L5- Citric acid cycle and amino acid catabolism
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What can pyruvate be broken down into
Pyruvate → Acetyl CoA
What can fatty acids be broken down into
fatty acids → Acetyl CoA
What can amino acids be broken down into
Can be broken down into pyruvate or Acetyl CoA
Whys is Acetyl CoA important
important fuel
combines with a 4 carbon compound to make a 6 carbon compound
which then gradually broken down in citric acid cycle through series of redox reactions forming CO2, and many reduced Co enzymes to be used in OP
also have a substrate level phosphorylation (can produce ATP or GTP depending on cell type)
What is the link reaction
conversion of Pyruvate into Acetyl CoA (links glycolysis to aerobic metabilsm)
Enzyme that does this si Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Produces → Co2 and NADH
the reaction is irreversible - Humans do not have the enzymes to do the backward reaction
What type of reaction is the link reaction
Oxidative decarboxylation reaction - very exothermic reaction
What happens in state of starvation to link reaction
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is inhibited
This is because low amount if glucose don’t want to be using ti on reactions we don’t need and reaction is irreversible so cannot get it back
In citric acid cycle where are most of the enzymes
in Matrix
EXCEPT FOR Succinate dehydrogenase which is in inner mitochondria membrane of ETC
its a different way to enter the ETC
Citric acid cycle
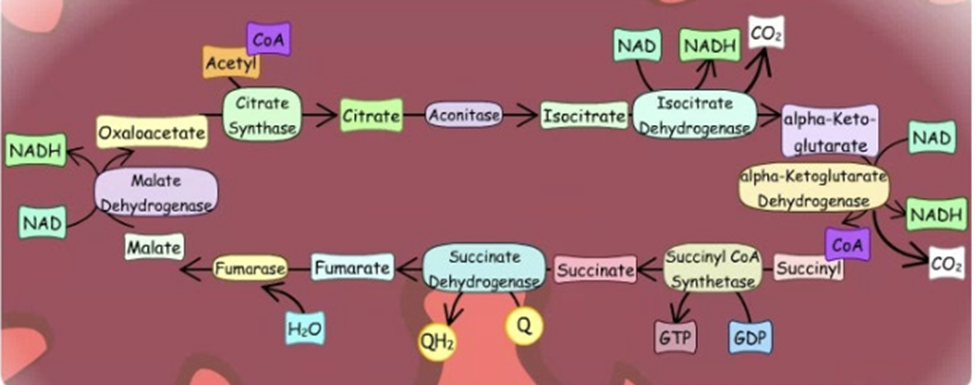
What else is refered to as complex 2
Succinate dehydrogenase but does not follow on form Complex 1
