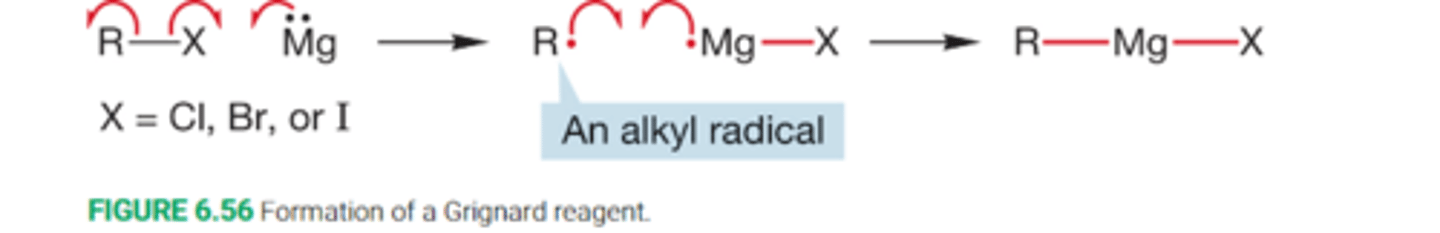Chemistry Chapter 6: Substituted Alkanes
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
6.2 Nomenclature of Substituted Alkanes
Define Alkyl halide
Compounds of the formula CnH2n+1X, where x is F, Cl, Br, or I
What are haloforms
CH3X
What are vinyl halides
H2C--CHX
What are allyl halides
H2C--CH-CH2X
What's important to note about primary, secondary, and tertiary carbons
It's important to note that primary, secondary, and tertiary carbons are all sp3 hybridized
We never refer to a vinyl carbon, a carbon part of a double bond, as being primary, secondary, or tertiary
How do we name alcohol
Find the longest carbon chain that includes the carbon attached to the alcohol
Drop the "e" in the parent name and adding the suffix "ol"
Giving the OH group the lowest possible number because ti has priority
Labeling all other substituents in the prefix alphabetically
Allyl alcohol
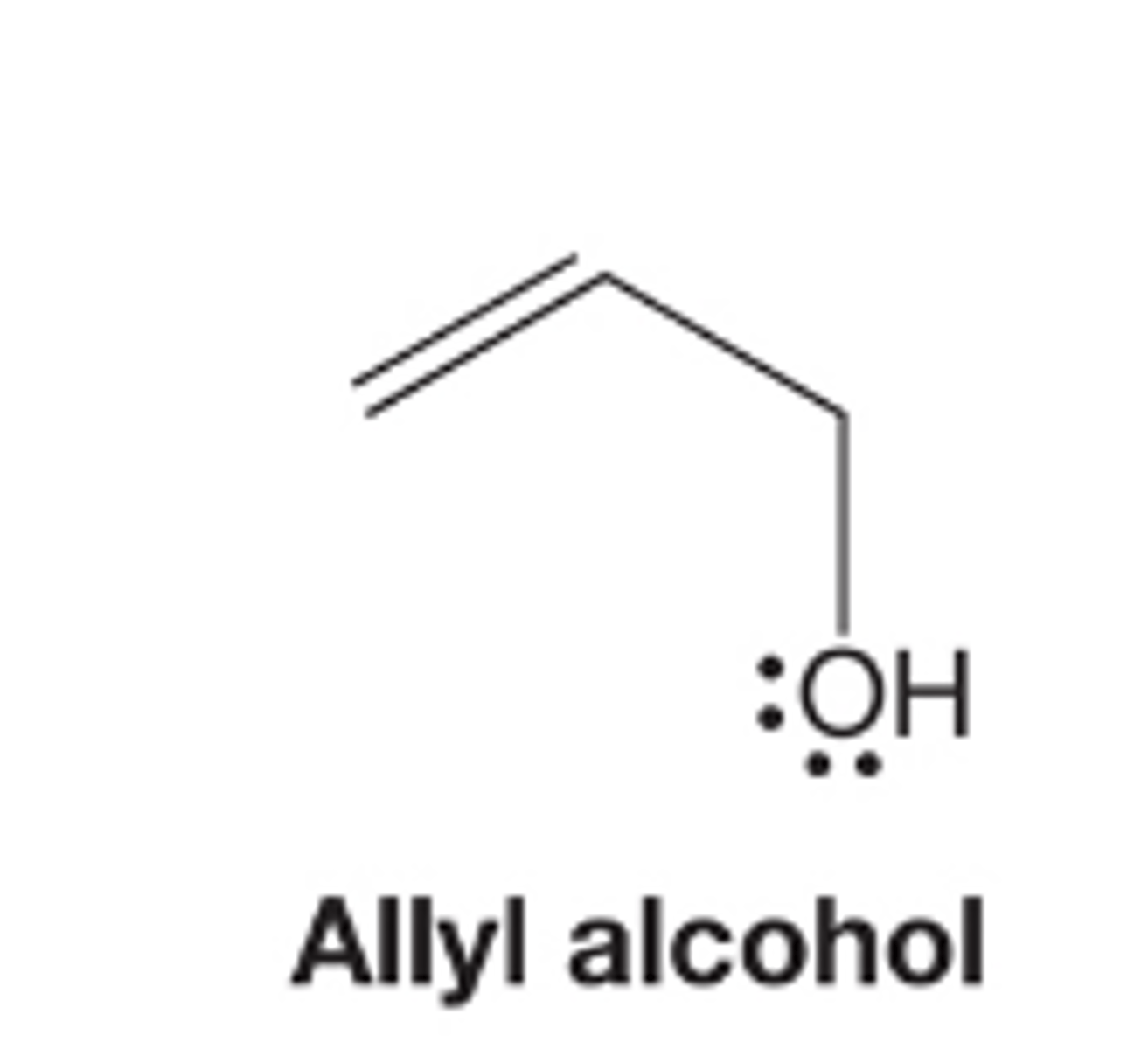
trans-Crotyl alcohol
Benzyl Alcohol
Phenol
Amyl Alcohol
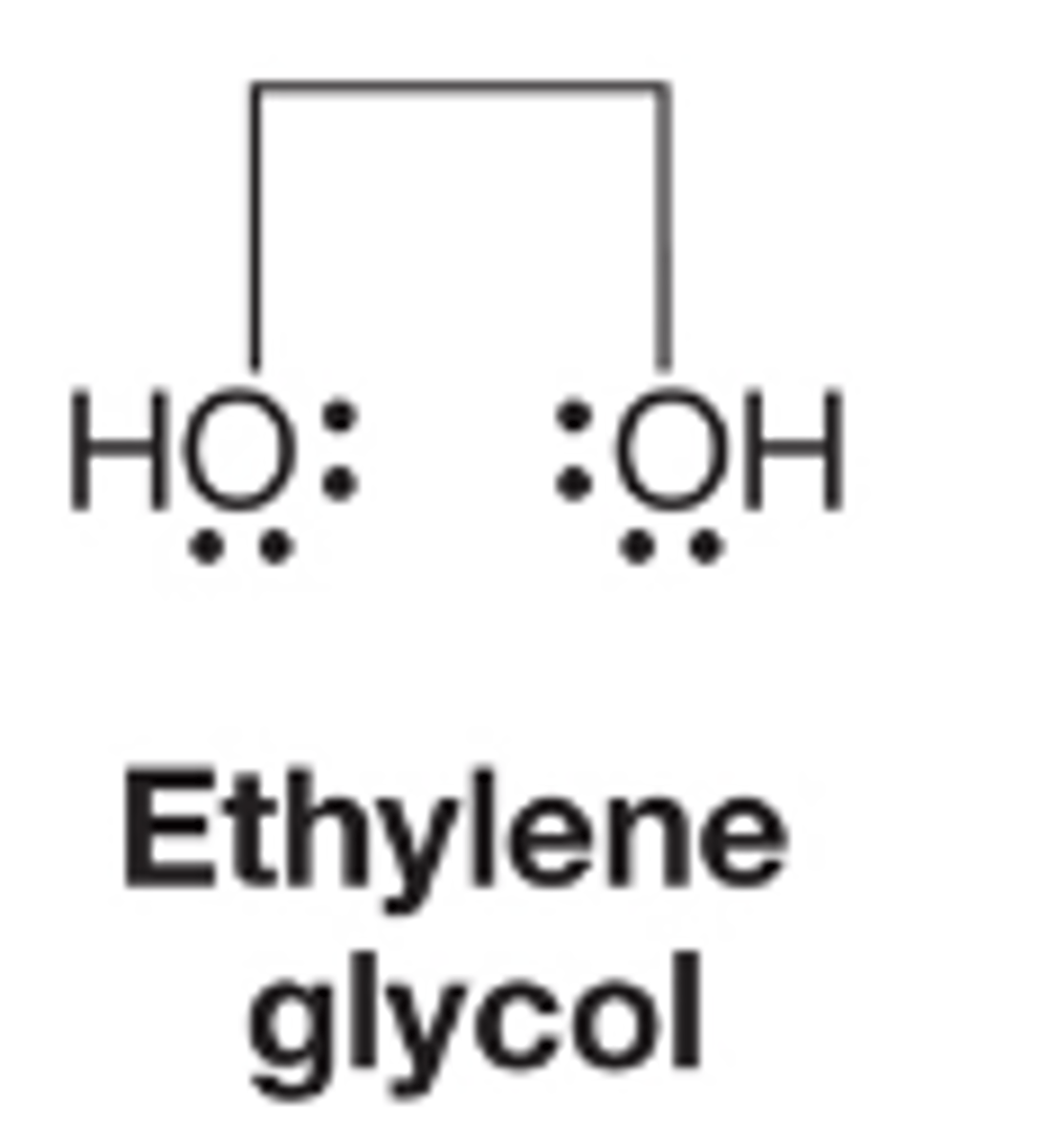
ethylene glycol
Glycerol
What are molecules containing 2 OH groups called
Molecules containing two OH groups are called diols, but there is an often used common name, glycol
note that in the naming of molecules with two OH groups the final "e" of the alkane parent compound is not dropped
What are amines
Amines are derivative of ammonia, NH3
Successive replacement of a hydrogen on ammonia leads to primary, secondary, and tertiaryamines(NH2R, NHR2, NR3)
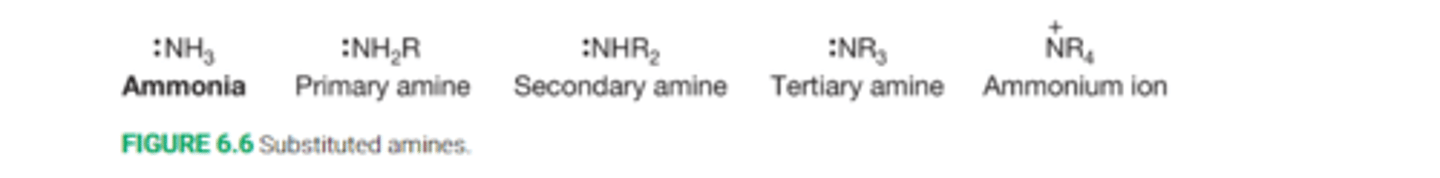
What are ammonium ion
Quaternary nitrogen compounds that are positively charged are called ammonium ions R4N+
How are primary amines named?
