
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
de diagnose depressie wordt gesteld aan de hand van deze kenmerken
wat zijn passief suicidale gedachten
bijv de Px denkt dat het beter zou zijn wanneer hij niet meer wakker zou worden, of hij hoopt dat hij niet meer zal ontwaken
wat zijn actief suicidale gedachten
Wanneer de wanhoop toeneemt, kan de patiënt daadwerkelijk plannen gaan ontwikkelen om een eind aan zijn leven te maken
bij depressie, wanneer is het zelfmoord risico het grootst
Een bijzonder fenomeen is dat de kans op suïcide niet het grootst is wanneer de depressie het diepst is. Dat komt omdat de patiënt dan zo depressief is dat hij zelfs de energie niet kan opbrengen om een zelfmoordpoging te ondernemen. Het risico neemt paradoxaal genoeg toe wanneer de zeer diepe depressie iets opklaart en de patiënt de fut krijgt om daadwerkelijk een poging te ondernemen. Een dergelijke situatie doet zich nogal eens voor in het begin van de behandeling. Daar kan niet genoeg voor gewaarschuwd worden
welke psychiatrische aandoeningen moet je vooral uitsluiten bij vermoeden van depressie
een bipolaire stemmingsstoornis of een psychotische stoornis (eg. schizo) door te vragen naar manische symptomen, wanen en hallucinaties
bijzondere gaven

Als een depressieve stoornis wordt overwogen, dan moeten x worden uitgesloten
somatische oorzaken
Welke somatische aandoeningen kunnen zich presenteren met een beeld dat lijkt op een depressieve stoornis
Gelijkende symptomencomplexen, zoals bij hypothyreoïdie, dementie of de ziekte van Parkinson.
dwang vs drang gedachten
"Dwang" verwijst naar een onweerstaanbare behoefte om bepaalde handelingen uit te voeren, vaak om angst of ongemak te verminderen. Deze handelingen worden meestal uitgevoerd volgens bepaalde regels of op een rituele manier. In een psychologische context wordt dwang vaak geassocieerd met obsessief-compulsieve stoornis (OCD).
Voorbeelden van dwang kunnen zijn:
Het herhaaldelijk controleren of de deur op slot is
Het herhaaldelijk wassen van de handen om besmetting te voorkomen
Het ordenen van objecten op een specifieke manier
"Drang" daarentegen verwijst naar een sterk verlangen of impuls om iets te doen. Het is minder intens dan dwang en wordt meestal niet geassocieerd met angst of ongemak. Drang kan worden geassocieerd met verlangens of behoeften, zoals het verlangen om te eten of te slapen.
Voorbeelden van drang kunnen zijn:
Het verlangen om een stuk taart te eten
De behoefte om te slapen na een lange dag
Het verlangen om een film te kijken
wanneer verwijz je bij een depressieve stoornisnaar de specialistische ggz
pas bij gecompliceerde situaties bijv:
verhoogd suïciderisico
depressieve stoornis of suïcidepoging in het verleden
positieve familieanamnese voor depressieve stoornissen of suïcidepogingen
manische episodes in de voorgeschiedenis die een aanwijzing zijn voor een bipolaire stoornis
psychotische kenmerken zoals schuldwanen of paranoïde wanen
postpartumdepressie met inadequate verzorging van het kind
recidief depressie met ernstig sociaal disfunctioneren
recidief depressie met grote lijdensdruk
recidief depressie met ernstige psychische comorbiditeit
psychosis spectrum disorder is characterised by 1 or more of
delusion, hallucination, disorganised speech or behaviour
psychosis spectrum disorder classification
schizophrenia
schizophreniform
schizoaffective
delusional disorder (waanstoornis)
brief psychotic disorder
catatonia
due to susbtance/meds/somatic disease
schizophrenia manifests between…
16 and 30
wat voor sort symp optreden bij schizo
positive
negative
cognitive
other
positive symptoms in schizo
symp of impaired sense of reality
delusions/wanen (denken inhoud)
hallucinations
symp due to cognitive disorganisation (the form of thought) = desorganisatie (denken vorm)
most common hallucinations in schizo
auditory
delusions in schizo
Common
Subjects differ
Delusions of reference (betrekkingswanen)
= believing that everyday events have a unique special meaning, eg. Songs on the radio contain messages intended specifically for them
Delusions of the loss of normal boundaries of mental function
= characteristic of schizo, they think:
people can take thoughts out of their head (thought withdrawal/gedachteonttrekking) or
