Comprehensive Tissues and Membranes: Types, Functions, and Locations
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Tissues
Group of cells that carry out specialized activities.
Histo
Tissue.
Ology
Study of.
Pathologists
Study of cells and tissue; diseased.
Patho
Disease.
Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surfaces, cavity linings, hollow organs, ducts, and glands.
Connective Tissue
Protects and supports, binds organs together, stores energy reserves as fat.
Muscle Tissue
Generates the force needed to make structures move.
Nervous Tissue
Stimulates action potential to coordinate body functions.
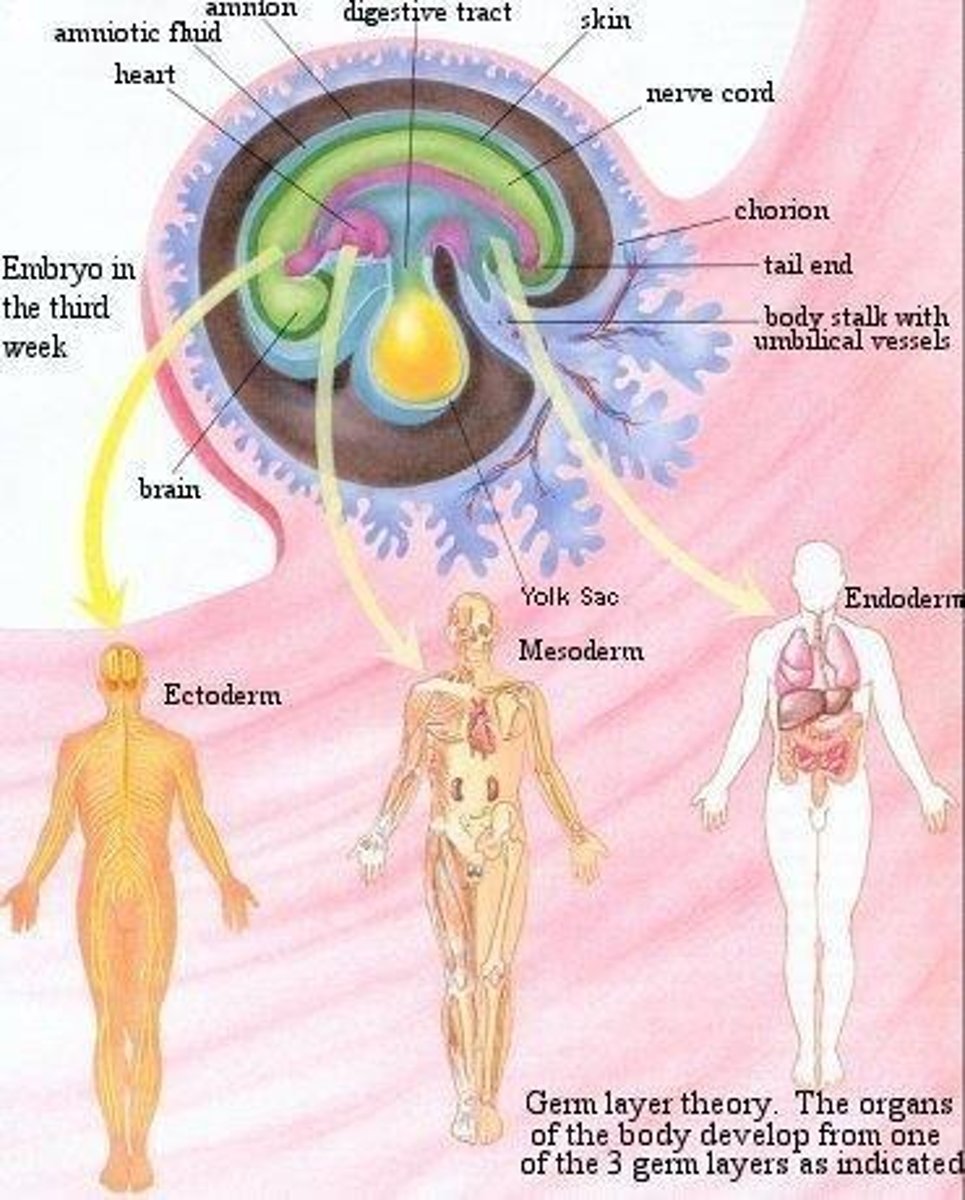
Ectoderm
The primary layer which gives rise to the nervous system and the epidermis of skin.
