AS level OCR Physics
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
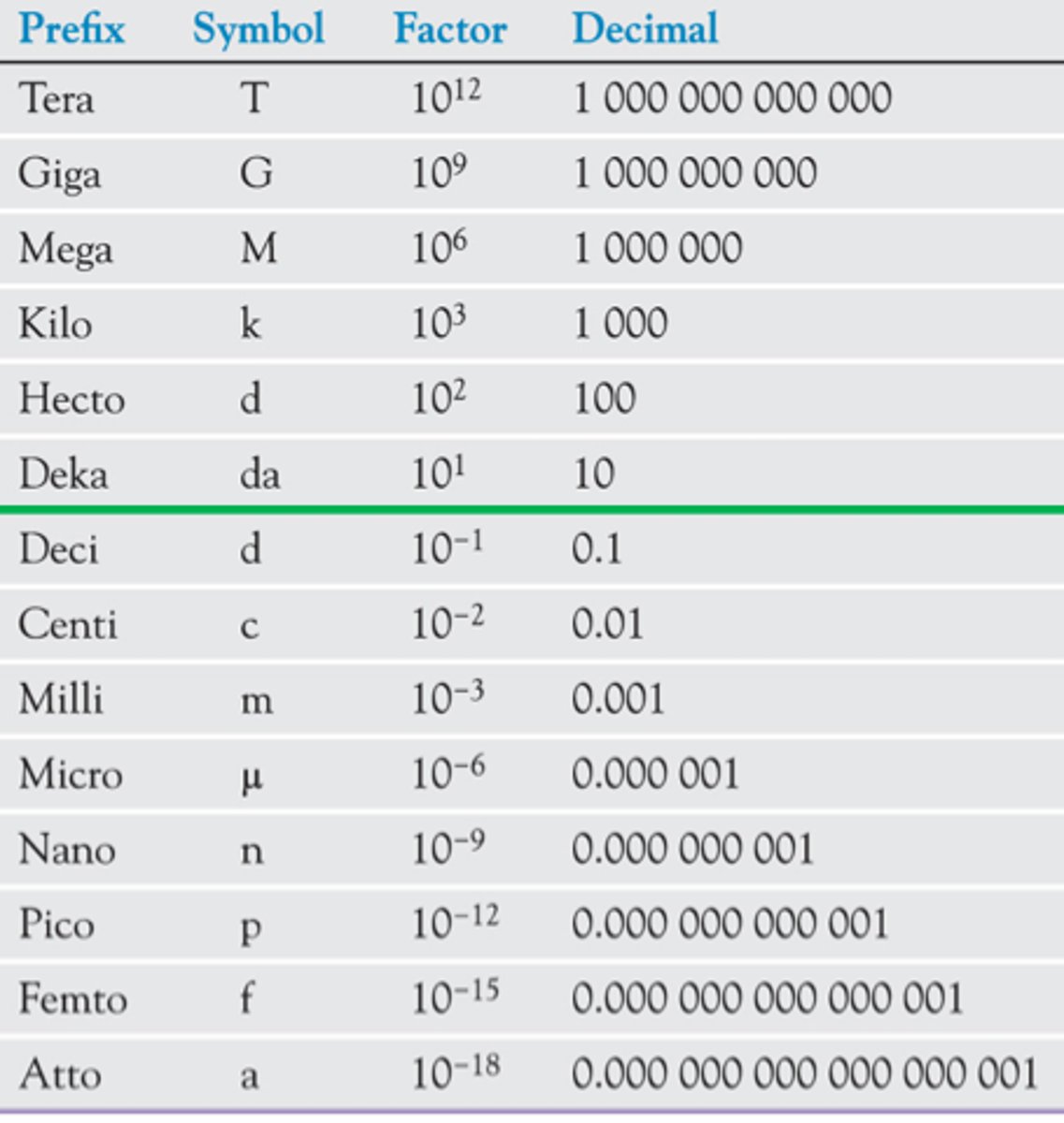
Prefix units
Uncertainties
Adding or subtracting- Add the absolute uncertainties
Multiplying or dividing- Add the percentage uncertainties
Raising to a power- Multiply the percentage uncertainties by the power
Percentage uncertainty in the gradient
uncertainty = ½(line of best fit - line of worst fit)
Percentage uncertainty = uncertainty ÷ gradient of best fit line (× 100)
Speed
Rate of change of distance
Displacement
The distance an object has travelled in a given direction
Velocity
Rate of change of displacement
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity
Scalars
mass, time, temperature, speed, energy
Vectors
displacement, force, velocity, acceleration
Acceleration
Change in velocity divided by time