Primary amines are commonly named by using the name of the substituent R, and appending the suffix "amine"
How are secondary and tertiary amines in which the R groups are the same named?
dialkylamines, trialkylamines
Amines in which the two R substituents are different have the substituents named in alphabetical order
What is the IUPAC convention for naming amines
Find the longest carbon chain with the carbon attached to nitrogen and use that parent hydrocarbon name
Replace the "e" at the end of the parent carbon chain with "amine"
Number the chain such that the amine has the lowest possible number
Label all substituents in the prefix in alphabetical order
Secondary and tertiary amines will have the alkyl group listed in alphabetical order in the prefix as N-alkyl or N,N dialkyl if the groups are the same
What if a molecule contains both an Amine and an alcohol group
The IUPAC system has the alcohol group with a higher priority than the amine group
So if the molecule contains both an amine and and an alcohol will be named as the alcohol, with the amine listed as amino in the prefix
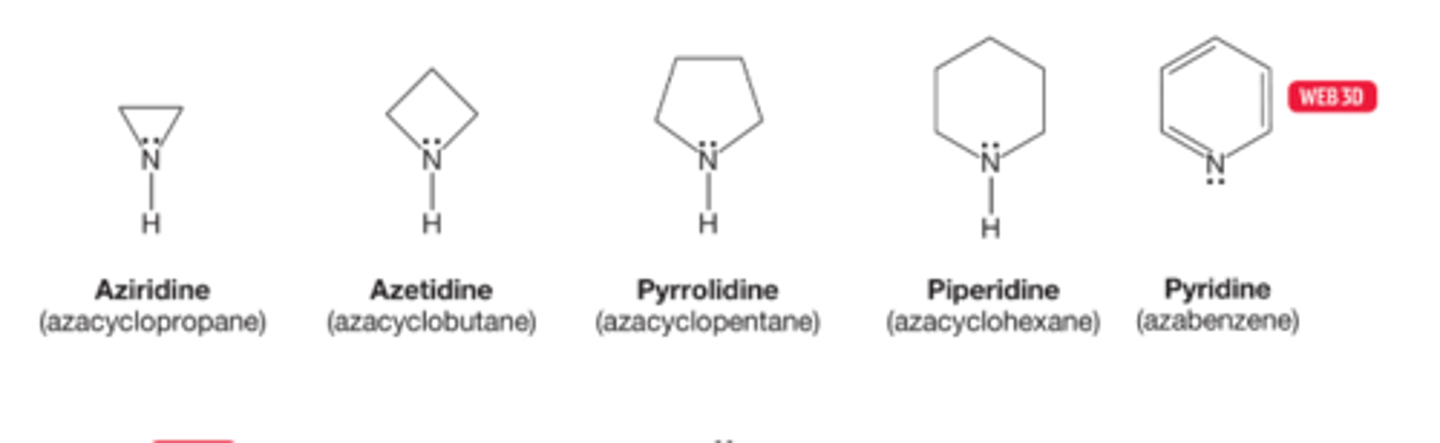
How are cyclic amino compounds named?
cyclic amino compounds are widely found in nature and are almost invariably known by there common names
These compounds are often named as "aza" analogues of an all carbon system
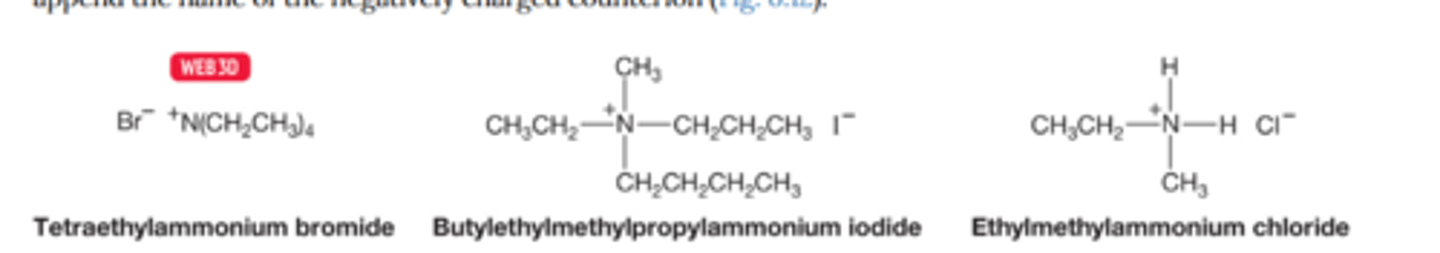
How are ammonium ions named
Ammonium ions are named by alphabetically attaching the substituents in the prefix
Don't forget to include the name of the negatively charged counter ion
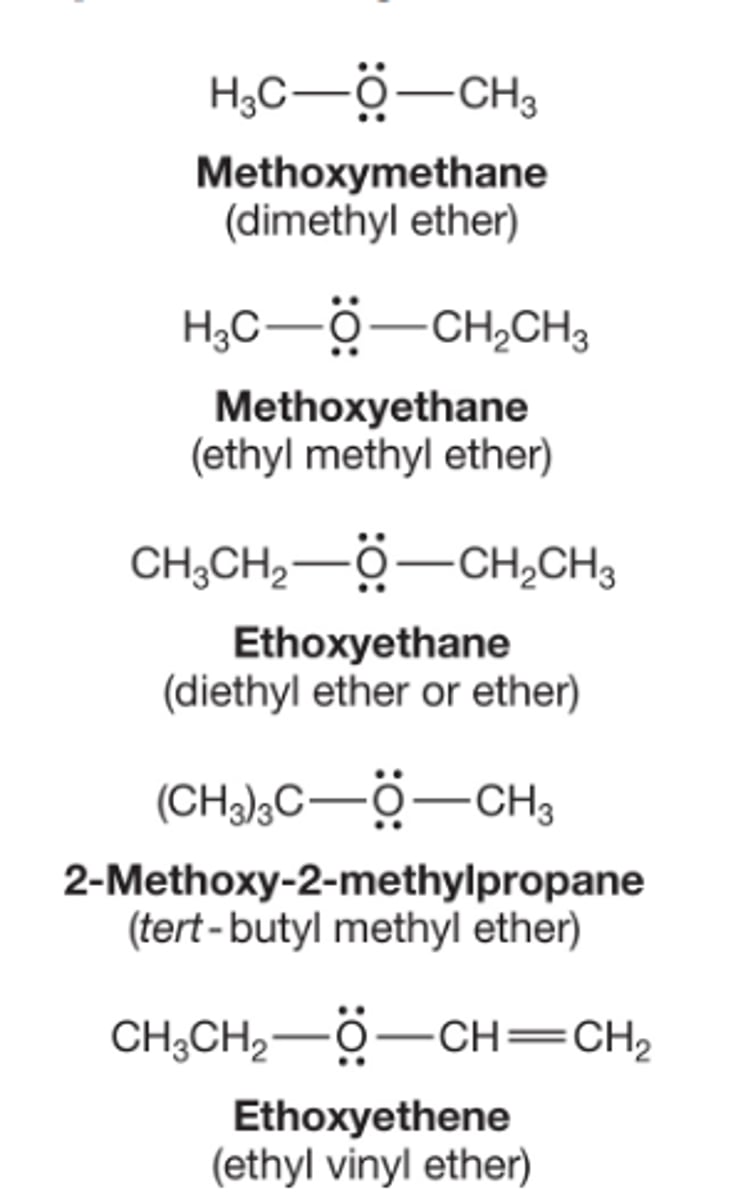
How are ethers named in the common scheme and IUPAC scheme
Ethers are compounds that have the form R-O-R or R-O-R'