people can insert them (thought insertion/gedachteninbrengen) beyond their control (delusions of influence/beinvloedingswanen)
people can hear what they think
may also believe that they can transmit their thoughts (thought transmission/gedachten uitzending) → feeling of loss of mental boundaries
May also have an abrupt blocking of their train of thought (gedachtestops/sperrung)
can be accompanied by thinking that this block was due to external interference (thought interference/gedachtbelemmering)
May believe that everything around them has changed
which delusions are characteristic in schizo
Delusions of the loss of normal boundaries of mental function
= characteristic of schizo, they think:
people can take thoughts out of their head (thought withdrawal/gedachteonttrekking) or
people can insert them (thought insertion/gedachteninbrengen) beyond their control (delusions of influence/beinvloedingswanen)
people can hear what they think
may also believe that they can transmit their thoughts (thought transmission/gedachten uitzending) → feeling of loss of mental boundaries
thought withdrawal, insertion, transmission and delusions of influence
Delusions of the loss of normal boundaries of mental function = characteristic of schizo → think that people can take thoughts out of their head (thought withdrawal) or can insert them (thought insertion) beyond their control (delusions of influence), may also believe that they can transmit their thoughts (thought transmission) → feeling of loss of mental boundaries
the voices in schizo often…
criticise the patient or order them to do things (imperative hallucinations)
talk about the patient in 3rd person
imperative hallucinations
hallucinations/voices ordering the patient to do things
what positive symp in schizo manifest due to cognitive disorganisation
vorm van het formele denken
Affect the speed and coherence of thought
Incoherence = unable to follow the train of thought
Less severe symptoms = patient makes illogical connections or lose their head, eg
Derailment (ontsporing)
tangentiality
getting bogged down (verzanden)
May invent new words = neologism
May take abstract terms literally (concretisme)
neologism
= inventing new words
a positive symp in schizo due to cognitive disorderganisation
schizo typically starts with…
negative symptoms, positive occur later (sometimes years)
negative symp in schizo
Affective blunting (affectieve vervlakking) = reduced or absent emotional reactions
soms is er ook geringe of afwezig mimiek
Avolition (initiatiefverlies) = reduction in independent motor activity and action
Apathy
Poverty of thought (gedachtearmoede) = experiencing few thoughts
Alogia or poverty of speech = speech is confined to what is absolutely necessary
Anergia
Social withdrawal
zelfverzorging etc worden minder goed uitgeveord
avolition
reduction in independent motor activity and action
alogia
or poverty of speech = speech is confined to what is absolutely necessary
negative symp in schizo are often accompanied by x
cognitive and social functional impairments
De aandoening debuteert dikwijls met negatieve symptomen
which symp are most difficutl to influence in schizo
negative
Langer bestaande x in psychose hangen samen met een ongunstige prognose
ernstige negatieve symptomen
secundaire negatieve symptomen
soms worden negatieve symptomen gedeeltelijk veroorzaakt door antipsychotica , soms trekken patiënten zich terug omdat ze vanuit hun wanen bang zijn voor anderen , soms zijn de negatieve symptomen gedeeltelijk het gevolg van te weinig stimulatie (eg. bij verblijf op een afdeling)
negative schizo symp vs depressive symp
Depressive symptoms have subjective sadness, hopelessness (uitzichtloos) and often feelings of guilt (schuldgevoelens) and suicidal thoughts
Patients with negative symptoms often have no subjective uniforms
But they can both occur together
Overigens maken zeer veel patiënten met schizofrenie een aanpassings- of rouwperiode, dan wel een depressieve episode mee
cognitive symp in schizo
slowed down info processing speed (vertraging van de informatieverwerkingssnelheid)
disorders of attention and working memory
verbal and visual memory may be impaired
executive function disorders can be a major problems → affect reasoning and problem solving esp.