Displacement=
Average velocity × Time
Vertical velocity=
V × Sin θ
Displacement
Area under velocity-time graph
Time taken=
Number of frames × (1 second / frame rate)
Stopping distance=
Thinking distance + Braking distance
Inertia
Resistance to a change in velocity
Pressure=
h × ρ(density) × g
When the force isn't in the same direction as the movement
W= F × x × Cos θ
P= F × v × Cos θ
Power=
Force × Velocity
K.E.=
Work done
K.E.=
Force × Displacement
K.E.=
Mass × Acceleration × Displacement
Hooke's law
Force is proportional to extension
K
Force constant
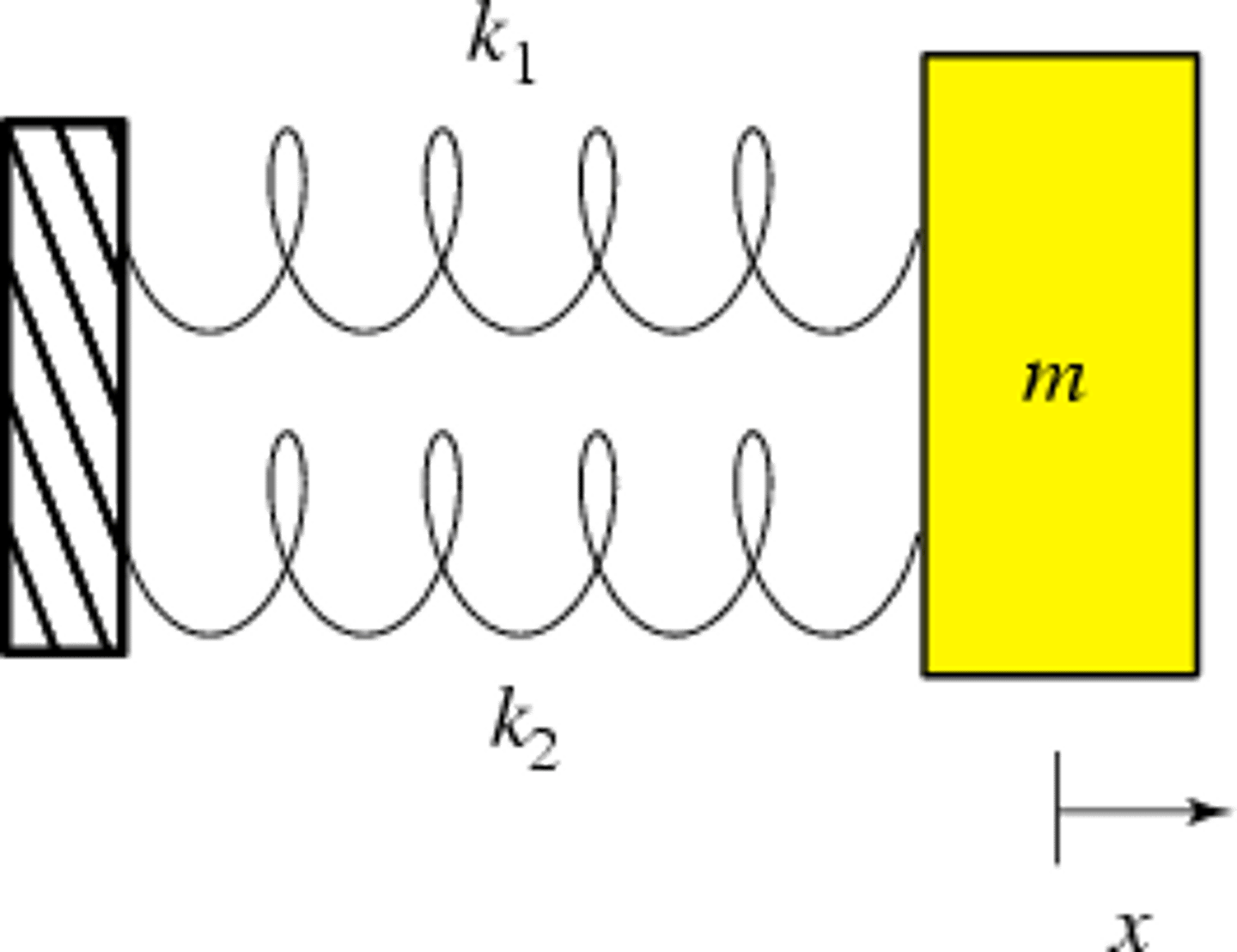
K in series
1/K = 1/K1 + 1/K2
K in parallel
K = K1 + K2
Tensile stress, σ=
Force / Area
Tensile strain, ε=
Extension / Length
Work done=
½ × F × x
Force=
K × x
Elastic potential energy=
½ × k × x²
Young modulus=