In the common scheme, the two alkyl group attached to the oxygen are listed in alphabetical order and the word ether is appended
In the IUPAC system, ethers are named as Alkoxy (RO) alkanes, and groups are listed in the prefix in alphabetical order
An ether is a subordinate group, which means in the IUPAC system it can only be named as a prefix
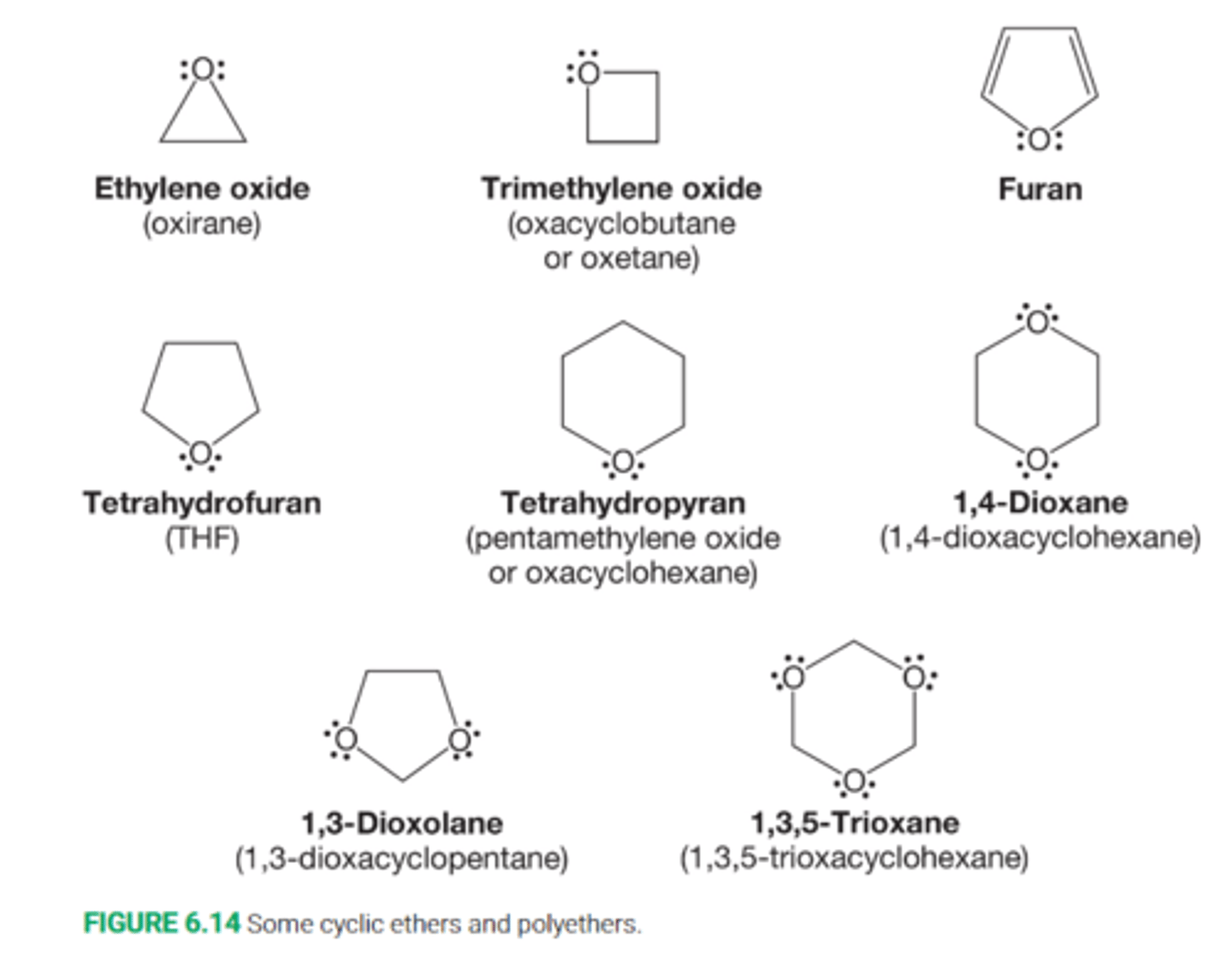
How are cyclc ethers named
Cyclic ethers are named as either oxa ring compounds or as oxides by counting the number of methylene groups within the ring
So a cyclopentane with an oxygen atom in the ring can become either oxacyclopentane or tetramethylene oxide
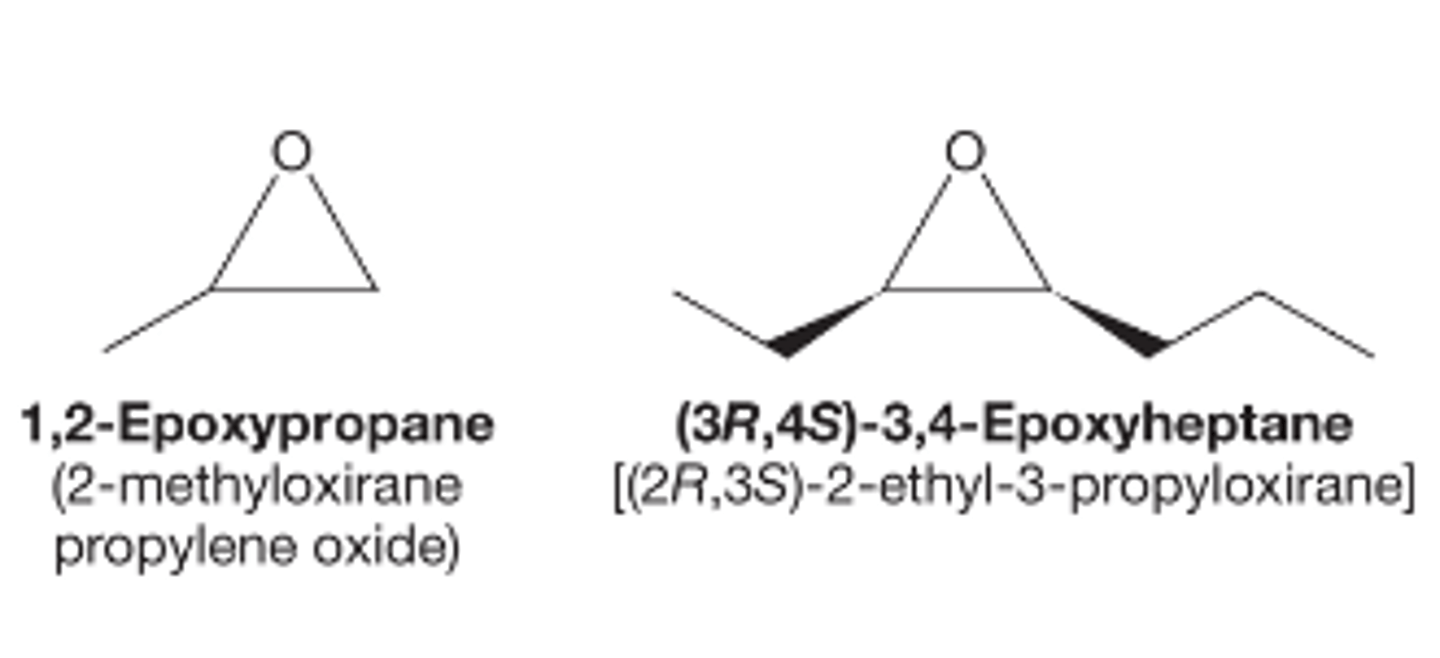
How do we name epoxides?
Three-membered rings have their own naming schemes due to the frequency at which they are encountered
The most versatile IUPAC method has you treat the epoxide as a substituent. It has you fin dthe longest carbon chain and then use the term epoxy in the prefix for the two carbons attached to the ring oxygen
6.3 Structure of substituted alkanes
Describe the structure of alkyl halides
Simple alkyl halides are nearly tetrahedral, which means the carbon that the halogen is attached to is approximately sp3 hybridized
The bond in alkyl halides involved an overlap between a carbon's sp3 orbital and the orbital of the halogen whose principle quantum number ranges from n=2 to n=5
The c-x bond length increases and bond strength decreases as we read down the periodic table
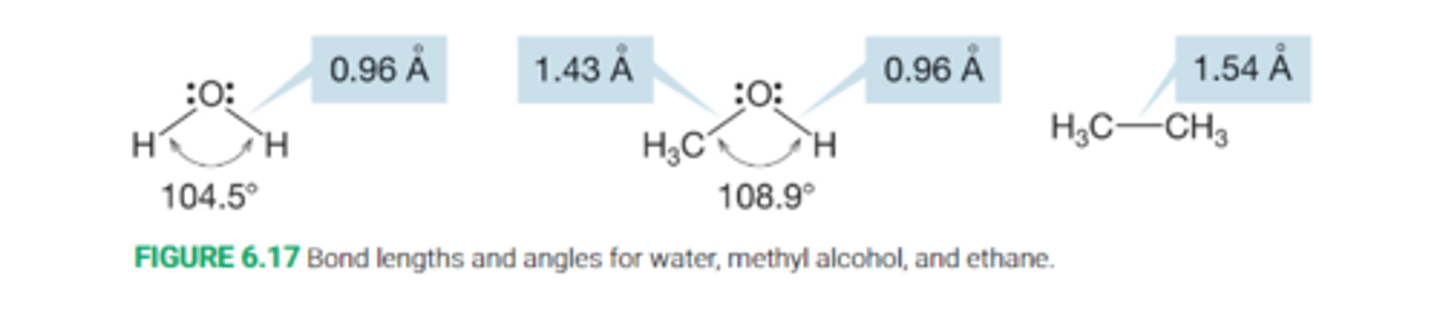
Describe the bond angles in alcohols
Alcohols are derivative of water, and thus they somewhat resemble water in structure.
The bond angle is expanded a bit from 104.5 degrees in H-O-H to 108.9 degrees in simple alcohols R-O-H
The O-H bond length in alcohols is very little changed from the O-H bond in water.
