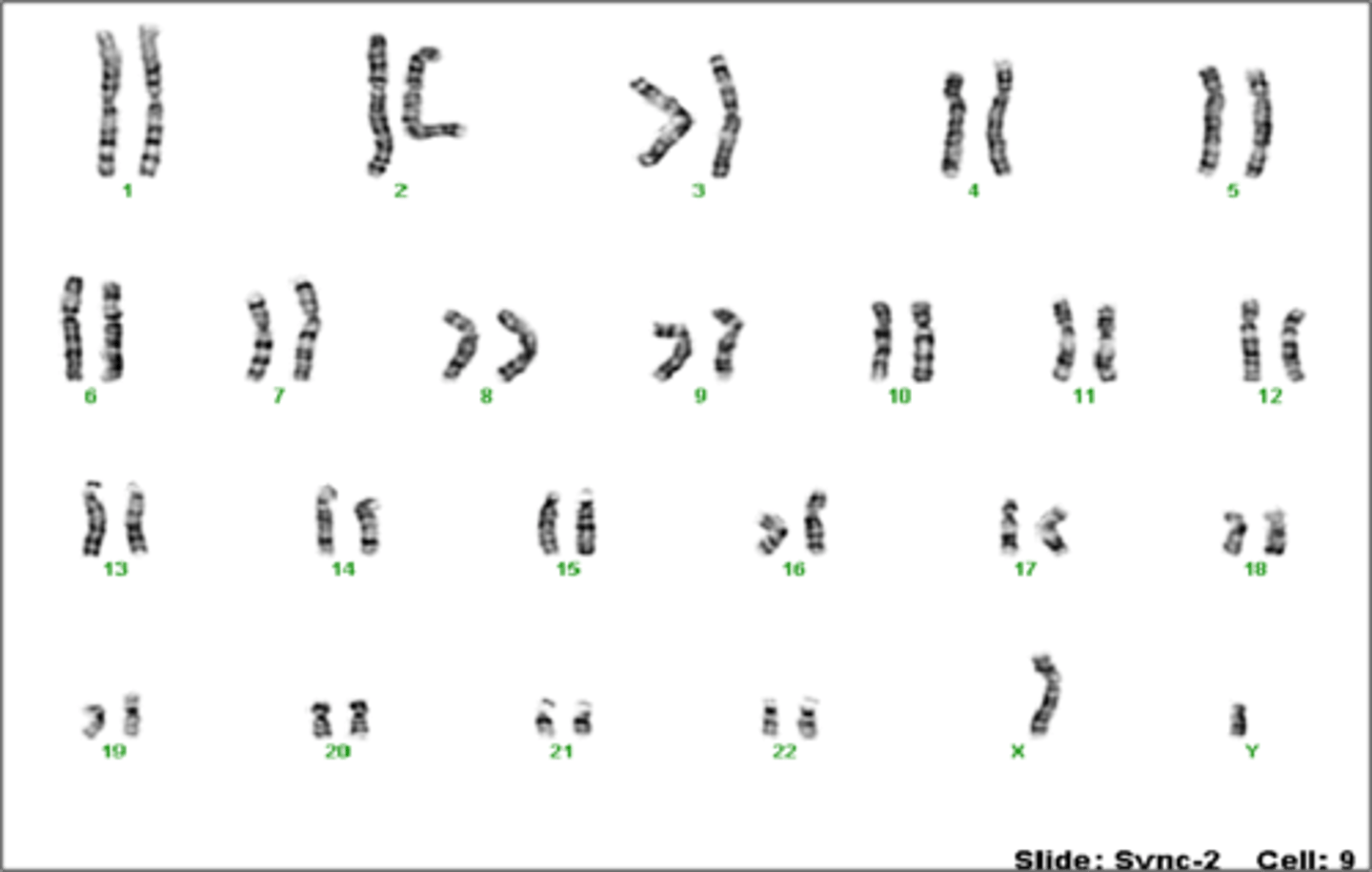
In this karyotype, the baby's gender is _______.