Tensile stress / Tensile strain
Energy per unit volume=
½ × Stress × Strain
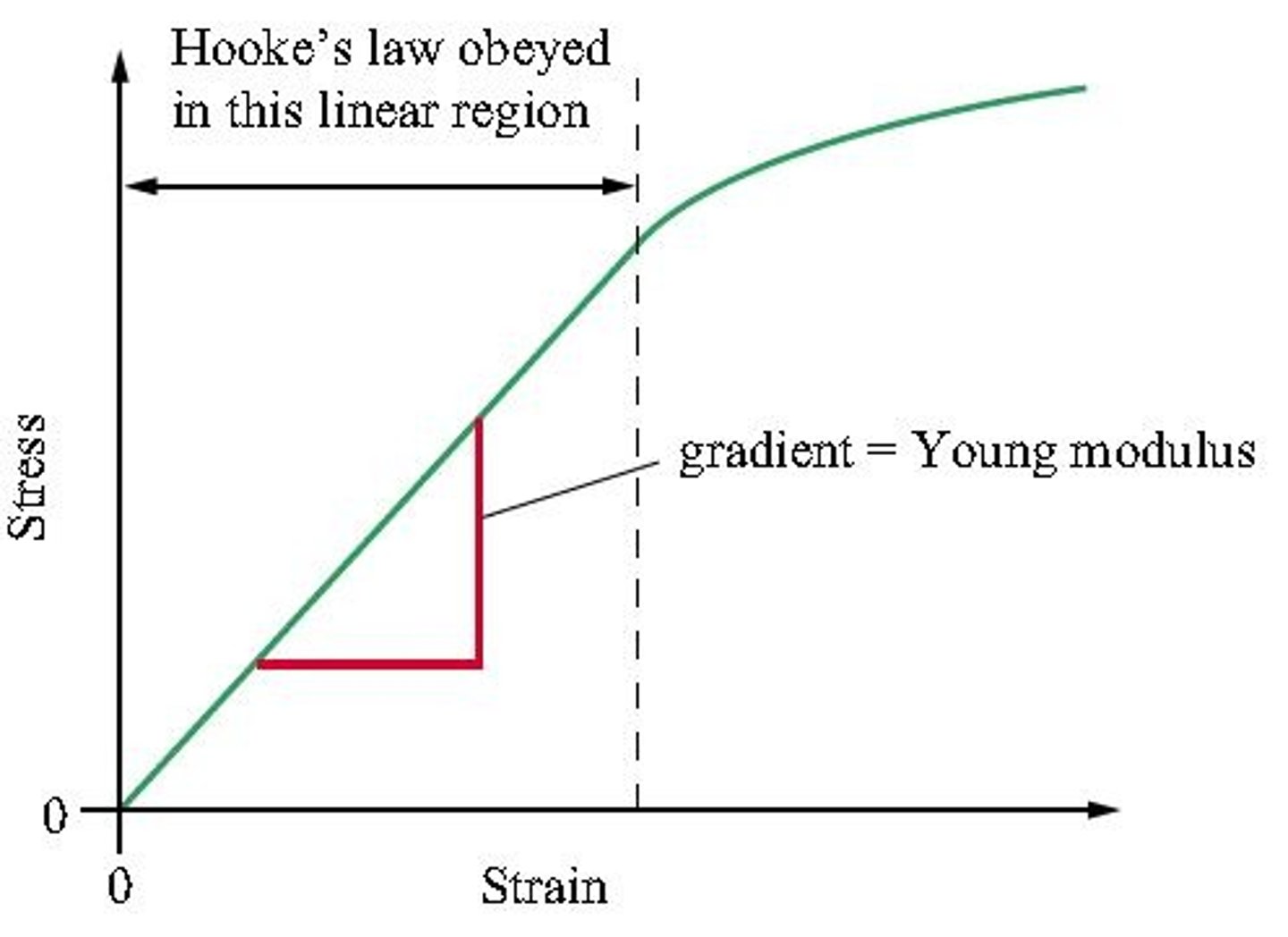
Limit of proportionality
The graph is no longer a straight line
The material stops obeying Hooke's law
Returns to its original shape if stress were removed
Elastic limit
The material behaves plastically
No longer returns to its original state if stress were removed
Yield point
Plastic deformation takes place with a constant or reduced load
The material stretches without any extra load
Conservation of momentum
Momentum before = Momentum after
Elastic collision
Momentum is conserved and kinetic energy is conserved
Inelastic collision
Momentum is conserved but some kinetic energy is lost
Impulse (Ns)
Change in momentum
F × ΔT
Newton's 1st law
Force is needed to change velocity

Newton's 2nd law
Force...