The C-O bond in alcohols is shorter and stronger than the C-C bond in ethane
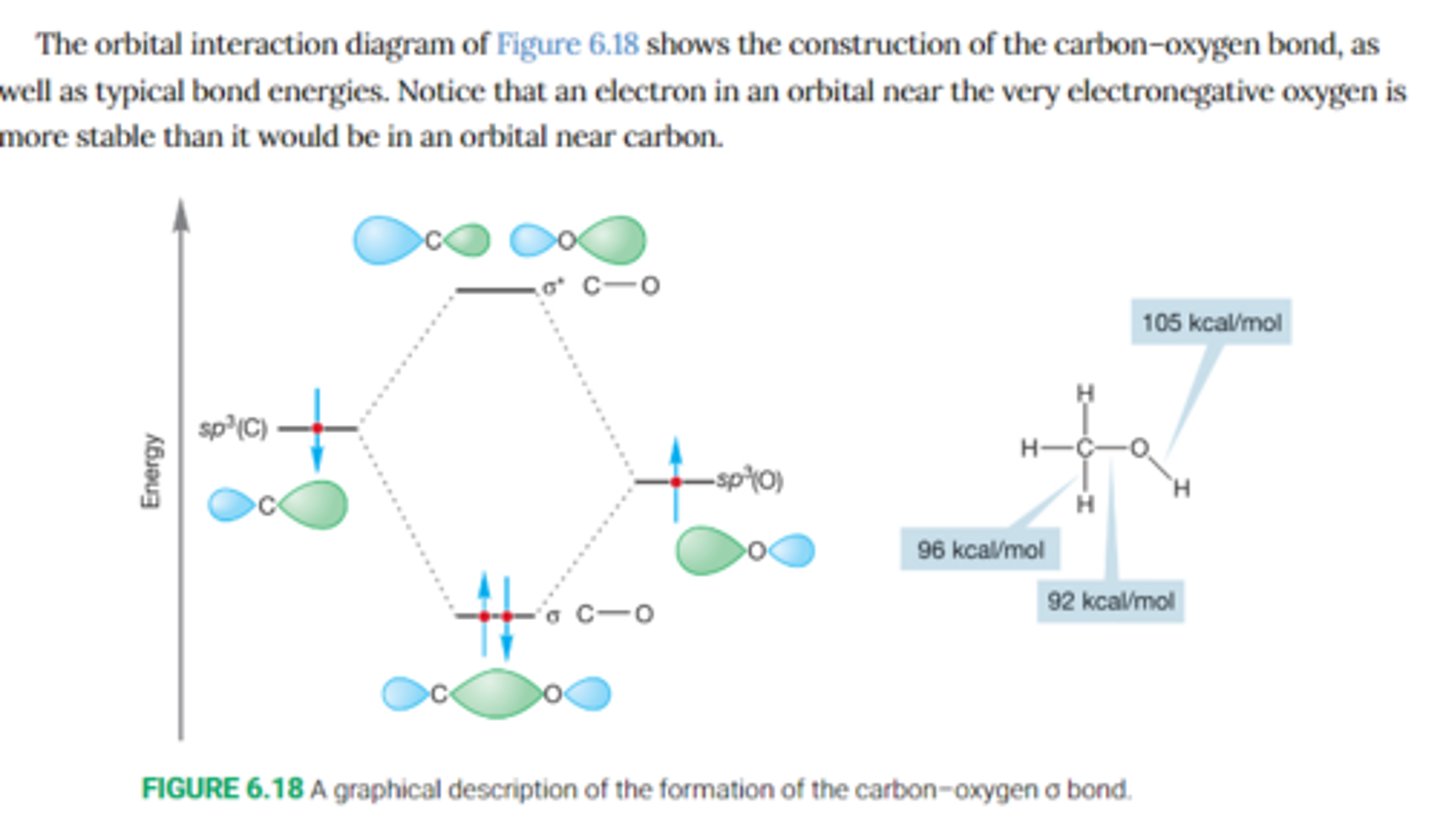
Describe the orbital interaction diagram for the formation of the carbon-oxygen in methyl alcohol
Notice how an electron in an orbital near the electronegative oxygen atom is more stable than it would be in an orbital near carbon
Describe the bond lengths in amines
In simple amines, the N-H bond length is shorter than the C-C bond length in alkanes
SImple amines are hybridized approximately sp3 at the nitrogen and are thus pyramidal. The bond angles are close to 109.5 but cannot be exactly the tetrahedral angle
Describe the bon dangles in amines
In tertiary amines where all three substituents are the same, the R-N-R bond angles are the same
But for less symmetrical amines, all three R-N-R angles cannot be the same
Describe amine inversion
The most important structural feature of amines comes from the lone pair of nonbonding electrons acting as the fourth subtituent on the pyramid
The pyramid as a result can undergo an "umbrella flip" amine inversion, forming a new mirror image pyramid
The nitrogen is also capable of being a stereogenic center
Define Amine inversion
The conversion of one pyramidal form of an amine into the other through a planar, sp2-hybridized transition state
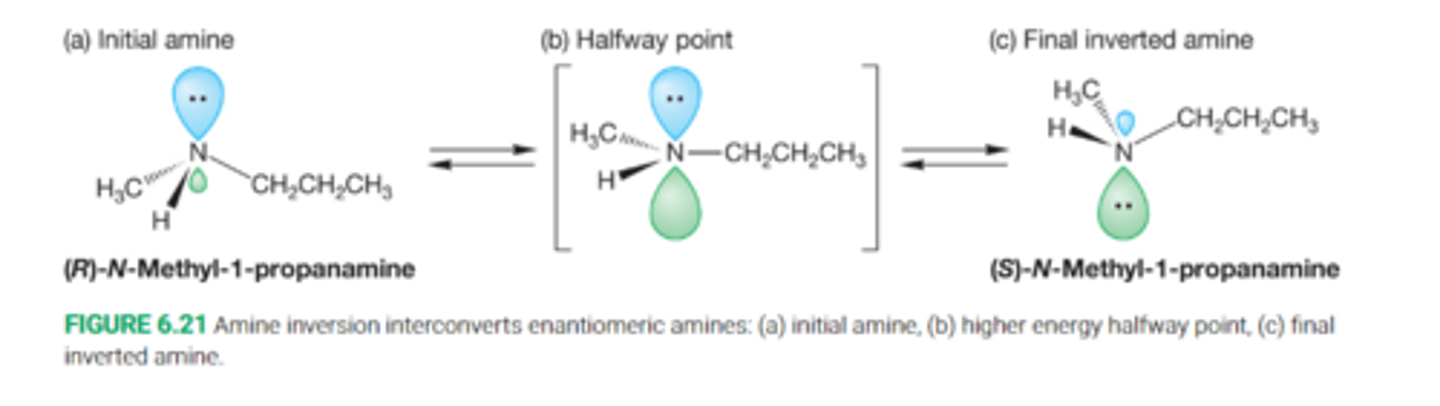
Describe the energy barrier to amine inversion
The barrier to inversion in amines is very low, only about 5-6kcal/mol, and isolation of one isomer, even at low temperature, is very difficult
Inversion is too facile, rapid inversion interconverts enantiomeric amines
Describe the bond length and angles in ether
The C-O bond length in ethers is similar to the C-O bond length in alcohols, and the opening of the angle from H-O-H(104.5) to R-O-H(109) to R-O-R(112) continues.
Because the bond angles in ehter is 112, we can say that the oxygen is approximately sp3 hybridized
6.4 Properties of Substituted Alkanes
Describe the polarity of substituted alkanes
Substituted alkanes are polar molecules. halogens are relatively electronegative atoms and strongly attract the electrons in the carbon-halogen bond of alkyl halides, which have a dipole moment of approximately 2D
Describe the polarity of alcohols
In alcohols, the presence of the electronegative oxygen atom ensures that bonds are strongly polarized and that a substantial dipole moment exist
Because of this, alcohols are strongly associated through dipole-dipole interactions and through extensive hydrogen bonding
Define hydrogen bonding
A low-energy bond between a pari of electrons on an electronegative atom such as oxygen, nitrogen, or flourine to a hydrogen on a oxygen, nitrogen or fluorine
Describe hydrogen bonding in terms of alcohols
Hydrogen bonding interactions can be quite strong, 5kcal/mol
This has the effect of increasing the boiling point of alcohols far above that of alkanes
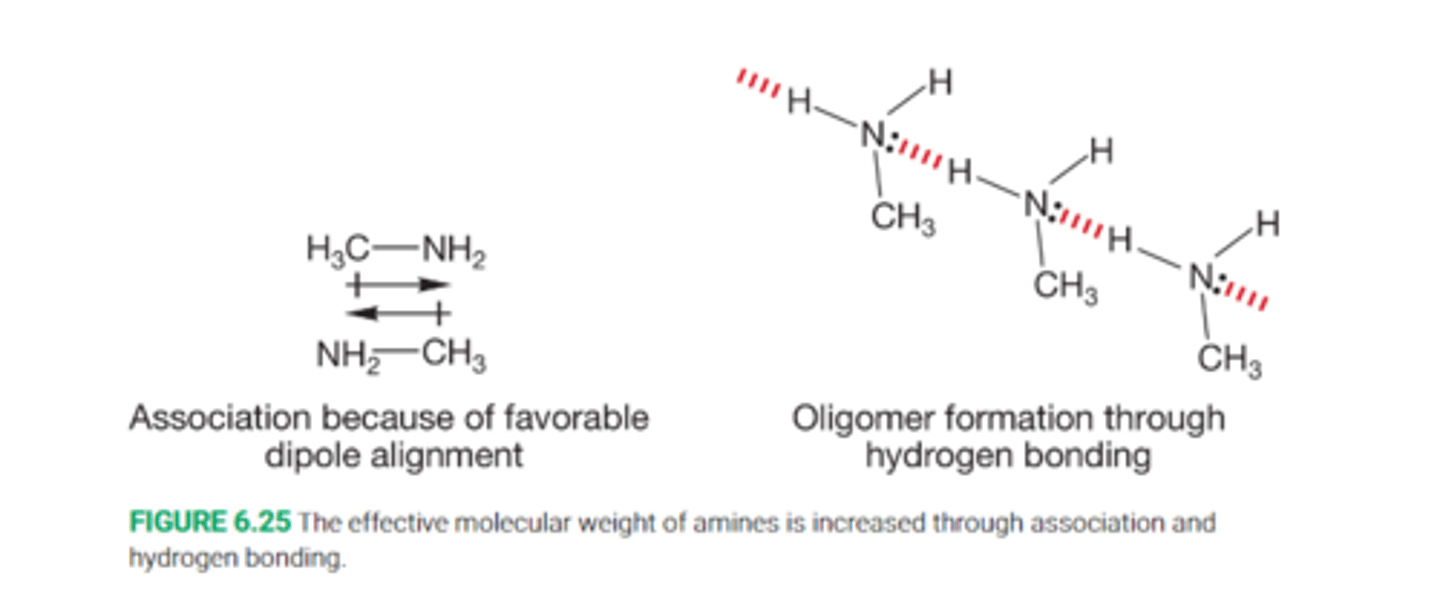
Describe hydrogen bonding in terms of amines
Amines, like alcohols, have higher boiling point than hydrocarbons ofsimilar molecular weigh tdue to hydrogen bonding
Though this effect is not as great as in alvohols due to the reduced electronegativity of nitrogen
Describe the bp of tertiary amines
In tertiary amines, hydrogen bonding cannot occur, and thus the boiling point decreases
Describe the polarity of ethers
Ethers are polar, but only for the smallest classes of ethers do polarity effect physical properties
For example, diethyl ether has nearly the same boiling point as pentane and is only modestly soluble in water
Are alkyl halideseither basic or acidic?
Alkyl halides are neither acids nor bases.
They cannot donate a proton and have no basic lone electron pairs
Are alcohol and amines acidic or basic?
Alcohol and amines, can be proton donors, and because of their lone electron pairs, can be bases as well
Derive the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of an acid in water

relate pka values to the strength of an acid
The stronger the acid, the lower the pka value
any compound with a pka lower than 5 is regarded as a reasonably strong acid
any compound with a pka below 0 is regarded as a very strong acid
Describe protonation of an alcohol
Protonation converts an alcohol into an intermediate oxonium ion.
Without protonation, breaking the R-OH bond would be very difficult, because both positive R+ and negative OH- ions would have to be formed. Thus we saythat hydroxide is a poor leaving group and alcohols do not ionize easily.