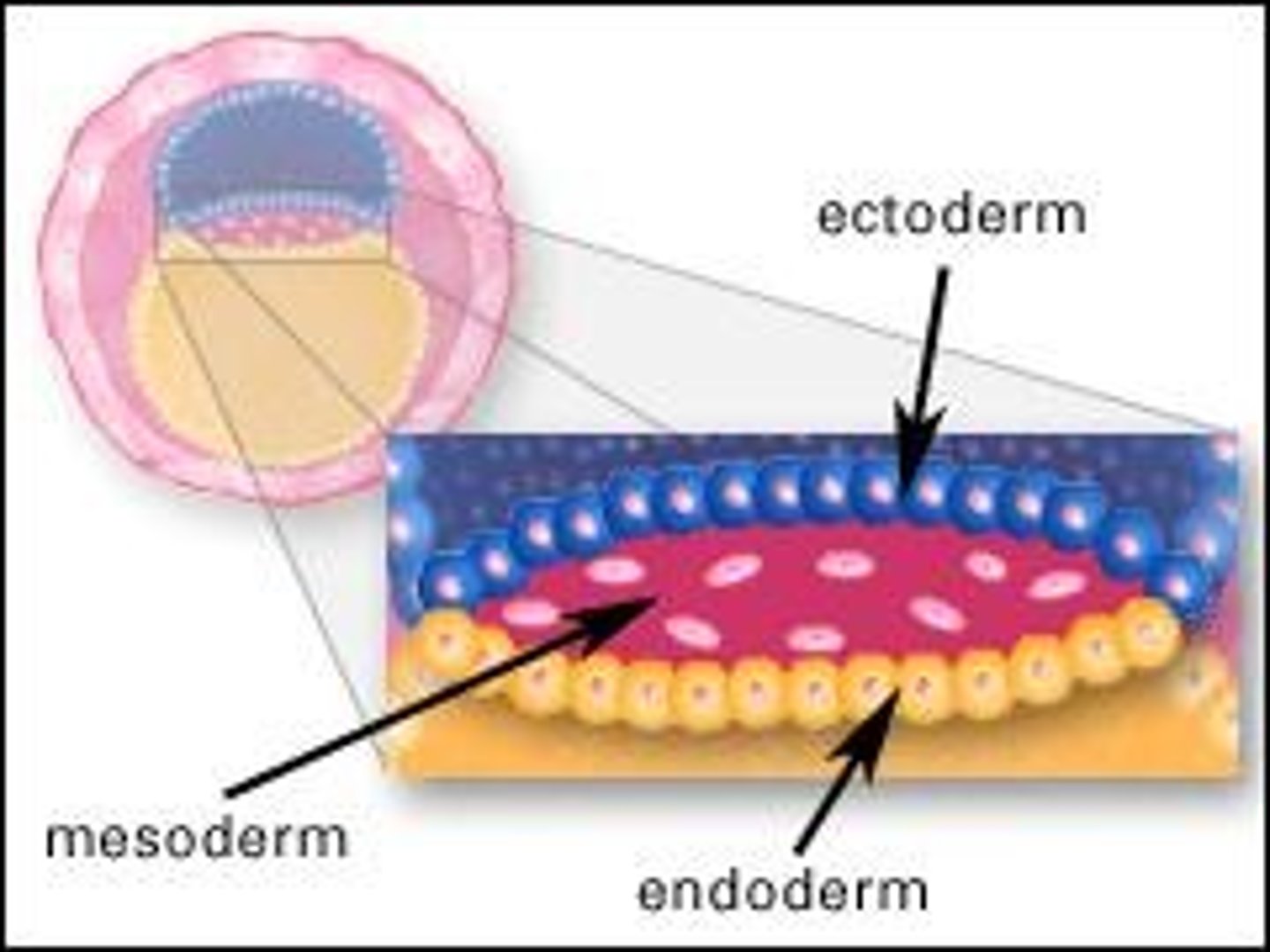
Mesoderm
The middle germ layer which gives rise to connective tissue, blood, muscles.