Rate of change of momentum
Change in momentum / Time
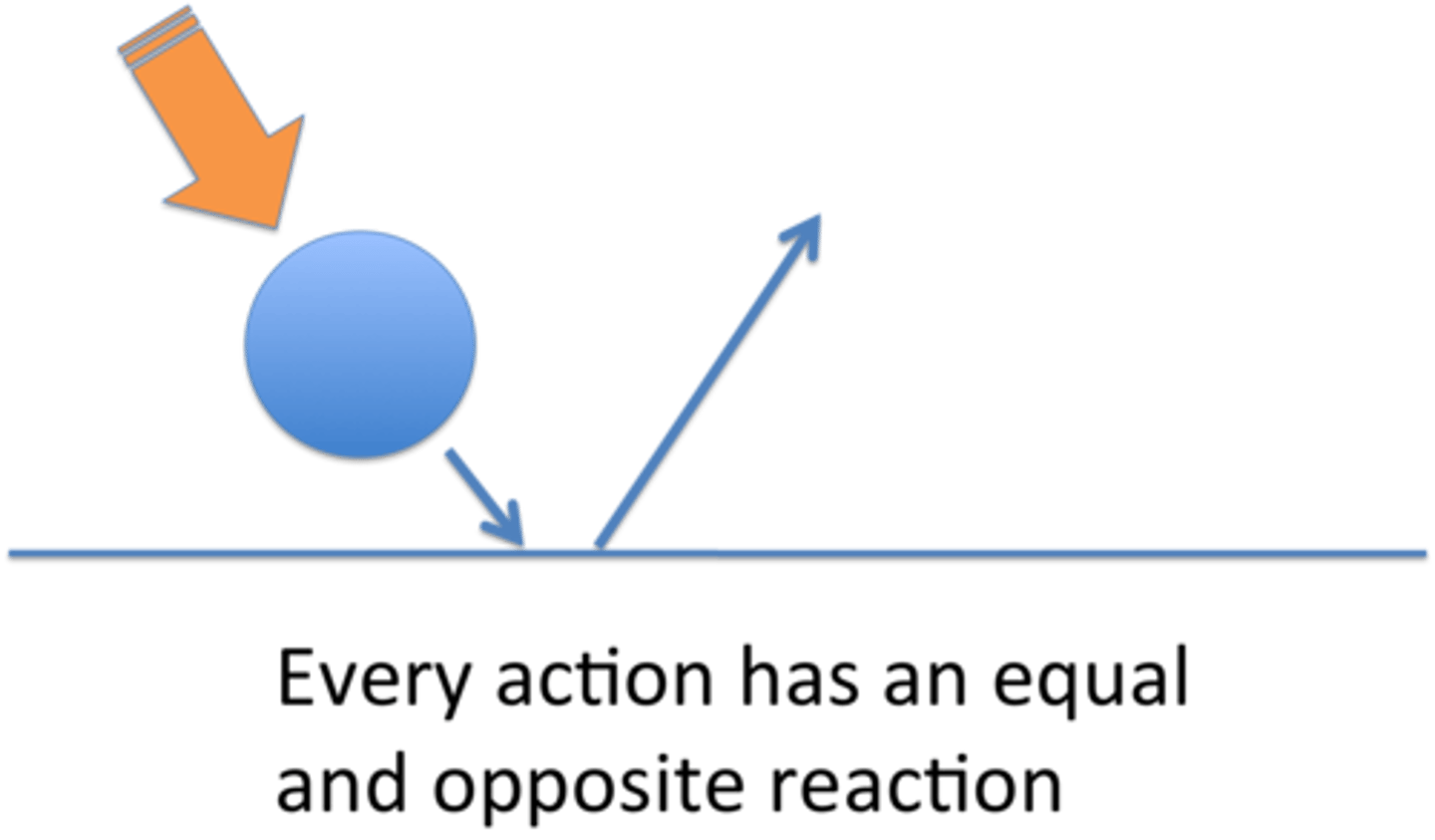
Newton's 3rd law
Each force has an equal, opposite reaction force
Current
Rate of flow of charge
One coulomb
The amount of charge that passes in one second when the current is one ampere
Potential difference
Work done per unit charge
One volt
The p.d. is one volt when you do one joule of work moving one coulomb of charge
1 V = 1 J / C
Current=
Anev
One ohm
If a p.d. of one volt makes a current of one amp flow through the component
Resistivity (Ohm metres)
The resistance of a 1m length with a 1m² cross-sectional area
Resistivity=
RA / L
Power=
V × I
Work done=
VI × T