After protonation however, the leavingn group is no longer hydroxide, but water, formation of the neutral molecule wawter is a much easier process
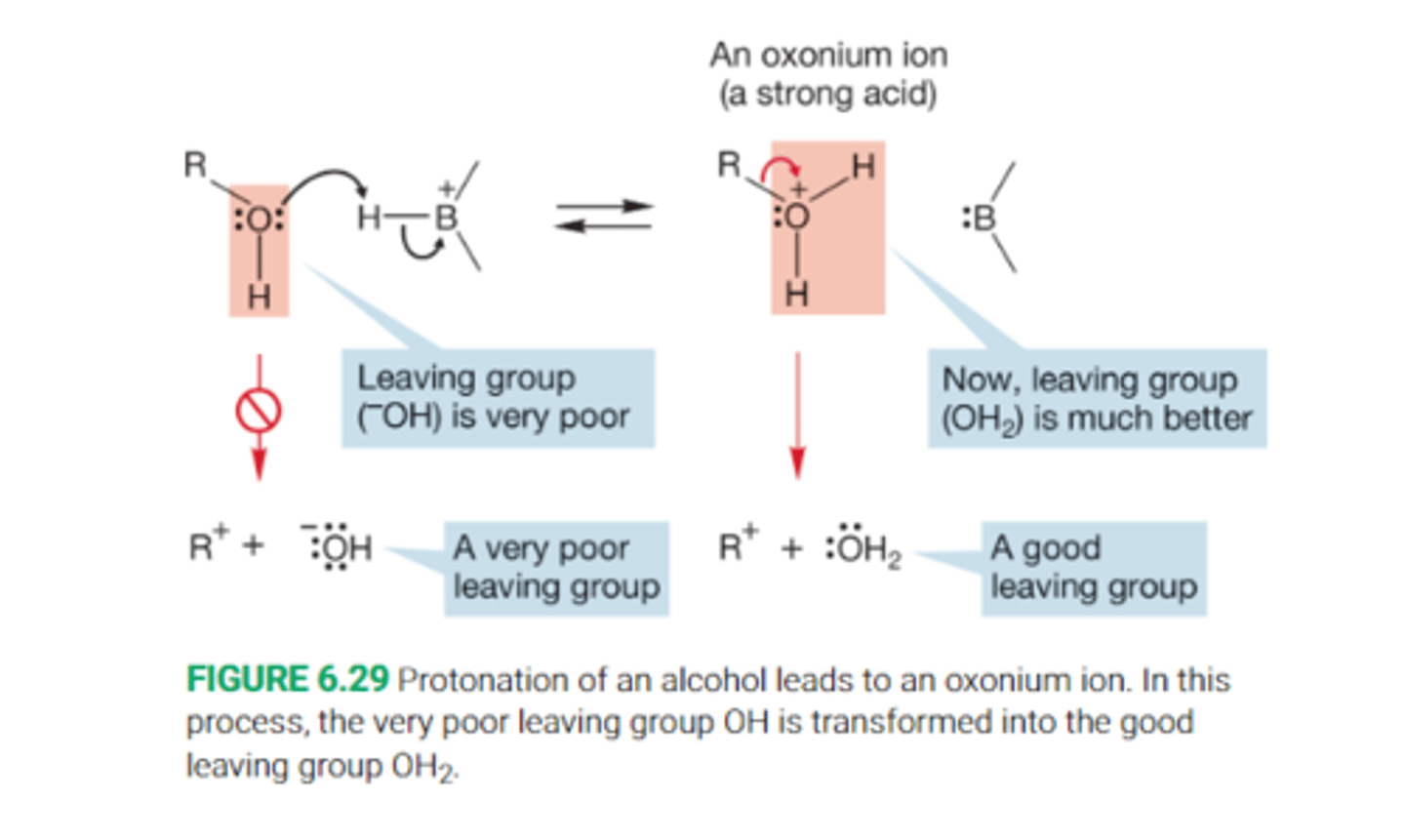
Describe the strength of protonated alcohols
When an alcohol is protonated it turns into an intermediate oxonium ion, ROH2+. This makes the oxygen of the alcohol carry a positive charge. The consequence of this protonation is that the alcohol becomes a much stronger acid
What is the challenge with protonating alcohols?
The problem with protonating alcohols is that it requires a very strong acid, this is because alcohols are not naturally very strong proton donors or acceptors.
Yet once the alcohol is protonated, the oxonium ions are much more effective at donatinh protons
Describe the pka values of oxonium ions formed from alcohols
oxonium ions formed from alcohols have 'pka values in the -2 range
What does bronsted acidity depend on?
bronsted acidity depends on the hydroxyl hydrogen. Loss of this hydrogen to a proton acceptor, a bronsted base, leads to the conjugate base of the alcohol, called the alkoxide ion. (RO-)
Define alkoxide ion
the conjugate base of an alcohol, RO-
Compare the acidity of alcohols to water
alcohols are about as acidic as water
How come the more alkyl groups on the alcohol, the weaker acid it is?
This is largerly due to the inductive effect of alkyl groups and the stabilization of the conjugate base
Alkyl groups donate electrons through what's called an inductive effect, and as a result, electron density is pushed towards the moreo electronegative oxygen atom. This serves to make the OH bond less polar, and make the alcohol less likely to donate a proton
When an alcohol loses a proton, an alkoxide ion is formed, the stabilization of this conjugate base of the alcohol is crucial. Alkyl groups destabilize the negative charge on the oxygen because they donate electron density to the oxygen atom, this serves to make the conjguate base of the alcohol less stable, meaning the alcohol is less likely to donate a proton in the first place
Why is the explanation that alkyl groups are electron donating not correct?
Research has shown that the order of acidity of a list of alcohols was reversed in the gas phase. Thus the intrinsic acidity of the alcohol was opposite to that foun din solution
The acidity order measured in the solvent represent a powerful effect of the solvent, not the alcohol itself
Describe the stability of organic ion
Organic ions are almost all unstable species, and the formation of the alkoxide anion depends critically on how easy it is to stabilize them through interaction with solvent molecules, called solvation
Describe the difference in acidity between tert-Butyl alcohol and Methyl alcohol in solution
tert-Butyl alcohol is a weaker acid than methyl alcohol in solution due to the large tert-Butyl alkoxide ion is difficult to solvate.
The more alkyl groups, the more difficult it is for stabilizing solvent molecule to approach
describe the acidity of alcohols in the gas phase
In the gase phase, the intrinsic properties of the alcohols themselves determine their acidity. In this phase, alkyl groups serve to stabilize the alkoxide ion by delocalizing elewctron density through a process called hyperconjugation
Define hyperconjugation
The interaction of electrons in ansp3 hybridized orbital with an empty orbital
Describe the basic properties of amines
Like water and alcohols, amines are Bronsted bases.
Ammonia, primary, secondary, tertiary amines are all weak bases
Protonation of an amine leads to the formation of the ammonium ion
This is important in biological chemistry, when biological reactions neeed a base, it is often amine that plays that role
Describe how we can measure the basicity of amines
If the ammonium ion is a strong acid, the related amne must be a weak base.
That means, the higher the pka value of the acid, the stronger the conjugate base will be
Why does methylamine's ammonium ion have a higher pka than ammonium?
Recall that the more substituted a carbocation ion is, the more stable it becomes.
Similarly, the more substituted an ammonium ion, the more stable it is and the less likely it is to give up a proton, resulting in a higher pka value
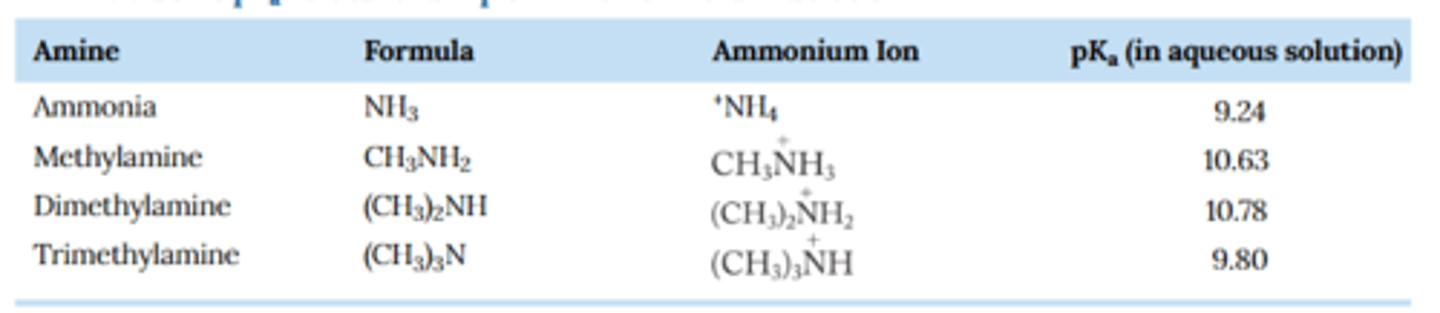
Why does trimethylammonium have a lower pka than dimethyl ammonium?
In the liquid phase, this graph doesn't seem to make sense, how can a more substituted ammonium ion be less stable?