can be overlap with autism spectrum disorder in metacognitive function symptoms ie. mentalising ability + social knowledge, perception and decision making
other symptoms in schizo (not pos, neg or cogni)
symptoms found in the DSM-5 in addition to those in the photo:
psychomotor function → abnormal or bizarre behaviour eg, catatonia, also psychomotor retardation w/ sequencing and coordinating motor actions
mood → depression or mania
emotion inconsistent w/ the situation (eg. laughing when talking about something sad/treurig) = inappropriate affect
schizophrenia criteria

schizophreniform vs schizophrenia
phreniform → meets criterion A for schizophrenia but lasts at least 1 month but less than 6 months
can be that they had it for 4 months and it went away or theyre on their 4th month and it hasnt left yet but its still <6 m
what are positive prognostic factors for schizophreniform
acute onset (within 4 weeks of the first change in functioning), confusion or perplexity at the peak of the psychotic episode, good premorbid functioning and absence of flat affect
what % of schizophreniform eventually meet the criteria for schizophrenia
70%
which schizo symptoms are associated w/ poor prognosis
long standing negative symp
negative schizo symp. can also be caused by…
antipsychotics or due to them withdrawing due to their delusions
= ‘secondary’ negative symp.
catatonia
a group of symptoms that usually cause apparent unresponsiveness to external stimuli and apparent inability to move normally in a person who is apparently awake
but, can also present w/ excessive movement (eg. grimasseren)
patients may copy the doctors movements, words and facial expressions (even in the akinetic type (ie. most common) they may not respond to you but only copy words you said) → echomimie
neurological exam may reveal catalepsy, negativism or wavy flexibility/flexibilitas cerea (???***)
if severe → risk of harming themselves or others, high fever and exhaustion/uitputting
occurs in many psychiatric disorders but also in autism, metabolic diseases, cancer, cranial injury etc
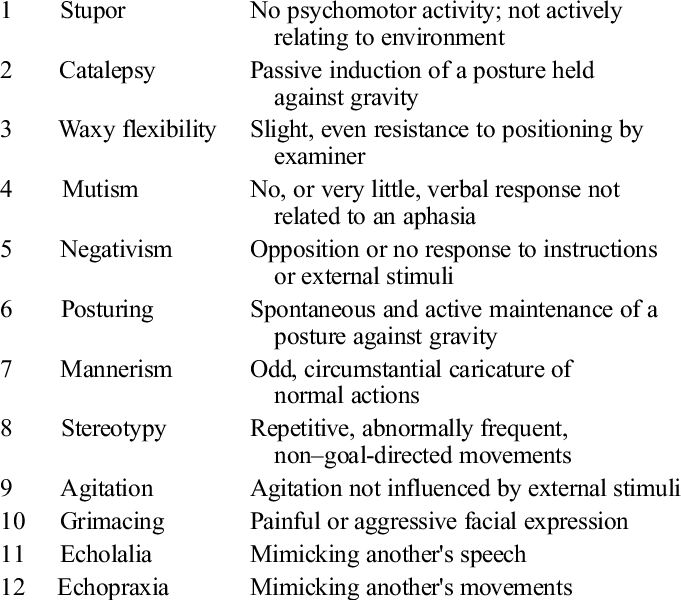
schizoaffective disorder
ie. schizo + mood disorder → depressive and/or manic symptoms present for most of the time while they’re suffering from schizo AND at least 2 weeks of psychosis (delusions + hallucinations) w/o a mood disorder
group of disorders
must be the mood disorder ON the schizo, not the opposite way around
course is better than schizo, esp. if the main feature is the mood disorder not the psychosis

psychotic symptoms during a depressive disorder vs a depressive/manic mood during a psychotic disorder
1st is just a mood disorder
2nd might be schizoaffective disorder
schizoaffective criteria

delusional disorder usually starts around…
40
its rare
heeft een chronisch beloop
the content of the delusions in delusional disorder is related to…
the patients position in relation to other people
de positie van de patiënt tegenover anderen
delusions in delusional disorder vs delusions in schizophrenia/phreniform/affective
in delusional disorder
the delusions are NOT bizarre and outside the ‘sphere of influence/invloedssfeer’
there are NO negative symptoms
function is not markedly impaired other than delusions = functioneren is betterlijk normaal
are there hallucinations in delusional disorder
rare but if they occur, theyre related to the delusions
types of delusions in delusional disorder