Power × Time
e.m.f, ε=
V + v
The total amount of work the battery does on each coulomb of charge
Resistance in series
Total R = R1+ R2 + R3
Resistance in parallel
1/Total R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
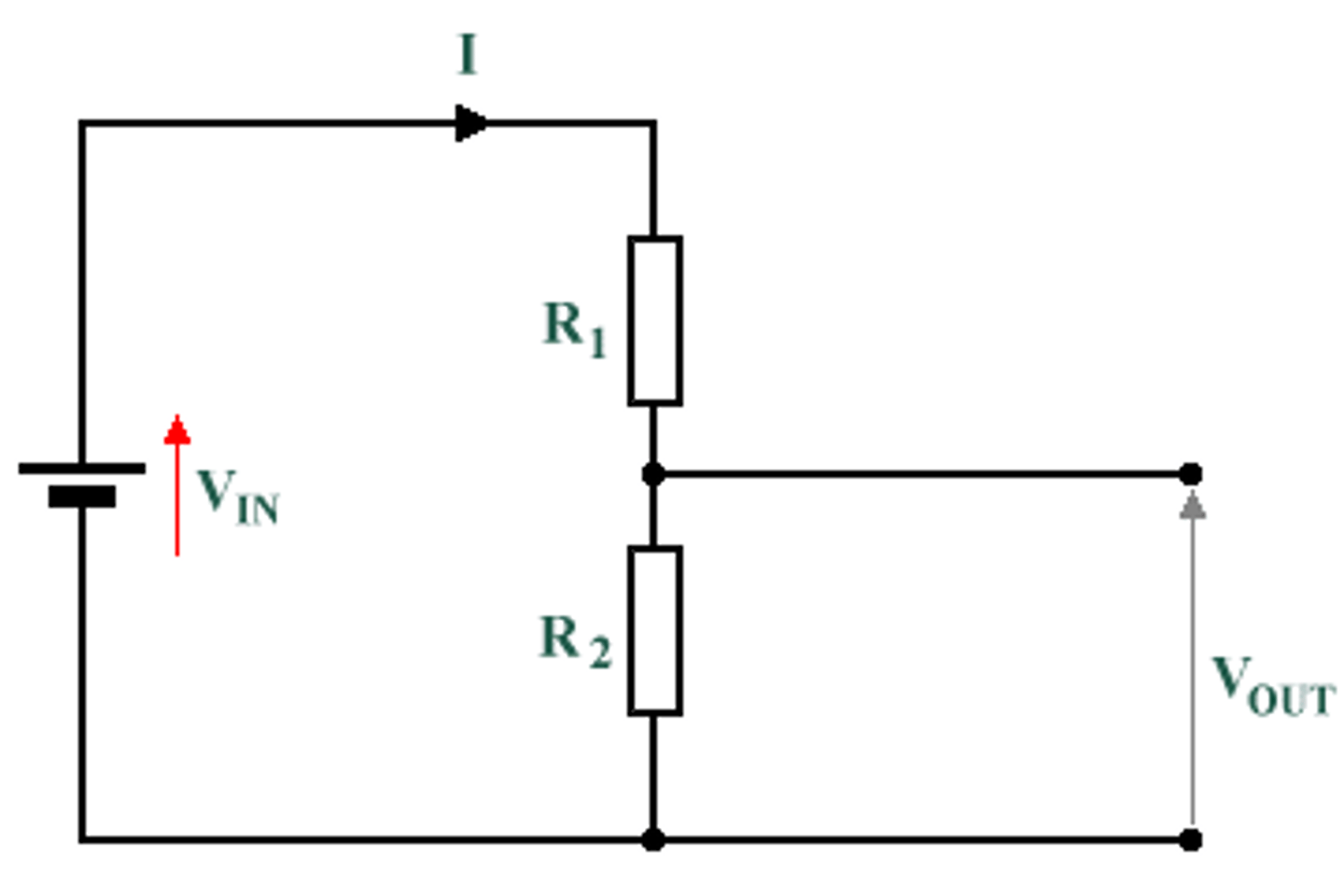
Potential divider (circuit with a voltage source and resistors in series)
V1 / V2 = R1 / R2
Intensity (W/m²)
Power / Area
Intensity
Intensity is the rate of flow of energy per unit area perpendicular to the direction of travel of the wave
Intensity is proportional to amplitude squared
Intensity ∝ Amplitude²
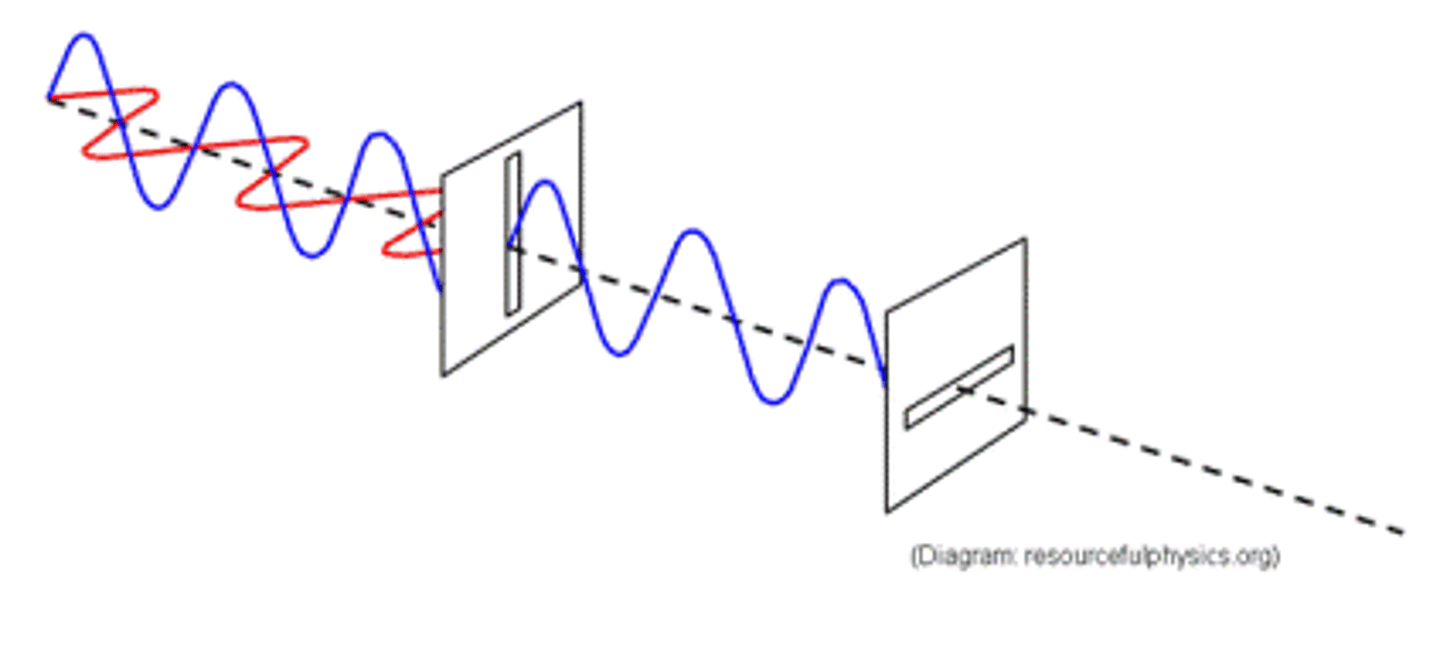
Polarised wave
Oscillates in one direction