Again we look to the gase phase and see a trend that we would expect, the more substituted the ammonium ion, the higher its pka
So now we can assume that there must be some efffect present in solution that is not present in the gas phase
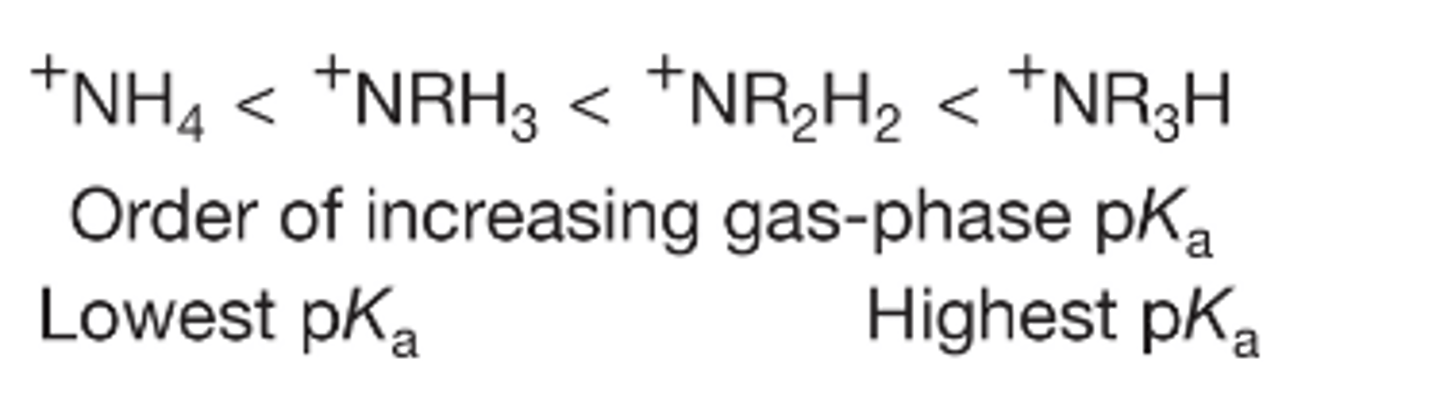
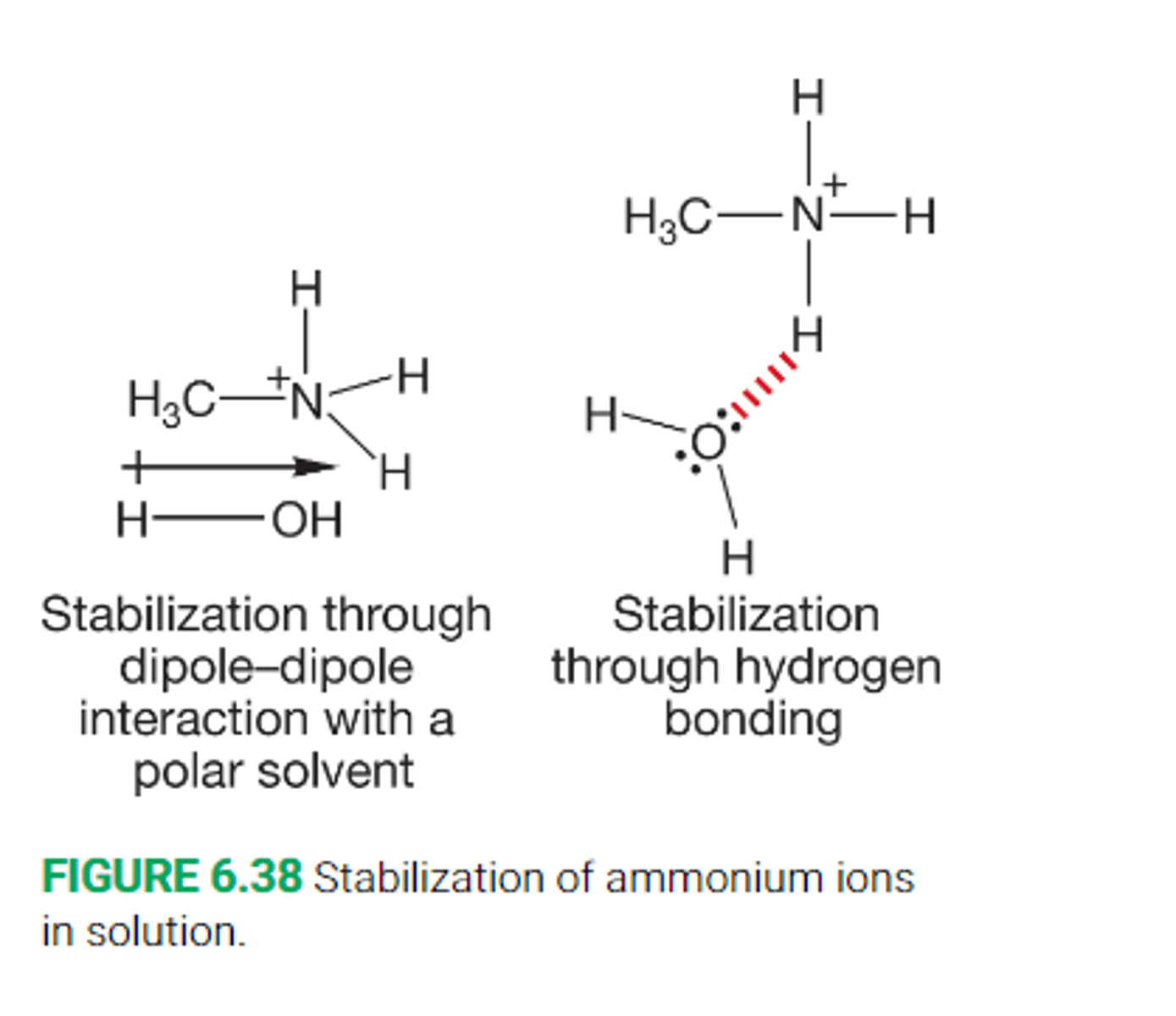
How are ions in solution stabilized?
By either electrostatic stabilization or through hydrogen bonding
What are the two effects that alkyl groups have on the stability of the ammonium ion
The alkyl group helps to stabilize the ammonium ion by dispersing the charge
it destabilizes the ion by interfering with solvation by making intermolecular solvation more difficult
Describe the effect of adding additional methyl groups on the acidity of the ammonium ion
Little steric interference with solvation occurs when we replace one hydrogen with a methyl group in ammonium, and further more there is stabilization, so pKa increases by a full unit
Replacing a second hydrogen with a methyl group yields a balance between steric hindrance of solvation and stabilization of the ammonium ion, the result is no net change in the pKa
Replacing a third hydrogen with a methyl group now results in the steric hindrance of solvation being far greater than the stabilization derived from a more substituted nitrogen atom
Describe the effect of adding additional methyl groups on the acidity of the ammonium ion in the gas phase
In the gas phase, solvation does not occur, and the ammonium ion only derives the stabilization from being more substituted, so only the stabilizing effects remain
Describe the value of pkb in relation to base strength
the lower the pkb, the stronger the base
Amines have a pkb of around 4, which makes them quite strong b ases compared to other organic molecules
Compare the basicity of amines and alcohols
Amines are much more stronger bases than alcohols are, it is much harder to remove a proton from ammonium that it is from hydronium
Why is the oxonium ion more acidic than the ammonium ion
oxygen is a more electronegative atom than nitrogen and thus bears the positive charge less well.
Discuss the removal of a proton from a primary or secondary amin
Removal of a proton from an amine yields an amide ion
An amide ion is less stable than an alkoxide ion due to the negative charge being borne on the less electronegative nitrogen atom
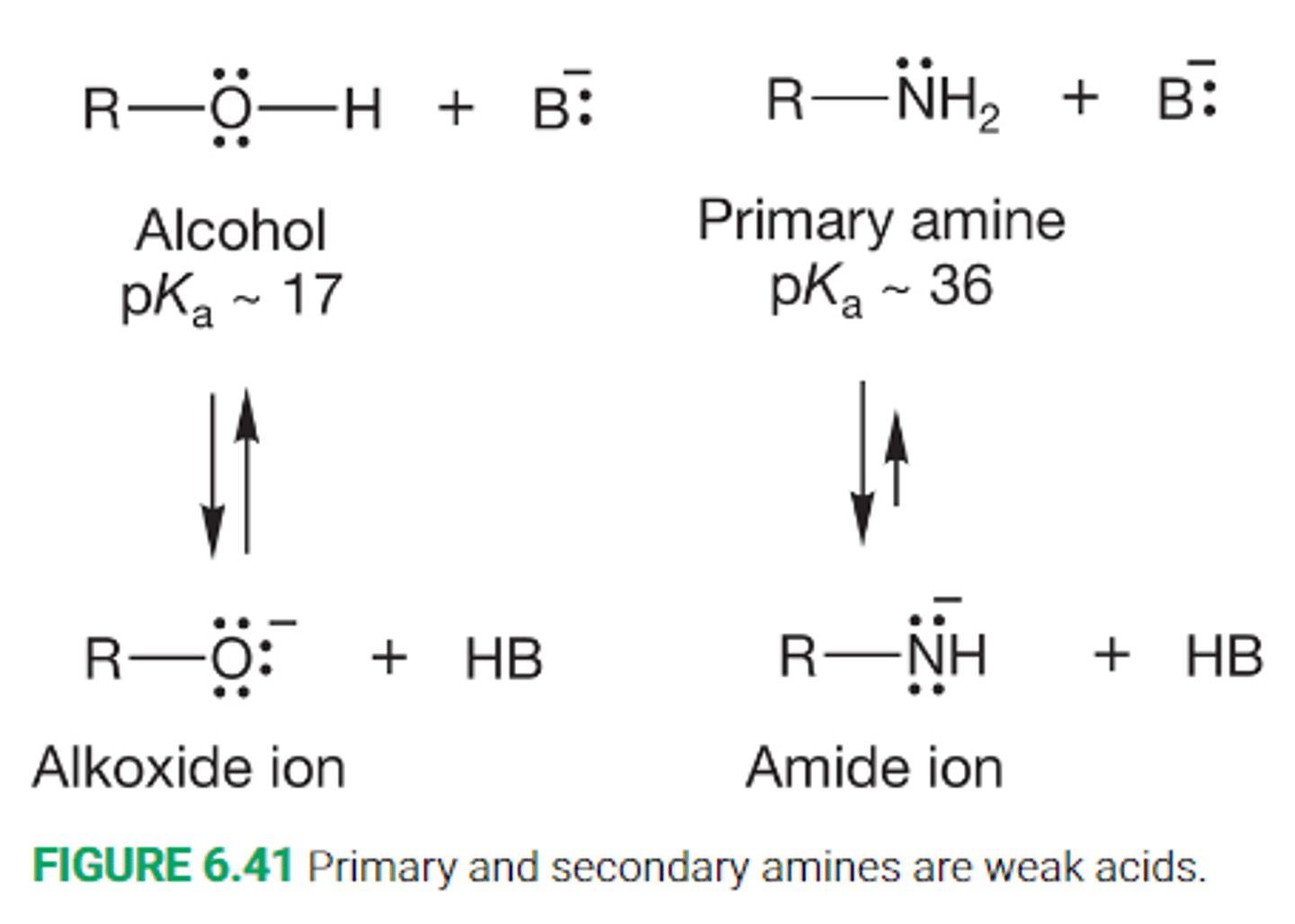
Describe the overall acidity and basicity of amines and amide ions
amines are good bases but relatively poor acids
The conjugate bases of amines, the amid ion, or an even stronger base than the amine itself
What are the factors the determine the acidity of a compound?
ISHARE
Induction
Size
Hybridization
Aromaticity
Resonance
Electronegativity
How the inductive effect on acidity
Inductive effects are transmitted through sigma bonds
Any bond between two different atoms are polarized towards the more electronegative pair
Explain the difference in acidity between trichloroethanol and ethanol
Trichloroethanol has a pka nearly 4 units below that of ethanol.
The key here is to look at the conjugate base following the deprotonation of the two alcohols. If we look at trichloroethanol, the C-Cl bonds stabilize the nearby negative charge on the oxygen atom by withdrawing electrons through the sigma bond framework
Anything that stabilizes a conjugate base will make it easier to remove that hydrogen to get that conjugate base
Explain the effect of size on acidity
Generally the large the atom, the better it is at bearing the negative charge.