persecutory/paranoid
belief one is going to be harmed (dat ze zich tekortgedaan (?) of benadeeld door instanties of door een partner)
also includes jealousy delusions
vergiftigingswaan, de achtervolgingswaan en de ontrouwwaan (ook wel jaloersheidswaan genoemd)
referential (ideas of reference)
belief that certain gestures, comments, or environmental cues are directed at oneself
grandiose (grootheidswanen)
belief that the individual has exceptional abilities, wealth, or fame
i think erotomanic and paranormal wanen fall under this
erotomanic = de patiënt is ervan overtuigd dat een belangrijk iemand op hem verliefd is
paranomale = de patiënt is ervan overtuigd dat hij paranormale vermogens heeft
nihilistic
conviction that a major catastrophe will occur
somatic
beliefs focused on bodily function or sensation
erotomanic
false belief that another individual is in love with them
delusional disorder criteria
characterised by >1 month of delusions w/o other psychotic symptoms

waanstoornis prognose/Tx
Patienten zoeken geen behandeling , en ze wijzen deze vaak met kracht af. Het opbouwen van een therapeutische samenwerking is dan ook meestal bijzonder moeilijk. Soms lukt het om overeenstemming te bereiken om te praten over de gevolgen van de waanstoornis zonder deze als waanstoornis te omschrijven. Vereenzaming , relatieproblemen en conflicten kunnen zo het onderwerp van gesprek worden en soms kun je patiënten helpen dergelijke problemen te verminderen . Antipsychotica worden vrijwel nooit geaccepteerd. Wanneer antipsychotica bij bijvoorbeeld een parasietenwaan wel worden ingenomen , kan dit een duidelijke vermindering van de wanen geven
brief psychotic disorder
least serious psychosis spectrum disorder
full recovery after a short time
often follows a stressful period
rest and support and short term antipsychotics may be indicated
DSM-5:
meets criterion A for schizo
>1 day but <1 month with eventual full return to the premorbid level of functioning
when is a delusion not bizarre
when its unlikely but can very much be true (eg. they think theyre married to a celebrity, its not IMPOSSIBLE but its just not true)
bizarre would eg. be ‘aliens live in my home’
are there prodromal symptoms for schizo
yes sometimes, eg.
sadness
anxiousness
irritability
social withdrawal
compulsion
subclinical symptoms of psychosis eg. illusions, ideas of reference, magical thinking etc
cognitive symptoms eg. distractibility and difficulty concentrating
when do first signs of schizo usually appear
during adolescence, somewhat later in women than men
symp sometimes develop after…
a period of delving into philosophical, religious (godsdienst) or spiritual matters
what predicts a 1st episode of schizo (psychotische decompensatie)
no specific symp or factors accurately predict a 1st episode
x in young people w/ mild psychotic symptoms is associated with a markedly increased risk of transition to a psychosis spectrum disorder
social withdrawal behaviour (sociaal-terugtrekgedrag)
so theyre high risk i guess
x for patients at ‘ultra high’ risk reduces the risk of transition to a psychosis spectrum disorder and the severity of symptoms
cognitive behavioural therapy
clinical pres of psychotic disorders usually stabilises after…
5-10 years
sometimes experience a marked improvement in middle age
welke symp staat op de voorgrond in de later stadia van psychose
