Angiosperms:Flower and Fruits
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
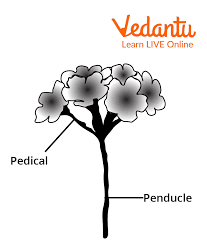
What is the pedicel of a flower?
The stalk of a individual flower in a inflorescence, and the peduncle is the stalk of a inflorescence
What does the carpel contain?
The ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization and the carpel develops into the fruit wall.
What are the fertile parts of a flower?
The stamens and carpels, the sepals arise below the petals, and stamens arise below the carpel.
Collectively, what do the sepals from?
The calyx
Collectively, the petals form the?
The Corolla
The Perianth consists of all the what parts of a flower?
Together the calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals)
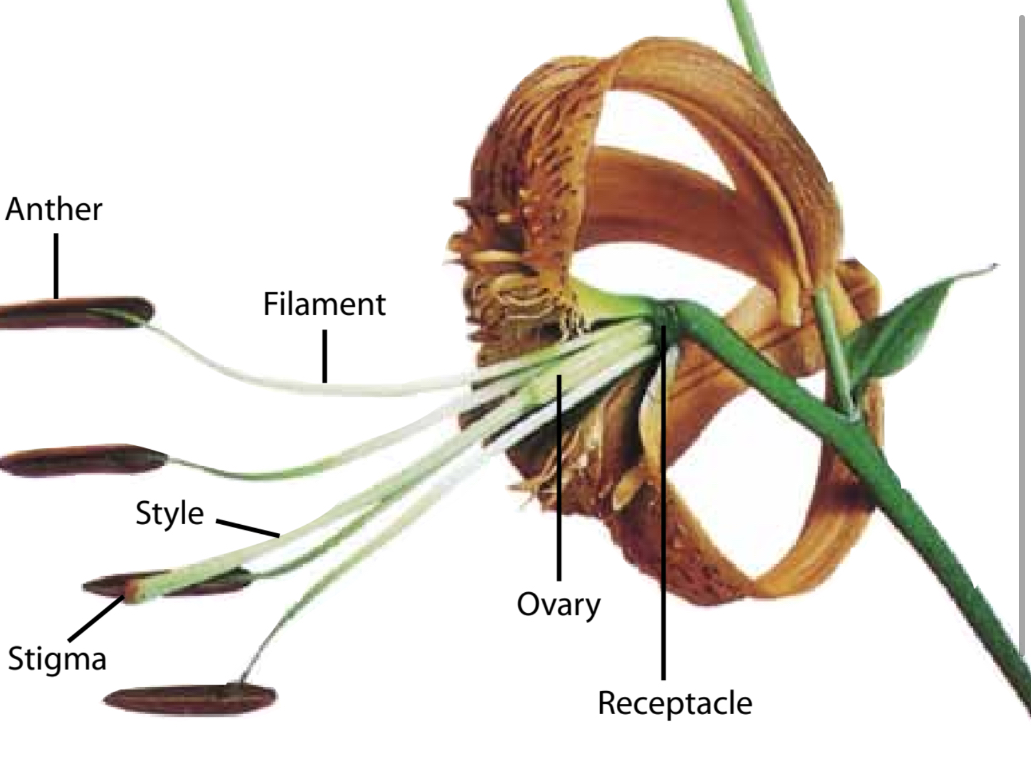
What are the characteristics of a stamen?
The pollen bearing part of the flower—> called the androecium (house of man) Microsporophyll
Contains pollen sacs
Contains 4 microsporangia
Where are the microsporangia located?
In the anther, they contains 4 microsporangia In two pairs
What does the gynoecium of a flower consist of?
(House of women)
The carpels- ovule bearing parts of the flower
Megasporophyllls that encloses one or more ovules
What portion of an carpel encloses an ovule?
The ovary, which is the lower part
What are the four whorls of the appendages
Sepals( calyx), the petals (corolla), the stamens( androecium), and the carpels (gynoecium)
In most flowers the individual carpels or groups of fused carpels are differentiated into 3 parts, what are they?
Lower part- ovary: encloses a ovule, Middle part: style, through which pollen tubes grow and upper part, stigma- receives the pollen
The style connects the what to the what?