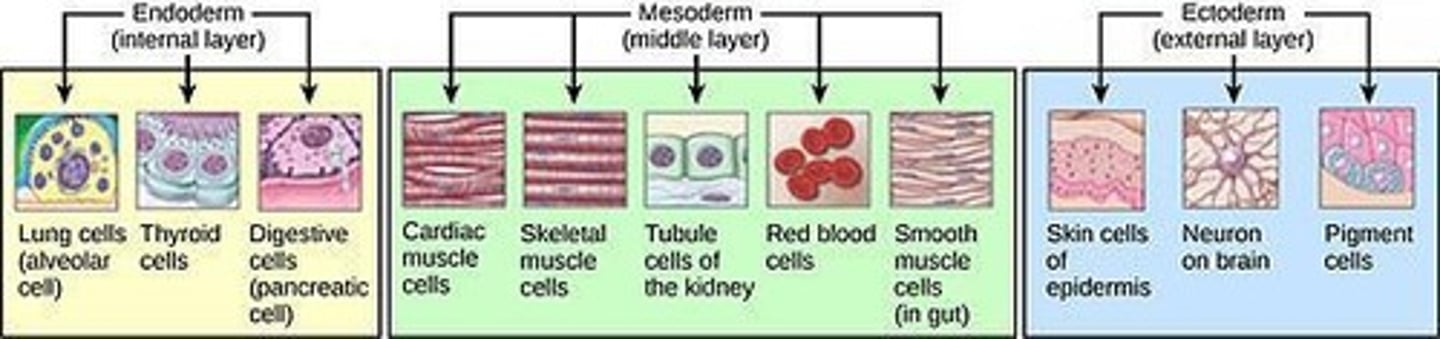
Endoderm
The lower germ layer that gives rise to the GI tract, urinary bladder, and respiratory tract.
Cell Junctions
Points of contact between adjacent membranes of various cell types.
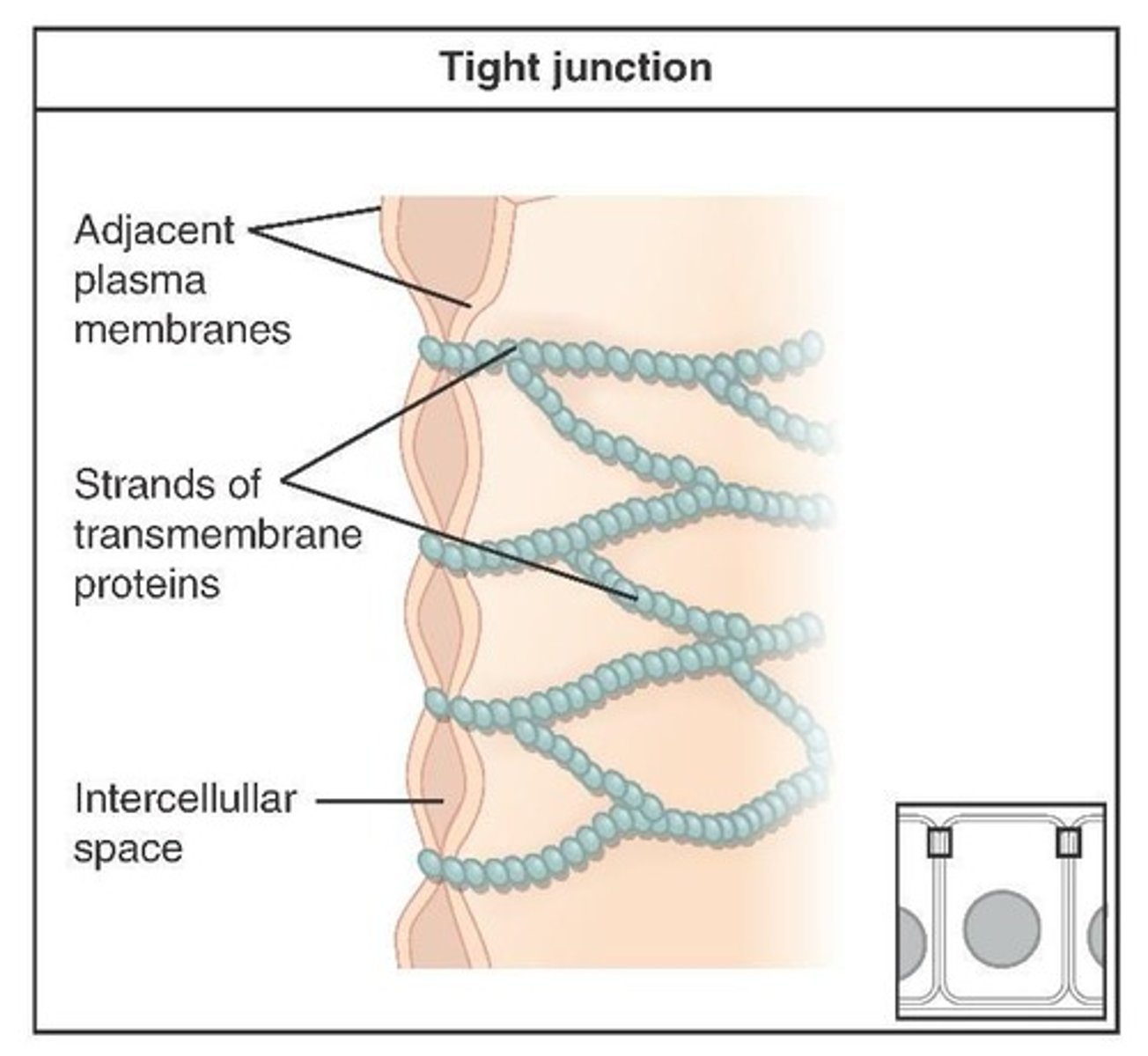
Tight Junctions
Fluid tight seal between cells to prevent leaking of substances into the blood or surrounding tissues.
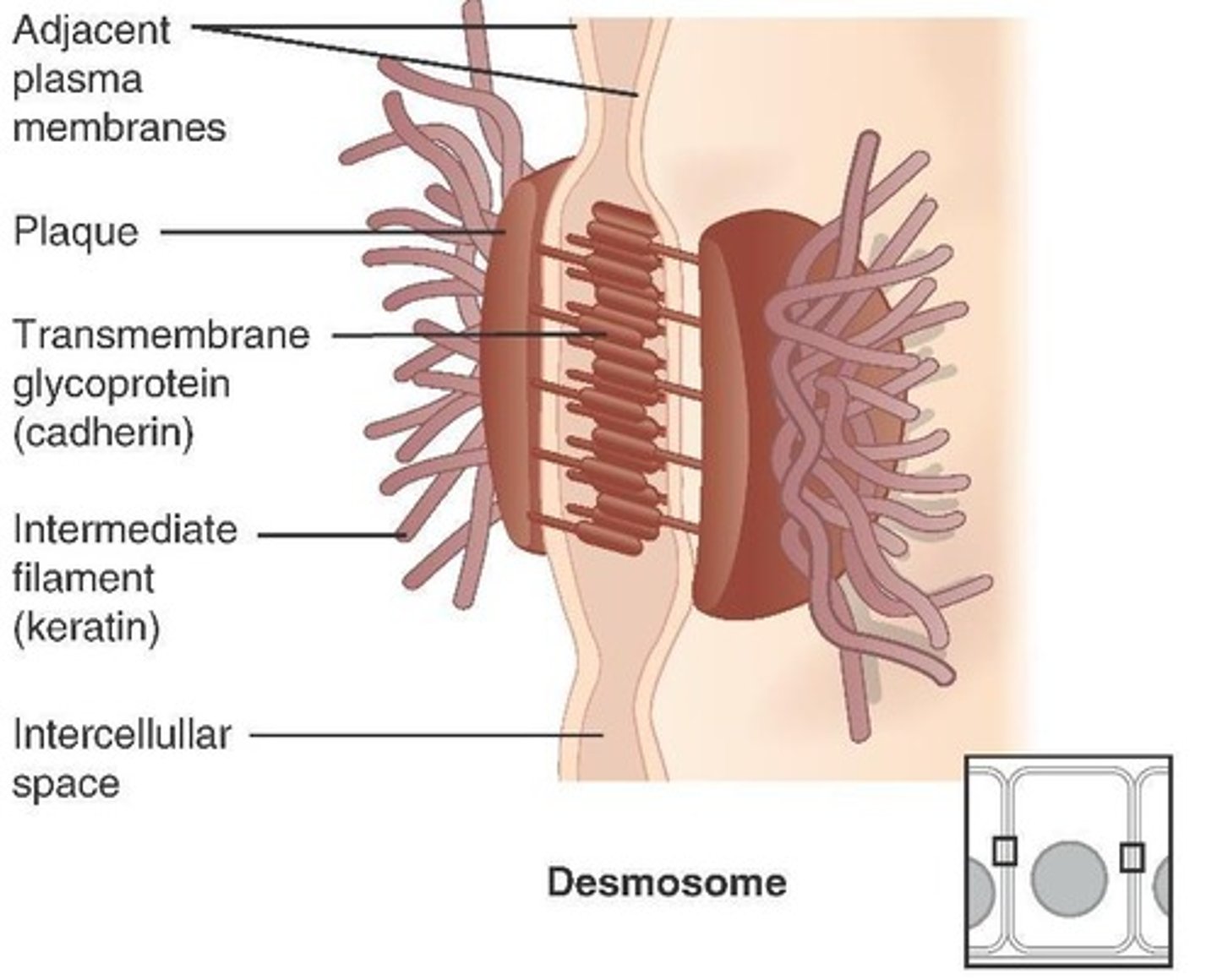
Desmosomes
Fasten cells to one another; common in stretched areas such as heart, uterus, outer skin.
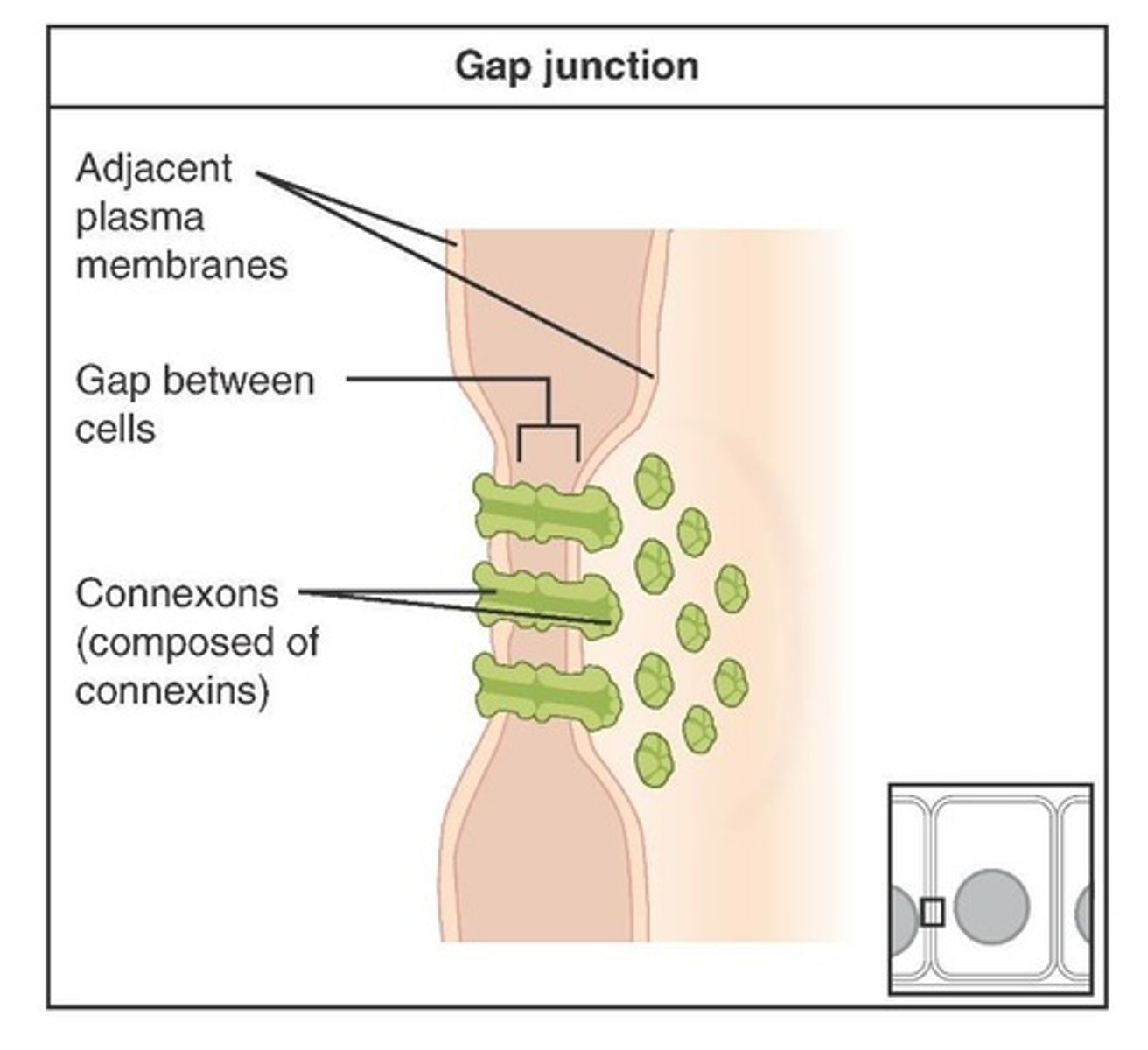