male
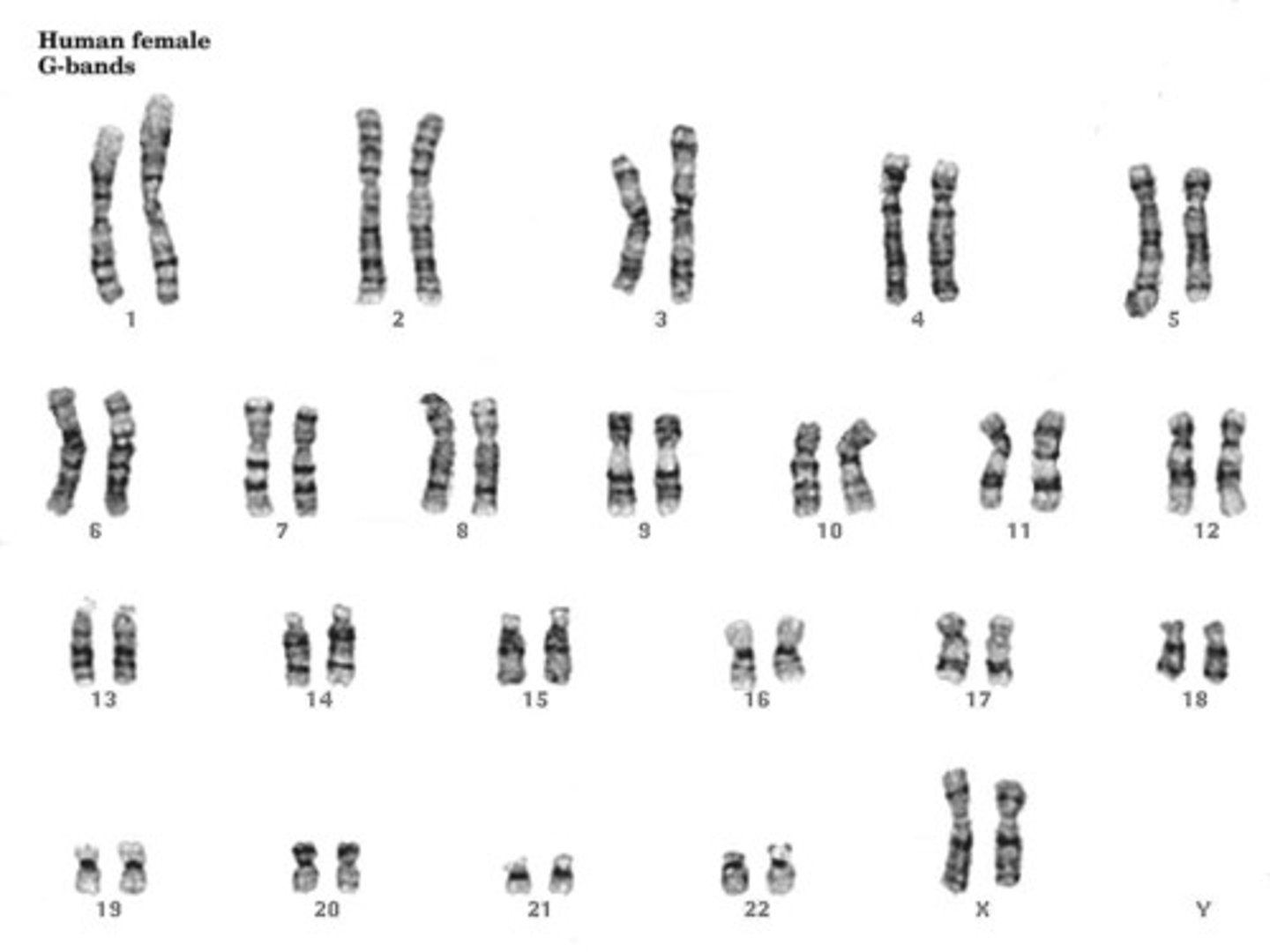
In this karyotype, the baby's gender is __________.