agitation often diminishes and the clinical presentation is dominated by negative symp
men with psychosis…
are more likely to suffer from negative symp and worse social functioning (and worse psychosis overall)
schizo patients have higher mortality from
accidents, illness and suicide
suicide, substance abuse in psychosis
6% die from suicide, risk is highest among young men living in isolation who experience frequent psychotic episodes
the risk of suicide is highest immediately after leaving the hospital
40% alcohol dependent, 20% abuse cannabis, 7% abuse cocaine
>75% smoke cigarettes → nicotine reduces the levels of antipsychotics → reduces some of their adverse effects
what thing do psychotic patients do that reduces the level of antipsychotics to/which reduce some of their adverse effects
smoke cigarettes
what risk is increased in schizo
metabolic syndrome
x + y in schizo = excessive mortality due to CVD
increased metabolic syndrome risk + cigarette smoking
schizo statements:
>60% will have been free from psychosis for the past 2 years after about 15-25 years of illness
after 15 years, 5% of an incidence cohort will have been admitted to a psychiatric hospital and only 7% will be living in sheltered housing
ie. vast majority will be living independently or with family
only 25% have a paid job
Ernstige psychosesymptomen gaan niet altijd samen met ernstig sociaal disfunctioneren en omgekeerd
schizo life expectancy
5-20 years shorter than average population
psychosis patients are by definition…
convinced that their ideas and experiences are true and therefore consider that they are not ill
schizo diagnostiek
Gebaseerd op de psychiatrische anamnese en het status-mentalisonderzoek
Dit wordt gecombineerd met de beschikbare informatie over de huidige episode en de hele ziektegeschiedenis: begin , aanleidingen (bijvoorbeeld middelengebruik) , duur, sociaal en professioneel functioneren en kwaliteit van leven. Bijzondere aandacht gaat uit naar eventuele familiale belasting
In de acute fase is het soms moeilijk om met een patiënt in gesprek te raken . De patiënt heeft vaak geen ziekte besef en vindt dat er met hem niets aan de hand is. De patiënt observeren kan dan helpen om de stoornis vast te stellen. Bij een huisbezoek bij een psychotische patiënt kan zijn chaotische, onverzorgde huishouden opvallen. Soms worden idiosyncratisch geordende gebruiksvoorwerpen aangetroffen: spullen die worden gebruikt om afluisteren door de buren te voorkomen, en radiostraling af te weren. Ook kan de patiënt er zelf vreemd of onverzorgd uitzien . Achter het vreemde uiterlijk schuilen vaak psychotische verklaringen, waarover de patiënt vertelt, als je hem ernaar vraagt en mits er vertrouwen ontstaan is. Bij observatie kan gedrag worden gezien dat te maken heeft met de hallucinatoire belevingen : patiënten kijken in de richting vanwaaruit ze de stemmen horen, stoppen vingers in de oren of dragen een koptelefoon , of voelen op de plaats waar op hun huid straling valt. Soms is de patiënt zwijgzaam of reageert hij afwijzend en agressief. Heteroanamnestische gegevens van familie , buren , huisarts of politie zijn vaak onontbeerlijk voor het vaststellen van de stoornis.
statement:
Wanneer er anamnestisch aanwijzingen zijn voor eerdere episoden (chronische schizofrenie) of achteruitgang in het premorbide functioneren, moet er bijzondere aandacht worden besteed aan de negatieve, cognitieve en depressiesymptomen.