Gap Junctions
Allow passage of chemical/electrical signals through connexons from cell to cell.
Simple Epithelium
Single layer; functions in osmosis, diffusion, absorption, and secretion.
Stratified Epithelium
Two or more layers; protects underlying tissues in areas of wear and tear.
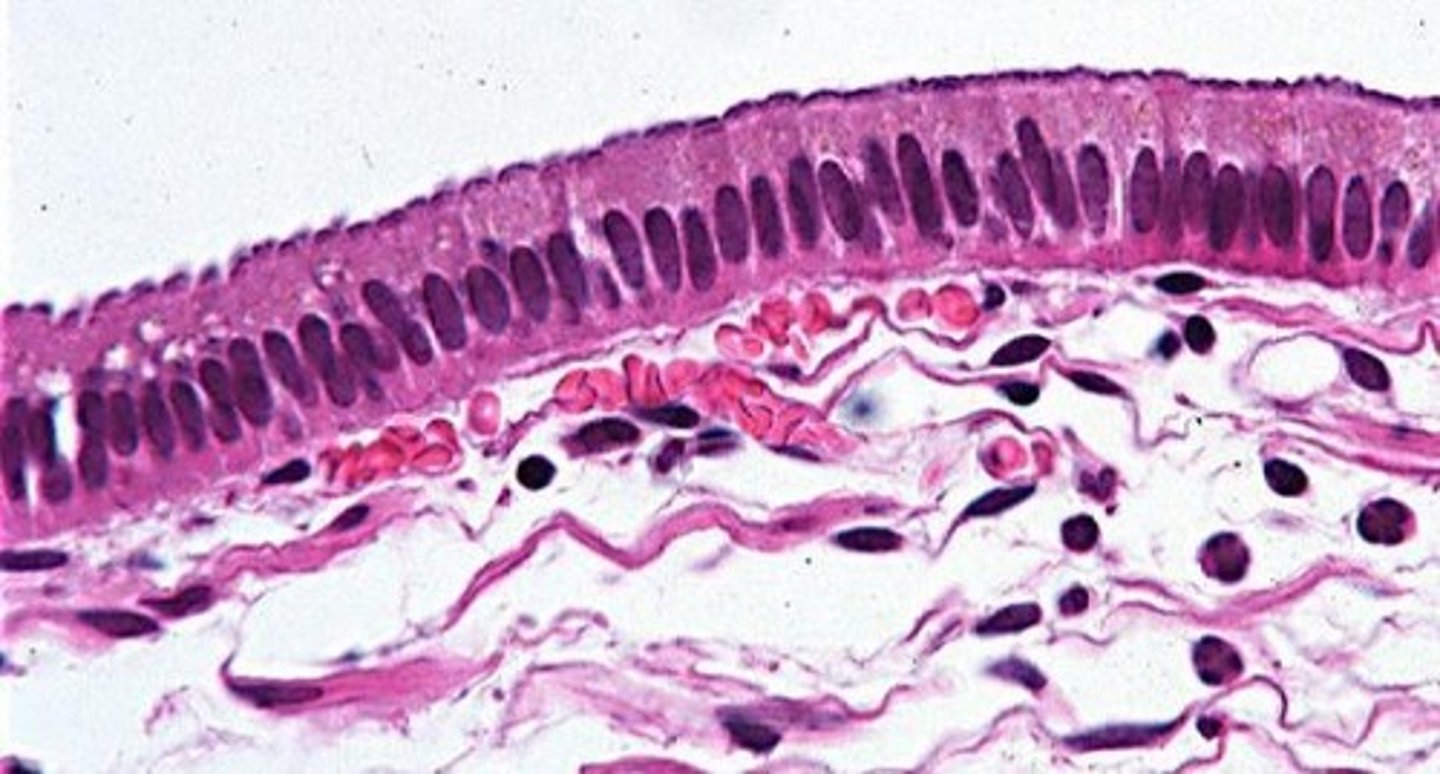
Pseudostratified Epithelium
One layer of mixed cells; functions in mucus secretion and movement.
Squamous Cells
Flat cells.
Cuboidal Cells
Thick, cube-shaped cells.
Columnar Cells
Tall, cylindrical cells.
Transitional Cells
Cells that vary in shape.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Function: Filtration, diffusion, osmosis, and secretion in serous membranes.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Function: Secretion and Absorption.
Simple Columnar Epithelium (Non-Ciliated)
Function: Secretion and Absorption; Microvilli and Goblet cells.
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function: Moves fluids and particles along passageways.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Functions: Mucus secretion & movement by cilia action.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Functions: Protection of superficial layers of skin, vagina, mouth, esophagus, tongue.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Location: Superficial Layers of Skin.
Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Location: Wet Surfaces (Mouth, Vagina, Tongue).
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Functions: Protection and limited secretion and absorption; rare type. Location: in the ducts of sweat glands and esophageal glands.
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Functions: Protection and secretion. Location: urethra, ducts of some glands, anal membranes, parts of the eye; uncommon.
Transitional Epithelium
Function: Accommodate distension in the urinary tract as fluid pressures vary. Stretched = Stratified Squamous; Relaxed = Stratified Cuboidal. Location: Lining of the ureters, urethra, and bladder.
Glandular Epithelium
The function of glandular epithelium is secretion.
Gland
A gland consists of one cell or a group of highly specialized epithelial cells secreting substances into ducts, onto a surface, or into the blood.