female
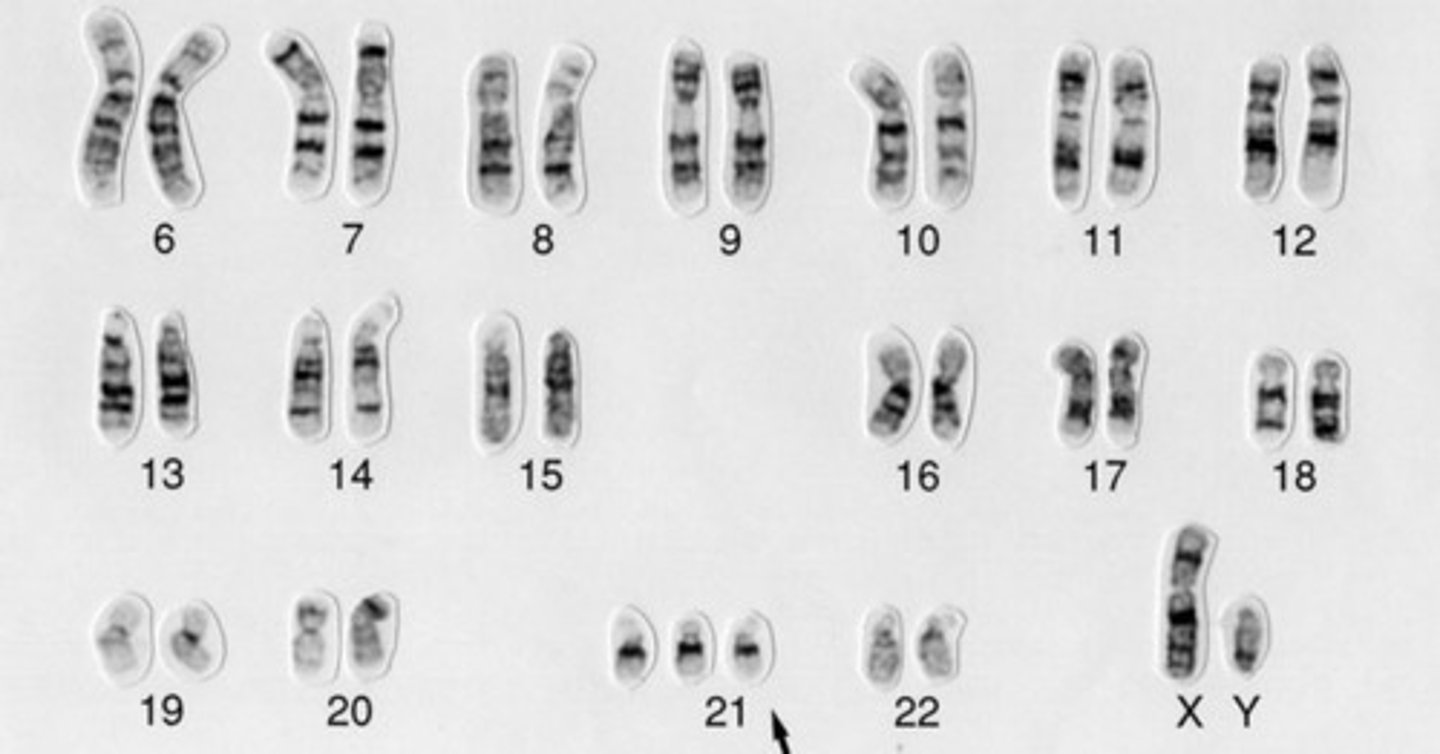
In this karyotype, the baby has a _________ in chromosome 21.
trisomy