So complex 1 and 2 produce something that can be used by complex 3
Does complex 2 generate energy to pump protons
NO does not pump our protons
When using succinate instead of NADH what do we end up with
only 6 protons being pumped
still get ½ O2 produced at end
has a lower P:O ratio as less ATP’s overall being made
In combination with the electron transport chain (which requires O2), the oxidative catabolism of 1 mole of acetyl CoA produces…
more than 10 moles of ATP
what does citric acid cycle rely on
ETC as only way to getr NADH → NAD and reduced CoQ back to CoQ
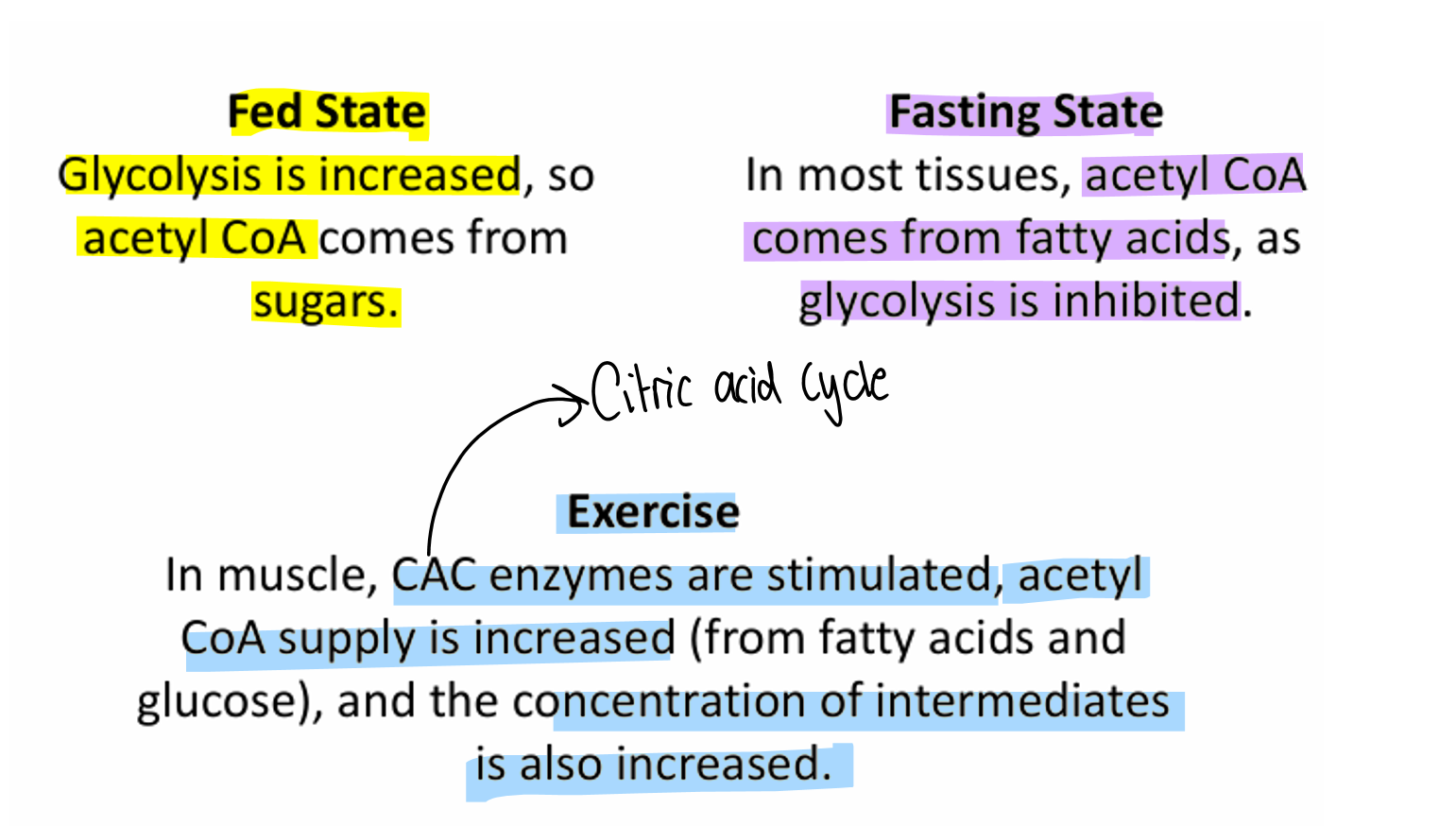
Regulation of Citric acid cycle
usually rate doese’t really change - not effected by fed or fasting state
if cell is using more energy than citric acid cycle increases
this is done by:
increasing activity of enxymes main ones ( Citrate synthase, isolactase dehydrigenase, alpha ketoglutamate dehydrigenase)
Icrease supply of Acetly CoA
Increase supply of intermediateds e.g. Oxolactetae or Alpha keto glutamate
Acetyl Co A sources in different states
What group is removed in amino acid catabolism
amine group
N is waste product urea which is excreted in urine
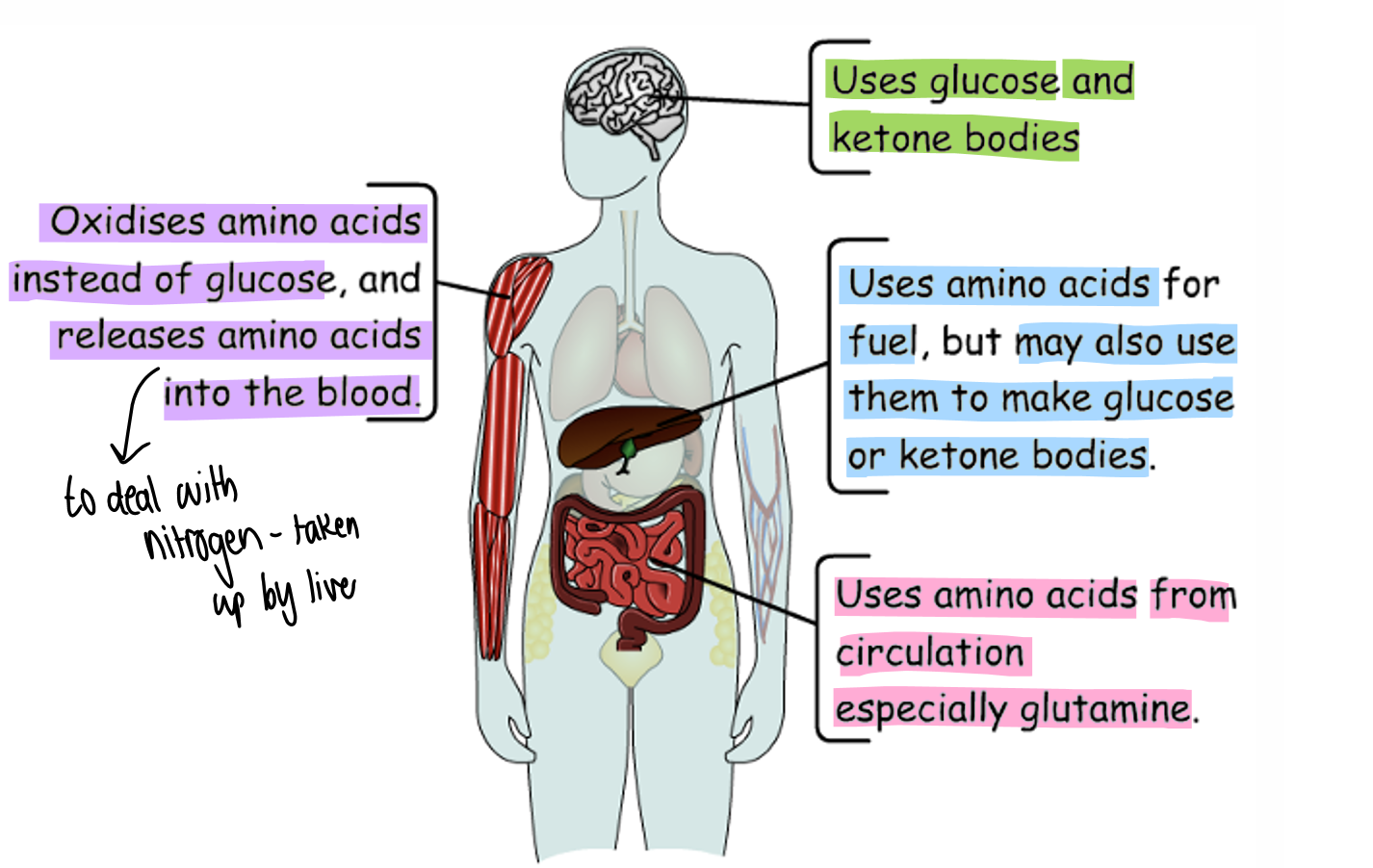
Amino acid catabolism in tissue
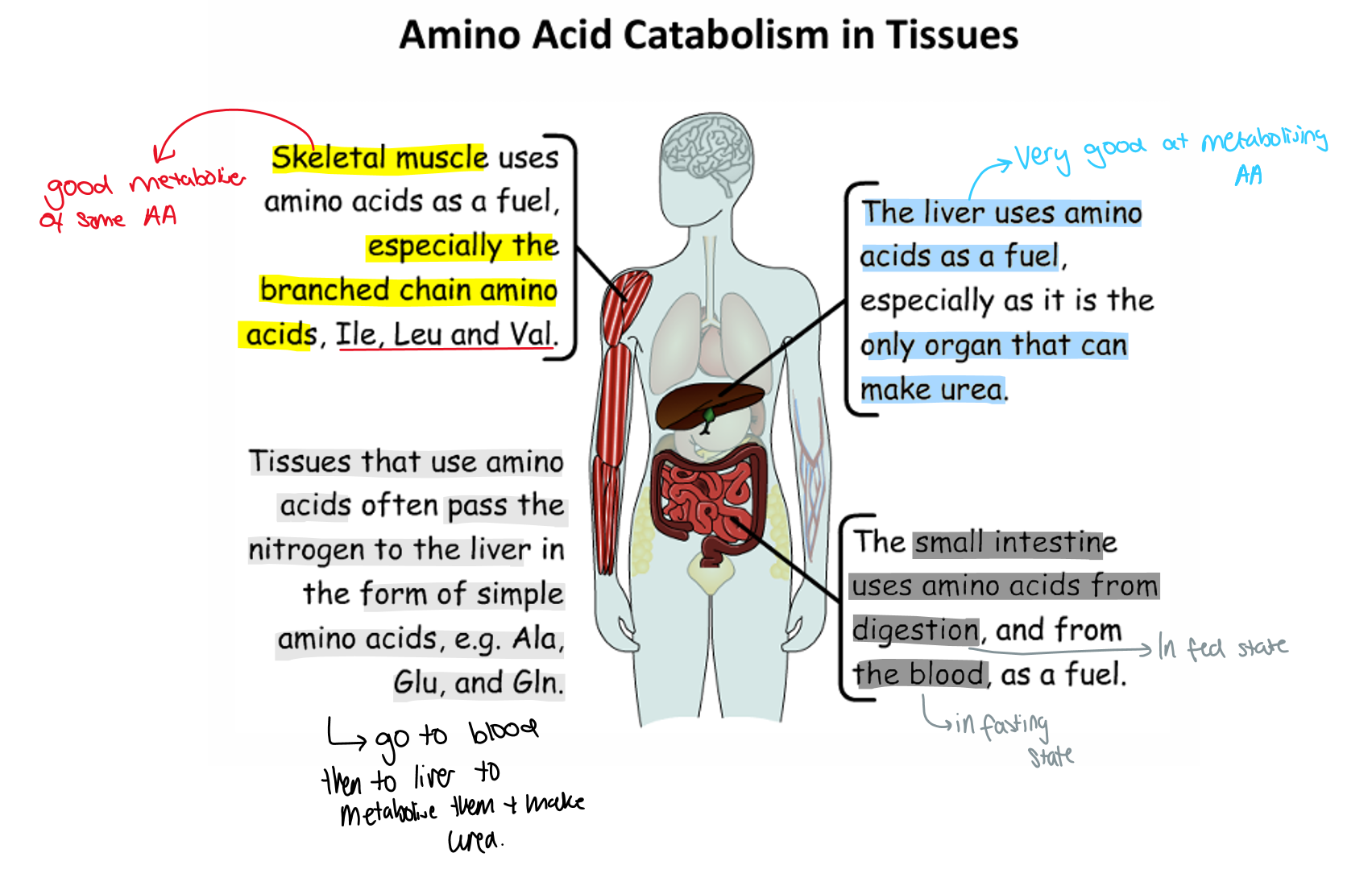
How many ways are there to break down amino acids
3
First way
Alanine → pyruvate
transfers N to alpha - keto glutarate to make glutamate through enzyme amino transferase
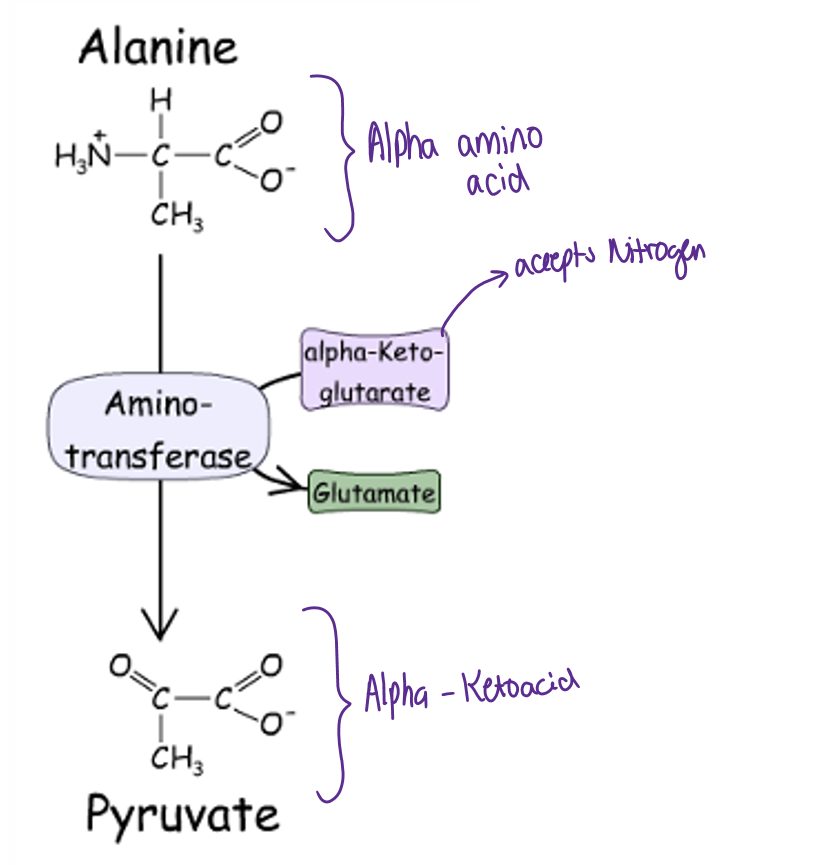
2nd way
Glutamate back to apha keto glutaminate through glutamate dehydrigenase
N lost as ammonia