The larger nucleus, with more positively charged protons, stabilizes a negative charge better than a smaller nucleus
Explain the difference in acidity between HF and HI
Furthermore, a small hydrogen makes a strong bond with a small flourine atom and a weak bond with a larger iodine atom due to very poor orbital overlap
Thus HF is a weaker acid than HI by a very large amount
This is a comparison within the same column of the periodic table
Explain the effects of hybridization on acidity
The more S character in an orbital, the lower in energy an electron in it is.
Thus an electron in an sp orbital is lower in energy than an electron in an sp2 orbital, which is lower in energy than an electron in an sp3 orbital
As a result, acetylenes are far stronger acids than alkenes, which are far stronger acids than alkanes
Explain the effect of resonance on acidity
Non solvated charged atoms are typically higher in energy than neutral atoms, which means that they are harder to form.
As a result, it is especially difficult to form ions in which the negative charge is localized on one atom
As a result, a molecule that gives a delocalized anion upon deprotonation is going to be a stronger acid than a molecule than give a localized anion upon deprotonation
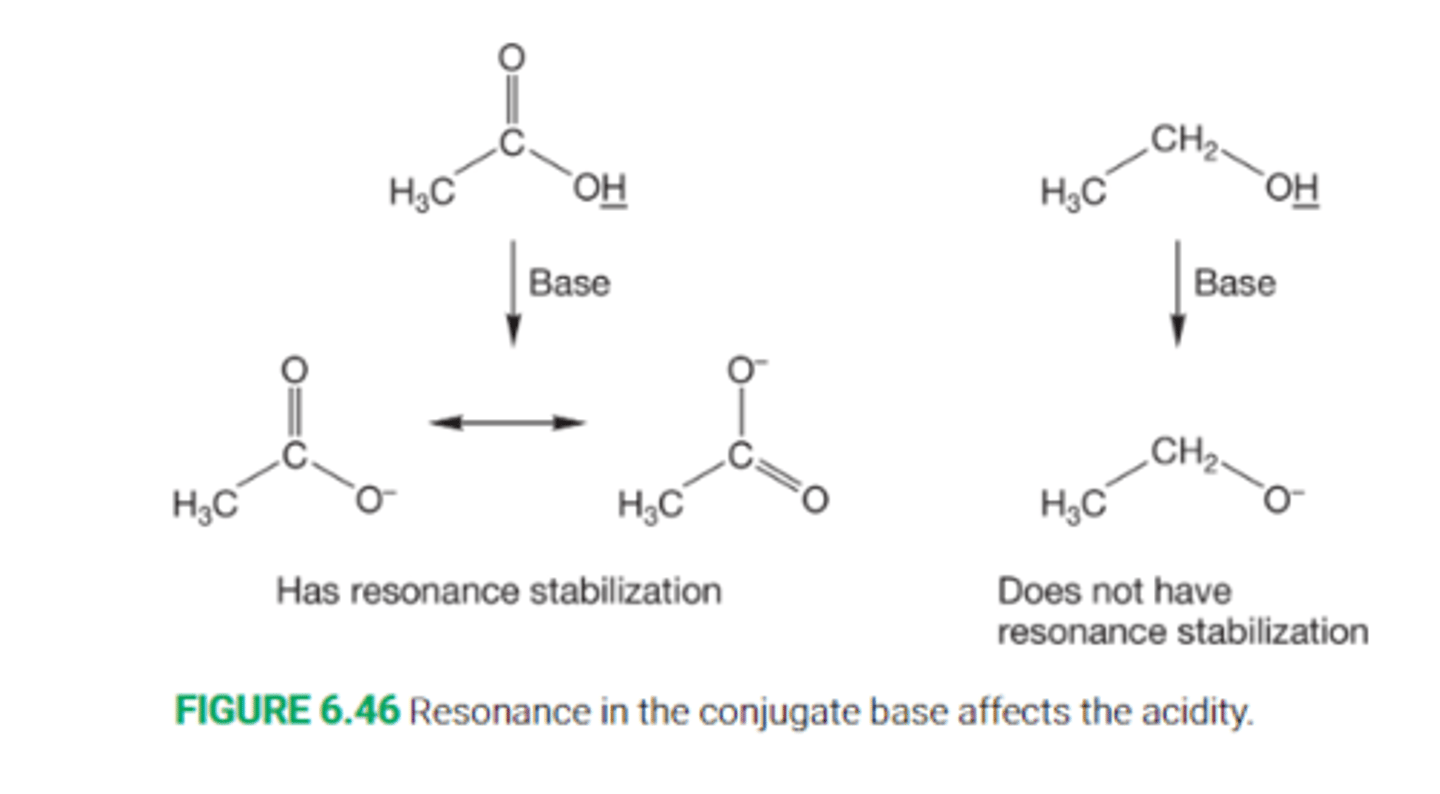
Describe the effect of electronegativity on acidiy
All else equal, it is easier to form an anion in which the negative charge is on the more electronegative atom than it is to form an anion where the charge is on the less electronegative atom
Thus HF is a much stronger acid than R-OH
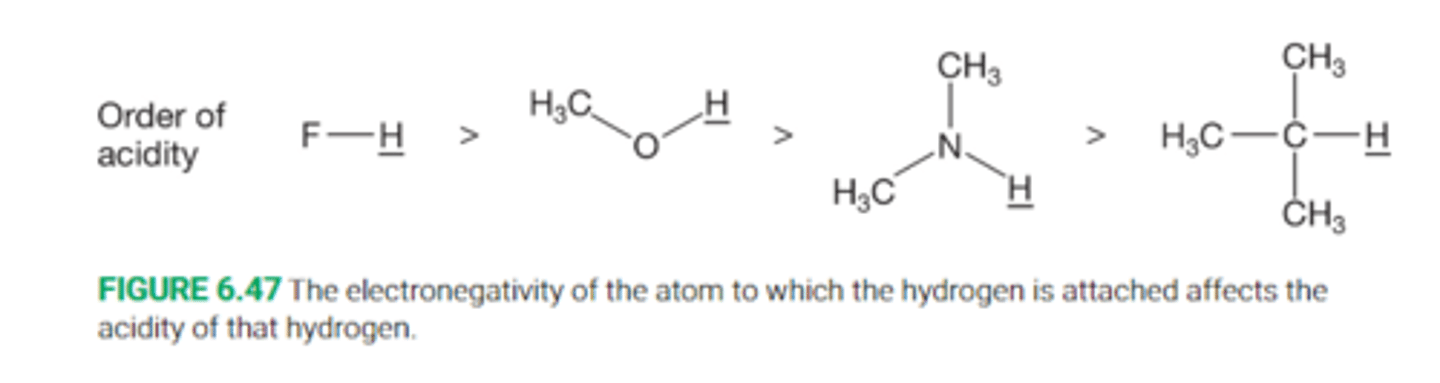
6.5 Solubility
How does hydrogen bonding occur
For hydrogen bonding to occur, there neweds to be a proton donor(NH2 or OH) and a proton acceptor(a lone pair of electrons)
What are protic solvents?
Solvents that can donate a proton are called protic solvents
Protic sovlents are typically polar and have high dielectric constants
What is a dielectric constant
a measure of the ability of a solvent to separate charges
What are aprotic solvents
Solvents that are not proton donors
How effective are protic solvents in dissolving polar molecules
Polar solvents are particularly good at dissolving molecules capable of hydrogen bonding
Formation of hydrogen bonds within solution is highly stabilizing
How effective are aprotic polar solvents at dissolving other polar molecules
Polar aprotic solvents can help disperse the partial charges in other aprotic polar molecules and thus dissolve them well
This occurs through alignment of opposite charges
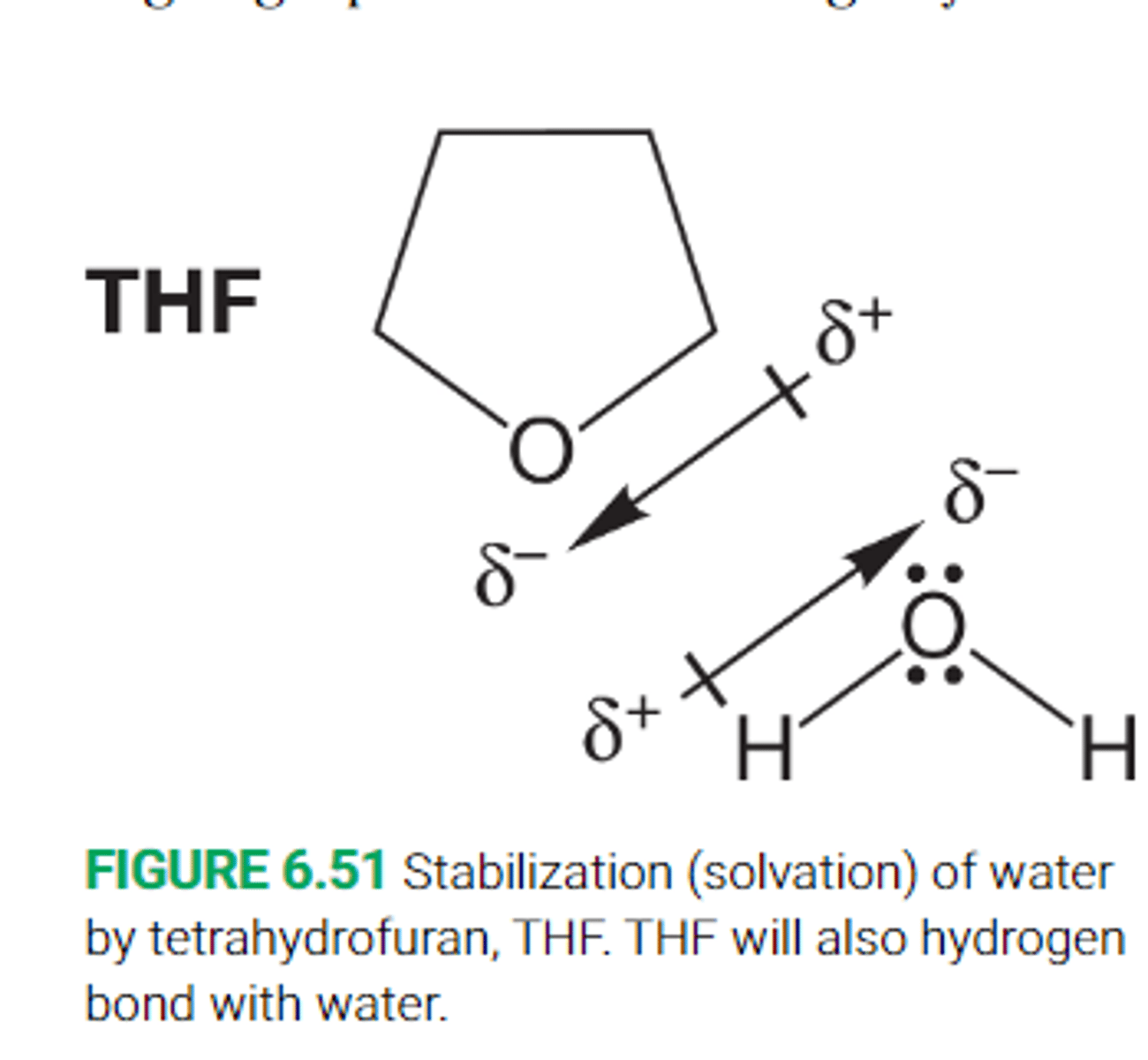
6.6 Formation of Substituted Alkanes
6.7 A reaction of alkyl halids" Synthesis of Alkanes
Why are alkyl halides important in synthetic chemistry?