welke middelen en aandoeningen kunnen psychose veroorzaken
Amfetamine, cocaïne en cannabis , maar ook geneesmiddelen met anticholinerge werking of bijvoorbeeld L-dopa
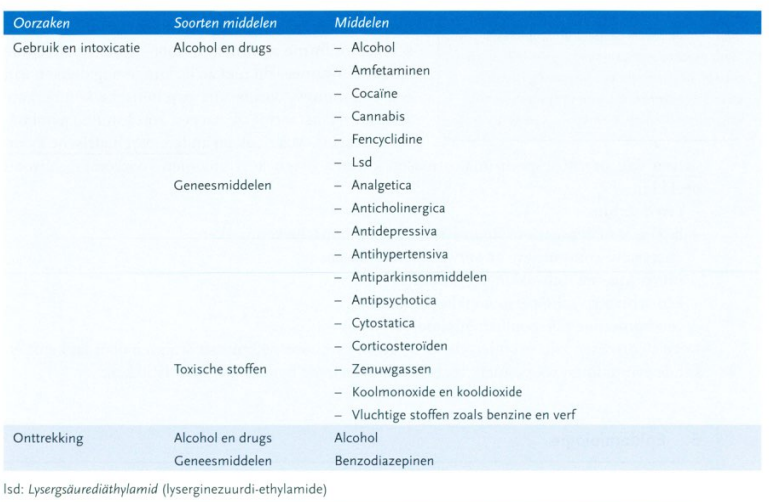
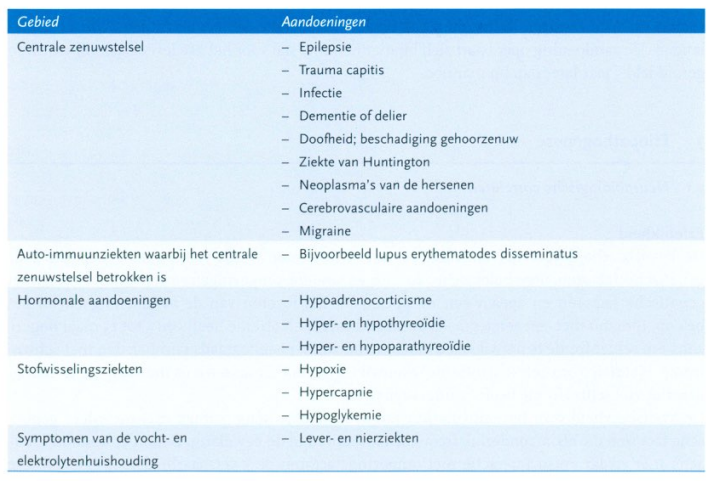
schizo openbaart zich bij mannen meestal voor x, bij vrouwen x
De aandoening openbaart zich bij mannen meestal voor het 25e levensjaar, bij vrouwen gemiddeld 5 jaar later dan bij mannen
De kwetsbaarheid voor het ontwikkelen van schizofrenie wordt voornamelijk bepaald door…
genetische factoren
Het risico om ook schizofrenie te ontwikkelen voor iemand wiens monozygote tweelingbroer of zus schizofrenie heeft, is ongeveer 50%
Iemand met een eerstegraads familielid met schizofrenie heeft een x maal hogere kans om schizofrenie te ontwikkelen dan iemand zonder eerstegraads familieleden met schizofrenie
5 tot 15
welke neurbiologische factoren spelen waarschijnlijk een rol bij het ontstaan van negatieve en positieve symptomen
Neurotransmitter
Ontregeling van de dopaminerge neurotransmissie (in samenhang met ontregeling van onder andere de glutaminerge neurotransmissie, waardoor GABA minder inhiberende invloed heeft op dopaminerge release)
Grofweg wordt verondersteld dat frontale hypodopaminerge transmissie vooral samenhangt met negatieve symptomen
^ + verminderde inhibitie → hyperdopaminerge transmissie in het limbische systeem → positieve symptomen
Er zijn veel aanwijzingen dat afwijkingen in de prefrontale cortex en het limbische systeem betrokken zijn
later is er hersen volumeverlies (neurodegeneratie)
psychosociale factoren die samen met psycho hangen
migratie, bevolkingsdichtheid
zo komt schizofrenie meer voor bij zowel de eerste als de tweede generatie van bepaalde groepen migranten
Het zou kunnen dat de door deze migranten waargenomen (crazy word to use here) discriminatie bijdraagt aan het risico om psychotisch te worden
Mogelijk verhogen deze psychosociale factoren via een toegenomen gevoel van onzekerheid en gebrek aan vertrouwen de waakzaamheid en gevoeligheid voor impulsen en indrukken
psychotraumatische gebeurtenissen in de jeugd, zoals mishandeling en seksueel misbruik
all of these increase the gevoeligheid van de dopaminerge neurotransmissie
x gebruik komt voor bij 5-10% van de jongeren met psychose
cannabis
er is een consistente associatie gevonden tussen cannabisgebruik en een tweevoudig risico op een psychosespectrumstoornis
het risico is vooral verhoogd als jongeren voor het 15e levensjaar starten met blowen, als ze veel blowen, en als ze m e-rijke en cannabidiolarme cannabisproducten gebruiken.