Refractive index=
c / v
When a light ray passes across a boundary between two materials
n1 × sin θ1 = n2 × sin θ2
Refractive index of first / second material- n1 and n2
Angle of incidence / refraction- θ1 and θ2
Sin C=
1 / n
Coherent
Same wavelength and frequency with a fixed phase difference
Two coherent sources needed to get interference patterns
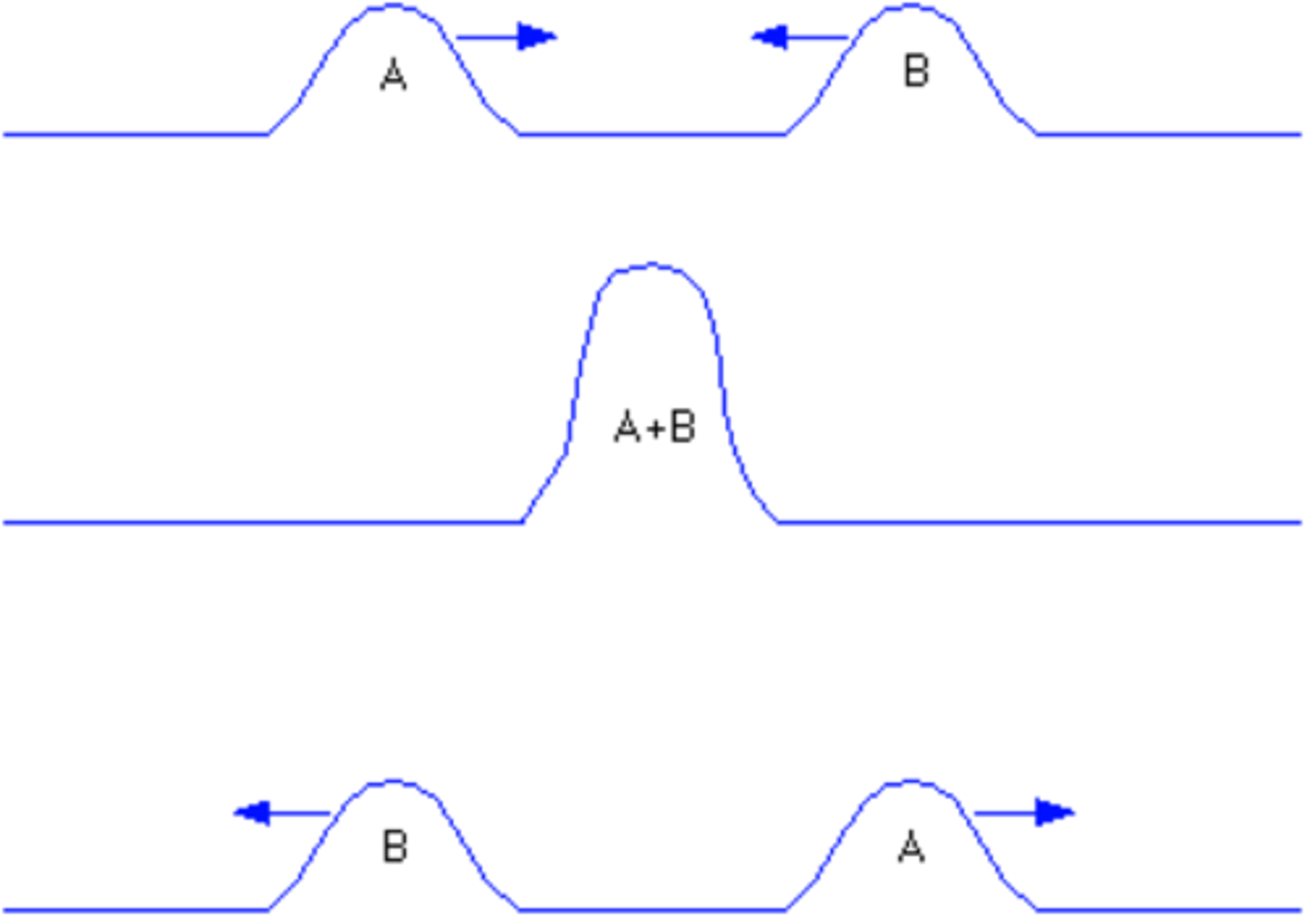
Constructive interference
Path difference is a whole number of wavelengths
Path difference = nλ
Destructive interference
Path difference is an odd number of half wavelengths
Path difference = (n + ½)λ
Fringe spacing, x=
λD / A
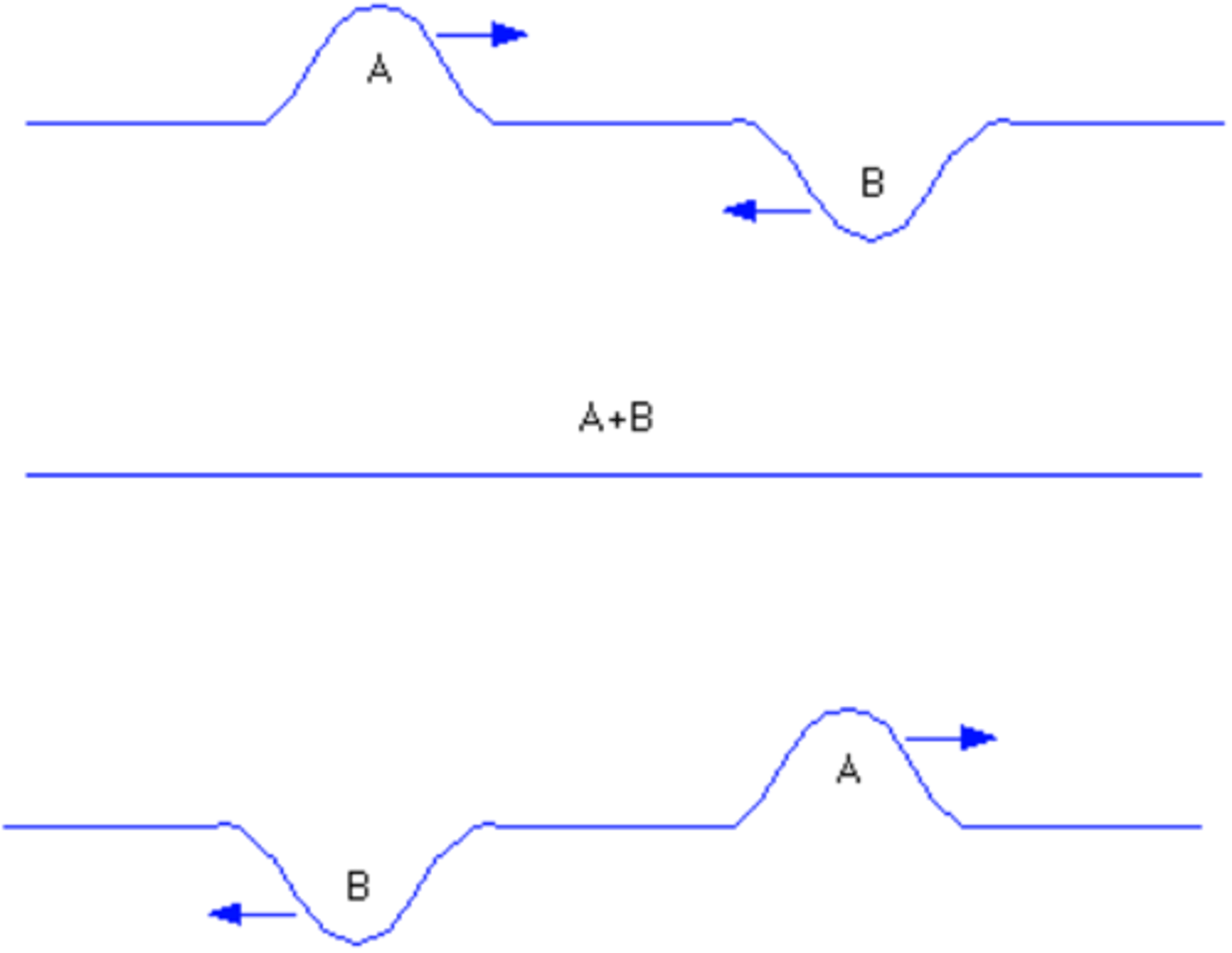