Alkyl halides are crucial in synthetic chemistry because they allow the formation of C-H and C-C bonds
What is a organometallic reagent?
A molecule that contains both carbon and a metel
Usually the carbon is at least partially covalently bonded to the metal
What happenswhen an alkyl halide is added to a cold mixture of either magnesium or lithium maetal and an ether?
When an alkyl halide is added to a cold mixture of either magnesium of lithium metal and an ether solvent(R-O-R solvent, typically diethyl ether or THF), the metal begins to dissolve in an exothermic reaction
The end result fo the reaction is either a grignard reagent or an organolithium reagent
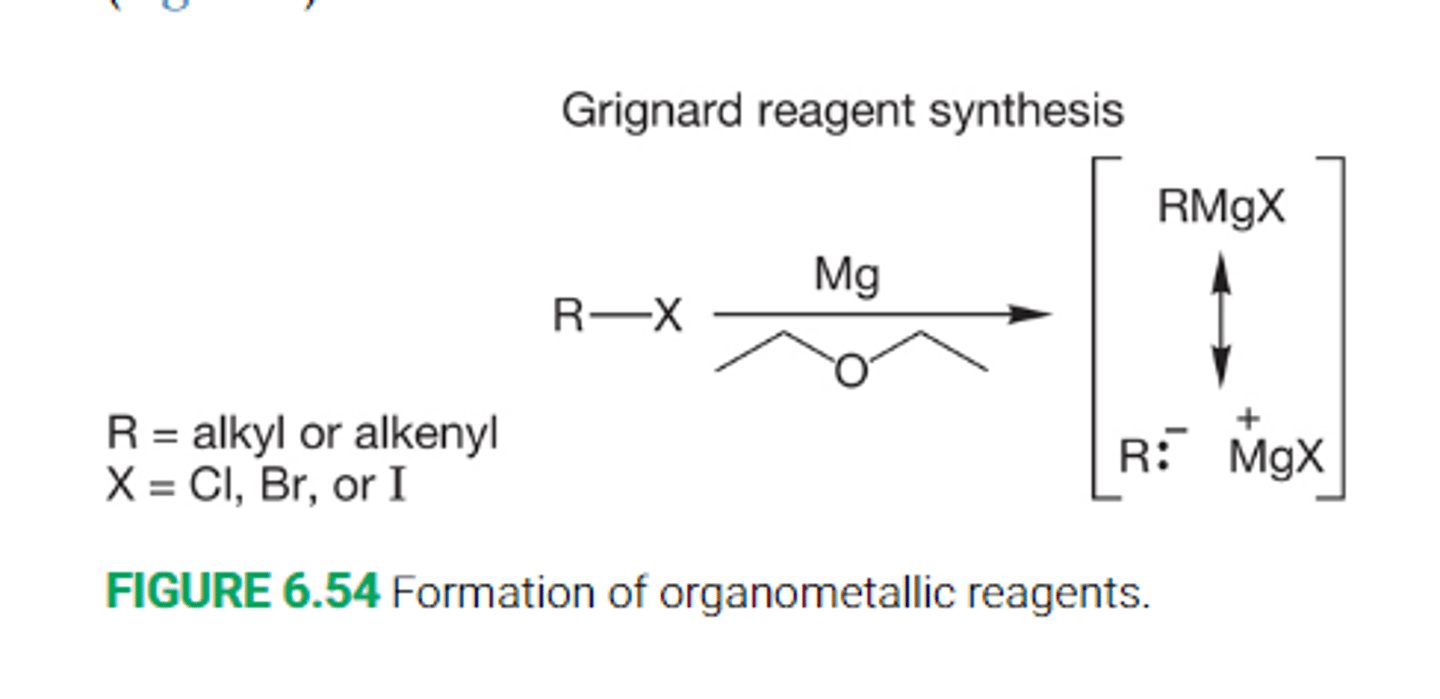
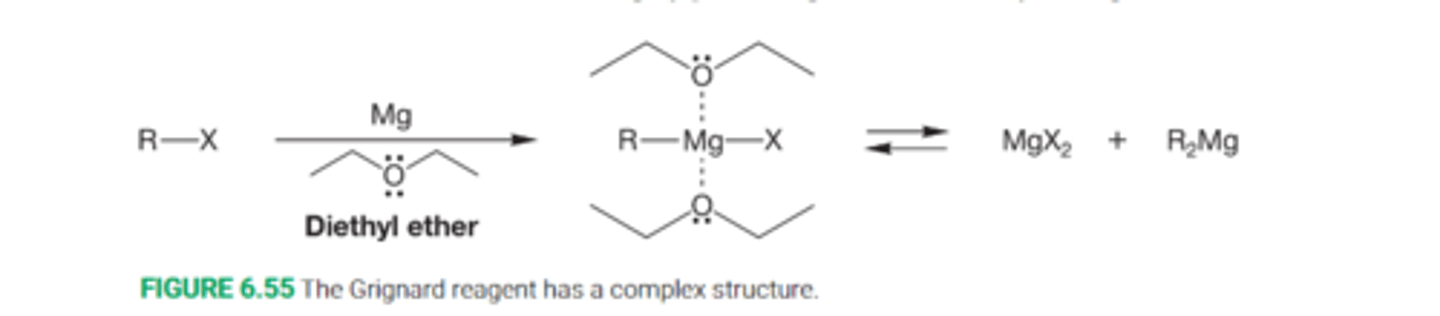
What is a Grignard reagent?
A strongly basic organometallic reagent formed from a halide and magnesium in an ether solvent
The simplest formulation is RMgX
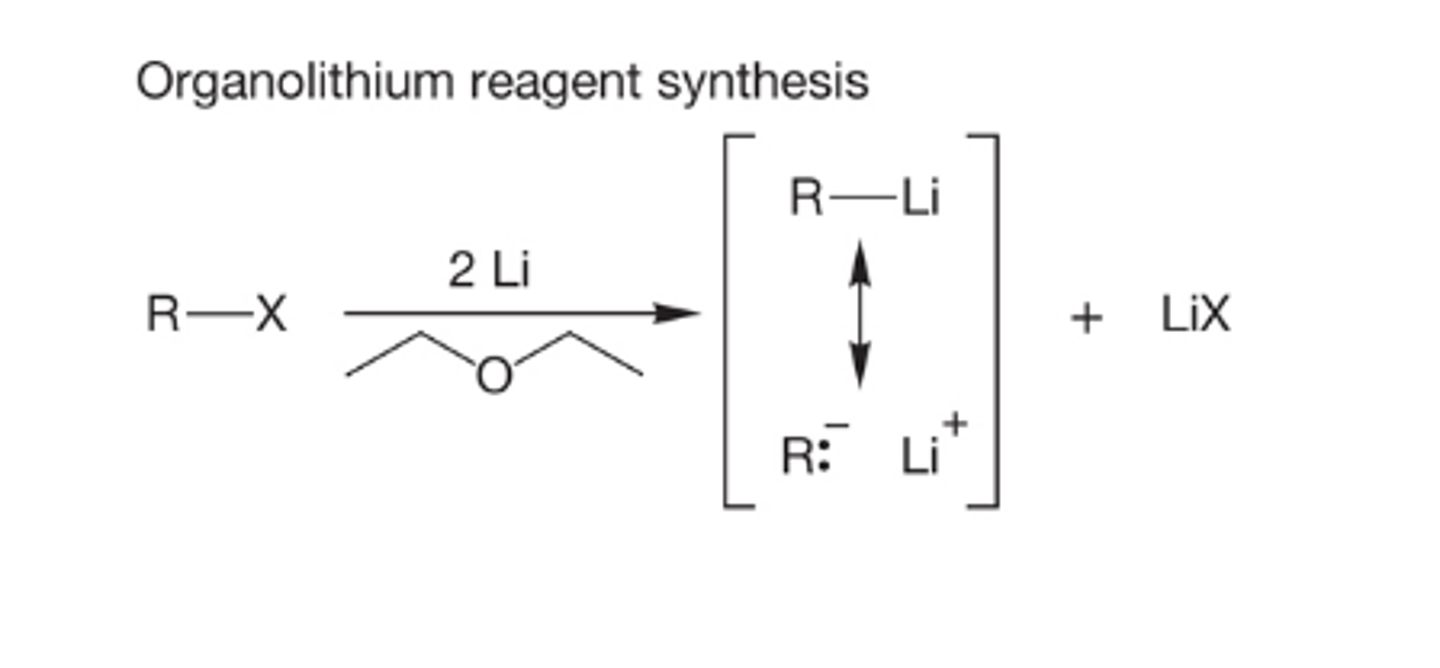
What is an organolitihum reagent
A strongly basic organometallic reagent, R-Li, formed from a halide and lithium
What is the reaction mechanism for Grignard reagent synthesis
What is the reaction mechanism for organolithium reagent synthesis
Describe the equilibrium of the Grignard reagent
The Grignard reagent is in equilibrium with a mixture of magnesium halide and dialkylmagnesium compounds. The Grignard reagent also incorporates two molecules of solvent
What ever the structure, grignard reagents are highly polar molecules that are very strong lewis bases
describe the radical-transfer reaction of the machanism fo the formation of a Grignard reagent