pre en perinatale RFs voor schizofrenie
schizo Tx
psychoeducatie
Er is beperkte gunstige langetermijneffecten zijn van psycho-educatie op sociaal functioneren en duur van heropnamen
antipsychotica
positieve symptomen zijn meestal goed te behandelen, en depressiesymptomen nemen vaak af
negatieve en cognitieve symptomen zijn moeilijker te beïnvloeden, hoewel er ook aanwijzingen zijn dat negatieve symptomen op de langere termijn kunnen verbeteren
psychosociale
psychotherapeutische
recidiveren treedt op bij x% van schizofrenie patienten die x
recidiveren treedt op bij 80% van schizofrenie patienten die stopped met het gebruik van antipsychotica
statement:
Voorafgaand aan een recidief treden geregeld dezelfde symptomen op die voorafgingen aan de eerste psychotische episode (bijv: verergering van negatieve symptomen , depressiviteit, en angst of agitatie)
we said before there are no signs of a first psychosis episode but there can be for repeating episodes (in either case there can be prodromes)
welke antipsychotica hebben een iets gunstiger effect op neg symp
amisulpride , clozapine , olanzapine en aripiprazol
haloperidol ook
welke antipsychotica hebben een iets gunstiger effect op depressie symp
Amisulpride , clozapine , olanzapine , quetiapine , sulpiride en aripiprazol hebben in vergelijking met de andere antipsychotica een iets gunstiger effect op depressiesymptomen
Quetiapine is ook geregistreerd voor bipolaire stoornissen en heeft een gunstig effect bij de depressieve stoornis
krachtigst antipsycho
clozapine
also the most bijwerkingen
antipsychoticum bijwerkingen
bewegingssymptomen (extrapiramidaal symptomen)
parkinsonisme
acathisie
acute dystonie
tardieve dyskinesie
subjectieve symptomen
bijv dysforie, sedatie
de mate van dopamine D 2 -bezetting door verschillende antipsychotica bepaalt het subjectieve welbevinden
metabole symptomen
metabool syndroom
overgewicht
CVD risico
seksuele symptomen
vermindering van libido, seksuele opwinding, orgasme of ejaculatie
verhoogd prolactin (aripiprazol can slightly decrease prolactin though because its a partial dopamineagonist?)
cardiale aandoeningen
maligne neurolepticasyndroom
gekenmerkt door een combinatie van koorts, spierrigiditeit en verhoogd serum creatinekinase (CPK)
agranulocytose
bij 1% van clozapine behandeling
patiënten met ernstige psychiatrische aan doeningen hebben een tweemaal verhoogde kans op x
esp with antipyschotica gebruik (i dont think just like that)
plotse hartdood
verlenging van het QTc-interval door diverse antipsychotica (onder andere droperidol en pimozide) zou hierbij een rol kunnen spelen

wat is de neuroleptic threshold
= de gemiddelde dosering haloperidolequivalent waarbij extrapiramidale symptomen ontstaan
deze is bij patiënten die nog niet eerder met antipsychotica zijn behandeld, ongeveer de helft van die van patiënten die wel eerder met antipsychotica zijn behandeld
statement psychose:
Bij onderhoudsbehandeling zijn er nauwelijks aanwijzingen dat het zinvol is de dosering te verlagen ten opzichte van de laagst effectieve dosering in de acute fase. Wanneer je dit toch wenst, is een doseringsverlaging met ongeveer 25% mogelijk. Je moet niet lager doseren dan de helft van de laagst effectieve dosering in de acute fase
Hierbij is het wel van belang dat ook voor de acute behandeling al de laagst mogelijke effectieve dosering moet worden gezocht.