Endocrine Glands
Function: Produce hormones; ductless glands that secrete directly into the bloodstream. Location: Thyroid, Pituitary, Adrenal Gland, Ovaries, and Testes.
Exocrine Glands
Function: Secrete products into ducts (tubes) that empty at the surface of covering and lining epithelium or onto a free surface. Examples: sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestive tract glands.
Merocrine (or Eccrine) Secretion
Forms the product and discharges from the cell completely. Example: Salivary Glands.
Apocrine Secretion
Product forms at apical surface and pinches off from rest of cell. Example: Mammary gland.
Holocrine Secretion
Accumulates secretory product in cytosol, cell dies, and is discharged with its product. Example: Sebaceous Gland (Acne).
Functions of Connective Tissue
Binds together, supports, and strengthens other body tissues; protects and insulates internal organs; the major transport system within the body (blood); the major site of stored energy reserves (adipose); the main site of immune responses.
Connective Tissue Composition
Connective tissue consists of two basic elements: cells and extracellular matrix.
Extracellular Matrix
The material between its widely spaced cells and consists of protein fibers and ground substance.
Fibroblasts
Large, flat cells responsible for the secretion of matrix compounds; most numerous.
Macrophages
Phagocytes that develop from monocytes and eat bacteria.
Plasma Cells
Synthesized from a B lymphocyte; secrete antibodies.
Mast Cells
Involved in the inflammatory response (histamine production) and also kill bacteria.
Adipocytes
Fat cells that store triglycerides.
Ground Substance
The component of a connective tissue between the cells and fibers; supports cells, binds them together, and allows the exchange of materials between blood and cells.
Hyaluronic Acid
Cell binding, lubricating joints, wound healing.
Chondroitin Sulfate
Adhesiveness for bone, cartilage, skin, and blood vessels.
Glucosamine
Maintains joint structure and function and reduces inflammation.
Collagen Fibers
Very strong and resist pulling forces, but they are not stiff, which promotes tissue flexibility.
Elastin Fibers
Strong but can be stretched up to 1½ times their relaxed length without breaking.
Reticular Fibers
Form the framework (stroma) of many internal soft organs; form the basement membrane.
Loose Connective Tissue
Provides strength, elasticity, and support to the subcutaneous layer of skin.
Dense Connective Tissue
Dense, closely packed collagen fibers that provide high tensile strength.
Cartilage
Extremely strong, but very flexible and elastic; provides smooth surface for reduction of friction.
Bone
Provides support, involved in movement, and the production of marrow (blood-forming).
Liquid Connective Tissue
Includes blood and lymph; involved in clotting and immunity.
Adipose Fat (White)
Used for insulation, energy reserve, and fat storage.
Adipose Fat (Brown)
Generates body heat in newborns that do not shiver; most mitochondria disappear as infants grow up.
Reticular Connective Tissue
A network of reticular fibers and reticular cells; forms the stroma of soft organs such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
Fibrocartilage
Extremely tough; acts as a shock absorber, found between ball and socket joints, intervertebral discs, meniscus of the knees.
Elastic Cartilage
Abundance of elastin for stretching capability; found in ears and epiglottis.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Attached to bones by tendons; functions in body movements, posture, and thermogenesis.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Composes the heart wall; functions in pumping blood to all parts of the body.
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Forms walls of many internal organs; functions in motion of internal organs.
Neuron
Conversion from stimulus response to action potential; consists of dendrites and axons.
Dendrites
React to stimuli.
Axons
Conductor of impulse.
Epithelial Membranes
Combination of an epithelial layer and underlying connective tissue.
Mucous Membranes
Line a body cavity that opens directly to the exterior; found in the digestive, respiratory, and reproductive systems.
Serous Membranes
Line body cavities that do not open directly to the exterior and cover the organs within the cavity.
Synovial Membranes
Line the cavities of some joints.
Tissue Repair
Replaces worn-out, damaged, or dead cells with healthy ones; varies by tissue type.
Aging and Tissue Repair
With aging, tissues heal more slowly and produce more scars.