The ovary to the stigma
What is the placenta?
The portion of the ovary where the ovules originate and remain attached until maturity
(Placentation)
What part of the flower receives the pollen?
The stigma
What is a locule?
Fused carpels, partitioned into two or more (chambers) of the ovary that contains the ovules (gynoecium)
A perfect flower contains what?
Include both stamens and carpels (bisexual)
What do dioecious species have?
If the staminate and carpellate flowers are found on separate plant (Two houses”)
-Ex: Willows and Hemp
What makes a flower complete
All four whorls, sepals, petals, stamens or carpels
In flowers that contain sepals, petals, and stamen attached below the ovary, what is it said to be?
Superior (lilies) also known as a hypogynous flower
In angiosperms, the mature male gametophyte contains how many cells?
The microgamtophyte consist of only three cells
In angiosperms, the mature female gamtophyte contains how many cells?
The megagametophyte consists of seven cells
In angiosperms, what does the ovary develop into?
After fertilization the ovule develops into a seed and the ovary develops into a fruit
Microsporocytes divide by ____, forming ___?
(Pollen mother cells) divide by meiosis and each gives rise to haploid microspores and with the formation of pollen grains.
When the microspore of an angiosperm divides, it gives rise directly to?
By mitosis forms a large vegetative cell/ tube cell and a small generative cell
In embryo sac development, the egg apparatus contains the egg cell and what?
Two short-lived cellular synergids, with a thicker and convoluted cell wall
In the center of the embryo Sac are the?
Polar nuclei, containing antipodal and the central cell
What is the mature gametophyte called?
The embyo sac
In the process of double fertilization, one sperm fuses with the ___, and the other sperm fuses with the ____/
One fuses with the egg and the other with the polar nuclei
In most angiosperms, the primary endosperm nucleus is?
It’s the most common type of embryo sac formation, fusion of one sperm nuclei with the two polar nuclei- triple fusion
Results in a Triploid (3n)- that provides food materials from the developing embryo
As the seed develops, the ovary wall becomes the?
Pericarp
The ovary wall thickens and becomes differentiated into layers: Exocarp(outer layer), mesocarp and endocarp (inner Layer)
What are the unique characteristics of the angiosperms?
Flower seeds enclosed by a carpel, double fertilization→ endosperm. A reduced three nucleate microgamtophyte and a reduced megagametophyte (7 cells and 8 nuclei)
Stamens with two pairs of pollen sacs and the presence of sieve-tube elements and companion cells in phloem
The most important flower-visiting animals in angiosperms evolution are?
Bees
Most flower pollenated by birds, what are the characteristics?
Copious thin nectar, with little odor, however the flowers are colorful (red and yellow most common)
Hibicius
Flowers that are Dull-colored with strong odors and producing copious nectar are most likely pollenated by?
Pollinated by Bats.
The red and blue pigments are stores in vacuoles in flowers are called?
Anthocyanins, which are water- soluble, and are important for photosynthesis
What does an accessory fruit develop from?
A natured ovary during maturation with noncapellary tissue (with some additional parts)
Contains accessory tissue
What does a parthenocarpic fruit lack?
These fruits may develop without fertilization and seed development
Lack seeds
Ex: pineapple, citrus, pumpkin and banana
What does a multiple fruit develop from?
They are derived from an inflorescence, from the combined gynoecium of many flowers ( fig, mulberry, pineapple)
What do simple fruit develop from?
A single carpel or from two or more united carpels (bean pod, cherry’s, tomato)
What are peaches, cherries and olives a part of ?
Drupes (stone fruits/ one seeded with skin like exocarp, fleshy, mseocarp, and stony endocarp
What are indehiscent fruits?
Dry and simple fruits, Do not split open at maturity and orginginate from a maturity ovary which only one seed develops
The fruit characteristics of the pea family is a ?
The Legume , resembles a follicle (single carpel that splits along one side), but its spilt on both sides
Mustard family- silque, formed of two carpels - split away from which they are attached
What are Dehiscent fruits?
Split open at maturity and contain several seeds/
What is the most common of dehiscent dry fruits?
Capsule, which are derived from compound ovary