Stationary wave
The superposition of two progressive waves with the same wavelength, moving in opposite directions
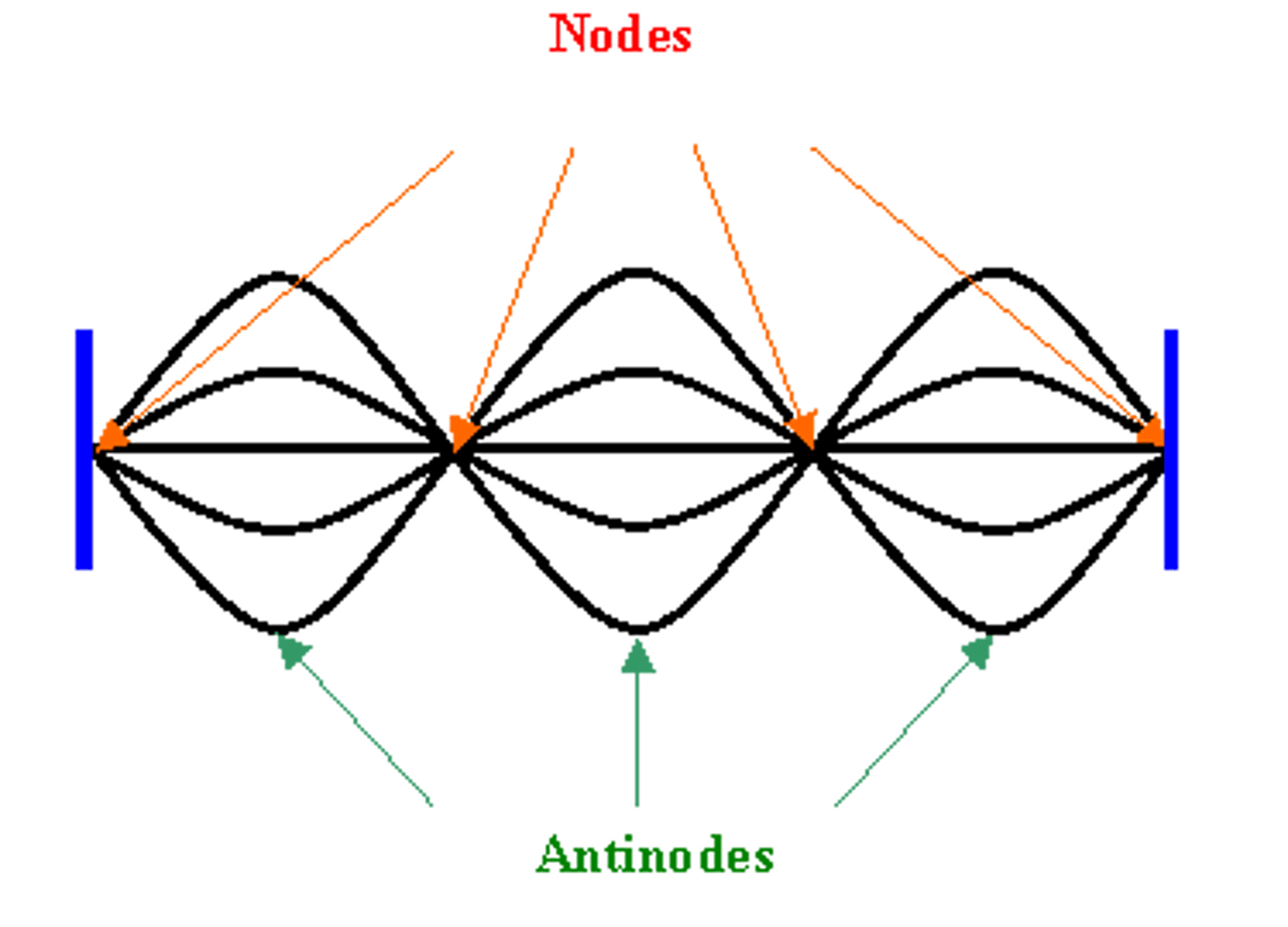
First harmonic
Second harmonic
Third harmonic
One antinode- half a wavelength
Two antinodes- one wavelength
Three antinodes- one and a half wavelengths
Photon
A quantum of EM radiation
E=
hf = hc / λ
Electronvolt
The kinetic energy gained by an electron when it is accelerated through a potential difference of one volt
1 eV = 1.6 × 10^-19 J
Photoelectric effect
1) No photoelectrons are emitted if the radiation has a frequency below a certain value (threshold frequency)
2) The photoelectrons are emitted with a variety of kinetic energies ranging from zero to some maximum value. The value of maximum kinetic energy increases with frequency and is unaffected by intensity
3) The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is proportional to intensity
Work function energy, Φ
Energy needed to break metallic bonds
Planck constant, h
6.63 × 10^-34 Js
Threshold frequency, f=
Φ / h
For electrons to be released
hf ≥ Φ
Maximum kinetic energy
hf=
Φ + max K.E.
de Broglie equation
λ=
h / p (momentum)
λ for electrons accelerated in a vacuum tube
Same size as electromagnetic waves in the X-ray part of the spectrum
Archimedes' principle
Upthrust = weight of fluid displaced