Get glutamate converted into a citric acid cycle intermediate – lots of amino acids when broken down from various citric acid intermediates
Third way
broken down to form Acetyl CoA
These amino acids that can do this are called ketogenic
This is because they can be used to make ketones
what are amino acids that are broken down to form pyruvate or CAC intermediates called
-called glucogenic because can be used to make glucose
Does amino acid catabolism occur in the fed state:
- Yes because in a meal tend to eat more amino acids than we require for protein synthesis
- High levels of amino acids in blood can be harmful so want to remove them
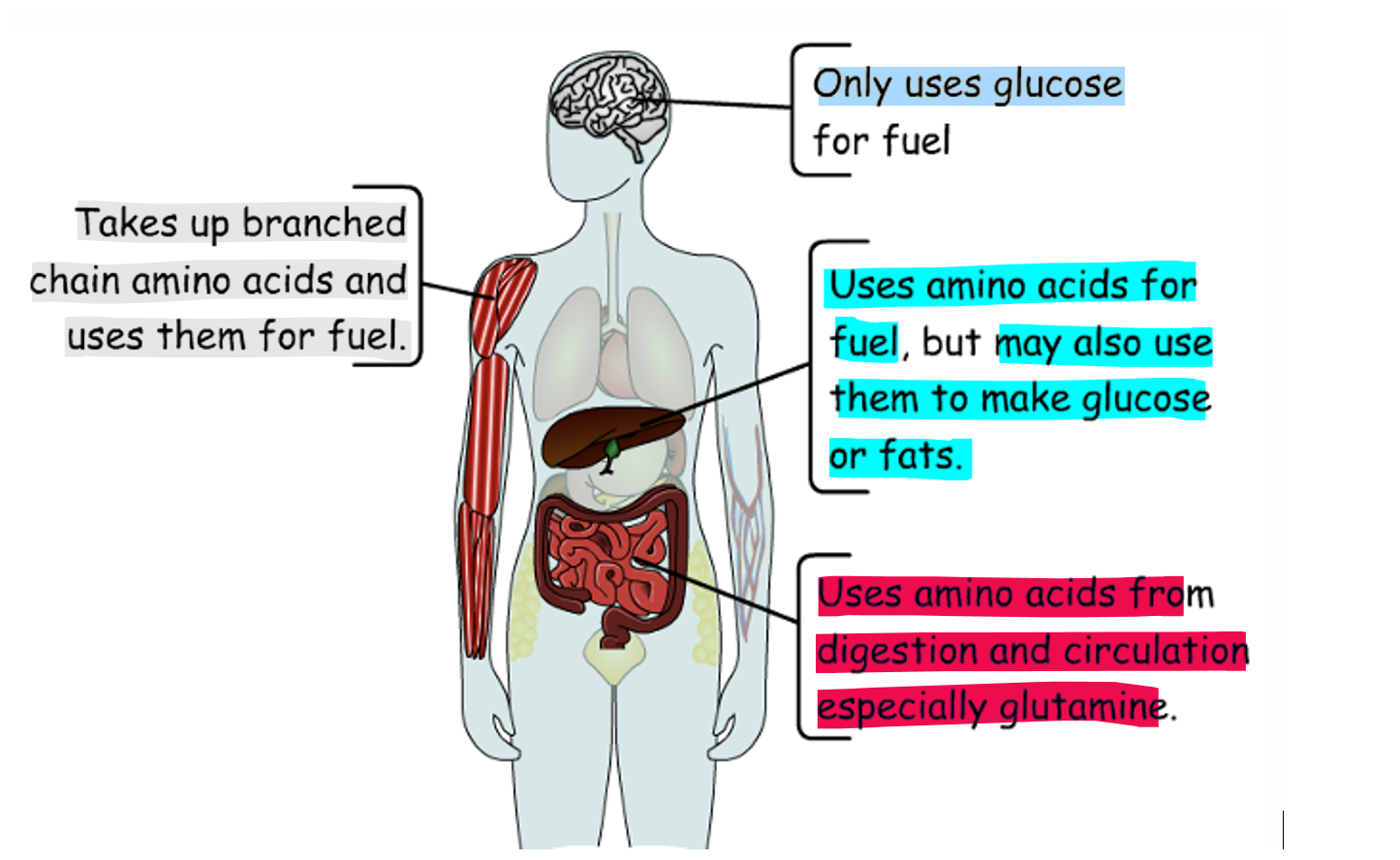
Amino acid metabolism in stavation
- In starvation increased metabolism of amino acids as want to avoid using up all the glucose that we have