De kans op succesvol stoppen met antipsychotica na remissie bij eerste episode patienten is x%
20
na meerdere psychotische episoden is de kans op succesvol stoppen vrijwel nihil
psycho intermitterende vs onderhouds behandeling
Intermitterende behandeling waarbij de medicatie wordt onderbroken en opnieuw wordt gestart als er vroege symptomen terugkeren, blijkt tweemaal zoveel recidieven op te leveren bij patiënten die meerdere psychotische episoden hebben gehad . Maar bij eerste-episodepatiënten die geen terugkeer van symptomen hebben gekregen bij verlaging van de dosering antipsychotica , bleek intermitterende behandeling waarbij antipsychotica herstart werden bij prodromale symptomen even goed als onderhoudsbehandeling. Daarom is een afbouwpoging verdedigbaar bij eerste-ep isodepatiënten die binnen een jaar volledig in remissie zijn geraakt en het extra recidiefrisico aanvaarden. Dit kan voor veel patiënten een overtuigende manier zijn om de noodzaak van onderhoudsbehandeling te onderzoeken
Er zijn enkele aanwijzingen dat een constante dopamine D2 -blokkade niet nodig is om een recidief te voorkomen . Dat zou kunnen impliceren dat minder frequent dan dagelijks doseren ook bij antipsychotica met korte halfwaardetijden goede resultaten kan opleveren . Er zijn aanwijzingen dat voortdurende blootstelling aan antipsychotica in de loop van de tijd de antipsychotische effectiviteit doet afnemen en het risico op bijwerkingen zoals tardieve dyskinesie doet toenemen.
>33% van psycho patienten gebruiken na 1 maand…
niet meer de geadviseerde antipsychotica, of niet langer de geadviseerde dosis
na 2 jaar is dit percentage opgelopen tot meer dan 75%
onvoldoende gebruiken van antipsychotica hangt samen met klinische opnamen, verminderd sociaal functioneren en een verminderd vermogen om werk en relaties te behouden
de bij psychosespectrumstoornissen frequent voorkomende cognitieve symptomen , gebrek aan structuur, verminderd ziekte-inzicht en beperkte sociale steun vergroten de kans op inadequaat medicatiegebruik
oplossing (?) = depot antipsychotica
additiestrategieen bij psychose
Lamotrigine toegevoegd aan vooral clozapine heeft een matig gunstig effect op negatieve symptomen
Antidepressiva in combinatie me t antipsychotica geven een gering gunstig effect op depressieve en negatieve symp tomen
Het is van belang dat de psychiater zich ervan bewust is dat negatieve symptomen kunnen samenhangen met verschillen de, soms moeilijk te onderscheiden factoren zoals depressiviteit, demotivatie, extrapirami dale bijwerkingen, sociaal isolement en onderstimulatie . Behandeling van negatieve symptomen moet altijd bestaan uit niet-farmacologische interventies. Wat betreft cognitieve symptomen zijn er nog geen bewezen werkzame en klinisch toepasbare additiestrategieën waarbij een geneesmiddel toegevoegd aan antipsychotica een verbetering geeft
wat % van schizofrenie px zijn (partieel) therapieresistent
en wat is daarna geindiceerd
30%
dan is een proefbehandeling met clozapine geïndiceerd Wanneer er na 4 maanden geen respons optreedt, is de kans op een latere respons zeer klein geworden
Clozapine moet voldoende hoog worden gedoseerd volgens een langzaam oplopend opbouwschema. Je moet voorzichtig zijn en monitoren vanwege initiële orthostatische hypotensie, risico op epileptische insulten en het risico op aganulocytose
psychologische behandeling van psychose bestaat uit
7 vormen
cognitieve gedragstherapie
gezinsinterventies
psychomotorische therapie
muziektherapie
counseling en steunende psychotherapie
opingstrategieën bij hallucinaties
cognitieve remediatie
wat kan de ernst van hallucinaties en depressiviteit verminderen
cognitieve gedragstherapie
wat kan de therapietrouw bij psychose verbeteren
cognitieve gedragstherapie
x bij hallucinaties leveren in onderzoek geen consistente gunstige effecten op
copingstrategieen (bijv oordoppen gebruiken, afleiding zoeken, gedachtestoptechnieken, neuriën of zingen)