Enzymes and the Regulation of Enzyme Activity
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
How do Exergonic Reactions work?
Proceeds w/ a net release of free energy and is spontaneous
How do Endergonic Reactions work?
Absorb free energy from surroundings and is non-spontaneous
How important is chemical bond breaking/formaion?
Involved in every reaction
What is Activation Energy (or Free Energy of Activation)?
Initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction
How is Activation Energy often supplied?
As thermal energy that reactants absorb from surroundings
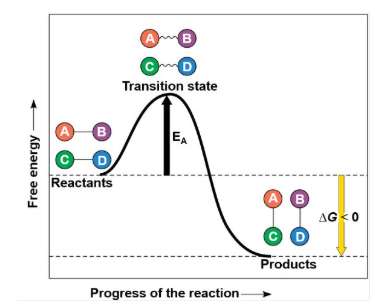
What type of Reaction is this Energy Profile for?
Exergonic
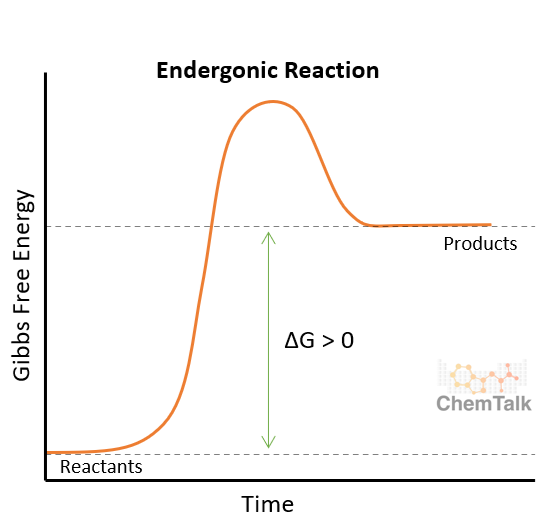
What type of Reaction is this Energy Profile for?
Endergonic
What happens in Catalysis?
Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering Ea barrier
Do Enzymes affect free energy?
No, hasten reactions that would eventually occur
What is an Enzyme Substrate?
Reactant that an enzyme acts on
How is the Enzyme-Substrate Complex formed?
Enzyme binds to substrate, activity of the enzyme converts substrate to product
What is the Active Site?
Region on enzyme where substrate binds
What is Induced Fit of a Substrate?
Brings chemical groups of active site into positions that enhance their catalytical ability
How much of an Enzyme is needed?
Very small amounts can have substantial metabolic effects because they’re used repeatedly in catalytic cycles
How can Active Sites lower an Ea Barrier?
Orienting
Straining
Microenvrionment
Bonding
Orienting substrates correctly
Straining substrate bonds
Providing favourable microenvironment
Covalently bonding to substrate
What is the relationship between the rate of Enzyme-catalysed reactions and Substrate Conc?
Rate speeds up when substrate conc increases
What is the result of all Enzyme Active Sites being engaged?
Enzyme is saturated - reaction rate only increases by adding more enzyme
What happens after the Substrates enter the active site?
Holding
Conversion
What happens to the AS?
Substrates held in AS by weak interactions
Substrates converted to products, products released
AS available for new substrates
What Environmental Factors affect Enzymes?
Temperature and pH
What are Cofactors?
Inorganic/Organic non-protein enzyme helpers
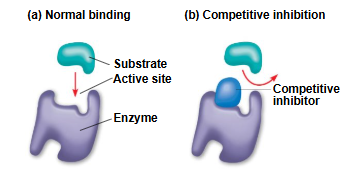
How do Competitive Inhibitors work?
Bind to AS compete w/ substrate
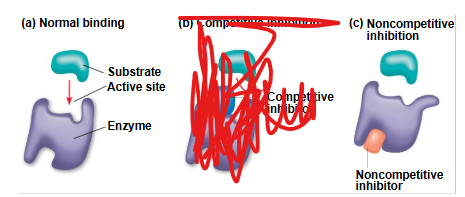
How do Non-Competitive Inhibitors?
Bind to another part of enzyme causing to change shape and makes AS less effective
What are Examples of Enzyme Inhibitors?
Toxins, poisons, pesticides, antibiotics
What would result if Metabolic Pathways weren’t tightly regulated?
Chemical chaos
How does the cell regulate metabolic pathways?
Switching on/off genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating enzyme activity
How does Allosteric Regulation affect Enzyme Activity?
Inhibit/stimulate it
When does Allosteric Regulation occur?
Regulatory molecule binds to a protein at 1 site and affects protein’s function at another
What does the binding of an activator do?
Stabilises inactive form of the enzyme
What is Cooperativity?
Form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity
How do substrate prime enzymes?
1 substrate primes an enzyme to act on additional substrate molecules more readily
Why is cooperativity allosteric?
Binding by a substrate to 1 AS affects catalysis in a different AS
What happens in Feedback Inhibition?
End product of a metabolic pathway shuts down pathway
What does Feedback Inhibition prevent?
Prevents a cell from wasting chemical resources by synthesising more product than needed