Physics CH 11: Harmonic Motion
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Simple Harmonic Motion
vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium
Restoring Force
a force that acts to bring an object back to equilibrium
Damping
the gradual loss of amplitude of something in harmonic motion; due to friction
Hooke's Law
restoring force = -displacement x constant
pendulum
A device that swings back and forth due to the force of gravity
bob
a mass at the end of a pendulum
gravity
source of restoring force in pendulum
gravity and spring force
sources of restoring force in mass-spring systems
amplitude
For a wave or vibration, the maximum displacement on either side of the equilibrium (midpoint) position.
Period (T)
time taken for one complete vibration
Frequency (f)
the measure of how many oscillations per time
Hertz
the unit of frequency, equal to one cycle per second
reciprocal
relationship between frequency and period
length and gravity
factors that affect period of a pendulum
mass and spring constant
factors that affect period of a spring system
wave
A disturbance that transfers energy from place to place
mechanical wave
A wave that requires a medium through which to travel
medium
Material through which a wave travels
electromagnetic waves
transverse waves consisting of changing electric fields and changing magnetic fields
pulse
a single wave through a medium
periodic wave
A repetitive series of connected pulses
transverse wave
A wave in which the particles of the medium move perpendicularly to the direction the wave is traveling
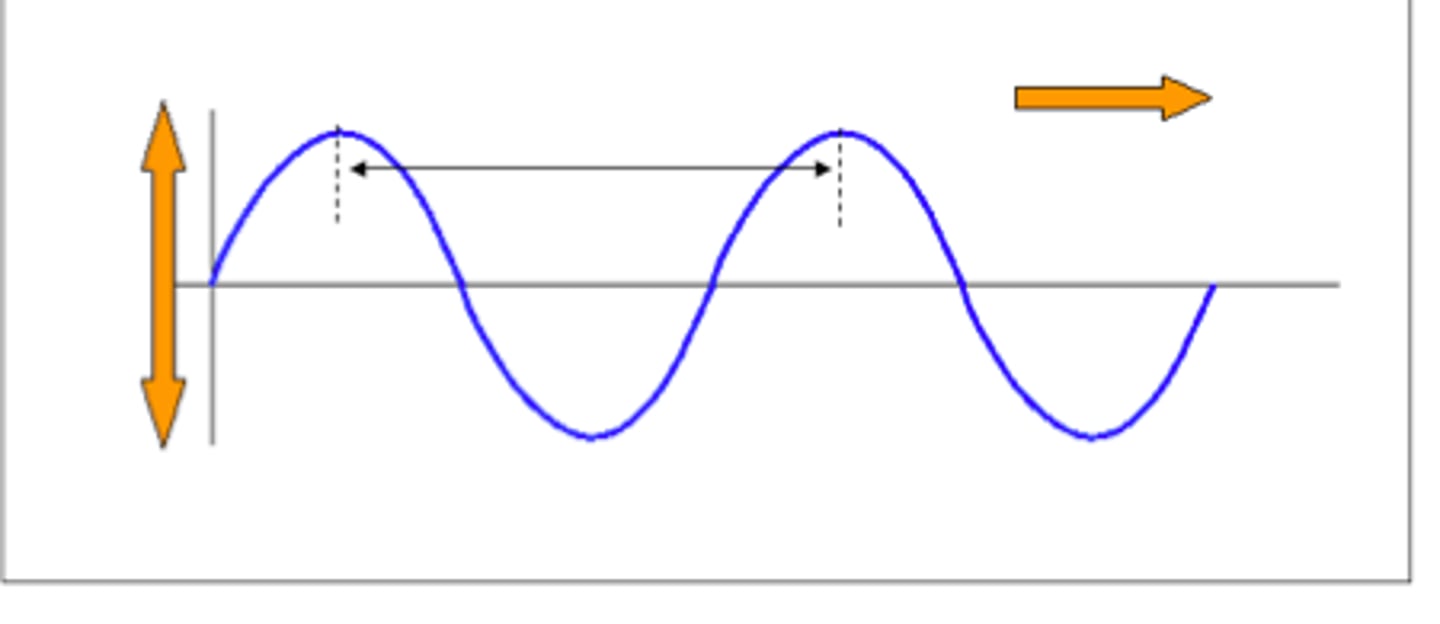
longitudinal wave (compression wave)
A wave in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels
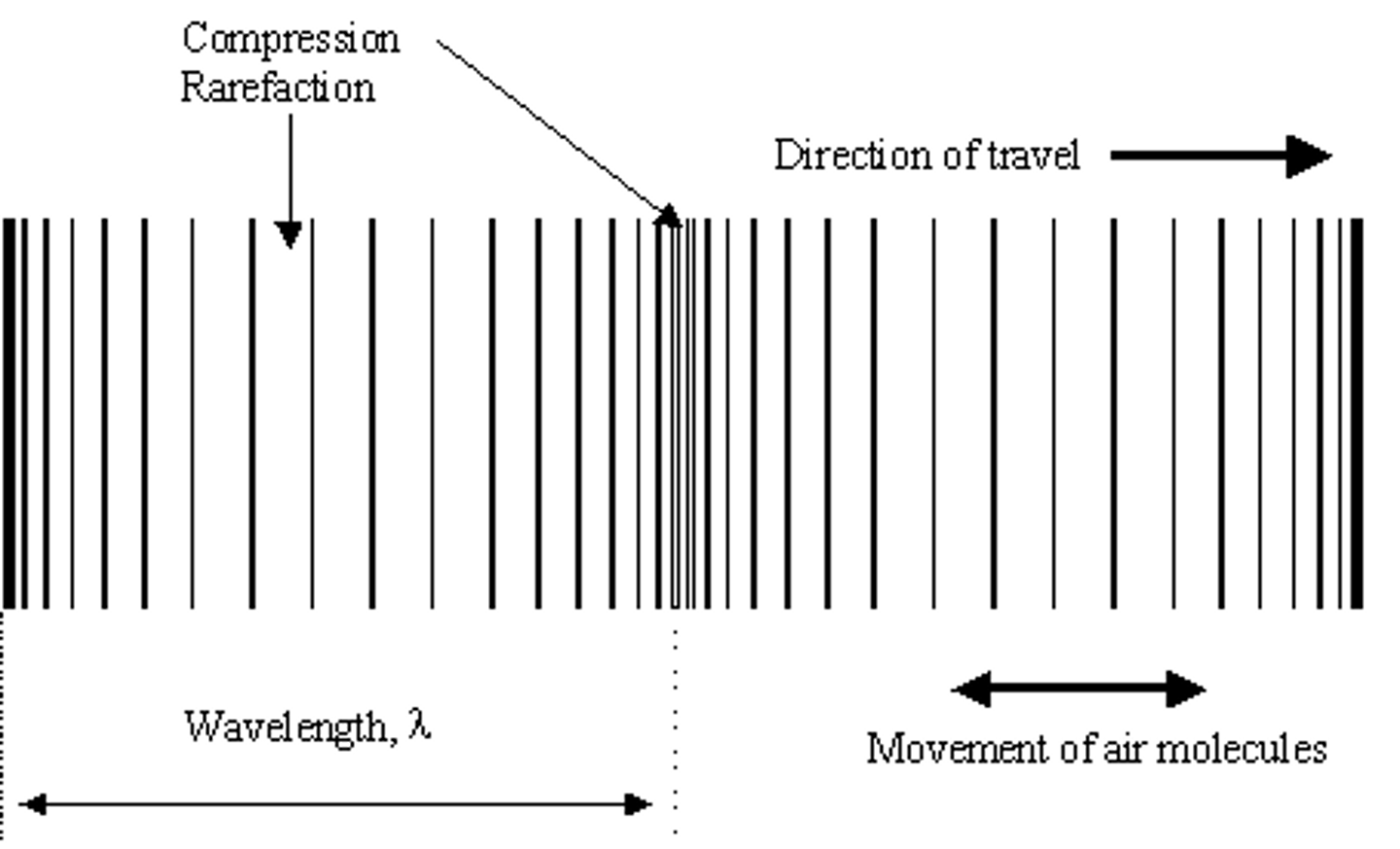
rarefaction
a part in a longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart
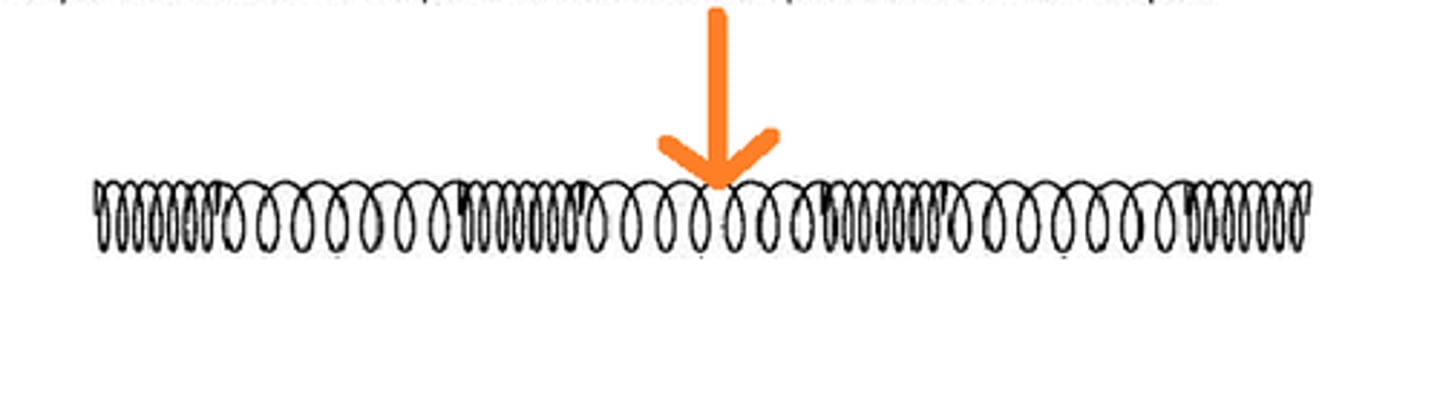
compression
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together.
superposition of waves
Overlap of two waves at a point in space
constructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a larger amplitude
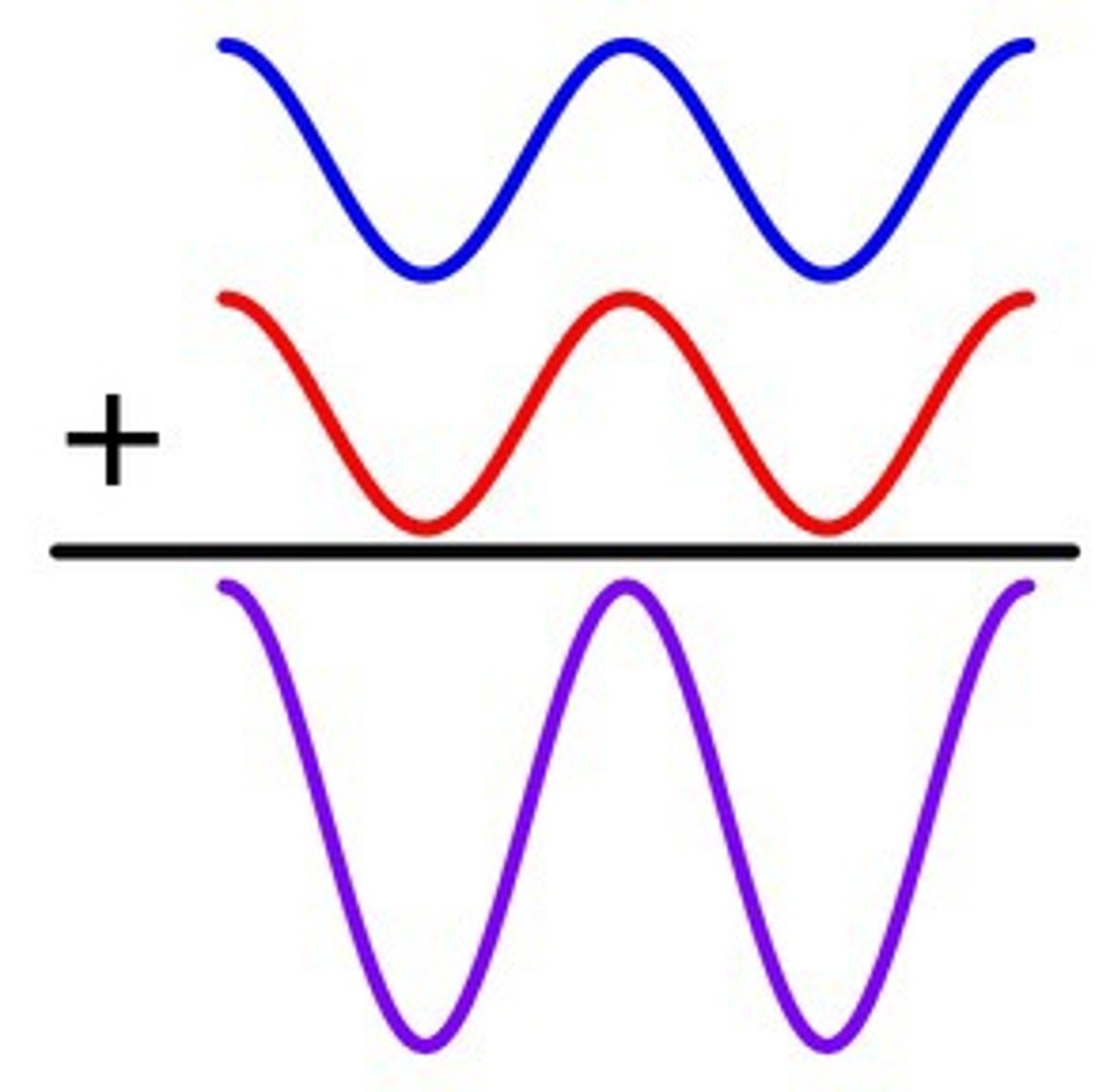
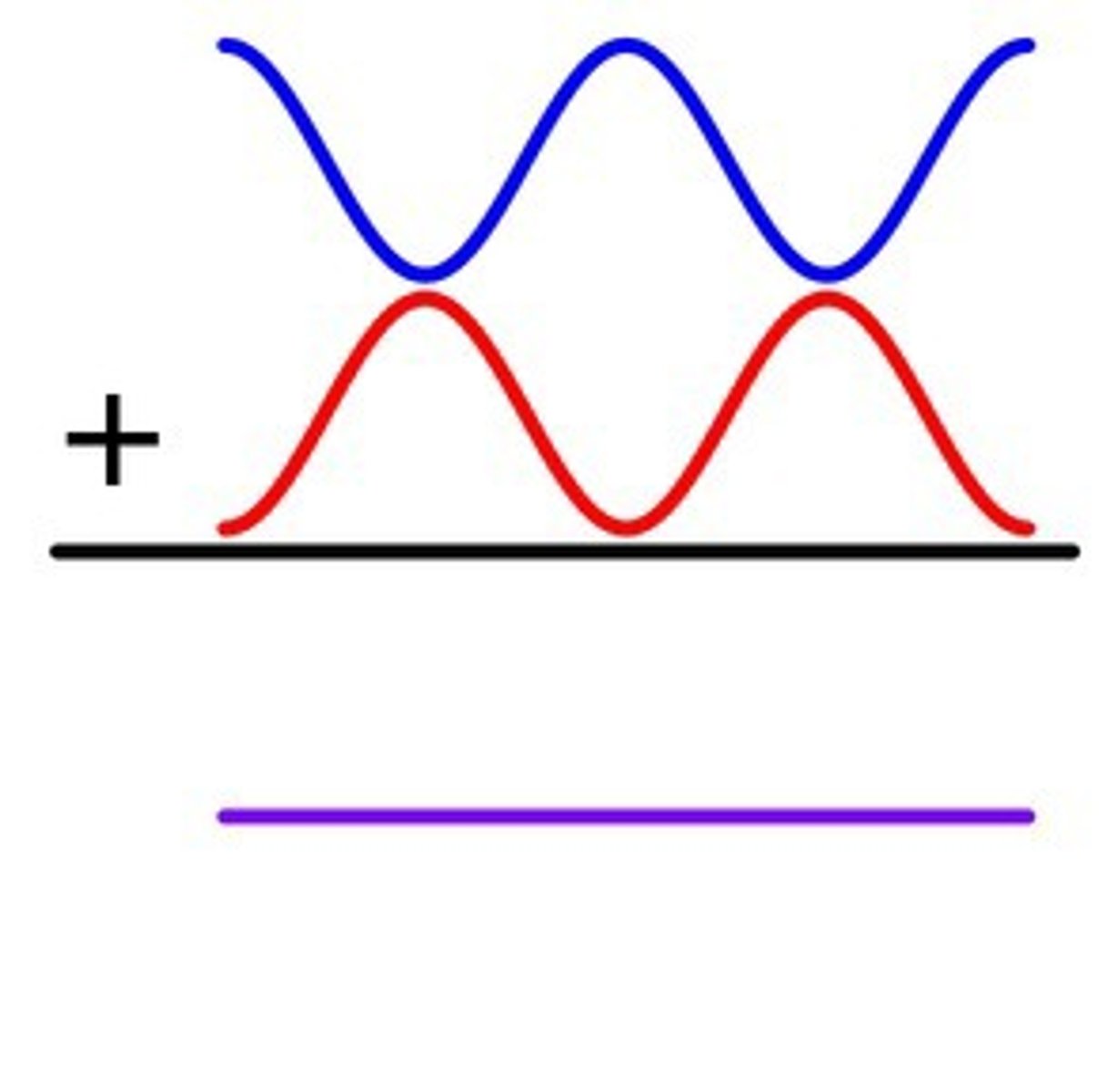
destructive interference
The interference that occurs when two waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude
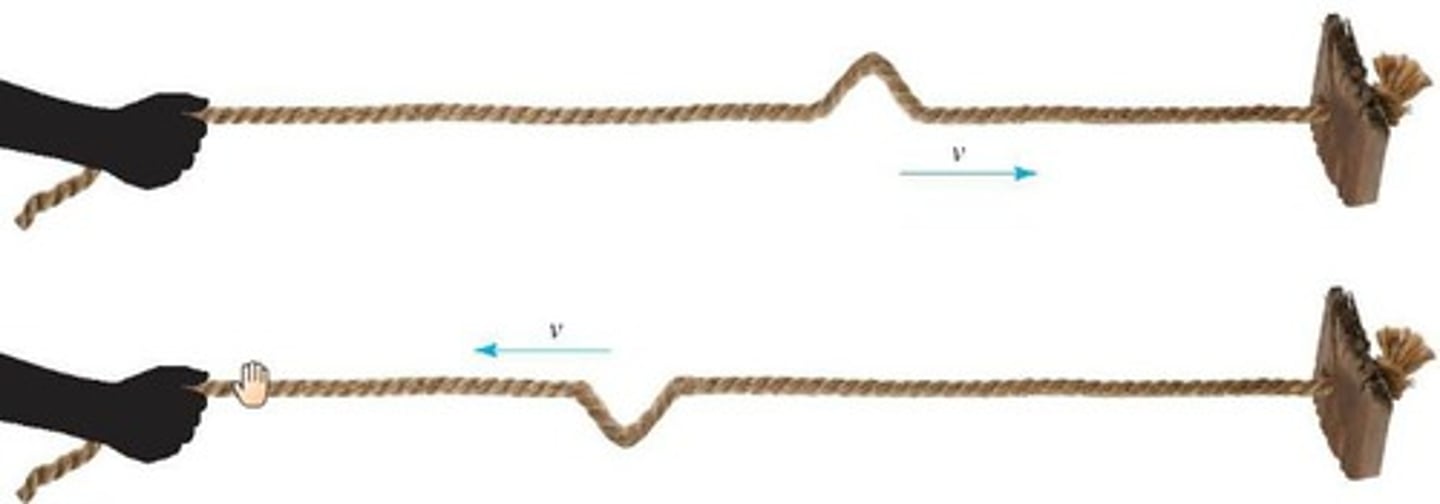
At a fixed boundary, waves are
reflected and inverted
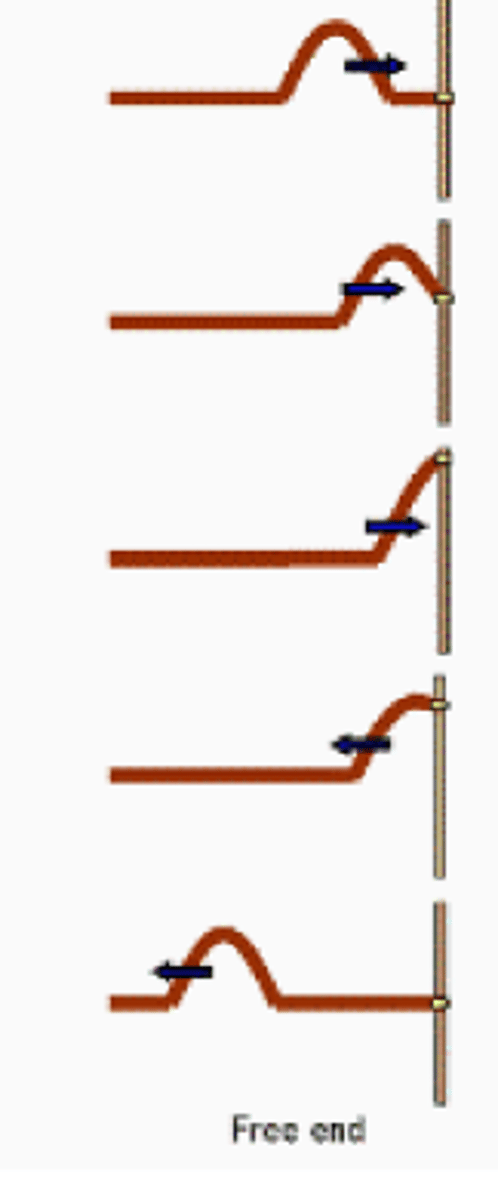
At a free boundary, waves are
reflected but not inverted
standing waves
-produced by perfect and in sync interference of traveling wave and reflected wave
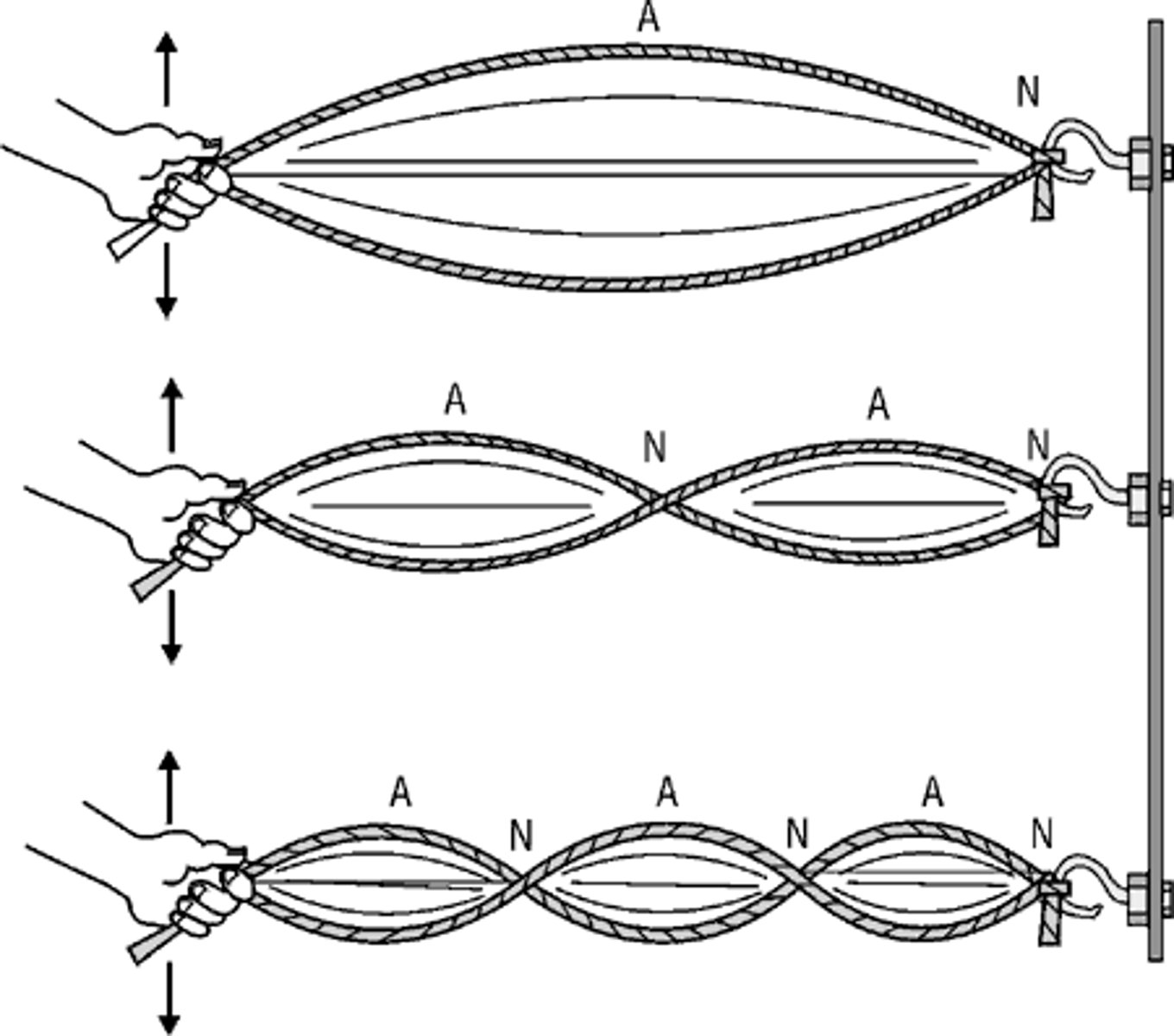
node
A point of zero amplitude on a standing wave
antinode
A point of maximum amplitude on a standing wave